@zhangyy
2021-09-17T16:36:35.000000Z
字数 9203
阅读 830
ansible的Playbook
ansible系列
一: playbook介绍
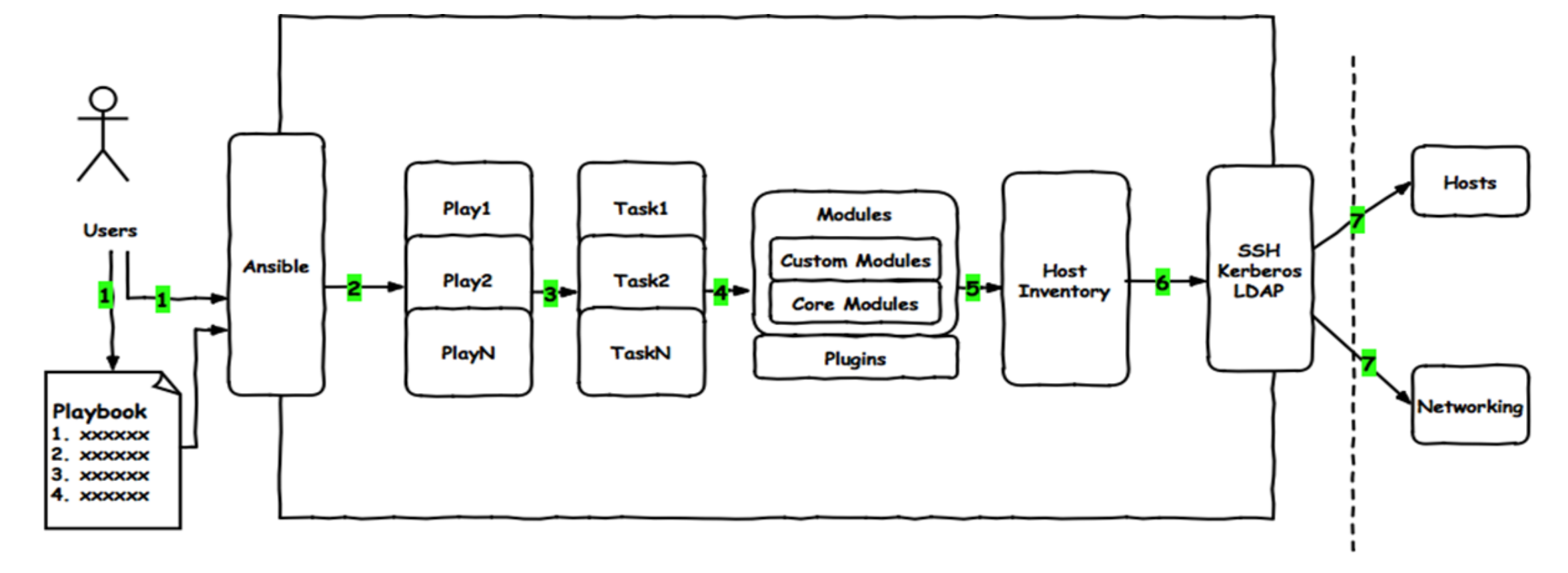
playbook 剧本是由一个或多个"play"组成的列表play的主要功能在于将预定义的一组主机,装扮成事先通过ansible中的task定义好的角色。Task实际是调用ansible的一个module,将多个play组织在一个playbook中,即可以让它们联合起来,按事先编排的机制执行预定义的动作Playbook 文件是采用YAML语言编写的
二: yaml 语言
2.1 yaml的语言介绍
YAML:YAML Ain't Markup Language,即YAML不是标记语言。不过,在开发的这种语言时,YAML的意思其实是:"Yet Another Markup Language"(仍是一种标记语言)YAML是一个可读性高的用来表达资料序列的格式。YAML参考了其他多种语言,包括:XML、C语言、Python、Perl以及电子邮件格式RFC2822等。Clark Evans在2001年在首次发表了这种语言,另外Ingydöt Net与Oren Ben-Kiki也是这语言的共同设计者,目前很多最新的软件比较流行采用此格式的文件存放配置信息,如:ubuntu,anisble,docker,kubernetes等YAML 官方网站:http://www.yaml.organsible 官网: https://docs.ansible.com/ansible/latest/reference_appendices/YAMLSyntax.html
2.2 YAML 语言特性
YAML的可读性好YAML和脚本语言的交互性好YAML使用实现语言的数据类型YAML有一个一致的信息模型YAML易于实现YAML可以基于流来处理YAML表达能力强,扩展性好
2.3 yaml 语言简介
YAML语法简介在单一文件第一行,用连续三个连字号"-" 开始,还有选择性的连续三个点号( ... )用来表示文件的结尾次行开始正常写Playbook的内容,一般建议写明该Playbook的功能使用#号注释代码缩进必须是统一的,不能空格和tab混用缩进的级别也必须是一致的,同样的缩进代表同样的级别,程序判别配置的级别是通过缩进结合换行来实现的YAML文件内容是区别大小写的,key/value的值均需大小写敏感多个key/value可同行写也可换行写,同行使用,分隔key后面冒号要加一个空格 比如: key: valuevalue可是个字符串,也可是另一个列表YAML文件扩展名通常为 yml 或 yaml
2.4 支持的数据类型
YAML 支持以下常用几种数据类型:标量:单个的、不可再分的值对象:键值对的集合,又称为映射(mapping)/ 哈希(hashes) / 字典(dictionary)数组:一组按次序排列的值,又称为序列(sequence) / 列表(list)
2.5 scalar 标量
key对应valuename: wangage: 18使用缩进的方式name:wangage:18标量是最基本的,不可再分的值,包括:字符串布尔值整数浮点数Null时间日期
字典由多个key与value构成,key和value之间用 :分隔, 并且 : 后面有一个空格,所有k/v可以放在一行,或者每个 k/v 分别放在不同行格式account: { name: wang, age: 18 }使用缩进方式account:name: wangage: 18范例:#不同行# An employee recordname: Example Developerjob: Developerskill: Elite(社会精英) #同一行,也可以将key:value放置于{}中进行表示,用,分隔多个key:value# An employee record{name: "Example Developer", job: "Developer", skill: "Elite"}
List 列表列表由多个元素组成,每个元素放在不同行,且元素前均使用"-"打头,并且 - 后有一个空格, 或者将所有元素用 [ ] 括起来放在同一行格式course: [ linux, golang, python ]
也可以写成以 - 开头的多行course:- linux- golang- python数据里面也可以包含字典course:- linux: manjaro- golang: gin- python: django范例:#不同行,行以-开头,后面有一个空格# A list of tasty fruits- Apple- Orange- Strawberry- Mango#同一行[Apple,Orange,Strawberry,Mango]范例:YAML 表示一个家庭name: John Smithage: 41gender: Malespouse: { name: Jane Smith, age: 37, gender: Female } # 写在一行里name: Jane Smith #也可以写成多行age: 37gender: Femalechildren: [ {name: Jimmy Smith,age: 17, gender: Male}, {name: Jenny Smith, age:13, gender: Female}, {name: hao Smith, age: 20, gender: Male } ] #写在一行- name: Jimmy Smith #写在多行,更为推荐的写法age: 17gender: Male- {name: Jenny Smith, age: 13, gender: Female}- {name: hao Smith, age: 20, gender: Male }
