@zhongdao
2018-02-26T07:46:45.000000Z
字数 99700
阅读 12857
区块链设计与实现笔记v1
拟定目录大纲:
0. 前言
1. 区块链原理机制与背景
2. 区块链基本结构
3. 加解密算法实现
4. 区块数据结构从定义到初步实现
5. 区块节点读取与验证
6. 节点和应用程序之间协议
7. 节点之间沟通
8. 侧链设计原理
9. 侧链开发
10. 智能合约设计原理
11. 智能合约开发
12. 计算机基础
13. Linux相关说明
14. 程序开发语言相关说明
15. 密码学相关说明
16. 资料链接
若有更正请联系: 李君
邮件: junlicn@foxmail.com
2017.10.31
实际自动导航目录:
- 区块链设计与实现笔记v1
- 0.前言
- 1. 区块链原理机制与背景
- 2.区块链基本结构
- 3. 加解密算法实现
- 4. 区块数据结构从定义到初步实现
- 5. 区块节点读取验证与挖矿
- 6. 应用和节点程序之间协议
- 7. 节点之间沟通
- 8. 侧链设计原理
- 9. 侧链开发
- 10. 智能合约设计原理
- 11. 智能合约开发
- 12. 计算机基础
- 13. Linux相关说明
- 14. 程序开发语言相关说明
- 15. 密码学相关说明
- 16. 资料链接
目录不可见时访问: https://www.zybuluo.com/zhongdao/note/933849
0.前言
0.1 内容来源
区块链技术开发公开课:
授课老师: 辕询, 李涛涛
直播地址: http://www.itdks.com/dakashuo/playback/1428
0.2 笔记缘起
根据老师公开课上讲的内容, 构造一个完整笔记,便于学习和掌握. 随着课程的进展, 不断添加和整理.
此文档的完整内容来自:公开的课程内容、源代码,资料、搜索引擎搜到的资料、相关技术书籍上的资料等, 我对内容做了整理,使得易于阅读和条理化,对于部分代码添加了注释和自己的理解, 若有错误请沟通纠正。
其中引用到一些同学的笔记内容或者截图,其他笔记内容来源者包括: 程书芝, 袁丁逸涵, 郜晶, liuhongshuo, 谭东雷, 潘杰 ...
笔记编写过程中有张博成,pz100等对错误之处给出了的修订建议.
要特别感谢老师依据开源传统所教授的内容.
0.3 内容概要
创造一个易于理解说明的区块链.从理论到程序实现.
为了便于对编程不熟悉的同学学习和备查,也增加了所需要的相关的内容.
具体内容参考本文目录,
1. 区块链的基本结构;2. 为什么私钥最重要,以及随机数 –> 私钥 -> 公钥 -> 地址的生成过程;3. 每个区块链程序都由三种基本协议组成a) A协议:节点内部的规则,数据格式、交易规则、加密/解密算法等;b) B协议:应用程序与节点沟通的协议;c) C协议:节点之间沟通的协议;4. 区块间隔和冲突处理机制;5. 计算机的数据存储及区块链数据结构。
0.4 第三期每次课程摘要
- 第1节:
主要内容:1. 区块链的基本结构;2. 为什么私钥最重要,以及随机数 –> 私钥 -> 公钥 -> 地址的生成过程;3. 文件系统的结构;4. 每个区块链程序都由三种基本协议组成a) A协议:节点内部的规则,数据格式、交易规则、加密/解密算法等;b) B协议:应用程序与节点沟通的协议;c) C协议:节点之间沟通的协议;5. 区块间隔和冲突处理机制;6. 计算机的数据存储及区块链数据结构。
- 第2,3节:
本周的两次课程当中,辕询老师深入拆解比特币的结构,从代码层面向同学们展示了比特币的设计。并通过代码演示,详细的展示了私钥、公钥、地址和区块的生成过程。通过课后的作业练习,让同学们动手生产私钥、公钥和区块,从代码层面理解比特币的原理。 - 第4节
周三第4次课,网络编程。辕询老师讲解C语言中套接字函数的用法,并在稍后带同学们使用C语言套接字实现了客户端之间的简单通讯程序。 - 第5节
周六第5次课,使用C语言重构代码。辕询老师带同学们回顾区块结构,说明PHP加密函数的兼容性问题,并带领大家使用C语言重新实现区块结构的生产过程。 - 第6节
周日第6次课,由密码学主讲李涛涛老师,为同学们讲解区块链中使用的加密算法,并带领同学们深入探讨什么是HASH,为什么要使用HASH等问题。 - 第7课
使用C语言重写区块链生成过程。复习区块结构,Transaction的数据结构,Head的数据结构,使用C语言实现Transaction、Head的生成过程。 - 第8课
密码学第2次课,讲解了ECDSA(elliptical curve digital signaturealgorithm)椭圆曲线数字签名算法。
一. 什么是椭圆曲线数字签名算法ECDSA(EllipticalCurve digital Signature Algorithm)
二. ECC (elliptical curve cryptography)和ECDSA的关系
三. 为什么使用ECDSA
四. ECDSA在区块链中的应用
五. ECDSA的编程实现 - 第9课,区块数据解析,如何将一个区块的数据读取出来。
一. 使用scan方法读取transaction的片段长度
二. 使用build方法构造一个length + data的数据结构
三. 将build方法生成的指针存储到无类型(void)链表
四. 使用循环读取链表内容
课程调整
本周确定了新增8次课时的上课时间,每周五、周日增加一次授课。调整后每周授课4次,分别为周三、周五、周六及周日。 - 第10课 -第13课 验证及通过有限状态机和Sockets来接收区块数据.
区块的接收及验证过程
通过TCP接收区块数据
验证格式
记录valence(区块交易数量)
验证内容
验证input,transaction, index参数格式
验证output格式
验证签名,使用publc,signature,address进行ECC验证
验证总输入 大于等于 总输出
验证剩余输入 大于等于 矿工费
验证头部
检查时间:大于上7个区块的平均时间, 保持区块链的时间是不断增加的
检查工作量证明:TARGET是否少于或者等于协议规定的TARGET。
检查交易的merkle tree
通过有限状态机(Finite State Machine)对接收的区块数据进行验证。
- 第14课
更换了助教. ? 讲解了挖矿难度, One Chain 观点. - 第15课
如何用指针链表来存储区块便于遍历, 同时演示挖矿的概念和代码实现过程 - 第16课
通过网络监听并存到storage结构里. 也讲述了节点网络构造和收发钱原理.
代码实现: cnn.c
以后的规划:
- 测试验证函数
- 每一个C协议的操作落实
- 支持超过一个私钥
- 生成一个文件来保存别的节点的IP和端口为下次连接做准备
- 扔掉我们造的storage,改用SQL
最大的2个目标:
- 智能合约 smart contracts
- 侧链 sidechains.
第17课
我们创造的链与BTC的对比, BTC的最全文档在 https://en.bitcoin.it/wiki/Main_Page
根据文档讲解协议.讲解了BTC的智能合约script, 介绍了各种钱包.
讲解了实现虚拟机的php代码.第18课
阅读了以太坊的技术规范的黄皮书, 修改了php设计的虚拟机.第19课
讲解了区块链的安全性问题. 几种安全方面的攻击原理与特点. 讲解了php的语言实现., 对比我们实现的virtual machine 同 php7的虚拟机实现. 如果区块链的存储要更改,可以改为类似实现, 用hashtable.
(组成: 256个bucket, 指针列表, 元数据.)第20课
基于php开发的wiki, 目前的操作系统界面,浏览器等背景.
侧链的原理, blockstream公司的开源侧链模板项目element.第21课
讲解了基于php的wiki如何嵌入插件, 例如从 https://developers.coinbase.com/docs/wallet/guides/price-data 获取json的BTC价格,显示在wiki里. 和区块链结合的原理. 讲解了侧链的原理,钱如何转移.SPV的细节说明.第22课
第23课
第24课
讲解了虚拟机中的script representation of integer. C语言实现
重温了如何编写基于stack machine的script, 简洁的实现fibbonacci 等.
1. 区块链原理机制与背景
1.1 解释比特币
2008年,署名中本聪的作者在讨论加密的邮件列表中,发表论文:A Peer to Peer Electronic Cash System. 2009年1月,Bitcoin网络诞生,代码开源.
比特币(bitcoin),一种去中心化的点对点的网上货币,在没有任何资产担保、内在价值或者中心发行者的情况下维持着价值。
传统互联网解决了信息的传递,而基于区块链的比特币解决了价值的传递.
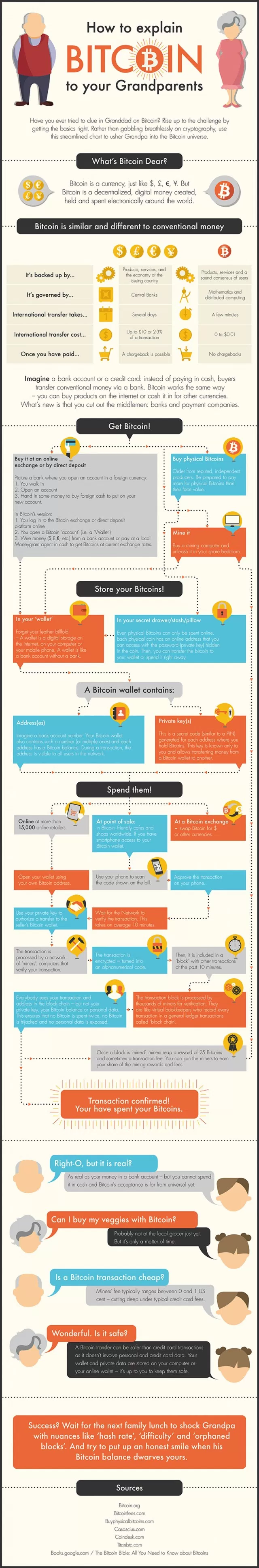
1.2 区块链与比特币机制图示
区块链起源于bitcoin,
通过分布式账本,去中心化的存储,去第三方中介,解决了信任问题.
以区块链技术为核心的系统会形成如下的效果:
1. 全球化的, 没有中心节点, 数据分布式地存储在系统的各个节点上, 即使绝大部分节点毁灭了,只要还有1个节点存在,就可以重建并还原区块链数据.
2. 自治的交易体系,所有节点都是对等的,每个节点都可以自由加入和离开,按照相同的规则达成共识,自行产生区块并且同步数据,无需人工参与.
3. 按照合约执行,各个节点按照既定的运行规则执行,一旦出现违背规则的行为,就会被其他节点抛弃;智能合约包括在每个交易中,交易验证必须先运行智能合约,只有通过验证交易才能被接受.
4. 数据公开透明,不能被篡改,交易之间有一定的关联性,容易追溯.
下图是比特币的交易的运行机制解释:

1.2.1 区块链应用
Below is a quick description of each of the use cases:
App development: Proof of ownership of modules in app development
Digital content: Proof of ownership for digital content storage and delivery
Ride-sharing: Points-based value transfer for ride-sharing
Digital security trading: Ownership and transfer
Digitization of documents/contracts: Digitization of documents/contracts and proof of ownership for transfers
Decentralized storage: Decentralized storage using a network of computers on blockchain
Company incorporations: Digitizing company incorporations, transfer of equity/ownership and governance
Decentralized Internet and computing resources: Decentralized Internet and computing resources to cover every home and business
Home automation: Platform to link the home network and electrical devices to the cloud
Digital identity: Provides digital identity that protects consumer privacy
Escrow/custodian service: Escrow/custodian service for the gaming industry; loan servicing and e-commerce
IT portal: A smart contract IT portal executing order fulfillment in ecommerce/manufacturing
Patient records: Decentralized patient records management
Digitizing assets: Improves anti-counterfeit measures
Reputation management: Helps users engage, share reputation and collect feedback
Prediction platform: Decentralized prediction platform for the share markets, elections, etc.
Enables authenticity of a review: Enables authenticity of a review through trustworthy endorsements for employee peer reviews
Marketplace for sales and purchases of digital assets: Proof of ownership and a marketplace for sales and purchases of digital assets
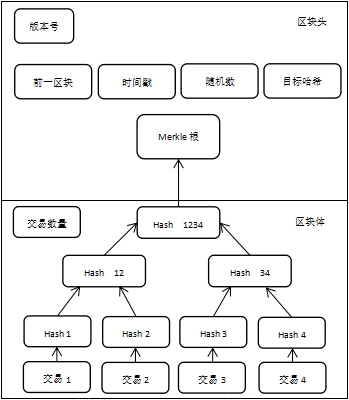
1.3 区块链数据结构图示
在比特币社区里,Transaction 被简称为 TX
https://en.bitcoin.it/wiki/Protocol_documentation
区块链概要图示
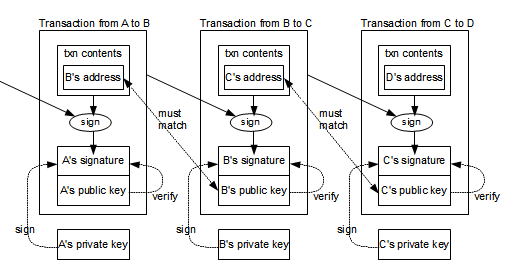
交易图示

交易与基本节点结构
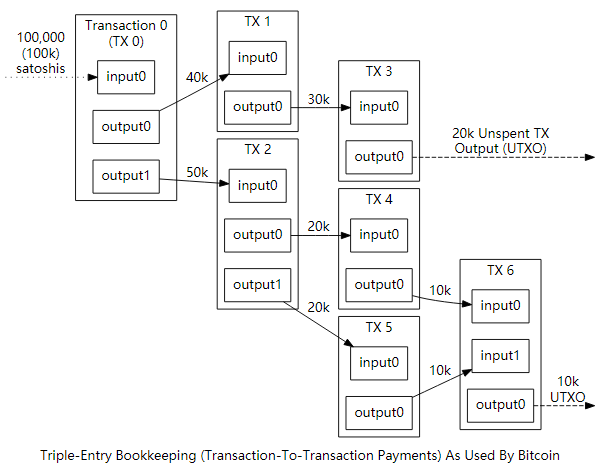
没有余额的概念, 一个人的资产来自以往的所有交易.
1.4 知识点
UTXO
UTXO 代表 Unspent Transaction Output。
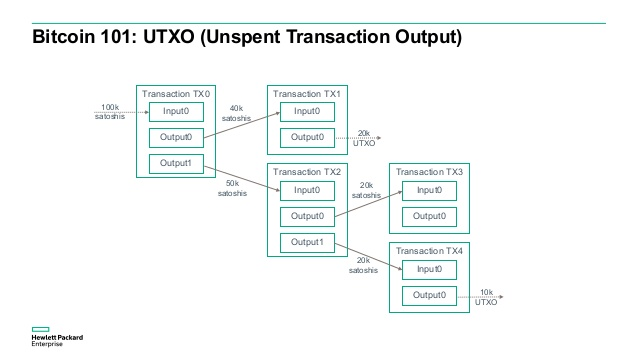
要理解UTXO,最简单的办法就是把一枚比特币从诞生到在商海中沉浮的经历描述一下。我们假设一个这样的场景:张三挖到12.5 枚比特币。过了几天,他把其中 2.5 枚支付给李四。又过了几天,他和李四各出资 2.5 比特币凑成 5 比特币付给王五。
如果是基于账户的设计,张、李、王三人在数据库中各有一个账户,则他们三人的账户变化如下图所示:
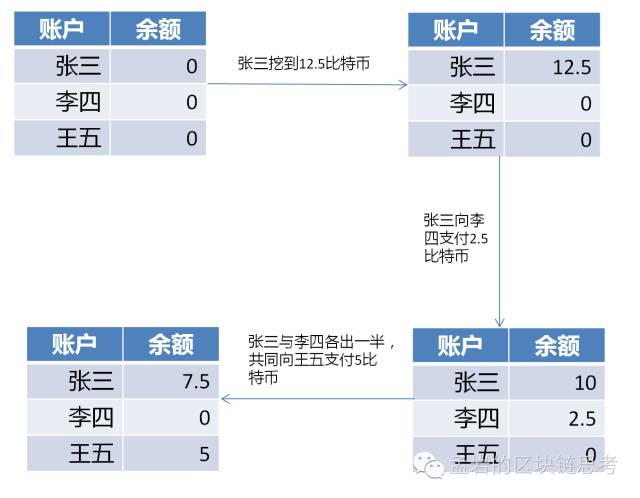
在比特币中,这个过程是通过 UTXO 实现的,图示如下:

上图来自: http://8btc.com/article-4381-1.html
当我们说张三拥有 10枚比特币的时候,我实际上是说,当前区块链账本中,有若干笔交易的 UTXO 项收款人写的是张三的地址,而这些 UTXO 项的数额总和是 10。因为在比特币系统里,一个人可以拥有的地址资源,可谓取之不尽用之不竭。要知道自己的一大堆地址里一共收了多少UTXO,人是算不过来的,需要由比特币钱包代为跟踪计算。
SPV
钱包不用下载所有的交易记录就能验证.
钱包
2012 发明了思维钱包的概念, 容易猜, 钱被偷盗的可能性增加了.
冷钱包:
所有的私钥都是从数字来的, 从随机生产器来的. 自己指定的
不联网的计算机, 把数字存在上面.
联网的计算机把不签名的交易 放在u盘上, 然后
理论上, 病毒影响 U盘.
更安全的是, 造一个地址, 从来不发钱. 只用来收钱.
发一次, 冷地址就变热地址了.