2.6 三种常见的数据格式
XML:Extensible Markup Language,可扩展标记语言,可用于数据交换和配置JSON:JavaScript Object Notation, JavaScript 对象表记法,主要用来数据交换或配置,不支持注释YAML:YAML Ain't Markup Language YAML 不是一种标记语言, 主要用来配置,大小写敏感,不支持tab
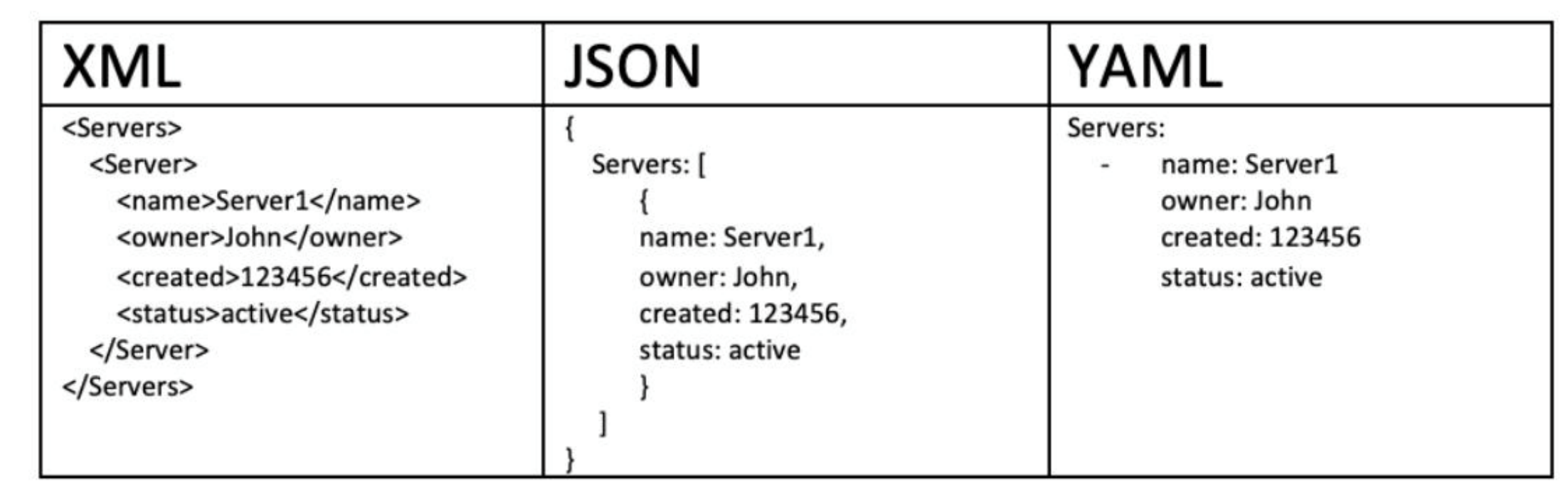
可以用工具互相转换,参考网站:https://www.json2yaml.com/http://www.bejson.com/json/json2yaml/
2.7 Playbook 核心组件
官方文档https://docs.ansible.com/ansible/latest/reference_appendices/playbooks_keywords.html#playbook-keywords一个playbook 中由多个组件组成,其中所用到的常见组件类型如下:Hosts 执行的远程主机列表Tasks 任务集,由多个task的元素组成的列表实现,每个task是一个字典,一个完整的代码块功能需最少元素需包括 name 和 task,一个name只能包括一个taskVariables 内置变量或自定义变量在playbook中调用Templates 模板,可替换模板文件中的变量并实现一些简单逻辑的文件Handlers 和 notify 结合使用,由特定条件触发的操作,满足条件方才执行,否则不执行tags 标签 指定某条任务执行,用于选择运行playbook中的部分代码。ansible具有幂等性,因此会自动跳过没有变化的部分,即便如此,有些代码为测试其确实没有发生变化的时间依然会非常地长。此时,如果确信其没有变化,就可以通过tags跳过此些代码片断
2.8 hosts 组件
Hosts:playbook中的每一个play的目的都是为了让特定主机以某个指定的用户身份执行任务。hosts用于指定要执行指定任务的主机,须事先定义在主机清单中one.example.comone.example.com:two.example.com192.168.1.50192.168.1.*Websrvs:dbsrvs #或者,两个组的并集Websrvs:&dbsrvs #与,两个组的交集webservers:!dbsrvs #在websrvs组,但不在dbsrvs组案例:- hosts: websrvs:appsrvs
2.9 remote_user 组件
remote_user: 可用于Host和task中。也可以通过指定其通过sudo的方式在远程主机上执行任务,其可用于play全局或某任务;此外,甚至可以在sudo时使用sudo_user指定sudo时切换的用户- hosts: websrvsremote_user: roottasks:- name: test connectionping:remote_user: magedusudo: yes #默认sudo为rootsudo_user:wang #sudo为wang
2.10 task列表和action组件
play的主体部分是task list,task list中有一个或多个task,各个task 按次序逐个在hosts中指定的所有主机上执行,即在所有主机上完成第一个task后,再开始第二个tasktask的目的是使用指定的参数执行模块,而在模块参数中可以使用变量。模块执行是幂等的,这意味着多次执行是安全的,因为其结果均一致每个task都应该有其name,用于playbook的执行结果输出,建议其内容能清晰地描述任务执行步骤。如果未提供name,则action的结果将用于输出task两种格式:action: module arguments #示例: action: shell wall hellomodule: arguments #建议使用 #示例: shell: wall hello注意:shell和command模块后面跟命令,而非key=value范例:[root@ansible ansible]#cat hello.yaml---# first yaml file- hosts: websrvsremote_user: rootgather_facts: no #不收集系统信息,提高执行效率tasks:- name: test network connectionping:- name: excute commandcommand: wall "hello world!"
范例:---- hosts: websrvsremote_user: rootgather_facts: notasks:- name: install httpdyum: name=httpd- name: start httpdservice: name=httpd state=started enabled=yes
2.11 其它组件说明
某任务的状态在运行后为changed时,可通过"notify"通知给相应的handlers任务还可以通过"tags"给task 打标签,可在ansible-playbook命令上使用-t指定进行调用#SHELL脚本实现#!/bin/bash# 安装Apacheyum install --quiet -y httpd# 复制配置文件cp /tmp/httpd.conf /etc/httpd/conf/httpd.confcp/tmp/vhosts.conf /etc/httpd/conf.d/# 启动Apache,并设置开机启动systemctl enable --now httpd#Playbook实现---- hosts: websrvsremote_user: rootgather_facts: notasks:- name: "安装Apache"yum: name=httpd- name: "复制配置文件"copy: src=/tmp/httpd.conf dest=/etc/httpd/conf/- name: "复制配置文件"copy: src=/tmp/vhosts.conf dest=/etc/httpd/conf.d/- name: "启动Apache,并设置开机启动"service: name=httpd state=started enabled=yes
2.12 playbook 命令
格式ansible-playbook <filename.yml> ... [options]常见选项:--syntax-check #语法检查,可缩写成--syntax, 相当于bash -n-C --check #模拟执行,只检测可能会发生的改变,但不真正执行操作,dry run--list-hosts #列出运行任务的主机--list-tags #列出tag--list-tasks #列出task--limit 主机列表 #只针对主机列表中的特定主机执行-i INVENTORY #指定主机清单文件,通常一个项对应一个主机清单文件--start-at-task START_AT_TASK #从指定task开始执行,而非从头开始,START_AT_TASK为任务的name-v -vv -vvv #显示过程
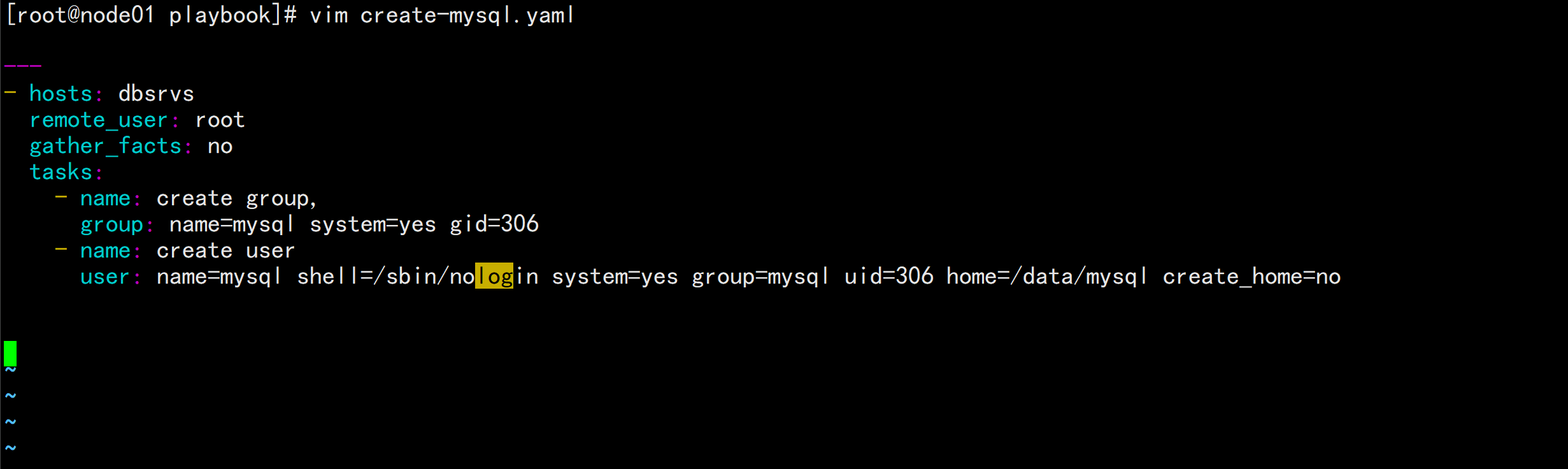
2.12.1 利用playbook 创建用户
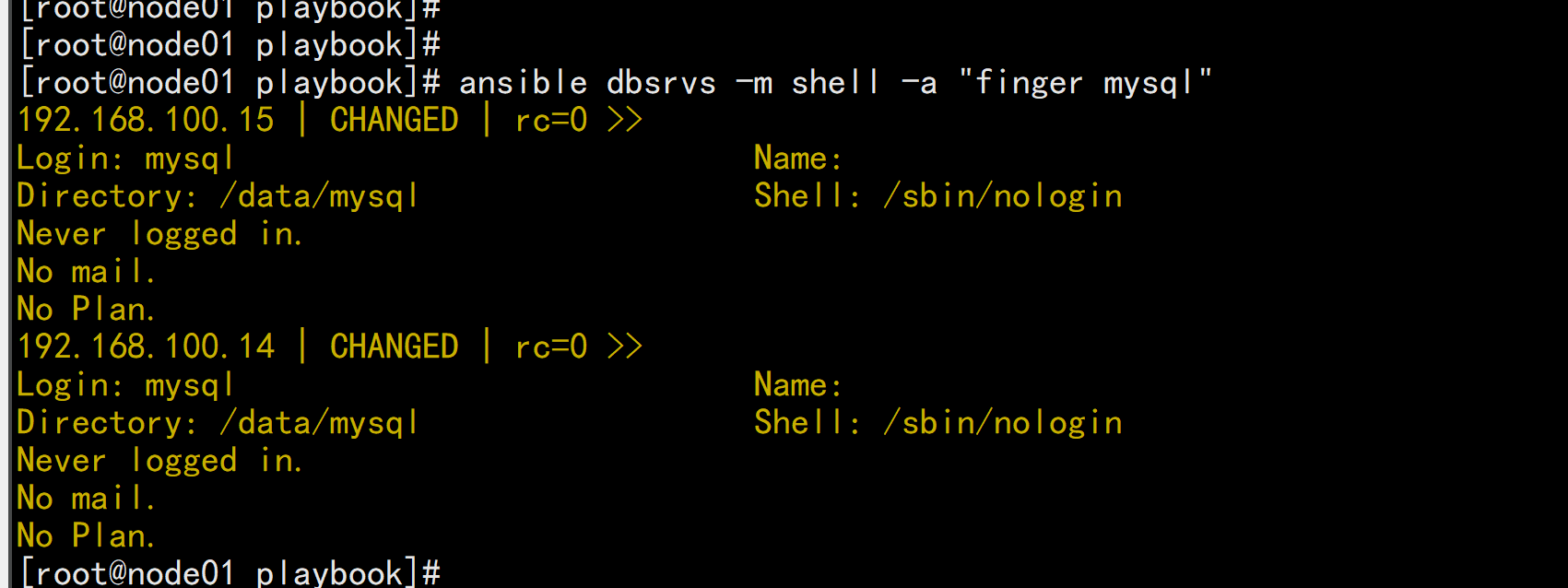
- hosts: dbsrvsremote_user: rootgather_facts: notasks:- name: create group,group: name=mysql system=yes gid=306- name: create useruser: name=mysql shell=/sbin/nologin system=yes group=mysql uid=306 home=/data/mysql create_home=no
ansible-playbook -C create-mysql.yaml
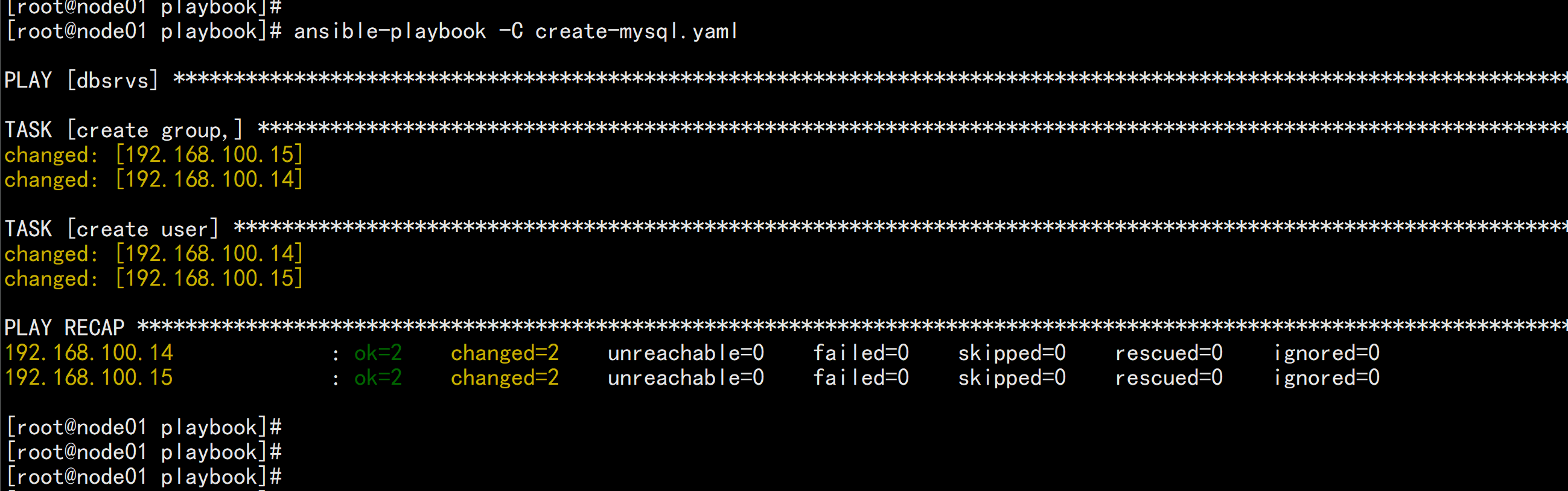
ansible-playbook create-mysql.yaml
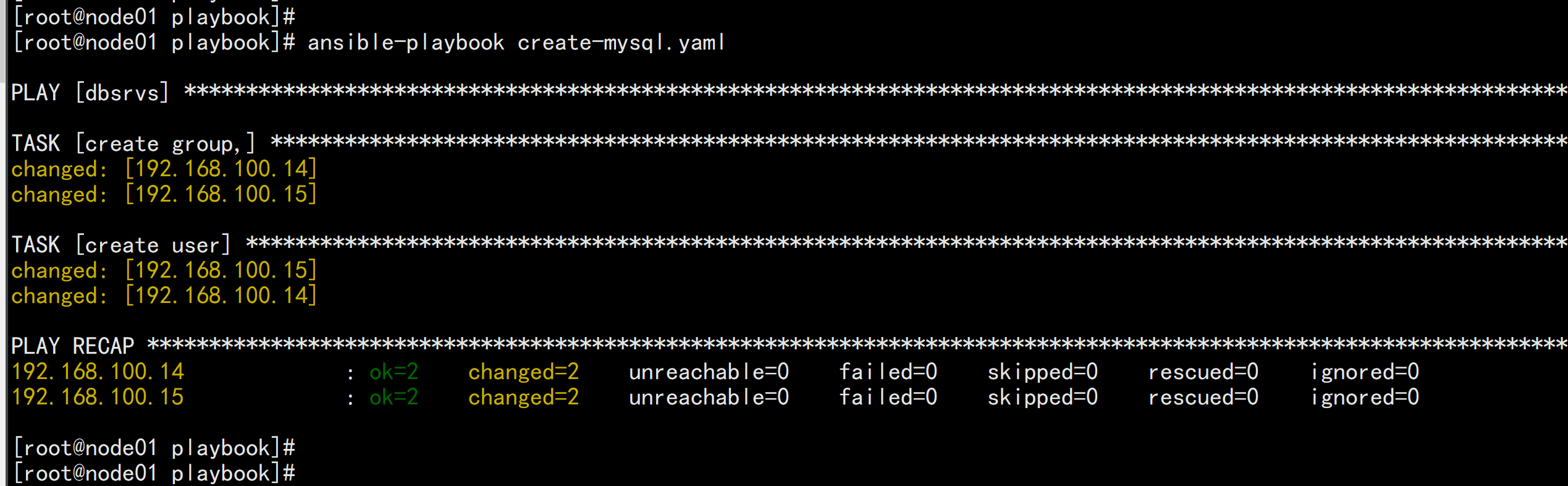
ansible dbsrvs -m shell -a "finger mysql"
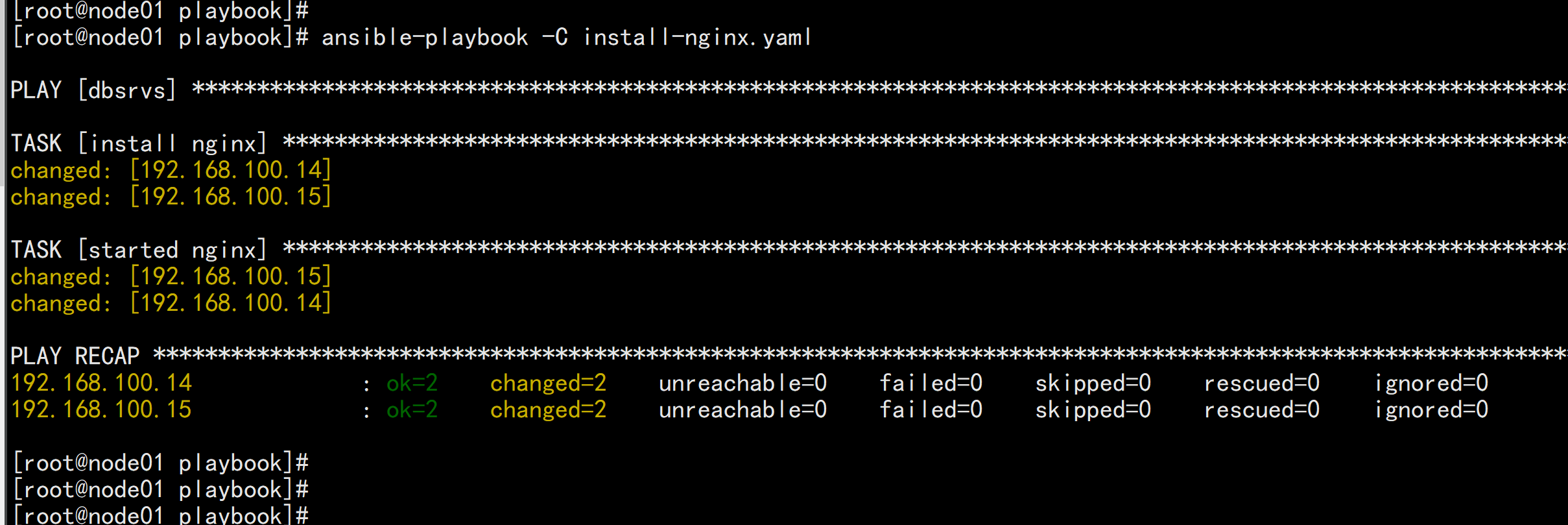
2.12.2 利用ansible 安装nginx
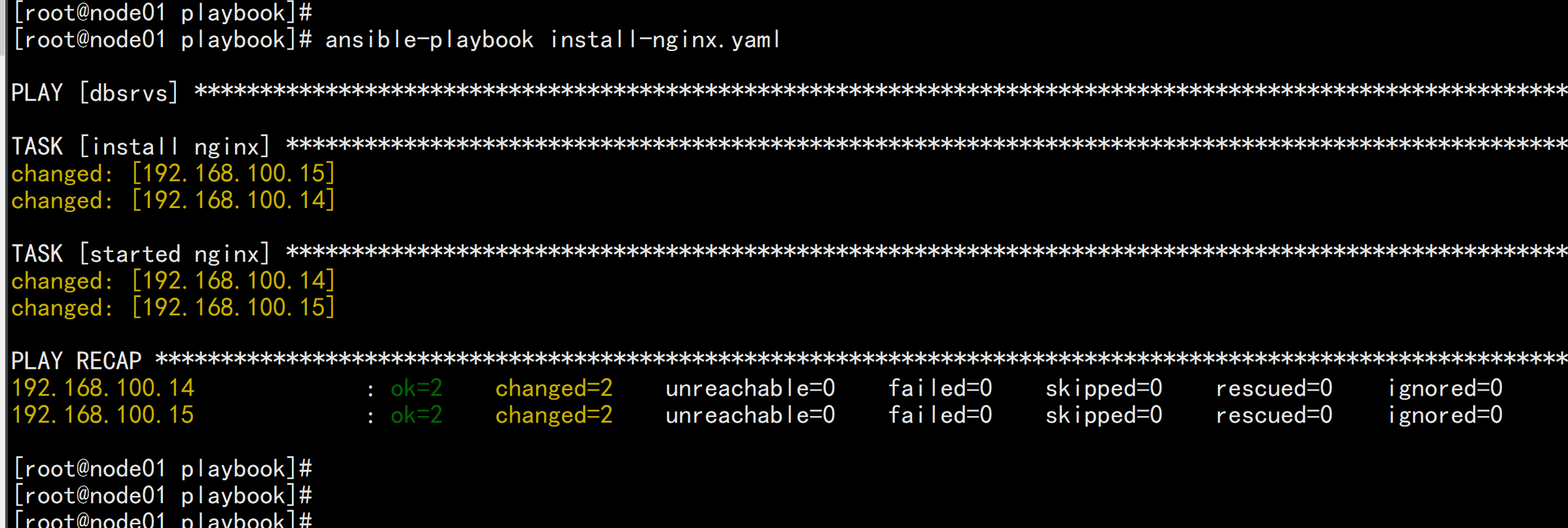
---- hosts: dbsrvsremote_user: rootgather_facts: notasks:- name: install nginxyum: name=nginx state=present- name: started nginxservice: name=nginx state=started enabled=yes