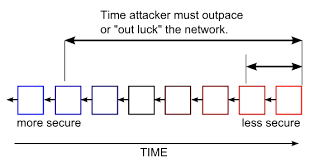
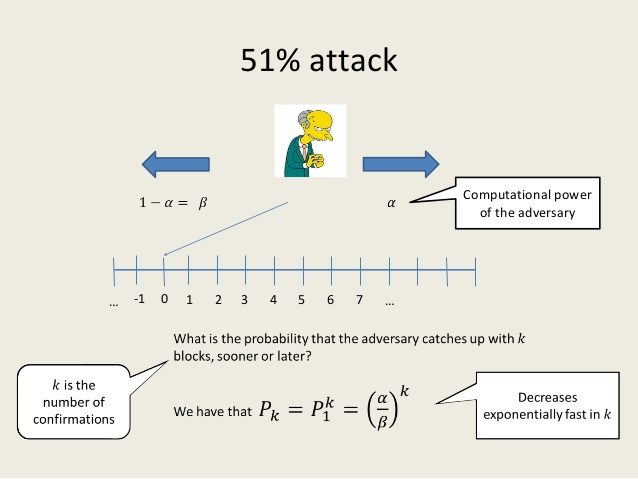
1.5 安全性
50% Attack 百分之五十攻击
控制超过51%算力的时候, 可以修改节点程序, 忽略某种交易.
也可以从一个旧节点开始,建立一条新的节点链,超过旧节点后的节点长度后, 原来就节点上的所有交易就被废弃了, 因为所有节点都开始挖最长的节点.


Transaction Malleability Attack 交易挠曲攻击
Double Spending Attack 重叠耗资攻击
Replay Attack 重放攻击
分叉时
DDoS Attack 分布服务扣缴攻击
Delay Attack 延迟攻击
Partition Attack 割据攻击
1.6 比特币特性
Signing-Only Wallets
两台电脑, 一个台连接网络,运行节点钱包,但没有私钥. 另外一台没网络的把私钥放上去.
这样能防止任何网络上的攻击者来偷钥匙钥匙.
很多企业都是这么做的. 对于复杂的usb病毒, windows之间用过的u盘, 放到linux下格式化.
这个的严格程度,还不如cold Wallets, 创造私钥,打印出来,毁灭计算机. 用时再输入到计算机.
2.区块链基本结构
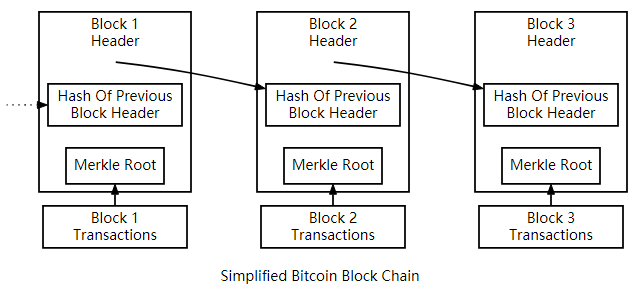
2.1 区块图示
结构示意:
或者如下图示意:
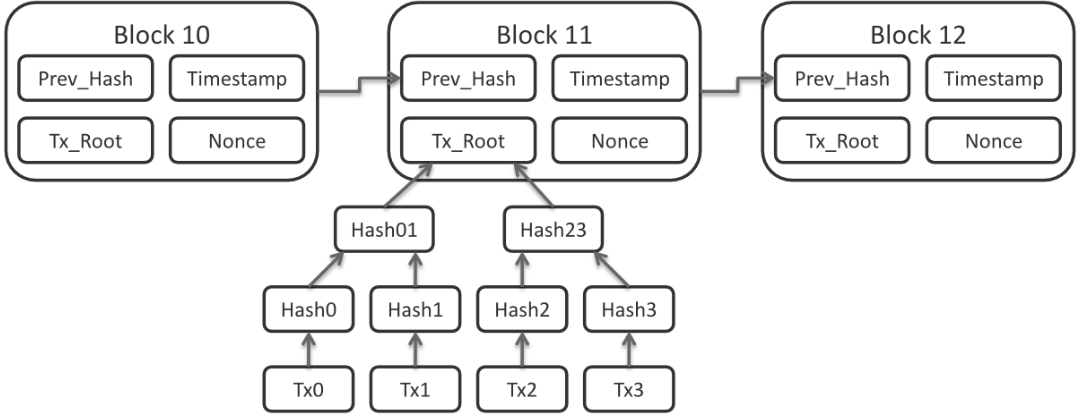
Merkle root 存的hash是为了确保身部所有的交易无法被修改.
Previous Hash是对前一个区块的头header的hash.
4个连续区块及相应交易的例子展示
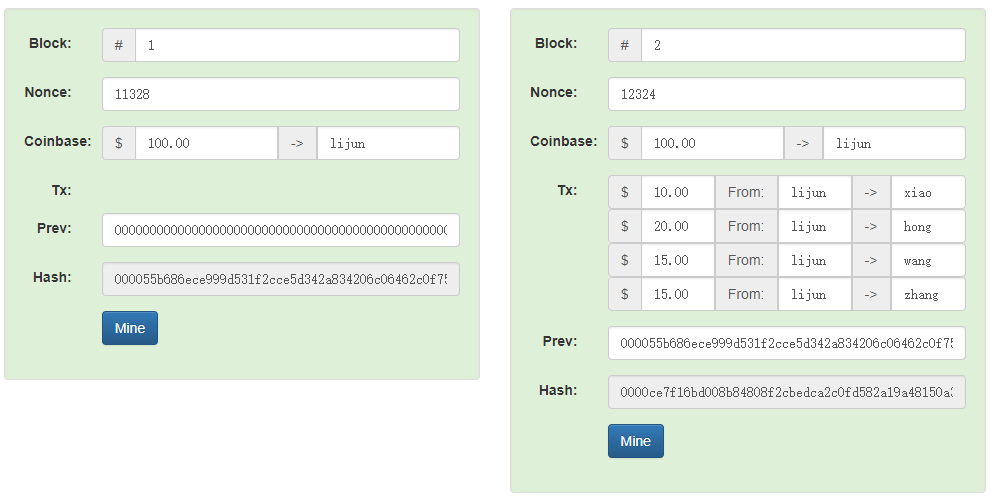
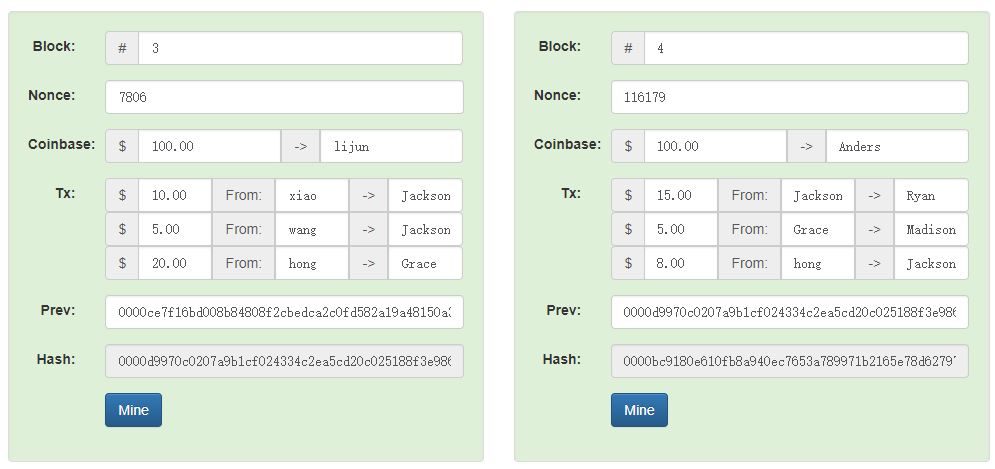
设计理念
During system design, the major data structure for the software are identified; without these, the system modules cannot be mean
software cannot be meaningfully repaired only rewritten.
从2008年末中本聪的白皮书发出到2009年初中本聪的程序完成,有4个月时间。
开始设计好了,后期的维护成本会很小。
一如Unix的设计理念。
2.2 区块定义
出于教学的目的,为了便于理解,CCN设计得非常简洁,保留了核心的部分,去掉了不必要的部分。
ConciseCoin(CCN)是一个数码货币系统。
BLOCK := HEAD, TRANSACTION*
HEAD := current(32), nonce(4), previous(32), target(32), time(4), valence(4)
TRANSACTION := A, B, C, INPUT*, OUTPUT*
INPUT := A, index(4), B, public(B), C, signature(C), transaction(32)
OUTPUT := A, B, address(B), amount(8)
HEAD - 5 attribute 108BYTEBODY - 1 or more TRANSACTIONTRANSACTION - 1 or more INPUT and OUTPUTCOINBASE (创始, 挖矿奖励)
HEADCURRENT: 32NONCE: 4PREVIOUS: 32 -> completely zero if genesis blockTARGET: 32TIME: 4BODYTRANSACTION #1INPUTS: 1个INDEX: 4 -> completely zeroPUBLIC: 0SIGNATURE: 0TRANSACTION: 32 -> completely zeroOUTPUTS: 1个ADDRESS: 灵活 -> miner's addressAMOUNT: 8 -> 50 或者 100 (挖矿奖励)TRANSACTION #2TRANSACTION #3INPUTS: 1个或者多个INDEX: 4PUBLIC: 灵活SIGNATURE: 灵活TRANSACTION: 32OUTPUTS: 1个或者多个ADDRESS: 灵活AMOUNT: 8
2.3 密码学算法实现步骤简要说明
随机数字 -> 私钥 -> 公钥 -> 地址
加密和解密最大的危险就是是否产生真正的随机数.
a = open ("/dev/arandom") 打开文件b = read (a 128) 随机数包括[0 - 256)c = get.private (b) 私钥d = get.public (c) 公钥e = get.address (d) 地址
2.4 交易过程说明
2.4.1 交易过程图示
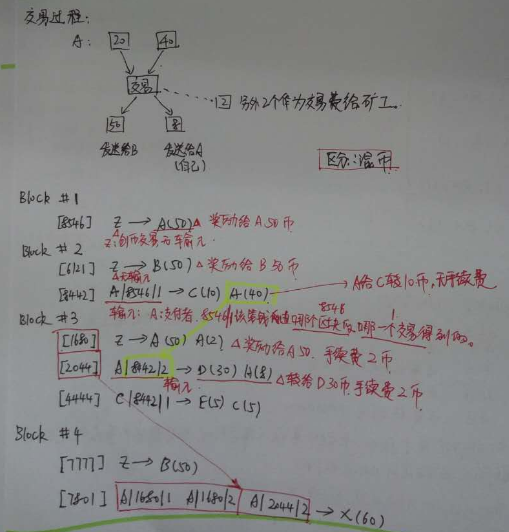
2.4.2 区块中第1个交易用于矿工
第1个交易是矿工奖励, Transaction中的output要设为矿工的地址, 这里的实现用公钥代替.所以构建时,要取得矿工的地址.
3. 加解密算法实现
3.1 安全库说明
不是操作系统或者标准化的函数库叫做第三方库.
libtomcrypt是个第三方库.
1. Libtomcrypt
2. OpenSSL
3.2 代码实现说明
3.2.1 md5
md5 输出 128bit, 每8bit为1个字节, 也就是16个字节, 1个字节2^8 [0,256)用2个字母表示(00-ff), 共计32个字母
换成sha256时, 需要把16字节out数组改为32字节out
// MD5输出128bit SHA1输出160bit SHA256输出256bit .// c语言里 %x表示16进制, 会输出2个字母.// SHA256 输出 256bit, 32个字节, 64个字符.#include "tomcrypt.h"int main(int count, char **arguments){hash_state md;unsigned char *in = "lijun", out[16];/* setup the hash */md5_init(&md);/* add the message */md5_process(&md, in, strlen(in));/* get the hash in out[0..15] */md5_done(&md, out);for(int i = 0; i < 16; i++){printf("%02x", out[i]); // %02x 表示输出2个字符的16进制,否则0时会省略掉.}printf("\n");return 0;}}
3.2.2 sha256
#include "stdio.h"#include "stdlib.h"#include "string.h"#include "tomcrypt.h" //密码库char *get_file(char *path){ //读取文件FILE *file;int length;char *contents;//获取文件长度file = fopen(path , "r+");fseek(file , 0 , SEEK_END); //跳到文件结尾length = ftell(file); //给出文件长度fseek(file , 0 ,SEEK_SET); //再跳回文件开头//分配内存,读取文件//! 最初的代码是length+1, 改为lengthcontents = malloc(length); //给文件分配内存fread(contents , 1 , length , file);//关闭文件, 系统同时打开的文件个数是有限的,约4900+fclose(file);return contents ; //返回文件内容}void main(){ //对文本进行Hash加密char *input , *output;int length;output = malloc(1000); //分配1000字节的内存length = 1000;input = get_file("essay.txt"); //读取文件register_hash(&sha256_desc); //激活哈希函数,必须!!hash_memory(find_hash("sha256") , input , strlen(input) , output , &leng)printf("%s" , output);//printf("%d%c" , length , 10); //打印长度//printf("%02x%c" , output[0] , 10); //打印第一个字符,%02x:十六进制}
3.2.3 获取私钥
unsigned char *get_private(unsigned int *length){prng_state random; // 随机生产器的状态.ecc_key key; //保存私钥和公钥的数据结构unsigned char *buffer;buffer = malloc(*length = 1000);// 随机生成器状态, 系统随机生成器, ?, 保存位置ecc_make_key(&random, find_prng("sprng"), 32, &key); //创建一个私钥// 把其私钥转换成可打印的字符串.ecc_export(buffer, length, PK_PRIVATE, &key);return buffer;}
3.2.4 获取公钥
unsigned char *get_public(unsigned int *length, unsigned char *private){ecc_key key;unsigned char *buffer;//导入私钥ecc_import(private, *length, &key);buffer = malloc(*length = 1000);// 输出公钥ecc_export(buffer, length, PK_PUBLIC, &key);return buffer;}
3.2.5 编码输出
Extra libraries: TomsFastMath library
每次使用tomcryp函数库时, 必须要有如下一行,这是它的固定规则:
ltc_mp = tfm_desc;
将private, public输出的生字节, 用base64转换成ASCII. 便于和其他人共享.
void main(){unsigned char *private, *public, *buffer;unsigned int length_private, length_public, length_buffer;ltc_mp = tfm_desc;register_prng(&sprng_desc); //激活函数register_hash(&sha256_desc);private = get_private(&length_private);length_public = length_private;public = get_public(&length_public, private);buffer = malloc(1000);// tomcrypt库函数_ecc_xxx 生产出自己的私钥, 生成的是生字节.memset(buffer, 0, 1000);base64_encode(private, length_private, buffer, &length_buffer);printf("%s%c%c", buffer, 10, 10);memset(buffer, 0, 1000);base64_encode(public, length_public, buffer, &length_buffer);printf("%s%c", buffer, 10);}
4. 区块数据结构从定义到初步实现
4.1 Head
4.1.1 结构说明
HEADCURRENT: 32NONCE: 4PREVIOUS: 32 -> completely zero if genesis blockTARGET: 32TIME: 4VALENCE: 4
4.1.2 程序数据结构
Head的长度固定是108字节, 所以不需要保存长度.
| 字段说明 | current | nounce | previous | target | time | valence |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 说明 | BODY的sha256输出,当前block的ID | 挖矿难度 | 前个区块的ID | 越大难度越小 | ?时间 | 交易个数 |
| 长度(字节) | 32 | 4 | 32 | 32 | 4 | 4 |
nounce , target 用于pow, 在链的最初不需要pow, 当有很多个节点创造block时才用到pow,
4.1.3 程序代码
unsigned char *get_head(unsigned char *root){unsigned char *complete, *y;unsigned int *x;complete = malloc(104);y = malloc(32);memcpy(y, root, 32);memcpy(complete, y, 32);x = malloc(4);*x = 0;memcpy(complete + 32, x, 4);y = malloc(32);memset(y, 0, 32);memcpy(complete + 36, y, 32);y = malloc(32);memset(y, 255, 32);memcpy(complete + 68, y, 32);x = malloc(4);*x = time(0);memcpy(complete + 100, x, 4);return complete;}
4.2 Body
4.2.1 Transaction-Input
4.2.1.1 结构说明
TRANSACTION #1 // 第一个区块.INPUTS: 1INDEX: 4 -> completely zeroPUBLIC: 0SIGNATURE: 0TRANSACTION: 32 -> completely zeroTRANSACTION #2,#3,... // 之后的区块INPUTS: 1个或者以上INDEX: 4PUBLIC: linghuoSIGNATURE: linghuoTRANSACTION: 32
4.2.1.2 程序数据结构
| 字段名 | A (总长) | index | B | public | C | Signature | Transaction的sha256 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 说明 | 总长 | 第几个Input | public长度 | 公钥 | 签名长度 | 签名 | 交易的hash, merkle root |
| 长度(字节) | 4 | 4 | 4 | B | 4 | C | 32 |
4.2.1.3 程序代码
unsigned char *get_input(unsigned int *total){// A index B public C signature transactionchar *private, *public, *complete;int length;int *x;unsigned char *y;private = get_private(&length);public = get_public(&length, private);complete = malloc(*total = 48 + length);x = malloc(4);*x = 48 + length;memcpy(complete, x, 4); // 放置总长x = malloc(4);*x = 0;memcpy(complete + 4, x, 4); //放置Index长x = malloc(4);*x = length;memcpy(complete + 8, x, 4); // 放置public的长度y = malloc(length);memcpy(y, public, length);memcpy(complete + 12, y, length); // 放置公钥public//!! 应该放置signature 的长度, 和 signature, 因为还未讲到signature的用法, 暂时先不放.x = malloc(4);*x = 0;memcpy(complete + 12 + length, x, 4); //放置Signature长度.y = malloc(32);memset(y, 0, 32);memcpy(complete + 16 + length, y, 32); // 放置Transaction ??return complete;}
4.2.2 Transaction-Output
4.2.2.1 结构说明
第1个交易中的Output
OUTPUTS: 1个ADDRESS: 大小不定 -> 矿工地址AMOUNT: 8字节 -> 100或者50
第2+个交易中的Output
OUTPUTS: 1个ADDRESS: 大小不定 -> 地址AMOUNT: 8字节
4.2.2.2 程序数据结构
| 字段名 | A | B | Address | Amount |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 说明 | 总长度 | 地址长度 | 交易地址 | 交易数量 |
| 长度(字节) | 4 | 4 | B | 8 |
4.2.2.3 代码
unsigned char *get_output(unsigned int *total){unsigned char *private, *public, *complete, *y;unsigned int length, *x, z;private = get_private(&length);public = get_public(&length, private);// len_A len_B address amount// 4 + 4 + B + 8complete = malloc(*total = 16 + length);x = malloc(4);*x = 16 + length;memcpy(complete, x, 4); // 设置总长 Ax = malloc(4);*x = length;memcpy(complete + 4, x, 4); // 设地址长度 By = malloc(length);memcpy(y, public, length);memcpy(complete + 8, y, length); // 设置地址, 暂时把公钥作为地址y = malloc(8);z = 1000;memcpy(y, &z, 4);memset(y + 4, 0, 4);memcpy(complete + 8 + length, y, 8); // 设置8字节的交易数量return complete;}
4.2.3 Transaction
4.2.3.1 结构说明
TRANSACTION #1INPUTS: 1INDEX: 4 -> completely zeroPUBLIC: 0SIGNATURE: 0TRANSACTION: 32 -> completely zeroOUTPUTS: 1ADDRESS: linghuo -> miner's addressAMOUNT: 8 -> 50 huozhe 100TRANSACTION #2TRANSACTION #3INPUTS: yige huozhe yishangINDEX: 4PUBLIC: linghuoSIGNATURE: linghuoTRANSACTION: 32OUTPUTS: yige huozhe yishangADDRESS: linghuoAMOUNT: 8
4.2.3.2 程序数据结构
Transaction
| 字段名 | A | B | C | Input* | Output* |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 说明 | 总长度(含自己) | 输入个数 | 输出个数 | 输入列表 | 输出列表 |
| 长度(字节) | 4 | 4 | 4 | B | C |
结构有变更.
4.2.3.3 程序代码(旧代码,待更改)
unsigned char *get_transaction(unsigned int *total){unsigned char *input, *output, *complete, *y;unsigned int length_input, length_output, *x;input = get_input(&length_input);output = get_output(&length_output);complete = malloc(*total = 12 + length_input + length_output);x = malloc(4); // A*x = 12 + length_input + length_output;memcpy(complete, x, 4);x = malloc(4);*x = 1; // B, 只有1个输入memcpy(complete + 4, x, 4);x = malloc(4);*x = 1; // C 只有一个输出memcpy(complete + 8, x, 4);y = malloc(length_input); // inputmemcpy(y, input, length_input);memcpy(complete + 12, y, length_input);y = malloc(length_output); // outputmemcpy(y, output, length_output);memcpy(complete + 12 + length_input, y, length_output);return complete;}
4.3 整体结构回顾与区块交易示例
4.3.1 头部和身部(交易)
头部
HEAD - 6 attribute 108BYTEBODY - 1 or more TRANSACTIONTRANSACTION - 1 or more INPUT and OUTPUTCOINBASE (创始, 挖矿奖励)
身部
HEADCURRENT: 32NONCE: 4PREVIOUS: 32 -> completely zero if genesis blockTARGET: 32TIME: 4VALENCE: 4BODYTRANSACTION #1INPUTS: 1个INDEX: 4 -> completely zeroPUBLIC: 0SIGNATURE: 0TRANSACTION: 32 -> completely zeroOUTPUTS: 1个ADDRESS: 灵活 -> miner's addressAMOUNT: 8 -> 50 huozhe 100TRANSACTION #2TRANSACTION #3INPUTS: 1个或者多个INDEX: 4PUBLIC: 灵活SIGNATURE: 灵活TRANSACTION: 32OUTPUTS: 1个或者多个ADDRESS: 灵活AMOUNT: 8
4.3.2 各部分具体定义
HEAD:
| 字段说明 | current | nounce | previous | target | time | valence |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 说明 | BODY的sha256输出 | 挖矿难度 | 前个区块的ID | 越大难度越小 | ?时间 | 交易个数 |
| 长度(字节) | 32 | 4 | 32 | 32 | 4 | 4 |
Transaction
| 字段名 | A | B | C | Input* | Output* |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 说明 | 总长度(含自己) | 输入个数 | 输出个数 | 输入列表 | 输出列表 |
| 长度(字节) | 4 | 4 | 4 | B | C |
INPUT:
| 字段名 | A (总长) | index | B | public | C | Signature | Transaction的sha256 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 说明 | 总长 | 第几个Input | public长度 | 公钥 | 签名长度 | 签名 | 交易的hash, merkle root |
| 长度(字节) | 4 | 4 | 4 | B | 4 | C | 32 |
OUTPUT:
| 字段名 | A | B | Address | Amount |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 说明 | 总长度 | 地址长度 | 交易地址 | 交易数量 |
| 长度(字节) | 4 | 4 | B | 8 |
4.3.3 区块交易实例
#1: 3930[8629] -> YUANXUN(100)#2: 4479[4140] -> YUANXUN(100)[7159] YUANXUN/8629/1 -> YUANXUN(99) PANPENG(1)A index B public C signature transaction
4.4 程序开发实现
4.4.1 常用函数设计
为了方便处理区块字段, 设计了相关函数. 简化常见的操作.
char *string_create(char *old, int length)char *string_create_improper(char *old)char *string_create_progression(int a)int string_measure(char *buffer)void string_update(char *object, char *buffer, int length)void string_update_4(char *object, int quantity)void string_update_8(char *object, uint64_t quantity)void string_update_initial(char *object, char *initial)char *string_eject(char *object)int scan(char *source)
4.4.2 区块及示例区块数据生成
需要说明的是, 因为老师对随机数字比字母单词更敏感,所以实例程序中的变量很多采用了数字来表示. 并无其他深意.
#define TFM_DESC#include "stdio.h"#include "stdlib.h"#include "string.h"#include "tfm.h"#include "tomcrypt.h"char *string_create(char *old, int length){char *new;int *_6157;new = malloc(length + 4) + 4;memcpy(new, old, length);_6157 = (int *) (new - 4);*_6157 = length;return new;}char *string_create_improper(char *old){char *new;int *_7193;new = malloc(strlen(old) + 4) + 4;memcpy(new, old, strlen(old));_7193 = (int *) (new - 4);*_7193 = strlen(old);return new;}char *string_create_progression(int a){char *c;int *_3919;c = malloc(a + 4) + 4;_3919 = (int *) (c - 4);*_3919 = 0;return c;}int string_measure(char *buffer){int *_4721;_4721 = (int *) (buffer - 4);return *_4721;}void string_update(char *object, char *buffer, int length){int *_9492;_9492 = (int *) (object - 4);memcpy(object + *_9492, buffer, length);*_9492 += length;}void string_update_4(char *object, int quantity){int *_7751, *_2888;_7751 = (int *) (object - 4);_2888 = (int *) (object + *_7751);*_2888 = quantity;*_7751 += 4;}void string_update_8(char *object, uint64_t quantity){int *_7751;uint64_t *_2888;_7751 = (int *) (object - 4);_2888 = (uint64_t *) (object + *_7751);*_2888 = quantity;*_7751 += 8;}void string_update_initial(char *object, char *initial){int *_8478, *_5970;_8478 = (int *) (object - 4);_5970 = (int *) initial;memcpy(object + *_8478, initial, *_5970);*_8478 += *_5970;}char *string_eject(char *object){char *new;int *_6558;_6558 = (int *) (object - 4);new = malloc(*_6558);memcpy(new, object, *_6558);return new;}char *get_maximal(){char *digest;digest = malloc(32);memset(digest, 255, 32);return digest;}char *get_minimal(){char *digest;digest = malloc(32);memset(digest, 0, 32);return digest;}int scan(char *source){int *size;size = (int *) source;return *size;}char *get_file(char *path) {FILE *file;int length;char *contents;file = fopen(path, "r+");fseek(file, 0, SEEK_END);length = ftell(file);fseek(file, 0, SEEK_SET);contents = malloc(length + 1);fread(contents, 1, length, file);fclose(file);return contents;}// same info, after ecc signature, output different sig length because of random number.char *get_signature(char *object, char *private){prng_state _1307;ecc_key _1317;int _1648;char *_5497;_5497 = malloc(1000);_1648 = 1000;ecc_import(private, string_measure(private), &_1317);ecc_sign_hash(object, string_measure(object), _5497, &_1648, &_1307, find_prng("sprng"), &_1317);return string_create(_5497, _1648);}unsigned char *get_private(unsigned int *length){prng_state random;ecc_key key;unsigned char *buffer;buffer = malloc(*length = 1000);ecc_make_key(&random, find_prng("sprng"), 32, &key);ecc_export(buffer, length, PK_PRIVATE, &key);return buffer;}unsigned char *get_public(unsigned int *length, unsigned char *private){ecc_key key;unsigned char *buffer;ecc_import(private, *length, &key);buffer = malloc(*length = 1000);ecc_export(buffer, length, PK_PUBLIC, &key);return buffer;}char *build_input(int _8626, char *_5409, char *_4051, char *_3775){char *_9016;int *_1933;_9016 = malloc(48 + string_measure(_5409) + string_measure(_4051));_1933 = (int *) _9016;*_1933 = 48 + string_measure(_5409) + string_measure(_4051);_1933 = (int *) (_9016 + 4);*_1933 = _8626;_1933 = (int *) (_9016 + 8);*_1933 = string_measure(_5409);memcpy(_9016 + 12, _5409, string_measure(_5409));_1933 = (int *) (_9016 + 12 + string_measure(_5409));*_1933 = string_measure(_4051);memcpy(_9016 + 16 + string_measure(_5409), _4051, string_measure(_4051));memcpy(_9016 + 16 + string_measure(_5409) + string_measure(_4051), _3775, 32);return _9016;}char *build_output(char *_7095, uint64_t _8432){char *_3516;int *_8347;uint64_t *_9910;_3516 = malloc(16 + string_measure(_7095));_8347 = (int *) _3516;*_8347 = 16 + string_measure(_7095);_8347 = (int *) (_3516 + 4);*_8347 = string_measure(_7095);memcpy(_3516 + 8, _7095, string_measure(_7095));_9910 = (uint64_t *) (_3516 + 8 + string_measure(_7095));*_9910 = _8432;return _3516;}char *get_sha256(char *buffer, int size){hash_state resource;char *digest;digest = malloc(32);sha256_init(&resource);sha256_process(&resource, buffer, size);sha256_done(&resource, digest);return digest;}char *get_md5(char *buffer, int size){hash_state resource;char *digest;digest = malloc(16);md5_init(&resource);md5_process(&resource, buffer, size);md5_done(&resource, digest);return digest;}char *get_merkle_root(char *old, int size){char *new, output[32], input[64];int index;if (size == 1) {return old;}if (size % 2) {new = malloc(32 * (size + 1));memcpy(new, old, size * 32);memcpy(new + size * 32, old + (size - 1) * 32, 32);return get_merkle_root(new, size + 1);}new = malloc(32 * size / 2);for (index = 0; index < size; index += 2) {memcpy(input, old + index * 32, 64);memcpy(new + (index / 2) * 32, get_sha256(input, 64), 32);}return get_merkle_root(new, size / 2);}void print_digest(char *digest){int index;for (index = 0; index < 32; index++)printf("%02hhx", digest[index]);printf("%c", 10);}// ------------------char *transaction_7159(int A, char *B, char *C, char *D, char *lichangli, char *panpeng){char *input_0, *output_0, *output_1, *transaction;input_0 = build_input(A, B, C, D);output_0 = build_output(lichangli, 99);output_1 = build_output(panpeng, 1);transaction = string_create_progression(12 + scan(input_0) + scan(output_0) + scan(output_1));string_update_4(transaction, 12 + scan(input_0) + scan(output_0) + scan(output_1));string_update_4(transaction, 1);string_update_4(transaction, 2);string_update(transaction, input_0, scan(input_0));string_update(transaction, output_0, scan(output_0));string_update(transaction, output_1, scan(output_1));return transaction;}char *block_3930(char *A){char *block;block = string_create_progression(108 + string_measure(A));string_update(block, get_sha256(A, string_measure(A)), 32);string_update_4(block, 0);string_update(block, get_minimal(), 32);string_update(block, get_maximal(), 32);string_update_4(block, time(0));string_update_4(block, 1);string_update(block, A, string_measure(A));return block;}char *block_4479(char *previous, char *A, char *B){char *block, *tree;tree = string_create_progression(64);string_update(tree, get_sha256(A, string_measure(A)), 32);string_update(tree, get_sha256(B, string_measure(B)), 32);block = string_create_progression(108 + string_measure(A) + string_measure(B));string_update(block, get_merkle_root(tree, 2), 32);string_update_4(block, 0);string_update(block, previous, 32);string_update(block, get_maximal(), 32);string_update_4(block, time(0));string_update_4(block, 2);string_update(block, A, string_measure(A));string_update(block, B, string_measure(B));return block;}char *transaction_8629(char *lichangli){char *input_0, *output_0, *progression;input_0 = build_input(0, string_create_improper(""), string_create_improper(""), get_minimal());output_0 = build_output(lichangli, 100);progression = string_create_progression(12 + scan(input_0) + scan(output_0));string_update_4(progression, 12 + scan(input_0) + scan(output_0));string_update_4(progression, 1);string_update_4(progression, 1);string_update(progression, input_0, scan(input_0));string_update(progression, output_0, scan(output_0));return progression;}char *transaction_4140(char *lichangli){char *input_0, *output_0, *progression;input_0 = build_input(0, string_create_improper(""), string_create_improper(""), get_minimal());output_0 = build_output(lichangli, 100);progression = string_create_progression(12 + scan(input_0) + scan(output_0));string_update_4(progression, 12 + scan(input_0) + scan(output_0));string_update_4(progression, 1);string_update_4(progression, 1);string_update(progression, input_0, scan(input_0));string_update(progression, output_0, scan(output_0));return progression;}
4.4.3 示例数据写入调用
完成了示例数据的写入, 就方便后面开发读取和验证的部分的代码的测试了.
int main(int count, char **arguments){ltc_mp = tfm_desc;register_prng(&sprng_desc);register_hash(&sha256_desc);char *A, *B, *C, *BLOCK_A, *BLOCK_B;char *_6301, *_1604, *_1215;char *buffer;int length;char *panpeng_address, *panpeng_public, *lichangli_address, *lichangli_public, *lichangli_private;_6301 = "MEwDAgcAAgEgAiEAy4Dqak+QdoTjLOneFcw45XLVvRo1pxlurO7CdnSiEmkCIEHKqUkf236XXyybfJWX8dhvHKJXHwJ2TKJ6f2J78OIiMEwDAgcAAgEgAiEAy4Dqak+QdoTjLOneFcw45XLVvRo1pxlurO7CdnSiEmkCIEHKqUkf236XXyybfJWX8dhvHKJXHwJ2TKJ6f2J78OIi";_1604 = "MEwDAgcAAgEgAiB/XlZGVRCrgg1QoZpLXP25dBxfE+l53GcrQT+rnOyMtQIhAPjOmLLKCkZeuk378KlQCLXGYcx3ZZNpYt2xqPTS6BC/";_1215 = "MG8DAgeAAgEgAiB/XlZGVRCrgg1QoZpLXP25dBxfE+l53GcrQT+rnOyMtQIhAPjOmLLKCkZeuk378KlQCLXGYcx3ZZNpYt2xqPTS6BC/AiEAuUgmCNAsw2ElO5hxpvAzJpKcdSuyiHV84R2jTPFVu7o=";buffer = malloc(1000);length = 1000;base64_decode(_6301, strlen(_6301), buffer, &length);panpeng_public = string_create(buffer, length);length = 1000;base64_decode(_1604, strlen(_1604), buffer, &length);lichangli_public = string_create(buffer, length);length = 1000;base64_decode(_1215, strlen(_1215), buffer, &length);lichangli_private = string_create(buffer, length);panpeng_address = string_create(get_md5(panpeng_public, 32), 16);lichangli_address = string_create(get_md5(lichangli_public, 32), 16);A = transaction_8629(lichangli_address);B = transaction_4140(lichangli_address);C = transaction_7159(1, lichangli_public, get_signature(A, lichangli_private), get_sha256(A, string_measure(A)), lichangli_address, panpeng_address);BLOCK_A = block_3930(A);BLOCK_B = block_4479(get_sha256(BLOCK_A, string_measure(BLOCK_A)), B, C);write(1, BLOCK_B, string_measure(BLOCK_B));}
5. 区块节点读取验证与挖矿
5.1 merkle tree 说明
Hash的计算简要示意
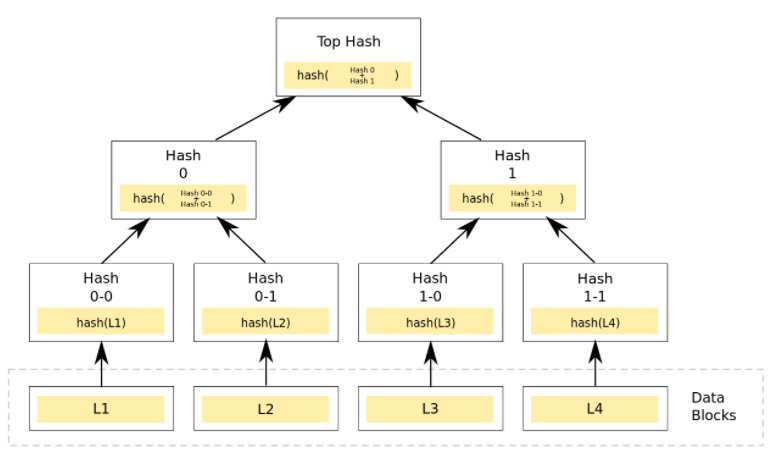
交易的hash计算与区块简要示意
5.1.1 递归函数定义
递归计算merkle root
先计算单个.