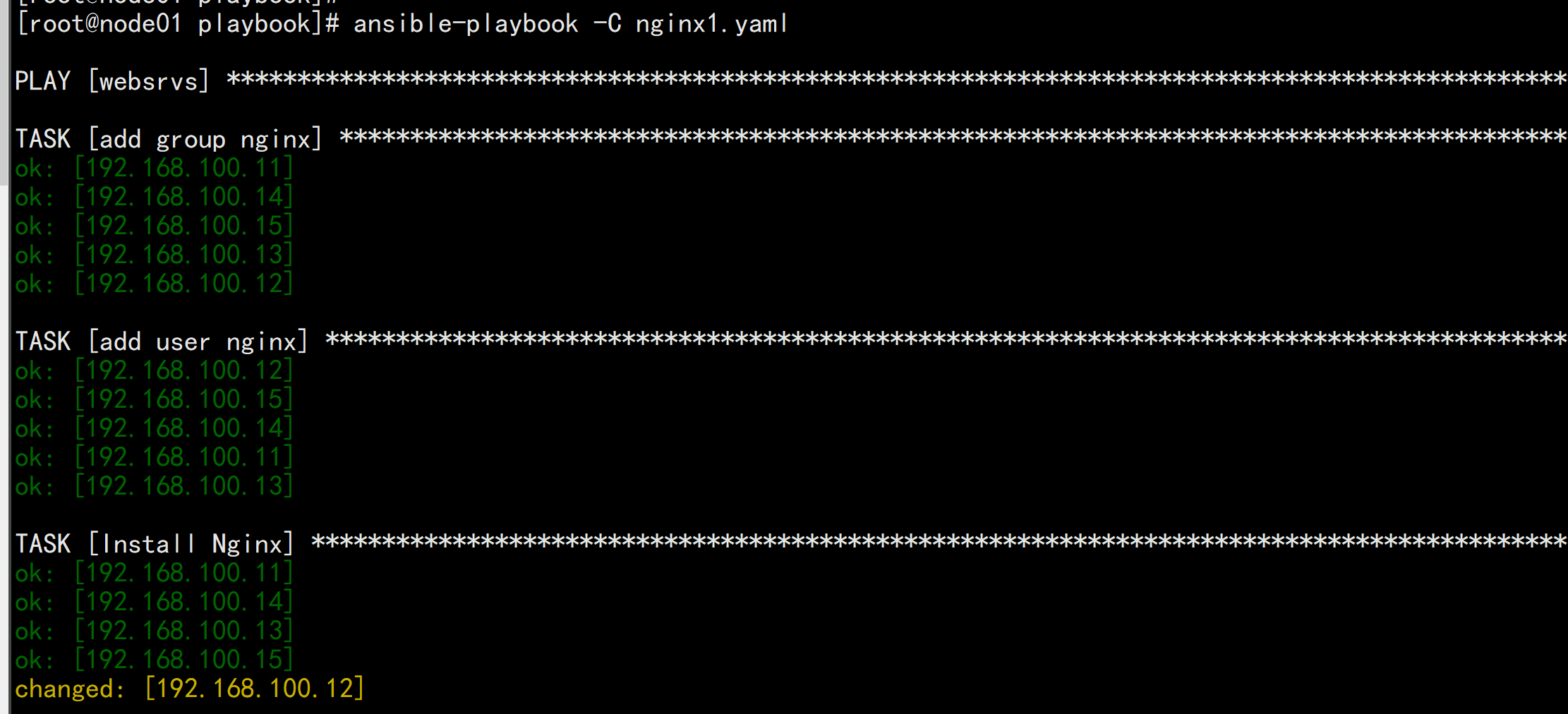
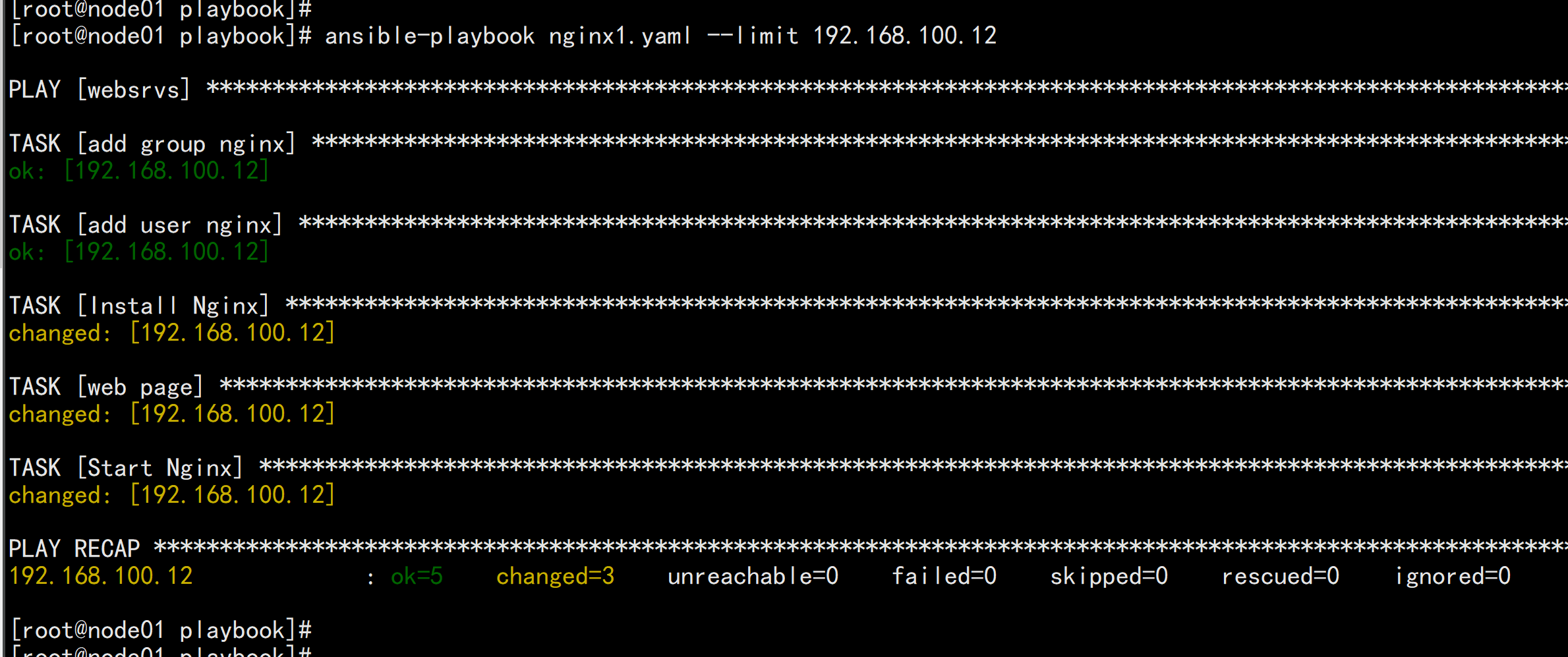
nginx1.yml:---# install nginx- hosts: websrvsremote_user: rootgather_facts: notasks:- name: add group nginxgroup: name=nginx state=present- name: add user nginxuser: name=nginx state=present group=nginx- name: Install Nginxyum: name=nginx state=present- name: web pagecopy: src=/root/files/index.html dest=/usr/share/nginx/html/index.html- name: Start Nginxservice: name=nginx state=started enabled=yes
ansible-playbook -C nginx1.yamlansbile-playbook nginx1.yaml --limit 192.168.100.12 [只针对其中某一台]
2.12.3 利用 playbook 安装和卸载 httpd
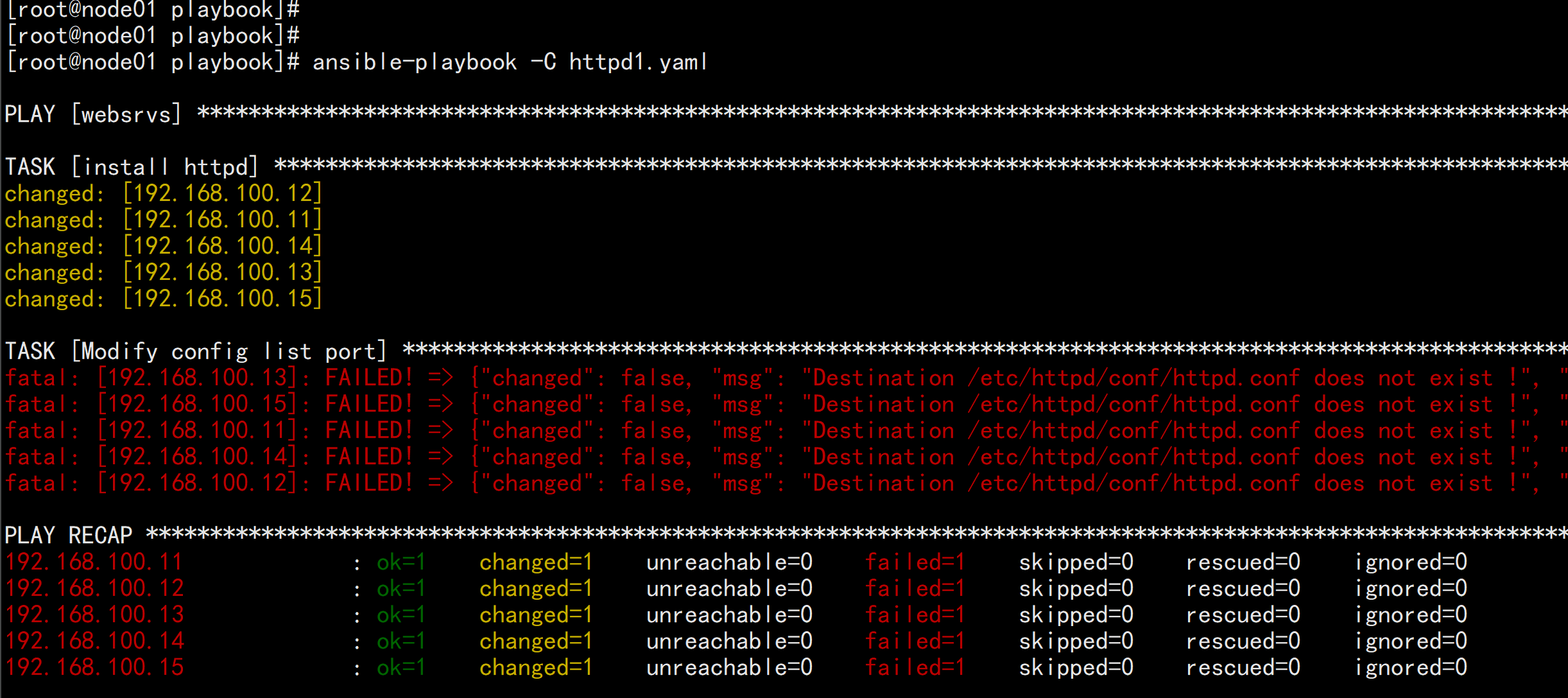
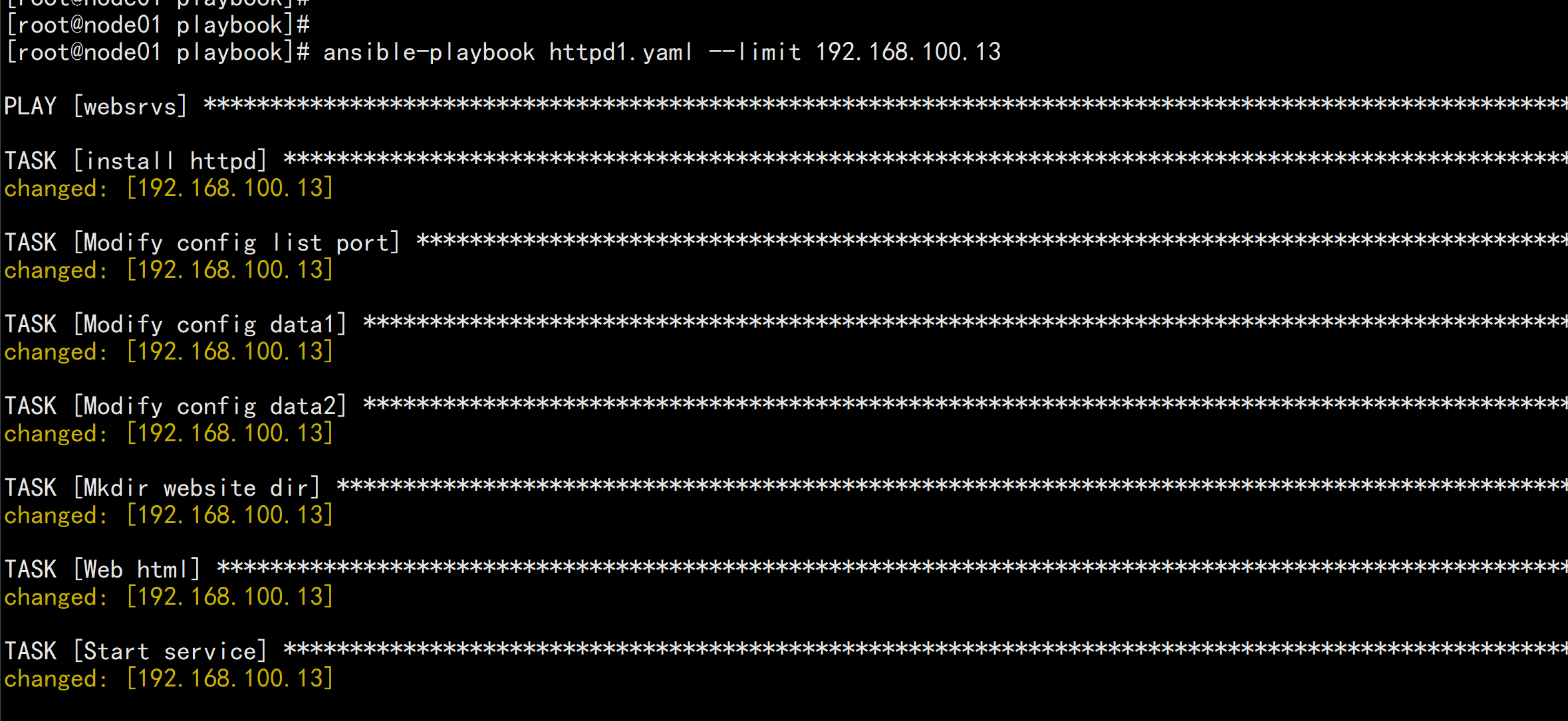
范例:httpd1.yml---#install httpd- hosts: websrvsremote_user: rootgather_facts: notasks:- name: install httpdyum: name=httpd state=present- name: Modify config list portlineinfile:path: /etc/httpd/conf/httpd.confregexp: '^Listen'line: 'Listen 8080'- name: Modify config data1lineinfile:path: /etc/httpd/conf/httpd.confregexp: '^DocumentRoot "/var/www/html"'line: 'DocumentRoot "/data/html"'- name: Modify config data2lineinfile:path: /etc/httpd/conf/httpd.confregexp: '^<Directory "/var/www/html">'line: '<Directory "/data/html">'- name: Mkdir website dirfile: path=/data/html state=directory- name: Web htmlcopy: src=/root/files/index.html dest=/data/html/- name: Start serviceservice: name=httpd state=started enabled=yes
ansible-playbook -C httpd1.yamlansible-playbook httpd1.yaml --limit 192.168.100.13
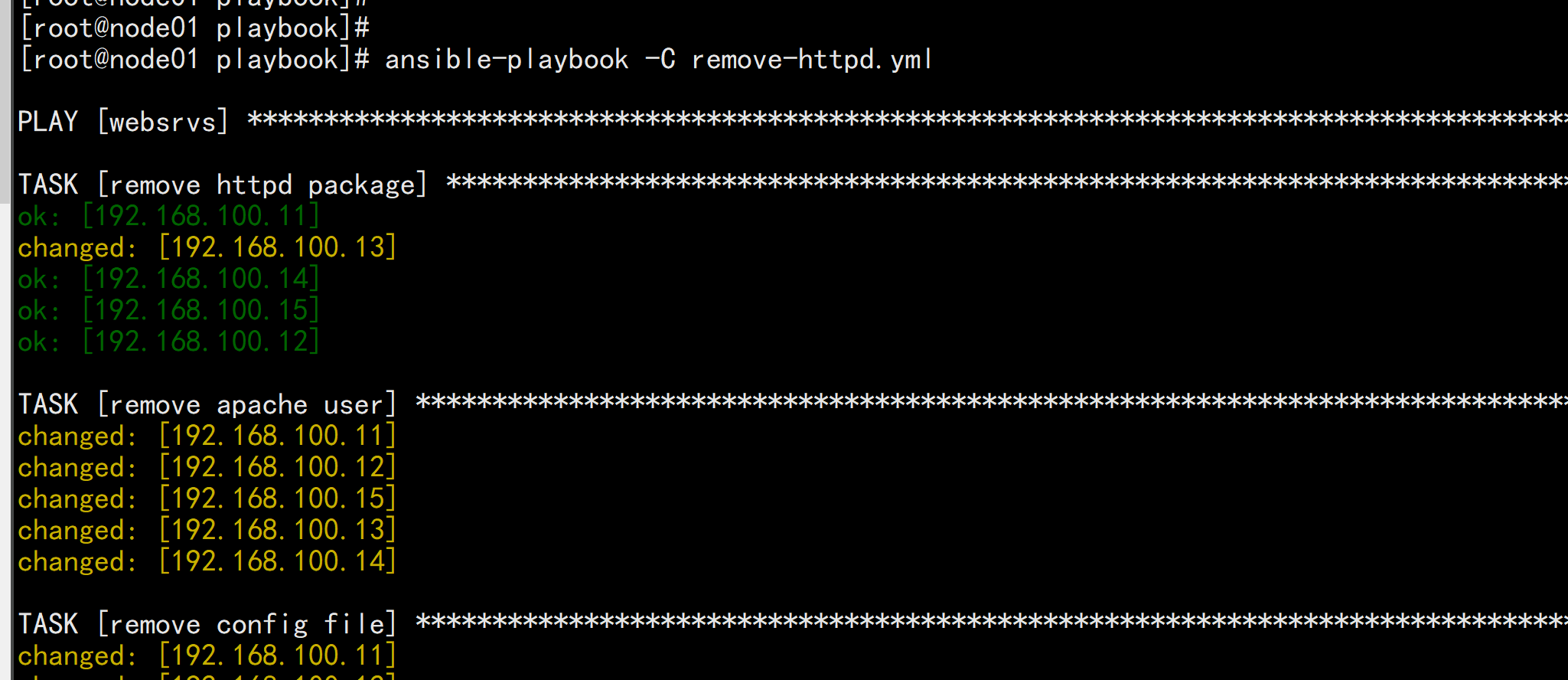
卸载:httpdremove_httpd.yml---- hosts: websrvsremote_user: rootgather_facts: notasks:- name: remove httpd packageyum: name=httpd state=absent- name: remove apache useruser: name=apache state=absent- name: remove config filefile: name=/etc/httpd state=absent- name: remove web htmlfile: name=/data/html/ state=absent