然后计算奇数的hash,
计算偶数的hash
pseudo code, author by Lijunmerkle_root(arr[])if(count(arr[]) ==1 ) return arr[0];if(count(arr[]) %2 )return sha256(merkle_root(arr[0,n-2]), arr[n-1])elsereturn shar256(merkle_root(arr[0,n/2-1]), merkle_root(arr[n/2, n-1]);
只有一个交易,merkle root就是对这个交易的hash.
- get_merkle_root(X) = X
- get_merkle_root(X0 , X1 , …… , X2n ) = get_merkle_root(X0 ,X1 ,…… ,X2n,X2n)
- get_merkle_root(X0 , X1 , …… , X2n-1 ) = get_merkle_root(SHA256(X0+X1), SHA256(X2+X3) ……)
function(x) {if (count(x) == 1 ) return x;if (count(x) %2) x.push[x, (}
5.1.2 php递归实现代码
<?phpfunction get_lines_file($file){$result = array();$contents = file_get_contents($file);$contents = explode(chr(10), $contents); //用换行符分割// linux 放10, windows会放13,10作为换行,所以删掉13foreach ($contents as $item) {$item = str_replace(chr(13), '', $item); // 去掉char13if (strlen($item) > 0)array_push($result, $item);}return $result;}/* 生成hash. 可以输出存到 文件里.$digests = array();foreach(range(1,100) as $number)$digests[] = hash('sha256', rand());*/$x = get_lines_file('digests.txt');var_dump(get_Merkle_root($x));function get_Merkle_root($digests){if (count($digests) == 1) {echo sprintf('Case #1: %d%c', count($digests), 10);return $digests[0];}if (count($digests) % 2) { // 奇数echo sprintf('Case #2: %d%c', count($digests), 10);$item = $digests[count($digests) - 1];array_push($digests, $item); // push, 把最后1个item复制return get_Merkle_root($digests);}echo sprintf('Case #3: %d%c', count($digests), 10);for ($i = 0, $s = count($digests) / 2; $i < $s; $i++) {$a = array_shift($digests); // 从左侧移出$b = array_shift($digests); // 组成一对计算hash.array_push($digests, hash('sha256', $a . $b)); //从右侧插入}return get_Merkle_root($digests);/* 另外一种方法, 新建一个数组reduced存放$i = 0;while($i < count($digests)){$merged= sprintf('%s%s',$digests[i[,$digests[i+1]);array_push($reduced, hash('sha256',$merged));$i += 2;}return get_Merkle_root($reduced);*/}
digests.txt的内容是100个随机数的hash值, 每行一个hash值.
$ head -3 digests.txtc5c77f852587da8a14d163e9be251c79590ac1354da79397b44b7e23e55d74704247c422e39497fc67e527dffe0ccbcd19dc9be0bd12ed2c9bc78ae4f64ce369e9f07edbdbdc7403a93903840a096944b7194d38a73b497531fb65a56541cab7
5.2 区块节点读取说明
创造节点之后, 读取区块相关内容信息, 并进行验证, 确认都是正确的.
再次回顾下数据结构:
Head的长度固定, 所以不需要保存长度. 这里设计为104
| 字段说明 | current | nounce | previous | target | time |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 说明 | BODY的sha256输出,当前block的ID | 挖矿难度 | 前个区块的ID | 越大难度越小 | ?时间 |
| 长度(字节) | 32 | 4 | 32 | 32 | 4 |
Transaction 旧设计
| 字段名 | A | B | Input* | C | Output* |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 说明 | 总长度 | 所有输入长度 | 输入 | 所有output长度 | 多个输出 |
| 长度(字节) | 4 | 4 | B | 4 | C |
Transaction 新设计
| 字段名 | A | B | C | Input* | Output* |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 说明 | 总长度(含自己) | 输入个数 | 输出个数 | 输入列表 | 输出列表 |
| 长度(字节) | 4 | 4 | 4 | B | C |
Head 后面跟多个Transaction. 其中第1个Transaction是创始交易, 用于矿工奖励.
Transaction
为了方便, 将上表中的 B, Input*, C, Output* 统一表示为后继内容Content.
| 字段名 | Head | Transaction#1 | Transaction#2 | T#3 | ... |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 说明 | 头部 | 总长度A和后继内容 | 总长度A和后继内容 | 总长度A和后继内容 | ... |
| 结构 | Head | A,Content | A,Content | A,Content | ... |
| 长度(字节) | 104 | A | A | A | ... |
5.2.1 基于字节的移动来读取内容
取得区块的生字节后, 可以通过指针来回移动, 获取相关内容. 指针到达的位置就是整数int长度的位置, 取*就可以得到其长度.
x+104, // 到达body,第一个交易.
x +104 +(*) // 达到第2个交易.
x +104 +(*) + (*) // 达到第2个交易.
C语言实现:
x = x + 104;x = x + (*x);x = x + (*x);
5.2.2 指针移动获得区块的不同变量
回顾Input的结构:
INPUT := A, INDEX, B, PUBLIC, C, SIGNATURE, TRANSACTION
通过指针移动获取相应变量地址
unsigned *A, *B, *CA = inputB = input + 8C = input + 12 + B
5.2.3 对区块里有多少交易进行计数
#include "stdio.h"#include "stdlib.h"#include "string.h"// 这里加了length存 读取出文件内容的长度.unsigned char *get_file(char *path, long *length) {FILE *file;unsigned char *contents;file = fopen(path, "r+");fseek(file, 0, SEEK_END);*length = ftell(file);fseek(file, 0, SEEK_SET);contents = malloc((size_t)*length);fread(contents, 1, (size_t)*length, file);fclose(file);return contents;}unsigned int slice(unsigned char *cursor, unsigned int length){unsigned char *limit;unsigned int *X;unsigned int count;limit = cursor + length; // 尾部cursor += 104;count = 0;while (cursor < limit) {X = (unsigned int *)cursor; //指针类型转换cursor += *X; // 跳到下个交易count++;}return count;}int main(int count, char **arguments){unsigned char *block;unsigned int length;block = get_file(arguments[1], &length);printf("%d%c", slice(block, length), 10);}
5.2.2 构造链表来读取交易
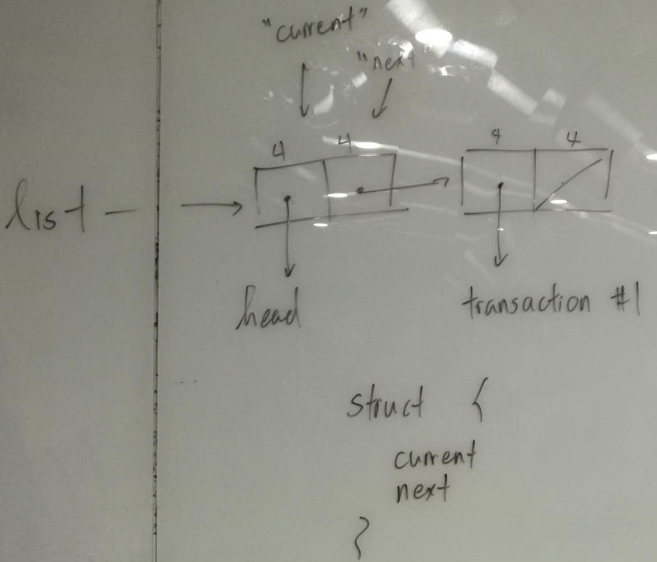
在上一个slice的基础上, 一边遍历,一边分配空间, 同时创造linklist来指向内容空间.
unsigned int slice(unsigned char *cursor, unsigned int length){unsigned char *limit, *transaction;unsigned int *X;void *list, *link;unsigned int count;limit = cursor + length; // 尾部cursor += 104;count = 0;while (cursor < limit) {X = (unsigned int *)cursor; //指针类型转换transaction = malloc(*X + 4) + 4; //获取新分配的内容空间的交易内容地址起始位置memcpy(transaction, cursor, *X); //保存内容, 长度为*X,即交易长度memcpy(transaction-4, X, 4); // 保存内容的长度.cursor += *X;count++;// 相当2个4字节指针,前一个装内容地址, 后一个装后list的地址// 这是一种比较粗糙的方式来构造linklist, 后面会介绍通过函数来构造.link = malloc(8);memcpy(link, transaction, 4);memcpy(link + 4, list, 4);list = link;}return count;}
5.3 区块节点存储的读取实现
5.3.1 区块链结构存储的处理程序规划
storage.add_block( $storage, $substance)storage.remove_block($storage, $identify)storage.get_block($storage, $identify)storage.load($storage, $identify) // 放内存storage.unload($storage, $identify) // 从内存中卸载. 放硬盘上 缓存storage.get_transaction($storage, $identify);//int *storage_load read_file() get_file()int *storage_unload write_file(path, substance, length)char *storage_get_block
可以用heap list vector or tree 来落实上面的函数, 在效率上会有差别, 但是效果一样.
5.3.2 如果是网络读取,则tcp接收区块.
1) 阅读 108个字节, 保存valence为Y
2) 读 4个字节, 保存为X
3) 读 X 个字节
4) 用副函数来确认此交易格式
5) 递归向 步骤2 一共 Y次
6) 做验证. (格式已经确认)
5.3.3 区块节点存储设计开发详细说明
规划设计:
Storage 的结构
// 容量, 创始的指针, 文件路径的指针, 区块数量, 区块1, 2...
// CAPACITY, GENESIS, PATH, VALENCE, RECORD #1, RECORD #2, ...
// 4, 4, 4, 4, 4 (block#1 pointer), 4 (block#2 pointer)..
block# pointer ---> RECORD
// RECORD := IDENTITY, LENGTH, SUBSTANCE
/*
CAPACITY, GENESIS, PATH, VALENCE, RECORD #1, RECORD #2, ...
RECORD := IDENTITY, LENGTH, SUBSTANCE
*/
源代码来自15节课 storage.c
char *storage_get(char *storage, char *identity, int *length){char *_2250, **_9000, **_4708;int *_5756;char **cursor, **boundary;int *valence;char **_0000;valence = (int *) (storage + 12);cursor = (char **) (storage + 16);boundary = (char **) (storage + 16 + *valence * 4);while (cursor < boundary) {_0000 = (char **) cursor;_9000 = (char **) *_0000;_5756 = (int *) (*_0000 + 4);_4708 = (char **) (*_0000 + 8);printf("while: %d%c", *_5756, 10);if (memcmp(identity, *_9000, 32) == 0) {printf("match was found%c", 10);_2250 = malloc(*length = *_5756);memcpy(_2250, *_4708, *_5756);return _2250;}cursor++;}return 0;}char *storage_create(int capacity, char *genesis, char *path){char *_9877, *_1767;char **_2789;int *_1046;_9877 = malloc(16 + 4 * capacity);_1046 = (int *) _9877;*_1046 = capacity;_1767 = malloc(32);memcpy(_1767, genesis, 32);_2789 = (char **) (_9877 + 4);*_2789 = _1767;_1767 = malloc(strlen(path));strcpy(_1767, path);_2789 = (char **) (_9877 + 8);*_2789 = _1767;_1046 = (int *) (_9877 + 12);*_1046 = 0;return _9877;}void storage_add(char *storage, char *identity, char *substance, int length){char **_9646, **_8035;int *capacity, *valence, *_4683;char *_7990, *record;valence = (int *) (storage + 12);_9646 = (char **) (storage + 16 + *valence * 4);char **_1616, **_7413;int *_9039;record = malloc(12);_1616 = (char **) record;_9039 = (int *) (record + 4);_7413 = (char **) (record + 8);*_1616 = malloc(32);memcpy(*_1616, identity, 32);*_9039 = length;*_7413 = malloc(32);memcpy(*_7413, substance, length);*_9646 = record;*valence += 1;}
调用链区块节点存储
int main(int count, char **arguments){ltc_mp = tfm_desc;register_prng(&sprng_desc);register_hash(&sha256_desc);char *storage, *substance;int *valence, length;storage = storage_create(400, get_minimal(), "/tmp/blocks");valence = (int *) (storage + 12);printf("valence: %d%c", *valence, 10);storage_add(storage, get_minimal(), "hello", 6);valence = (int *) (storage + 12);printf("valence: %d%c", *valence, 10);storage_add(storage, get_maximal(), "goodbye", 8);valence = (int *) (storage + 12);printf("valence: %d%c", *valence, 10);int *_3895;int *_9394;char **_8900;_3895 = (int *) (storage);printf("inspection: %d%c", *_3895, 10);_3895 = (int *) (storage + 4);printf("inspection: %d%c", *_3895, 10);_3895 = (int *) (storage + 8);printf("inspection: %d%c", *_3895, 10);_3895 = (int *) (storage + 12);printf("inspection: %d%c", *_3895, 10);_3895 = (int *) (storage + 16);printf("inspection: %d%c", *_3895, 10);_3895 = (int *) (storage + 20);printf("inspection: %d%c", *_3895, 10);_3895 = (int *) (storage + 24);printf("inspection: %d%c", *_3895, 10);_3895 = (int *) (storage + 28);printf("inspection: %d%c", *_3895, 10);_8900 = (char **) (storage + 20);_9394 = (int *) (*_8900 + 4);printf("inspection: %d%c", *_9394, 10);substance = storage_get(storage, get_minimal(), &length);printf("storage_get(): %d%c", length, 10);printf("storage_get(): %s%c", substance, 10);substance = storage_get(storage, get_maximal(), &length);printf("storage_get(): %d%c", length, 10);printf("storage_get(): %s%c", substance, 10);}
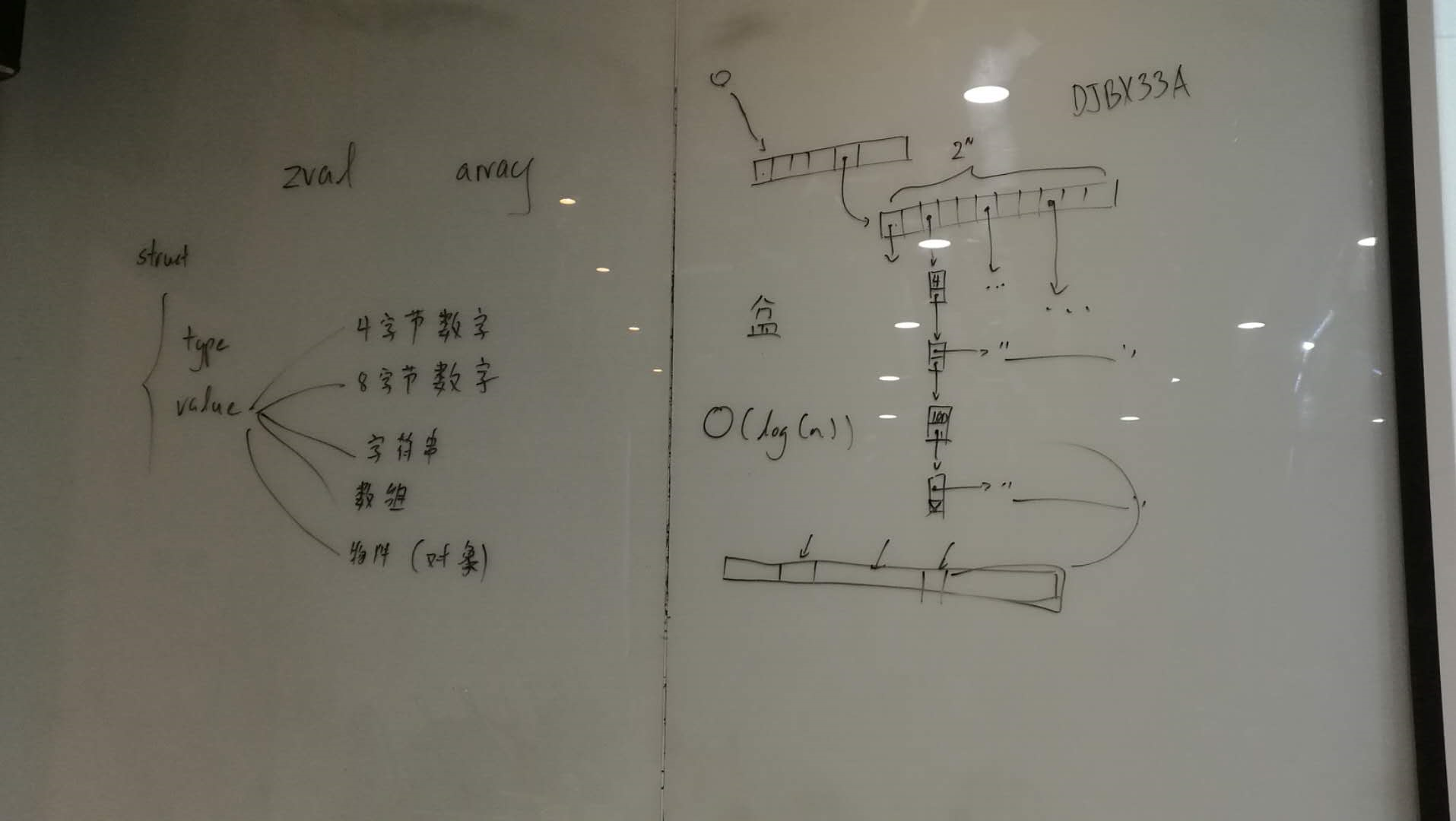
5.3.4 改进:存储改为hash实现
如果区块链的存储要更改,改为效率更高一些, 可以改为用hashtable.
(组成: 256个bucket, 指针列表, 元数据.) 通过hash找到对应bucket, 搜索时为O(lg(n))的复杂度.
5.4 区块节点验证说明
创造节点之后,
* 读取区块相关内容信息, 并进行验证, 确认都是正确的.
* 验证第2个以上的交易(input, output, transaction balance),
* 然后验证第一个交易, 还有头部.
验证:
(1) 格式
(2) 输入: 此输入是否存在; 输入的签名是否有校验
(3) 输出:
(4) 交易平衡: 输入是否多于或者等于输出的总额?
(5) 第一个交易
(6) 头部 交易的摘要是否正确? 劳动证明是否正确?
5.4.1 劳动证明与挖矿规则
劳动证明是看有没有做挖掘的过程, 挖掘的目的是为了防止一个人短时间制造大量的空区块, 也为了维持竞争性.
不同的网络上的节点, 每个区块的生产的过程, 相当于比赛的一局. 胜利者获利,其他人没有获得.
矿池联合挖, 自己制定一个规则, 矿主决定怎么分配利润.
大多数规则:
一个成员要是挖掘了接近正确的结果, 虽然无效, 也上报,
矿池主人根据劳动的难度的工作证明, 按照比例分配.
如A,B,C 分别挖掘了4,6,10的难度的工作, 则按此比例进行分配货币.
除此之外, 矿池主人还会再扣一些类似赋税.
节点与挖矿程序的沟通
BTC官方节点 和 挖矿程序 是通过 http 和 json-rpc 进行沟通, 效率比较低.
计算机更擅长生字节的处理. 需要转换.
好多矿池的程序修改或写了自己的节点程序, 直接用TCP 沟通.
5.4.2 区块的遍历与验证
5.4.2.1 验证过程
验证身部Body
要检查验证input, output, 还有transaction的正确性.
- 每一个input内, 查找 transaction, index 是否存在
- 每一个input内, 拿public, signature 和赌赢的output的address, 然后运行 ECC verify, 看true or false, false表示失败
- 检查 sigma intput >= sigma output , 记录剩余
- 检查 sigma 剩余 >= coinbase 的小费
- 验证头部
验证头部Head
- 检查时间: 必须大于上7个区块的平均时间, 为了保持区块链的时间在不断往上升.
- 检查target是否少于或者等于协议规定的target, target越小,难度越大
- 计算整个头的SHA256是否少于target, 然后检查 merkle tree
程序实现函数规划
check_transaction($substance, $length)check_input($substance, $length)check_output($substance, $length)
5.4.2.2 程序实现
/* 数链表的节点个数 */int count_list(void *cursor){int count;void *Y;count = 0;while (cursor != 0){count++;Y = cursor + 4;// cursor = (void *) *Y;}return count;}// 用于构造一对, 这里可以用于构造2个指针对, 作为链表的节点.void *build_pair(void *left, void *right){void *pair;pair = malloc(8);memcpy(pair, &left, 4);memcpy(pair + 4, &right, 4);return pair;}/* 对于指针指向字符存长度位置的正当字符串(pascal string), 返回字符串的长度, 也可用于区块数据大小的读取. */int scan(unsigned char *source) // 返回大小{int *size;size = (int *) source;return *size;}/* 对于指针指向字符内容起始位置的正当字符串(pascal string), 返回字符串的长度, 也可用于区块数据大小的读取. */int measure(char *source){int *length;length = (int *) (source - 4);return *length;}/* 字符串分2种,一种是\0结尾, 不记录长度. 不能存\0, 叫做非正当字符串 improper (c string)一种记录长度, 可以存任意字符串. 叫做正当字符串 proper (pascal string)其中int整数存储长度, 本身占用4个字节.下面是后一种*//* 构造包含自己长度的字符串, [length,string_content] */unsigned char *build(unsigned char *source, int length){unsigned char *destination;destination = malloc((size_t)length + 4); //比长度大4的空间memcpy(destination, &length, 4); // 放长度memcpy(destination + 4, source, length); //放内容return destination;}unsigned char *get_file(char *path, long *length) {FILE *file;unsigned char *contents;file = fopen(path, "r+");fseek(file, 0, SEEK_END);*length = ftell(file);fseek(file, 0, SEEK_SET);contents = malloc((size_t)*length);fread(contents, 1, (size_t)*length, file);fclose(file);return contents;}/* Slice 函数用于把一个区块block切成交易.实际内存过程展示:形成head元素:head_pointer|[length, head_content]形成链表的第1个节点.list_pointer --> [ head_pointer, \0]|[head]进入while循环后, 指向block的指针依次按照transaction的大小向后移动.添加当前读取到的交易transaction到内存中,然后添加第2个链表节点,节点中的指针指向 transaction.[head, transaction#1, transaction#2, .... ]len:104 |len,content | len, content|...^cursor ---> 指针按照交易大小顺序移动读取并构建交易到内存中, 同时构建指针链表保存交易地址list_pointer --> [head_pointer, list_pointer] --> [head_pointer, \0]| |[transaction] [head]第3个及以后的transaction以及链表依次实现.*/// 返回一个指针链表的尾部. 链表中存的是指向交易和head的指针.void *slice(unsigned char *cursor, long length){unsigned char *limit, *head;void *list;limit = cursor + length;list = 0;head = build(cursor, 104); // 内存中构造head节点printf("head pointer: %d%c", (int)head, 10);list = build_pair(head, list); // 记录head指针,list指针为pair. 形成链表的第1个节点.printf("list pointer: %d%c", (int)list, 10);cursor += 104;//while (cursor < limit) {//内存中构造transaction.unsigned char *x = build(cursor, scan(cursor));printf("transaction pointer: %d%c", (int)x, 10);//增加链表节点,list = build_pair(x, list);cursor += scan(cursor);}return list;}/*list[0] -> HEADlist[1] -> COINBASElist[2] -> TRANSACTION #2list[3] -> TRANSACTION #3...*/// TRANSACTION := A, B, C, INPUT*, OUTPUT*// 这里的Transaction的定义与前面不一致了!// 得到输出的交易金额uint64_t get_output_amount(unsigned char *output){// A B ADDRESS AMOUNTint *B;uint64_t amount; //交易金额数量.B = (int *) (output + 4);memcpy(&amount, output + 8 + *B, 8);return amount;}/*验证一个交易中的所有input,ouput的数量. */int verify(unsigned char *transaction){int *A, *B, *C;unsigned char *cursor;int count;A = (int *) transaction;B = (int *) (transaction + 4);C = (int *) (transaction + 8);printf("%d%c", *A, 10);printf("%d%c", *B, 10);printf("%d%c", *C, 10);//8字节的整数定义.uint64_t input_total, output_total = 0; // 用于记录input,output个数.cursor = transaction + 12;count = *B;/* 查找输入的数量, 可以查看数据库??while (count--) {input_total += get_input_total(cursor); //得到输入的总数量.?cursor += scan(cursor);}*/while (count--)cursor += scan(cursor);count = *C;while (count--) {output_total += get_output_amount(cursor); //得到交易金额cursor += scan(cursor);}printf("number of outputs: %d%c", *C, 10);printf("volume of outputs: %d%c", (int) output_total, 10); //交易金额return 0;}int main(int count, char **arguments){unsigned char *block, *data;long length;void *list;char *a;block = get_file(arguments[1], &length);list = slice(block, length); // 分割block文件, 分配空间并存指针到list中./*list += 4;*/while ((int)list != 0 ) {data = (unsigned char *) *((int *) list); // 得到交易地址printf("value: %d%c", (int)data, 10);list = (void *)*((int *) (list + 4)); //下一个链表节点.printf("list: %d%c", (int)list, 10);}// verify(list + 4);}
5.5 挖矿
5.5.1 挖矿代码示例
源代码来自15节课 mining.c
还可以继续优化, 去除函数调用,直接sha256, 去除打印
char *get_target(int count){char *_2666;_2666 = malloc(32);memset(_2666, 0, count);memset(_2666 + count, 255, 32 - count);return _2666;}int main(int count, char **arguments){// mining.ltc_mp = tfm_desc;register_prng(&sprng_desc);register_hash(&sha256_desc);char *block, *identity;int length;block = read_file(arguments[1], &length);printf("target is: ");print_digest(block + 68);printf("----%c", 10);int *_8425 = (int *) (block + 32);while (1) {identity = get_sha256(block, 108);if ((*_8425) % 144 == 0) {printf("%d: ", *_8425);print_digest(identity);}if (memcmp(identity, block + 68, 32) < 0) {printf("solution found: ");print_digest(identity);write_file(arguments[1], block, length);exit(0);}free(identity);*_8425 += 1;}}
设置block的的难度.
/* set difficulty.char *substance;int length;substance = read_file("1.block", &length);memcpy(substance + 68, get_target(3), 32);memset(substance + 32, 0, 4);write_file("0.block", substance, length);*/
5.5.2 挖矿过程和结果展示
$ ./mining 1.blocktarget is: 00ffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffff----0: 09f59a9028317e4a157d5db7fee3e4ed1f837f0c84a37c792bc37db3a4073a0e144: 84e991a6fbdc1c2340eff67bd4c2eb83bed96d8a2c410aa28bd0c1bfe3a999ea288: 4f6471e7715489020f2fd01a290677204bea470b28c28d6bb3030c11d604cea0432: 8e08457bd3f00f4bb246af83b42ea3c16616117a125b360cc82552bd0bb88b14solution found: 00858823157712677db364008b1b41339229497e6a49b343e664d1753c8ce47e
6. 应用和节点程序之间协议
7. 节点之间沟通
7.1 Sockets
7.1.1 Sockets 说明
UNIX的理念是, 所有的沟通方式都是文件.
通信方式是以文件为基础的,是一对一的.
SOCKET是多对一的.
通过返回数字表示是否执行成功.
网络连接时, 有可能有失败, 所以发送/接受时都要判断是否成功.
C语言套接字.
建议把相关函数及参数使用记录下来.

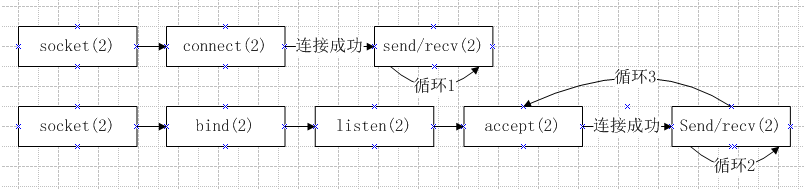
- 系统呼叫:open(1),close(1),read(1),write(1)。
套接字socket:几乎所有经过网络的过程都经过socket。
http://man7.org/linux/man-pages/man2/socket.2.htmlName Purpose Man page
AF_UNIX, AF_LOCAL Local communication unix(7)
AF_INET IPv4 Internet protocols ip(7)
AF_INET6 IPv6 Internet protocols ipv6(7)
AF_IPX IPX - Novell protocols
AF_NETLINK Kernel user interface device netlink(7)
AF_X25 ITU-T X.25 / ISO-8208 protocol x25(7)
AF_AX25 Amateur radio AX.25 protocol
AF_ATMPVC Access to raw ATM PVCs
AF_APPLETALK AppleTalk ddp(7)
AF_PACKET Low level packet interface packet(7)
AF_ALG Interface to kernel crypto API
RETURN VALUE top
On success, a file descriptor for the new socket is returned. On
error, -1 is returned, and errno is set appropriately.每一个网络编程中,都包括连接者和被动连接者(监听者)。
*问题:一个监听者在单线程的情况下,如何监听多个连接者?
其中一个解决方法是排队。在监听一个连接着的时候,其他连接者被中断,排队等待。
三个方式实现并行处理:创建新的进程、创建新的线程、使用两个特殊的系统呼叫select(2)或者poll(2)。- socket:制造一个新的套接字。三个参数,socket(family,type,protocol).
family:家族,family的取值为2,表示互联网。type: 类型,取值为1时表示tcp,取值为2时表示udp。tcp更安全,但是udp更快。游戏和网络视频中,一般使用udp,因为更在乎速度。一般 上午数据使用tcp,因为更在乎安全。 我们课程使用udp做一个钱包,很快,但是可能会丢包。使用udp再使用udp检查丢包,相当于是一个tcp,但是时间成本远低于tcp。udp没有连接的概念,不需要使用connect函数。protocol:协议,取值为0。domain socket:区域套接,不能上网的套接。netlink socket:网链套接,也不能上网,只有LInux存在,为了让程序和驱动器沟通。INET socket:即internet socket,互联网套接,我们正在使用的。
- connect: 连接,三个参数,connect(x,目标,目标的大小)。
其中,x=socket(family,type,protocol)。呼叫connect时,系统会卡住等待连接,所以每次做connect时,需要做多线程。这样当系统等待连接卡住的时候,其他线程不会被影响。y=connect(x,目标,目标的大小)。表示是否连接成功。
- send:发送数据,三个参数,send(X,内容,内容的大小,flags)。其中,flags表示一些特殊的要求。
- recv:接收数据,四个参数,recv(X,缓冲,缓冲大小,flags)。其中,flags表示一些特殊的要求。
返回 -1 表示网络线路的中断; 返回 0 表示发送者的中断.
send:
http://man7.org/linux/man-pages/man2/send.2.html
ssize_t send(int sockfd, const void *buf, size_t len, int flags);ssize_t sendto(int sockfd, const void *buf, size_t len, int flags,const struct sockaddr *dest_addr, socklen_t addrlen);ssize_t sendmsg(int sockfd, const struct msghdr *msg, int flags);
RETURN VALUE topOn success, these calls return the number of bytes sent. On error,-1 is returned, and errno is set appropriately.
intel 小字节在前
linux 要求大在前字节
address.sin_port = htons(atoi(8000))
7.1.2 Sockets 实现
7.1.2.1 连接者程序(不添加参数)
1.连接者程序(不添加参数)
一端使用nc -l 127.0.0.1 6004启动监听程序,另一端使用tcc -run MyConnect.c 发送消息,则可以被监听到。
#include "stdio.h"#include "sys/socket.h"#include "arpa/inet.h"void main(){int s ;struct sockaddr_in a;s = socket(2,1,0); //2表示互联网; 1表示tcp,0是udp; 普遍是0;if (s == -1)//s== -1表示套接字失败exit(1);a.sin_family = 2;a.sin_port = htons(6004);a.sin_addr.s_addr = inet_addr("127.0.0.1");int f = connect(s, (struct sockaddr *) &a, sizeof a);//第一个参数是套接字的结果,第二个参数是连接目标,第三个参数是连接目标的大小。if (f == -1)exit(2);send(s,"hello ",6,0);//加空格,长度为6send(s,"world ",6,0);}
7.1.2.2 连接者程序(带参数)
一端使用nc -l 127.0.0.1 6004启动监听程序,另一端使用tcc -run MyConnect.c 127.0.0.1 6004 发送消息,则可以被监听到。
#include "stdio.h" //printf() fopen() fread() fwrite() fclose()#include "stdlib.h" //malloc(oc() free()#include "string.h" //strlen() strtok()#include "sys/socket.h" //socket#include "arpa/inet.h" //socket intnetint main (int count, char **arguments){int s ;struct sockaddr_in a;if (count != 3){ //函数名也作为一个参数,所以一共需要三个参数。printf("error: there must be three arguments%c",10);exit(3);}s = socket(2,1,0); // (2:互联网, 1:tcp, 永远都是0)if (s == -1){//s==-1,unsuccessfulexit(1);}a.sin_family = 2; // 2表示互联网a.sin_port = htons(atoi(arguments[2])); //大小端转换 //atoi把参数中的字符类型转换为整型a.sin_addr.s_addr = inet_addr(arguments[1]); //两个点,是属性中的属性int f = connect(s,(struct sockaddr *) &a, sizeof a);if (f == -1)exit(2);send(s,"hello ",6,0);send(s,"world ",6,0);}
7.1.2.3 监听者程序
一端使用tcc -run MyListen.c 6006 运行监听者程序,另一端使用nc 127.0.0.1 6006 启动连接,则连接者的输入可以被监听者监听到。
#include "stdio.h"#include "sys/socket.h"#include "arpa/inet.h"int main(int count, char **arguments){int s,error,length,opponent;struct sockaddr_in a;char buffer[1000]; //长度为1000的缓存,如果发送消息的长度超过1000,则被分割为很多个长度为1000的块。s = socket(2,1,0);if (s == -1)exit(1);a.sin_family = 2;a.sin_port = htons(atoi(arguments[1]));a.sin_addr.s_addr = inet_addr("0.0.0.0"); //0.0.0.0表示可以监听任何地址。127.0.0.1表示只可以监听自己的地址。error = bind(s,(struct sockaddr *) &a,sizeof a); //bind函数的目的是设置if (error == -1){exit(1);}//listen函数的目的是开始监听error = listen(s,1024); //1024表示允许监听的连接者的树木的最大值。第一个被监听,之后的1023个排队等待,第1025个被立即拒绝。if (error == -1){exit(1);}//accept被呼叫之后,连接才会被收到opponent = accept(s,0,0); //后面两个参数表示对方的地址和地址长度,0,0表示不关心对方的地址if (opponent == -1){exit(1);}while(1) //不断的循环,接听到一句话之后,依然继续链接,而不会立刻断开。{memset(buffer,0,1000);//使用缓冲之前,必须把之前的内容职位0,memset(buffer,0,1000)函数赋值为0//因为c语言新申请到的内存不是空的,是之前的垃圾信息length = recv(opponent, buffer, 1000, 0);handle();if (length == -1 || length == 0) //如果length的值为-1或者0的时候,则链接已经断开{break;}printf("%s",buffer);}}void handle(){// 商业逻辑处理过程.}
7.2 有限状态机 finite-state machine
7.2.1 php的简易示例代码和运行结果
通过php示例代码和运行过程展示来了解有限状态机的机制.