ansible-playbook -C remove-httpd.ymlansible-playbook remove-httpd.yml --limit 192.168.100.13
2.12.4 利用 playbook 安装二进制的 MySQL 5.6
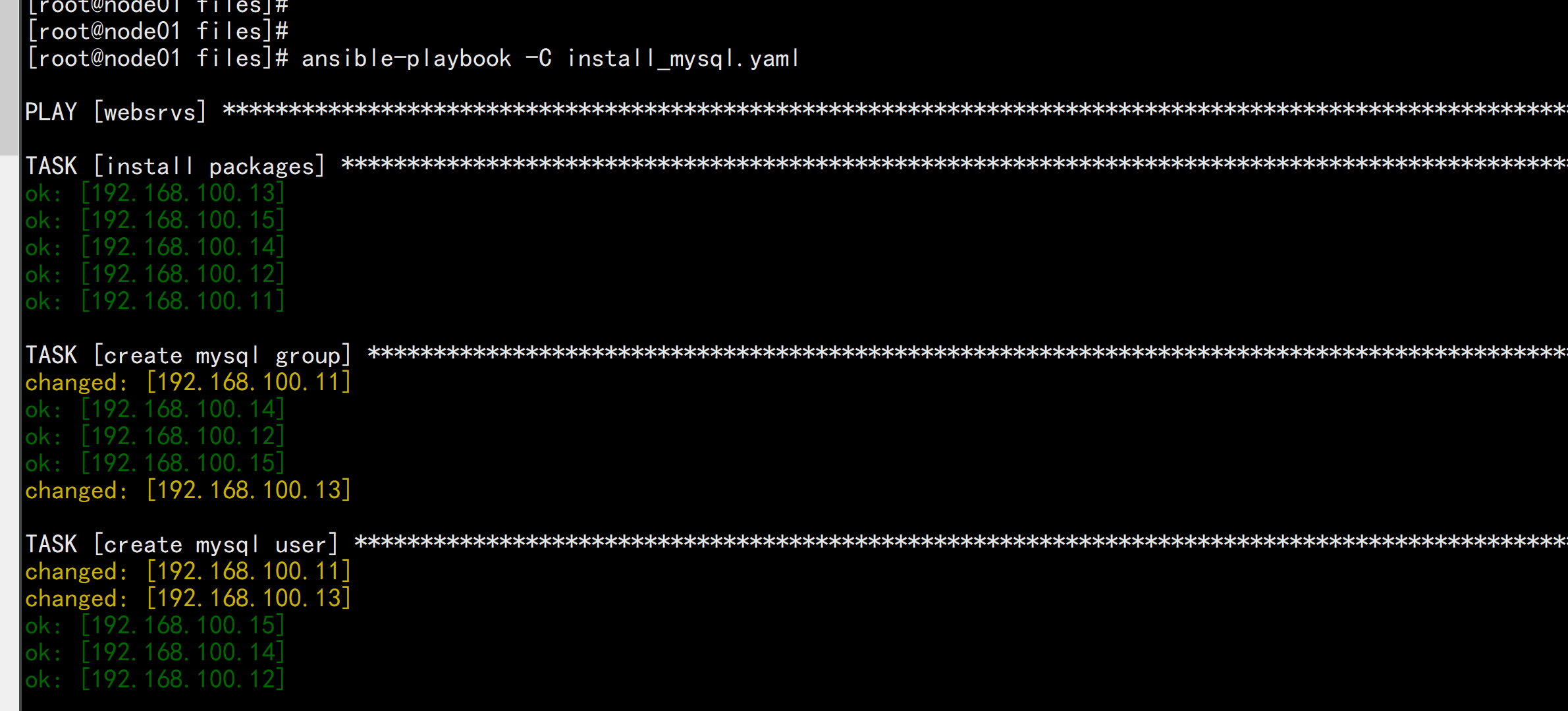
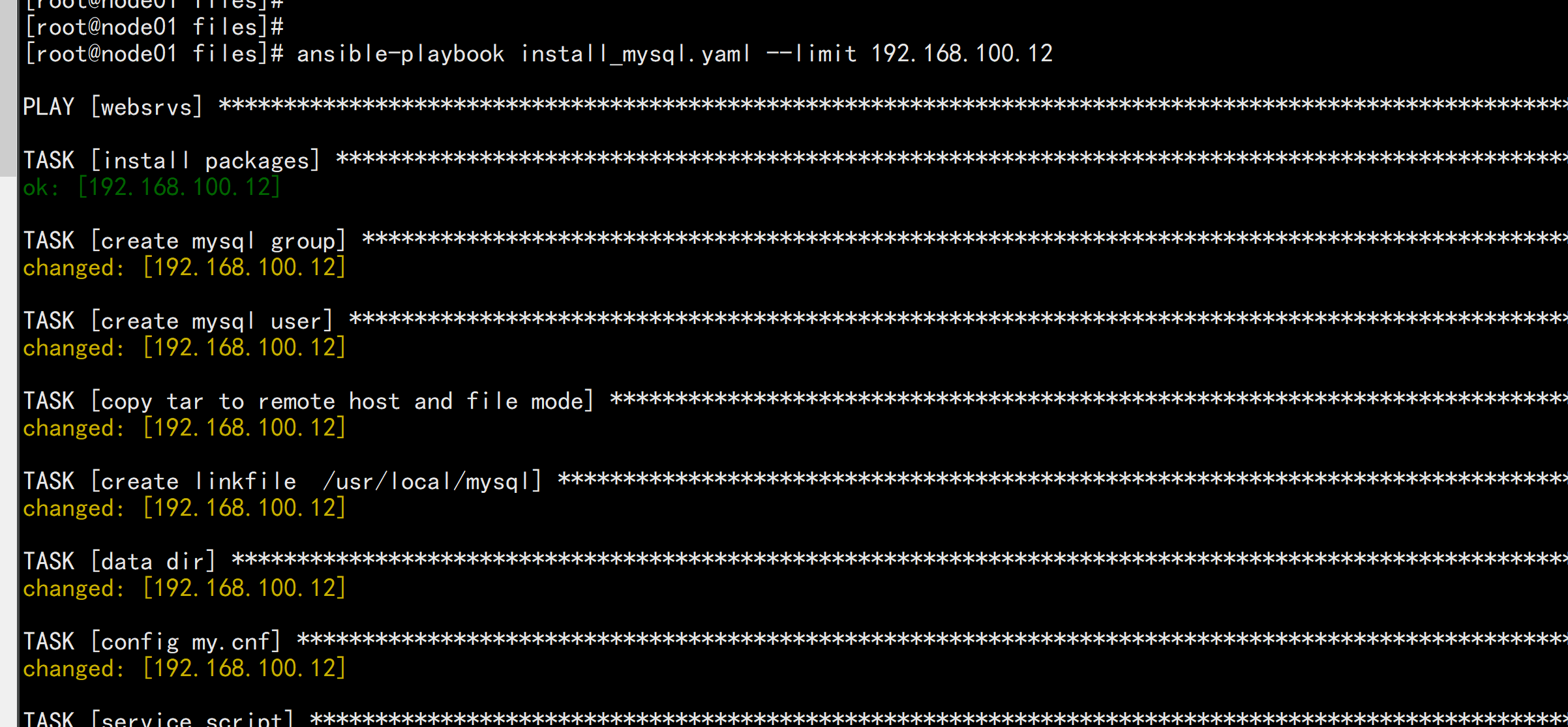
vim my.cnf---[mysqld]socket=/tmp/mysql.sockuser=mysqlsymbolic-links=0datadir=/data/mysqlinnodb_file_per_table=1log-binpid-file=/data/mysql/mysqld.pid[client]port=3306socket=/tmp/mysql.sock[mysqld_safe]log-error=/var/log/mysqld.log---vim secure_mysql.sh---#!/bin/bash/usr/local/mysql/bin/mysql_secure_installation <<EOFymagedumageduyyyyEOF---vim install_mysql.yaml----# install mysql-5.6.46-linux-glibc2.12-x86_64.tar.gz- hosts: websrvsremote_user: rootgather_facts: notasks:- name: install packagesyum: name=libaio,perl-Data-Dumper,perl-Getopt-Long- name: create mysql groupgroup: name=mysql gid=306- name: create mysql useruser: name=mysql uid=306 group=mysql shell=/sbin/nologin system=yes create_home=no home=/data/mysql- name: copy tar to remote host and file modeunarchive: src=/data/ansible/files/mysql-5.6.46-linux-glibc2.12-x86_64.tar.gz dest=/usr/local/ owner=root group=root- name: create linkfile /usr/local/mysqlfile: src=/usr/local/mysql-5.6.46-linux-glibc2.12-x86_64 dest=/usr/local/mysql state=link- name: data dirshell: chdir=/usr/local/mysql/ ./scripts/mysql_install_db --datadir=/data/mysql --user=mysqltags: data- name: config my.cnfcopy: src=/data/ansible/files/my.cnf dest=/etc/my.cnf- name: service scriptshell: /bin/cp /usr/local/mysql/support-files/mysql.server /etc/init.d/mysqld- name: enable serviceshell: /etc/init.d/mysqld start;chkconfig --add mysqld;chkconfig mysqld ontags: service- name: PATH variablecopy: content='PATH=/usr/local/mysql/bin:$PATH' dest=/etc/profile.d/mysql.sh- name: secure scriptscript: /data/ansible/files/secure_mysql.shtags: script----
ansible-playbook -C install_mysql.yamlansible-playbook install_mysql.yaml --limit 192.168.100.12