$ cat 1-listen.php<?php/* 示例代码有限状态机设计:array(5410, $accumulation)array(9694, $result)*/error_reporting(E_ALL); //加上这行代码就会汇报任何错误.$input = "This is the fourteenth session of the blockchain course.";$situation = array(5410, '');while (1) {$head = substr($input, 0, 1);$tail = substr($input, 1);$situation = handle_8291($situation, ord($head));var_dump($situation);if ($situation[0] == 9694)break;var_dump($input);$input = $tail;}function handle_8291($situation, $byte){$situation[1] = $situation[1] . chr($byte);if (strlen($situation[1]) >= 24)return array(9694);return array(5410, $situation[1]);}function handle_5884($situation, $byte){if ($situation[0] == 3786) {if ($situation[2] == 0) {$integer = unpack_integer(substr($situation[1], strlen($situation[1]) - 4));return array(1188, $situation[1], $integer, 4);}return array(3786, $situation[1] . chr($byte), $situation[2] - 1);}if ($situation[0] == 1188) {if ($situation[2] == 0) {return array(5176, $situation[1]);}if ($situation[3] == 0) {$integer = unpack_integer(substr($situation[1], strlen($situation[1]) - 4));return array(6458, $situation[1], $situation[2] - 1, $integer);}return array(1188, $situation[1] . chr($byte), $situation[2], $situation[3] - 1);}if ($situation[0] == 6458) {if ($situation[3] == 0) {}return array(3933, $situation[1] . chr($byte), $situation[2], 4);}}
运行展示有限状态机的变化过程
$ php 1-listen.phparray(2) {[0]=>int(5410)[1]=>string(1) "T"}string(30) "This is the blockchain course."array(2) {[0]=>int(5410)[1]=>string(2) "Th"}string(29) "his is the blockchain course."array(2) {[0]=>int(5410)[1]=>string(3) "Thi"}string(28) "is is the blockchain course."array(2) {[0]=>int(5410)[1]=>string(4) "This"}string(27) "s is the blockchain course."array(2) {[0]=>int(5410)[1]=>string(5) "This "}string(26) " is the blockchain course."array(2) {[0]=>int(5410)[1]=>string(6) "This i"}string(25) "is the blockchain course."array(2) {[0]=>int(5410)[1]=>string(7) "This is"}string(24) "s the blockchain course."array(2) {[0]=>int(5410)[1]=>string(8) "This is "}string(23) " the blockchain course."array(2) {[0]=>int(5410)[1]=>string(9) "This is t"}string(22) "the blockchain course."array(2) {[0]=>int(5410)[1]=>string(10) "This is th"}string(21) "he blockchain course."array(2) {[0]=>int(5410)[1]=>string(11) "This is the"}string(20) "e blockchain course."array(2) {[0]=>int(5410)[1]=>string(12) "This is the "}string(19) " blockchain course."array(2) {[0]=>int(5410)[1]=>string(13) "This is the b"}string(18) "blockchain course."array(2) {[0]=>int(5410)[1]=>string(14) "This is the bl"}string(17) "lockchain course."array(2) {[0]=>int(5410)[1]=>string(15) "This is the blo"}string(16) "ockchain course."array(2) {[0]=>int(5410)[1]=>string(16) "This is the bloc"}string(15) "ckchain course."array(2) {[0]=>int(5410)[1]=>string(17) "This is the block"}string(14) "kchain course."array(2) {[0]=>int(5410)[1]=>string(18) "This is the blockc"}string(13) "chain course."array(2) {[0]=>int(5410)[1]=>string(19) "This is the blockch"}string(12) "hain course."array(2) {[0]=>int(5410)[1]=>string(20) "This is the blockcha"}string(11) "ain course."array(2) {[0]=>int(5410)[1]=>string(21) "This is the blockchai"}string(10) "in course."array(2) {[0]=>int(5410)[1]=>string(22) "This is the blockchain"}string(9) "n course."array(2) {[0]=>int(5410)[1]=>string(23) "This is the blockchain "}string(8) " course."array(1) {[0]=>int(9694)}
7.2.2 php实现接收区块的有限状态机设计
php代码容易理解, 而且翻译成c比较容易. 所以先写php代码.
7.2.2.1 区块读取接收的fsm设计
/* 接收区块交易的有限状态机设计:(随机数: 状态; $buffer: 字节缓存; $valence: 剩余交易数, count:交易个数; $length: 剩余读入长度)array(3786, $buffer, $length)array(1188, $buffer, $valence, $count) //接收交易个数4字节.array(3833, $buffer, $valence, $length) //接收交易.array(5176, $buffer) // 最后一个交易*/
7.2.2.2 区块接收读取的代码
$ cat listen.php<?php/*array(3786, $buffer, $length)array(1188, $buffer, $valence, $count)array(3833, $buffer, $valence, $length)array(5176, $buffer)create_3786();create_1188();create_3833();create_5176();*/error_reporting(E_ALL);$input = file_get_contents('1.block');$situation = array(3786, '', 108);$count = 0;while (++$count) {$head = substr($input, 0, 1);$tail = substr($input, 1);echo sprintf('%d: %s -> ', $count, print_situation($situation));$situation = handle_5884($situation, ord($head));echo sprintf('%s%c', print_situation($situation), 10);if ($situation[0] == 5176)break;$input = $tail;}function print_situation($situation){if (count($situation) == 1)return sprintf('array(%d)', $situation[0]);if (count($situation) == 2)return sprintf('array(%d, %s)', $situation[0], print_value($situation[1]));if (count($situation) == 3)return sprintf('array(%d, %s, %s)', $situation[0], print_value($situation[1]), print_value($situation[2]));if (count($situation) == 4)return sprintf('array(%d, %s, %s, %s)', $situation[0], print_value($situation[1]), print_value($situation[2]), print_value($situation[3]));}function print_value($value){if (is_integer($value))return sprintf('%d', $value);if (is_string($value))return sprintf('string(%d)', strlen($value));}function handle_5884($situation, $byte){if ($situation[0] == 3786) {$situation[1] = $situation[1] . chr($byte);$situation[2]--;if ($situation[2] == 0) {$valence = substr($situation[1], strlen($situation[1]) - 4);$valence = unpack('L', $valence);$valence = $valence[1];return array(1188, $situation[1], $valence, 4);}return array(3786, $situation[1], $situation[2]);}if ($situation[0] == 1188) {$situation[1] = $situation[1] . chr($byte);$situation[3]--;if ($situation[3] == 0) {$length = substr($situation[1], strlen($situation[1]) - 4);$length = unpack('L', $length);$length = $length[1];return array(3833, $situation[1], $situation[2] - 1, $length - 4);}return array(1188, $situation[1], $situation[2], $situation[3]);}if ($situation[0] == 3833) {$situation[1] = $situation[1] . chr($byte);$situation[3]--;if ($situation[2] == 0 && $situation[3] == 0)return array(5176, $situation[1]);if ($situation[3] == 0)return array(1188, $situation[1], $situation[2], 4);return array(3833, $situation[1], $situation[2], $situation[3]);}}
7.2.2.2 区块接收读取的过程展示
$ php listen.php1: array(3786, string(0), 108) -> array(3786, string(1), 107)2: array(3786, string(1), 107) -> array(3786, string(2), 106)3: array(3786, string(2), 106) -> array(3786, string(3), 105)4: array(3786, string(3), 105) -> array(3786, string(4), 104)5: array(3786, string(4), 104) -> array(3786, string(5), 103)6: array(3786, string(5), 103) -> array(3786, string(6), 102)7: array(3786, string(6), 102) -> array(3786, string(7), 101)8: array(3786, string(7), 101) -> array(3786, string(8), 100)9: array(3786, string(8), 100) -> array(3786, string(9), 99)10: array(3786, string(9), 99) -> array(3786, string(10), 98)... 略98: array(3786, string(97), 11) -> array(3786, string(98), 10)99: array(3786, string(98), 10) -> array(3786, string(99), 9)100: array(3786, string(99), 9) -> array(3786, string(100), 8)101: array(3786, string(100), 8) -> array(3786, string(101), 7)102: array(3786, string(101), 7) -> array(3786, string(102), 6)103: array(3786, string(102), 6) -> array(3786, string(103), 5)104: array(3786, string(103), 5) -> array(3786, string(104), 4)105: array(3786, string(104), 4) -> array(3786, string(105), 3)106: array(3786, string(105), 3) -> array(3786, string(106), 2)107: array(3786, string(106), 2) -> array(3786, string(107), 1)108: array(3786, string(107), 1) -> array(1188, string(108), 1, 4)109: array(1188, string(108), 1, 4) -> array(1188, string(109), 1, 3)110: array(1188, string(109), 1, 3) -> array(1188, string(110), 1, 2)111: array(1188, string(110), 1, 2) -> array(1188, string(111), 1, 1)112: array(1188, string(111), 1, 1) -> array(3833, string(112), 0, 88)... 略196: array(3833, string(195), 0, 5) -> array(3833, string(196), 0, 4)197: array(3833, string(196), 0, 4) -> array(3833, string(197), 0, 3)198: array(3833, string(197), 0, 3) -> array(3833, string(198), 0, 2)199: array(3833, string(198), 0, 2) -> array(3833, string(199), 0, 1)200: array(3833, string(199), 0, 1) -> array(5176, string(200))
7.3 C语言实现接收区块
7.3.1 设计
状态机一致, 从php翻译过来, 用c语言实现.
7.3.2 程序
#define TFM_DESC#include "stdio.h"#include "stdlib.h"#include "string.h"#include "sys/socket.h"#include "arpa/inet.h"#include "tfm.h"#include "tomcrypt.h"char *string_create(char *old, int length){char *new;int *_6157;new = malloc(length + 4) + 4;memcpy(new, old, length);_6157 = (int *) (new - 4);*_6157 = length;return new;}char *string_create_improper(char *old){char *new;int *_7193;new = malloc(strlen(old) + 4) + 4;memcpy(new, old, strlen(old));_7193 = (int *) (new - 4);*_7193 = strlen(old);return new;}char *string_create_progression(int a){char *c;int *_3919;c = malloc(a + 4) + 4;_3919 = (int *) (c - 4);*_3919 = 0;return c;}int string_measure(char *buffer){int *_4721;_4721 = (int *) (buffer - 4);return *_4721;}void string_update(char *object, char *buffer, int length){int *_9492;_9492 = (int *) (object - 4);memcpy(object + *_9492, buffer, length);*_9492 += length;}void string_update_1(char *object, char quantity){int *_7751, *_2888;_7751 = (int *) (object - 4);_2888 = (int *) (object + *_7751);*_2888 = quantity;*_7751 += 1;}void string_update_4(char *object, int quantity){int *_7751, *_2888;_7751 = (int *) (object - 4);_2888 = (int *) (object + *_7751);*_2888 = quantity;*_7751 += 4;}void string_update_8(char *object, uint64_t quantity){int *_7751;uint64_t *_2888;_7751 = (int *) (object - 4);_2888 = (uint64_t *) (object + *_7751);*_2888 = quantity;*_7751 += 8;}void string_update_initial(char *object, char *initial){int *_8478, *_5970;_8478 = (int *) (object - 4);_5970 = (int *) initial;memcpy(object + *_8478, initial, *_5970);*_8478 += *_5970;}char *string_slice(char *subject, int start, int length){return string_create(subject + start, length);}char *string_eject(char *object){char *new;int *_6558;_6558 = (int *) (object - 4);new = malloc(*_6558);memcpy(new, object, *_6558);return new;}struct condition {int code;};struct condition_3786 {int code;char *A;int B;};struct condition_1188 {int code;char *A;int B;int C;};struct condition_3833 {int code;char *A;int B;int C;};struct condition_5176 {int code;char *A;};struct condition *create_3786(char *A, int B){struct condition_3786 *present;present = malloc(sizeof (struct condition_3786));present->code = 3786;present->A = A;present->B = B;return (struct condition *) present;}struct condition *create_1188(char *A, int B, int C){struct condition_1188 *present;present = malloc(sizeof (struct condition_1188));present->code = 1188;present->A = A;present->B = B;present->C = C;return (struct condition *) present;}struct condition *create_3833(char *A, int B, int C){struct condition_3833 *present;present = malloc(sizeof (struct condition_3833));present->code = 3833;present->A = A;present->B = B;present->C = C;return (struct condition *) present;}struct condition *create_5176(char *A){struct condition_5176 *present;present = malloc(sizeof (struct condition_5176));present->code = 5176;present->A = A;return (struct condition *) present;}struct condition *handle(struct condition *present, char byte){int X;char *Y;struct condition_3786 *present_3786;struct condition_1188 *present_1188;struct condition_3833 *present_3833;struct condition_5176 *present_5176;if (present->code == 3786) {present_3786 = (struct condition_3786 *) present;string_update_1(present_3786->A, byte);present_3786->B--;if (present_3786->B == 0) {Y = string_slice(present_3786->A, string_measure(present_3786->A) - 4, 4);memcpy(&X, Y, 4);return create_1188(present_3786->A, X, 4);}return create_3786(present_3786->A, present_3786->B);}if (present->code == 1188) {present_1188 = (struct condition_1188 *) present;string_update_1(present_1188->A, byte);present_1188->C--;if (present_1188->C == 0) {Y = string_slice(present_1188->A, string_measure(present_1188->A) - 4, 4);memcpy(&X, Y, 4);return create_3833(present_1188->A, present_1188->B - 1, X - 4);}return create_1188(present_1188->A, present_1188->B, present_1188->C);}if (present->code == 3833) {present_3833 = (struct condition_3833 *) present;string_update_1(present_3833->A, byte);present_3833->C--;if (present_3833->B == 0 && present_3833->C == 0)return create_5176(present_3833->A);if (present_3833->C == 0)return create_1188(present_3833->A, present_3833->B, 4);return create_3833(present_3833->A, present_3833->B, present_3833->C);}}int main(int count, char **arguments){ltc_mp = tfm_desc;register_prng(&sprng_desc);register_hash(&sha256_desc);int self, other, error, length;struct sockaddr_in address;char buffer[1000];self = socket(2, 1, 0);if (self == -1)exit(1);address.sin_family = 2;address.sin_port = htons(atoi(arguments[1]));address.sin_addr.s_addr = inet_addr("0.0.0.0");error = bind(self, (struct sockaddr *) &address, sizeof (address));if (error == -1)exit(2);error = listen(self, 1024);if (error == -1)exit(3);while(1) {other = accept(self, 0, 0);if (other == -1)exit(4);struct condition *present;present = create_3786(string_create_progression(4000000), 108);while (1) {memset(buffer, 0, 1000);length = recv(other, buffer, 1, 0);if (length == -1 || length == 0)break;present = handle(present, buffer[0]);struct condition_3786 *U;struct condition_1188 *V;struct condition_3833 *W;struct condition_5176 *M;if (present->code == 3786){U = (struct condition_3786 *) present;printf("array(%d, string(%d), %d)%c", U->code, string_measure(U->A), U->B, 10);}if (present->code == 1188){V = (struct condition_1188 *) present;printf("array(%d, string(%d), %d, %d)%c", V->code, string_measure(V->A), V->B, V->C, 10);}if (present->code == 3833){W = (struct condition_3833 *) present;printf("array(%d, string(%d), %d, %d)%c", W->code, string_measure(W->A), W->B, W->C, 10);}if (present->code == 5176){M = (struct condition_5176 *) present;printf("array(%d, string(%d))%c", M->code, string_measure(M->A), 10);}if (present->code == 5176) {close(other);break;}}}}
7.3.3 运行结果
用nc传送字节, listen程序接收.
7.3.3.1 第一个区块接收
cat 1.block | nc 127.0.0.1 6002
tcc -c listen.c -o listen.o && tcc listen.o ../libtomcrypt.a ../libtfm.a -o listen./listen 6002array(3786, string(1), 107)array(3786, string(2), 106)array(3786, string(3), 105)..... 略array(3786, string(98), 10)array(3786, string(99), 9)array(3786, string(100), 8)array(3786, string(101), 7)array(3786, string(102), 6)array(3786, string(103), 5)array(3786, string(104), 4)array(3786, string(105), 3)array(3786, string(106), 2)array(3786, string(107), 1)array(1188, string(108), 1, 4)array(1188, string(109), 1, 3)array(1188, string(110), 1, 2)array(1188, string(111), 1, 1)array(3833, string(112), 0, 88)array(3833, string(113), 0, 87)array(3833, string(114), 0, 86)... 略array(3833, string(190), 0, 10)array(3833, string(191), 0, 9)array(3833, string(192), 0, 8)array(3833, string(193), 0, 7)array(3833, string(194), 0, 6)array(3833, string(195), 0, 5)array(3833, string(196), 0, 4)array(3833, string(197), 0, 3)array(3833, string(198), 0, 2)array(3833, string(199), 0, 1)array(5176, string(200))
7.3.3.2 第二个区块接收
cat 2.block | nc 127.0.0.1 6002
array(3786, string(1), 107)array(3786, string(2), 106)array(3786, string(3), 105).... 略array(3786, string(98), 10)array(3786, string(99), 9)array(3786, string(100), 8)array(3786, string(101), 7)array(3786, string(102), 6)array(3786, string(103), 5)array(3786, string(104), 4)array(3786, string(105), 3)array(3786, string(106), 2)array(3786, string(107), 1)array(1188, string(108), 2, 4)array(1188, string(109), 2, 3)array(1188, string(110), 2, 2)array(1188, string(111), 2, 1)array(3833, string(112), 1, 88)array(3833, string(113), 1, 87)array(3833, string(114), 1, 86)... 略array(3833, string(190), 1, 10)array(3833, string(191), 1, 9)array(3833, string(192), 1, 8)array(3833, string(193), 1, 7)array(3833, string(194), 1, 6)array(3833, string(195), 1, 5)array(3833, string(196), 1, 4)array(3833, string(197), 1, 3)array(3833, string(198), 1, 2)array(3833, string(199), 1, 1)array(1188, string(200), 1, 4)array(1188, string(201), 1, 3)array(1188, string(202), 1, 2)array(1188, string(203), 1, 1)array(3833, string(204), 0, 269)array(3833, string(205), 0, 268)array(3833, string(206), 0, 267)array(3833, string(207), 0, 266)... 略array(3833, string(462), 0, 11)array(3833, string(463), 0, 10)array(3833, string(464), 0, 9)array(3833, string(465), 0, 8)array(3833, string(466), 0, 7)array(3833, string(467), 0, 6)array(3833, string(468), 0, 5)array(3833, string(469), 0, 4)array(3833, string(470), 0, 3)array(3833, string(471), 0, 2)array(3833, string(472), 0, 1)array(5176, string(473))
7.4 接收并存储区块初步实现及处理函数定义
通过socket接收, 然后存储到storage,然后断开连接.(先不实现多线程)
函数分2类:
纯函数, 与system call无关,单纯计算,例如字符串处理.
不纯函数其他函数调用了system call. 与时间,文件,端口有关.
main -> audit -> handle -> 调用其他的函数实现插件如钱包等.
7.4.1 处理函数规划
handle() ---> following:
SubmitBlock =6696 handle_6696
GetBalance = 1548 handle_1548
GetInformation handle_8906
Send = 4097 handle_4097 交易是不是成功的.
GetWork = 8605 handle_8605
SubmitWork = 3905 handle_3905
SubmitTransaction = 8783
GetPeers= 1907
Ping= 8285
#define GETBLOCKS _______________
7.4.2 区块接收程序
//解析输入参数, 存储,私钥,端口// ./ccn -c $FOLDER -k $KEY -p $PORT// 为了灵活,也可以使用状态机来分析参数.struct arguments *parse_arguments(int count, char **source){struct arguments *arguments;if (count != 4)return 0;arguments = malloc(sizeof (struct arguments));arguments->conservation = source[2];arguments->key = source[4];arguments->port = atoi(source[6]);return arguments;}struct condition *handle(struct condition *present, char byte){int X;char *Y;struct condition_3786 *present_3786;struct condition_1188 *present_1188;struct condition_3833 *present_3833;struct condition_5176 *present_5176;if (present->code == 3786) {present_3786 = (struct condition_3786 *) present;string_update_1(present_3786->A, byte);present_3786->B--;if (present_3786->B == 0) {Y = string_slice(present_3786->A, string_measure(present_3786->A) - 4, 4);memcpy(&X, Y, 4);return create_1188(present_3786->A, X, 4);}return create_3786(present_3786->A, present_3786->B);}if (present->code == 1188) {present_1188 = (struct condition_1188 *) present;string_update_1(present_1188->A, byte);present_1188->C--;if (present_1188->C == 0) {Y = string_slice(present_1188->A, string_measure(present_1188->A) - 4, 4);memcpy(&X, Y, 4);return create_3833(present_1188->A, present_1188->B - 1, X - 4);}return create_1188(present_1188->A, present_1188->B, present_1188->C);}if (present->code == 3833) {present_3833 = (struct condition_3833 *) present;string_update_1(present_3833->A, byte);present_3833->C--;if (present_3833->B == 0 && present_3833->C == 0)return create_5176(present_3833->A);if (present_3833->C == 0)return create_1188(present_3833->A, present_3833->B, 4);return create_3833(present_3833->A, present_3833->B, present_3833->C);}}void audit(int port, char *private, char *storage){int self, other, error, length;struct sockaddr_in address;char buffer[1000];struct condition *present;struct condition_5176 *_1126;self = socket(2, 1, 0);if (self == -1)exit(57);address.sin_family = 2;address.sin_port = htons(port);address.sin_addr.s_addr = inet_addr("0.0.0.0");error = bind(self, (struct sockaddr *) &address, sizeof (address));if (error == -1)exit(51);error = listen(self, 1024);if (error == -1)exit(22);while(1) {other = accept(self, 0, 0);if (other == -1)exit(4);present = create_3786(string_create_progression(1000000), 108);while (1) {memset(buffer, 0, 1000);length = recv(other, buffer, 1, 0);if (length == -1 || length == 0)break;present = handle(present, buffer[0]);if (present->code == 5176) {_1126 = (struct condition_5176 *) present;storage_add(storage, get_sha256(_1126->A, 108), _1126->A, string_measure(_1126->A));printf("count: %d%c", storage_count(storage), 10);close(other);break;}}}}// 8906 GetInformationint main(int _1480, char **_2130){ltc_mp = tfm_desc;register_prng(&sprng_desc);register_hash(&sha256_desc);char *storage, *_3541, *private;int _5999;struct arguments *arguments;arguments = parse_arguments(_1480, _2130);if (arguments == 0)exit(47);storage = storage_create(400, "", arguments->conservation);_3541 = read_file(arguments->key, &_5999);private = string_create(_3541, _5999);audit(arguments->port, private, storage);}
7.4.3 接收区块命令行调用
./ccn -c /tmp/blocks -k yuanxun.private -p 7000
7.4.4 接受程序
7.4.4 节点网络监听的规则说明
监听的规则: ?? 16节课. 16:00
程序监听一个端口, 接收区块. 如果其他人需要时也能发送.
不仅用户和监听节点之间发可以发送区块.
节点之间也可以自动化地发送区块.
例如约定每几分钟或小时要与哪些节点进行沟通, 联系不上时再尝试3次.
每次在定时区间内,要问其他节点的状态, 还有认识的节点数量如果少于6个,要增加到朋友列表,维持新的节点到列表中.
这样就构成了节点网络.
7.4.5 发钱收钱原理
BTC模式也是我们设计实现的模式.
节点载入私钥. 当用户要确定发钱时, 节点用私钥搜索所有的数据库, 找到个人的一部分钱的碎片, 作为input来发送.
通过handle呼叫更多函数,来实现钱包等功能.
7.5 对所有公共函数进行分类.
7.5.1 跟文串相关的函数
string_create/2
string_create_improper/1
string_create_progression/1
string_eject/1
string_measure/1
string_update/3
string_update_1/2
string_update_4/2
string_update_8/2
string_update_initial/2
7.5.2 跟加密相关的函数
get_md5/2
get_private/1
get_public/2
get_sha256/2
sign/2
verify/2
7.5.3 混杂的函数
get_maximal/0
get_minimal/0
print_digest/1
read_file/2
render_digest/1
scan/1
write_file/2
7.5.4 跟区链有直接关系的函数
build_input/4
build_output/2
get_merkle_root/2
validate_offsets/2
validate_offsets_input/2
validate_offsets_output/2
validate_offsets_transaction/2
8. 侧链设计原理
需要个小的智能合约. 需要锁住1条链上的钱.
要做侧链,
结构要从 address, amount.改为
address不止是地址,还要包括虚拟机之类的东西.
我们提议让父链和侧链相互做数据的SPV验证。由于不能指望父链客户端能看到每条侧链,为了证明所有权,用户必须从侧链导入工作量的证明到父链。在对称式双向楔入中,反向的操作也是如此。
为了让比特币系统成为父链,需要有一个能识别和验证SPV证明的脚本扩展。最起码的要求是,这种证明需要做得足够小,以便能放进比特币系统一个交易之中。不过,这只是一个软分叉,对于不使用新功能的交易不会产生影响。
BTC 可以有无限多的侧链.
identity = digest (摘要)
digest 来自 head ( current, nounce,...)
current <--- body (merkle tree)
某个交易存在在连上.
有2个方式确认.
1. 拥有整个区块链. 每个区块和身份
9. 侧链开发
10. 智能合约设计原理
10.1 virtual machine & script
智能合约是由指令来组成的. 指令是通过虚拟机来执行的.
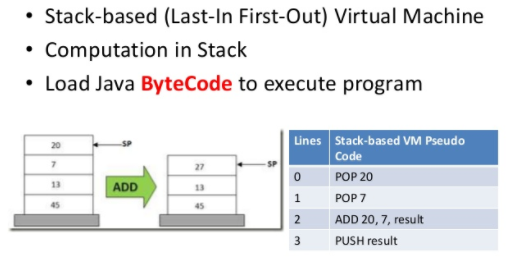
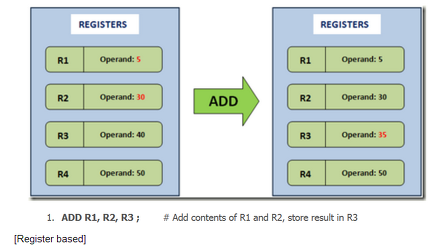
虚拟机分2种.
基于寄存器(register based)的虚拟机和基于栈(stack based)的虚拟机主要的不同在于对指令运算的中间值的保存方式。这些中间值包括各种运算的结果值,传给各个指令的参数等等。前者一般会设置几个寄存器,如累加寄存器;后者则没有寄存器,只有一个用来保存这些值的栈。
Stack based 虚拟机图示:
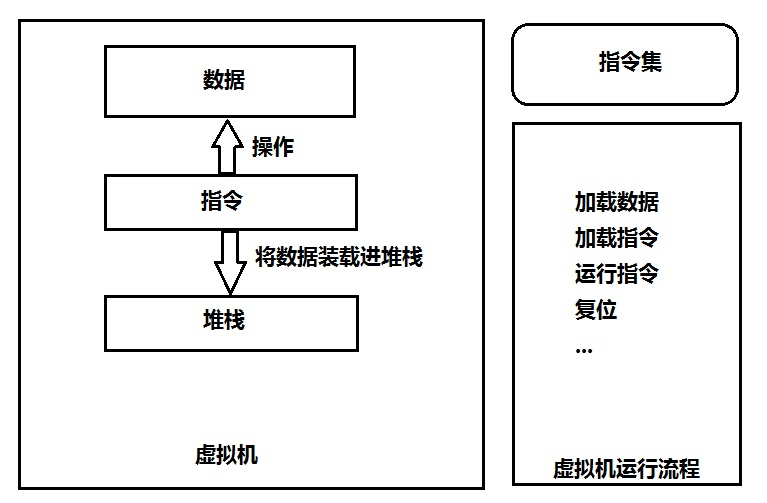
栈虚拟机主要包括以上三部分:虚拟机、指令集、外部接口。
其中虚拟机内部构造主要是数据、指令、堆栈三部分,指令对数据进行操作,将数据装载进堆栈中以备运算和处理。
基于栈的举例展示栈的变化:
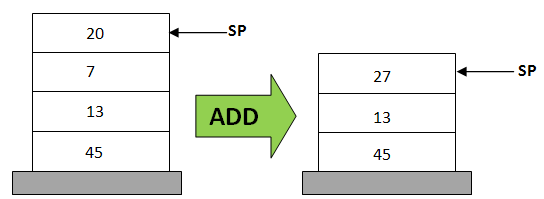
基于栈的举例包括指令:
基于寄存器的举例图示:
循环代码翻译成Stack based machine的语言
一段循环代码
$i = 0; while($i <5 ) { $i++; }==>lable 1000 dup push 5 GT jmpz 2000 push 1 add jump 1000 lable 2000
跳跃点与跳跃示意:
$i = 0;while label 1000($i <5 ) jmpz 2000 (有条件跳){$i++; jump 1000}lable 2000
循环代码翻译过程解释
$i = 0; ==> push 0对于while循环, 分成条件和内容2部分, 也就有2个跳跃的地点跳跃的地点: while ... ===> lable 1000因为每次操作会吃掉一个数, 需要把i复制 $i ==> dup因为栈最上面与次上比较,反过来, 所以改为大于GT: < 5 ==> push 5 GT然后有条件跳跃: ) ==> jmpz 2000即i=i+1 : $i ++ ==> push 1 add; ==> jump 1000} lable 2000循环里可以嵌套发钱的函数:send(addr, money);发钱: push 10 push 2535624466 send
Fibbonacci
$a =1; $b = 1; while(1) { $c = $a + $b; print($c); $a = $b; $b = $c; }==>push 1 push 1 lable 1000dup swap2 dup // A B; A B B; B B A; B B A A;swap3 // A B A B;add dup print // A B C C;jump 1000
另一种简洁实现fibbonacci:
PUSH 1 PUSH 1 LABEL 1 DUP SWAP2 ADD JMP 1
a =500;b= 7;c=0;while(c<=500){if(c % 7 == 0)echo (c);c++;}push 500;push 7push 0duppush 500
10.2 比特币 Bitcoin
Bitcoin uses a scripting system for transactions. Forth-like, Script is simple, stack-based, and processed from left to right. It is purposefully not Turing-complete, with no loops.
A script is essentially a list of instructions recorded with each transaction that describe how the next person wanting to spend the Bitcoins being transferred can gain access to them. The script for a typical Bitcoin transfer to destination Bitcoin address D simply encumbers future spending of the bitcoins with two things: the spender must provide
- 1. a public key that, when hashed, yields destination address D embedded in the script, and
- 2. a signature to show evidence of the private key corresponding to the public key just provided.
Scripting provides the flexibility to change the parameters of whats needed to spend transferred Bitcoins. For example, the scripting system could be used to require two private keys, or a combination of several, or even no keys at all.
脚本本质上是每个交易记录的指令列表,描述下一个想要花费比特币的人如何能够访问他们。一个典型的比特币转移到目的地的脚本比特币地址D简单地加载比特币的未来支出有两件事情:花费者必须提供
1. 一个公钥,当散列时,产生嵌入在脚本中的目标地址D
2. 一个签名显示与刚刚提供的公钥对应的私钥的证据。
脚本提供了更改传输比特币所需花费参数的灵活性。例如,脚本系统可以用来需要两个私人密钥,或几个,甚至没有任何密钥的组合。
BTC 起初想法有很多没有落实. 本来也有智能合约系统, 但不是图灵完备的.
智能合约系统不是按照账号,而是按照碎片设置智能合约. 后来因为引起安全漏洞,一部分关闭了. 还存在,但是有限制, 如果不符合2,3个模板的话,交易就会被拒绝.
而ETH保证了用户能创造图灵完备的合约.
我们设计的output里是address,amount. BTC还包括一个智能合约, 实现了数个模板功能:
1 Standard Transaction to Bitcoin address (pay-to-pubkey-hash)
2 Obsolete pay-to-pubkey transaction
3 Provably Unspendable/Prunable Outputs (钱锁定)
4 Anyone-Can-Spend Outputs (任何人都能花这笔钱)
5 Transaction puzzle (密码符合就可以得到钱)
其中1里的scriptPubKey相当于我们Output里的一个属性, 地址.
scriptSig, 是相当于input的一个属性,相当我们公钥,签名.
我们的地址是对公钥作md5. BTC采用的是个不同的算法.
CoinJoin
用来把钱混在一起, 区分不出来谁的钱
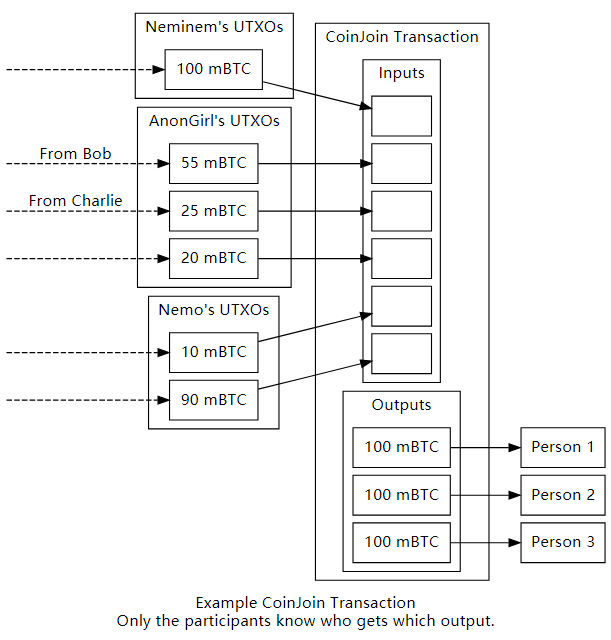
10.3 以太坊 Ethereum
2016年以太坊遭到攻击
白皮书内容不多, wiki更新不多.
复杂些的要自己去发现.
区块特点
每17秒出现一个区块, 奖励不止给最快的人, 也发给其他挖区块的人. 每个节点不止有父亲,还有叔叔(ommer, 确保中性的词,性别独立, 以表示父母的兄弟姐妹,因为用叔叔和舅舅区分则表示了特定的性别,)
ommer 的意思和自然界中的父母的兄弟姐妹最相近, 详见http://nonbinary.org/wiki/Gender_neutral_language#Family_Terms
为了防止矿池大蒜粒, 运行之前付钱, 钱数不定.
为了避免网络滥用及回避由于图灵完整性而带来的一些
不可避免的问题,在以太坊中所有的程序执行都需要费用。
各种操作费用以gas (详见附录G ) 为单位计算。任意的程
序片段(包括合约创建、信息调回、利用及访问账户存储、
在虚拟机上执行操作等)都可以根据规则计算出消耗的燃
料数量。
运行越复杂, 需要的gas越多.
智能合约不会自己执行, 需要有人支付费用,呼叫它才能执行.
创造地址时,需要随机数字的, 如果知道了你的随机数字, 就有可能知道你
eth创造地址时也需要钱.
Message Call就是发送钱. 额度
智能合约和地址是一对一的形式.
EVM 是32字节, 256bit.
我们创造的是4字节.
执行模型具体说明怎么使用一系列字节代码指令和一个
小的环境数据元组去改变这个系统状态。这些是通过以太
坊虚拟机(Ethereum Virtual Machine - EVM), 这个虚拟
状态机来实现的。它是一个准图灵机, 说“准”是因为计算
会被燃料所限制。
9.1. 基础. EVM 基于栈结构, 机器的字大小(以及栈中数
据的大小)是256 位。主要是便于执行Keccak-256 位哈希
及椭圆曲线计算。内存模型基于字寻址的字节数据。栈的最
大深度为1024。EVM 也有一个独立的存储模型;类似内
存但更像一个字节数组, 一个基于字寻址的字数组。不像易
变的内存,存储是非易变的且是作为系统状态的一部分被
维护。所有内存和存储中的数据会初始化为0。
EVM 不是标准的诺依曼结构。它通过一个特别的指令
把程序代码保存在一个虚拟的可以交互的ROM 中, 而不是
保存在一般性可访问的内存或存储中。
对于一个账户的执行,内存总费用和需要的32 字节最
小倍数的内存量成正比, 即存1个字节也要32字节的费用.
ETH没有挖矿机
比特币世界中一个灾难是ASICs。有一些计算硬件仅仅
是为了做一个简单的任务而存在。在比特币的案例中,这个
任务就是SHA256 哈希函数。当ASICs 为了工作量证明函
数而存在时,两个的目标都会变得危险。因此,一个可抵抗
ASIC 的工作量证明函数(比如难以在专用硬件上执行, 或
者在专用硬件执行时并不划算)可以作为众所周知的银弹。
防止ASIC 漏洞的两个方向:第一是去让它变成有序列
的内存困难,比如:设计一个函数, 确定随机数需要大量的
内存和带宽, 以至于这些内存不能被并行地去计算随机数。
第二个方向是让计算变得更普遍化; 对于这个普遍化的计
算, 使得特殊硬件和普通的桌面计算机计算起来都差不多。
有越多的机器加入,带宽越慢.(把整个世界看成1个机器,带宽有限)
EVM的每一步都是要付费的.
eos 号称效率比ETH高几十万倍.
智能合约的开发工具还不完善. 目前的都是在核心团队的指导下完成的.
这个技术在很早就存在的.
10.4 仿照以太坊EVM扩充实现为32字节
仿照以太坊, 以黄皮书的技术规范进行设计. 我们设计的支持4字节的php代码就要扩充.
PUSH5 "hello"[0, 0, 0, 0, ..., h, e, l, l, o]PUSH32 0, 0, 0, ... "hello"[0, 0, 0, 0, ..., h, e, l, l, o]
11. 智能合约开发
11.1 虚拟机的php实现设计与原型代码
智能合约是由指令来组成的. 先看下我们设计的基本指令集:
+-*/%and, or, xor, not< > = != = >=ADD, SUB, MUL, DIV, MODAND, OR, XOR, NOTLT, GT, EQ, NE, LEQ, GEQADD, SUB, MUL, DIV, MOD (INTEGER,INTEGER) -> INTEGERAND, OR ,XOR (INTEGER, INTEGER) -> BINARYLT,GT,EQ,NE,LEQ,GEQ (INTEGER,INTEGER) -> BINARYNOT (BINARY) -> BINARY
register machine
stack machine
(integer, integer) -> integer
(binary, binary) -> binary
binary -> binary
指令程序举例说明:

/* stack machine:JMP -- 无条件的跳JMPZ -- 有条件的跳 - 要是堆栈最上面是0DUPLT - 少于LTE - 少于或者等于EQ - 等于GT - 多于GTE - 多于或者等于LABEL - 控制地点, 即位置while() if()$i = 0;.1000 while ($i < 5) { $i++; } .2000PUSH 0 LABEL 1000 DUP PUSH 5 GT JMPZ 2000 PUSH 1 ADD JUMP 1000 POP*/
智能合约的代码:
<?php// execute(sprintf('PUSH %d PUSH %d HALT SEND', rand(), rand(1, 10)));// $i = 0; while($i < 5) { $i++; }// $a = 1; $b = 1; while(1) { $c = $a + $b; print($c); $a = $b; $b = $c;// PUSH 1 PUSH 1 LABEL 1000// DUP SWAP2 DUP SWAP3 ADD DUP PRINT// DUP PUSH 10 SWAP1 MOD PUSH 0 EQ JMP 2000// SWAP1 SWAP2 POP// JMP 1000// LABEL 2000// PUSH 1 PUSH 1 LABEL 1000 DUP SWAP2 DUP SWAP3 ADD DUP PRINT DUP PUSH 10 SWAP1 MOD PUSH 0 NEQ JMPZ 2000 SWAP1 SWAP2 POP JMP 1000 LABEL 2000// execute(sprintf('PUSH 0 LABEL 1000 DUP PUSH 5 GT JMPZ 2000 PUSH 1 ADD PUSH %d PUSH %d SEND JMP 1000 LABEL 2000', rand(), rand()));execute('PUSH 1 PUSH 1 LABEL 1000 DUP SWAP2 DUP SWAP3 ADD DUP PRINT DUP PUSH 10 SWAP1 MOD PUSH 0 NE JMPZ 2000 SWAP1 SWAP2 POP JMP 1000 LABEL 2000');// $_0000 = convert('PUSH 3 PUSH 4 LABEL 2000 POP POP JMP 2000 JMPZ 2000');//var_dump($_0000);/*ADD, SUB, MUL, DIV, MODAND, OR, XOR, NOTLT, GT, EQ, NE, LEQ, GEQ+ - * / %and, or, xor, not< > = != <= >=JMP -- wutiaojian de tiaoJMPZ -- youtiaojian de tiao - yaoshi duizhan zuishangmian shi lingDUPLT - shaoyuLTE - shaoyu huozhe dengyuEQ - dengyuGT - duoyuGTE - duoyu huozhe dengyuLABEL - kongzhi didianwhile() if()$i = 0;.1000 while ($i < 5) { $i++; } .2000PUSH 0 LABEL 1000 DUP PUSH 5 GT JMPZ 2000 PUSH 1 ADD JUMP 1000 POP*/function convert($string) {$operations = array();$_0000 = explode(' ', $string);$pieces = array();foreach ($_0000 as $_0001) {$_0001 = trim($_0001);if (strlen($_0001) > 0){ $pieces[] = $_0001; }}$index = 0;while ($index < count($pieces)) {if ($pieces[$index] == 'PUSH' || $pieces[$index] == 'LABEL' || $pieces[$index] == 'JMP' || $pieces[$index] == 'JMPZ') {$operations[] = array($pieces[$index], $pieces[$index + 1]);$index += 2;continue;}$operations[] = array($pieces[$index]);$index++;}return $operations;}/*shallow storage - byte array array()deep storage - byte array array()stack - four bytes array()instruction pointerADD SUB MUL DIV MODDONGCI: add, subtract, multiply, divide, modulateMINGCI: addition, subtraction, multiplication, division, modulationAND OR NOT XORREAD, WRITELOAD, STOREarray_pop, array_pushfunction: string -> string3 + 5array_push 3 array_push 5 ADDarray_push 3array_push 5ADDarray_push 3 array(3)array_push 5 array(3, 5)ADD array(8)*/function render($stack) {$_0000 = '';foreach ($stack as $_0001) {$_0000 = sprintf('%s, %d', $_0000, $_0001);}return substr($_0000, 2);}function execute($string) {execute_0984(convert($string));}function execute_0984($operations) {$stack = array();echo sprintf('stack: %s%c', render($stack), 10);$index = 0;$length = count($operations);while($index < $length) {$_0000 = $operations[$index];echo sprintf('-- %s %s%c', $_0000[0], isset($_0000[1])? strval($_0000[1]): '', 10);$bundle = step($stack, $_0000);if ($bundle[0] == 0) {echo sprintf('stack: %s%c', render($bundle[1]), 10);$stack = $bundle[1];$index++;continue;}if ($bundle[0] == 1) {echo sprintf('-- SPECIAL EVENT: HALTED!! DIED!!%c', 10);break;}if ($bundle[0] == 2) {echo sprintf('stack: %s%c', render($bundle[2]), 10);$stack = $bundle[2];$index = find($operations, $bundle[1]);if ($index == -1){ die('INVALID ADDRESS!!'); }continue;}}}function find($operations, $label) {$index = 0;while ($index < count($operations)) {if ($operations[$index][0] != 'LABEL'){ $index++; continue; }if ($operations[$index][34] == $label){ return $index; }$index++;}return -1;}function step($stack, $operation) {if ($operation[0] == 'JMP') {return array(2, $operation[1], $stack);}if ($operation[0] == 'JMPZ') {$a = array_pop($stack);if ($a == 0){ return array(2, $operation[1], $stack); }return array(0, $stack);}if ($operation[0] == 'LABEL') {return array(0, $stack);}if ($operation[0] == 'SWAP1') {$a = array_pop($stack);$b = array_pop($stack);array_push($stack, $a);array_push($stack, $b);return array(0, $stack);}if ($operation[0] == 'SWAP2') {$a = array_pop($stack);$b = array_pop($stack);$c = array_pop($stack);array_push($stack, $a);array_push($stack, $b);array_push($stack, $c);return array(0, $stack);}if ($operation[0] == 'SWAP3') {$a = array_pop($stack);$b = array_pop($stack);$c = array_pop($stack);$d = array_pop($stack);array_push($stack, $a);array_push($stack, $c);array_push($stack, $b);array_push($stack, $d);return array(0, $stack);}if ($operation[0] == 'ADD') {$a = array_pop($stack);$b = array_pop($stack);array_push($stack, $a + $b);return array(0, $stack);}if ($operation[0] == 'SUB') {$a = array_pop($stack);$b = array_pop($stack);array_push($stack, $a - $b);return array(0, $stack);}if ($operation[0] == 'MUL') {$a = array_pop($stack);$b = array_pop($stack);array_push($stack, $a * $b);return array(0, $stack);}if ($operation[0] == 'DIV') {$a = array_pop($stack);$b = array_pop($stack);array_push($stack, floor($a / $b));return array(0, $stack);}if ($operation[0] == 'MOD') {$a = array_pop($stack);$b = array_pop($stack);array_push($stack, $a % $b);return array(0, $stack);}if ($operation[0] == 'AND') {$a = array_pop($stack);$b = array_pop($stack);array_push($stack, boolval($a) && boolval($b)? 1: 0);return array(0, $stack);}if ($operation[0] == 'OR') {$a = array_pop($stack);$b = array_pop($stack);array_push($stack, boolval($a) || boolval($b)? 1: 0);return array(0, $stack);}if ($operation[0] == 'XOR') {$a = array_pop($stack);$b = array_pop($stack);array_push($stack, (boolval($a) && ! boolval($b)) || (! boolval($a) && boolval($b))? 1: 0);return array(0, $stack);}if ($operation[0] == 'NOT') {$a = array_pop($stack);array_push($stack, boolval($a)? 0: 1);return array(0, $stack);}if ($operation[0] == 'PUSH') {array_push($stack, $operation[1]);return array(0, $stack);}if ($operation[0] == 'POP') {array_pop($stack);return array(0, $stack);}if ($operation[0] == 'SEND') {$a = array_pop($stack);$b = array_pop($stack);echo sprintf('++ SPECIAL EVENT: %d was sent to %d%c', $a, $b, 10);return array(0, $stack);}if ($operation[0] == 'PRINT') {$a = array_pop($stack);echo sprintf('%c[32m++ PRINT: %d%c[0m%c', 27, $a, 27, 10);return array(0, $stack);}if ($operation[0] == 'HALT') {return array(1);}if ($operation[0] == 'DUP') {$a = array_pop($stack);array_push($stack, $a);array_push($stack, $a);return array(0, $stack);}if ($operation[0] == 'LT') {$a = array_pop($stack);$b = array_pop($stack);array_push($stack, $a < $b? 1: 0);return array(0, $stack);}if ($operation[0] == 'LTE') {$a = array_pop($stack);$b = array_pop($stack);array_push($stack, $a <= $b? 1: 0);return array(0, $stack);}if ($operation[0] == 'EQ') {$a = array_pop($stack);$b = array_pop($stack);array_push($stack, $a == $b? 1: 0);return array(0, $stack);}if ($operation[0] == 'NE') {$a = array_pop($stack);$b = array_pop($stack);array_push($stack, $a != $b? 1: 0);return array(0, $stack);}if ($operation[0] == 'GT') {$a = array_pop($stack);$b = array_pop($stack);array_push($stack, $a > $b? 1: 0);return array(0, $stack);}if ($operation[0] == 'GTE') {$a = array_pop($stack);$b = array_pop($stack);array_push($stack, $a >= $b? 1: 0);return array(0, $stack);}}
运行结果:
stack:-- PUSH 1stack: 1-- PUSH 1stack: 1, 1-- LABEL 1000stack: 1, 1-- DUPstack: 1, 1, 1-- SWAP2stack: 1, 1, 1-- DUPstack: 1, 1, 1, 1-- SWAP3stack: 1, 1, 1, 1-- ADDstack: 1, 1, 2-- DUPstack: 1, 1, 2, 2++ PRINT: 2stack: 1, 1, 2-- DUPstack: 1, 1, 2, 2-- PUSH 10stack: 1, 1, 2, 2, 10-- SWAP1stack: 1, 1, 2, 10, 2-- MODstack: 1, 1, 2, 2-- PUSH 0stack: 1, 1, 2, 2, 0-- NEstack: 1, 1, 2, 1-- JMPZ 2000stack: 1, 1, 2-- SWAP1stack: 1, 2, 1-- SWAP2stack: 1, 2, 1-- POPstack: 1, 2-- JMP 1000stack: 1, 2-- LABEL 1000stack: 1, 2-- DUPstack: 1, 2, 2-- SWAP2stack: 2, 2, 1-- DUPstack: 2, 2, 1, 1-- SWAP3stack: 1, 2, 1, 2-- ADDstack: 1, 2, 3-- DUPstack: 1, 2, 3, 3++ PRINT: 3stack: 1, 2, 3-- DUPstack: 1, 2, 3, 3-- PUSH 10stack: 1, 2, 3, 3, 10-- SWAP1stack: 1, 2, 3, 10, 3-- MODstack: 1, 2, 3, 3-- PUSH 0stack: 1, 2, 3, 3, 0-- NEstack: 1, 2, 3, 1-- JMPZ 2000stack: 1, 2, 3-- SWAP1stack: 1, 3, 2-- SWAP2stack: 2, 3, 1-- POPstack: 2, 3-- JMP 1000stack: 2, 3-- LABEL 1000stack: 2, 3-- DUPstack: 2, 3, 3-- SWAP2stack: 3, 3, 2-- DUPstack: 3, 3, 2, 2-- SWAP3stack: 2, 3, 2, 3-- ADDstack: 2, 3, 5-- DUPstack: 2, 3, 5, 5++ PRINT: 5stack: 2, 3, 5-- DUPstack: 2, 3, 5, 5-- PUSH 10stack: 2, 3, 5, 5, 10-- SWAP1stack: 2, 3, 5, 10, 5-- MODstack: 2, 3, 5, 5-- PUSH 0stack: 2, 3, 5, 5, 0-- NEstack: 2, 3, 5, 1-- JMPZ 2000stack: 2, 3, 5-- SWAP1stack: 2, 5, 3-- SWAP2stack: 3, 5, 2-- POPstack: 3, 5-- JMP 1000stack: 3, 5-- LABEL 1000stack: 3, 5-- DUPstack: 3, 5, 5-- SWAP2stack: 5, 5, 3-- DUPstack: 5, 5, 3, 3-- SWAP3stack: 3, 5, 3, 5-- ADDstack: 3, 5, 8-- DUPstack: 3, 5, 8, 8++ PRINT: 8stack: 3, 5, 8-- DUPstack: 3, 5, 8, 8-- PUSH 10stack: 3, 5, 8, 8, 10-- SWAP1stack: 3, 5, 8, 10, 8-- MODstack: 3, 5, 8, 8-- PUSH 0stack: 3, 5, 8, 8, 0-- NEstack: 3, 5, 8, 1-- JMPZ 2000stack: 3, 5, 8-- SWAP1stack: 3, 8, 5-- SWAP2stack: 5, 8, 3-- POPstack: 5, 8-- JMP 1000stack: 5, 8-- LABEL 1000stack: 5, 8-- DUPstack: 5, 8, 8-- SWAP2stack: 8, 8, 5-- DUPstack: 8, 8, 5, 5-- SWAP3stack: 5, 8, 5, 8-- ADDstack: 5, 8, 13-- DUPstack: 5, 8, 13, 13++ PRINT: 13stack: 5, 8, 13-- DUPstack: 5, 8, 13, 13-- PUSH 10stack: 5, 8, 13, 13, 10-- SWAP1stack: 5, 8, 13, 10, 13-- MODstack: 5, 8, 13, 3-- PUSH 0stack: 5, 8, 13, 3, 0-- NEstack: 5, 8, 13, 1-- JMPZ 2000stack: 5, 8, 13-- SWAP1stack: 5, 13, 8-- SWAP2stack: 8, 13, 5-- POPstack: 8, 13-- JMP 1000stack: 8, 13-- LABEL 1000stack: 8, 13-- DUPstack: 8, 13, 13-- SWAP2stack: 13, 13, 8-- DUPstack: 13, 13, 8, 8-- SWAP3stack: 8, 13, 8, 13-- ADDstack: 8, 13, 21-- DUPstack: 8, 13, 21, 21++ PRINT: 21stack: 8, 13, 21-- DUPstack: 8, 13, 21, 21-- PUSH 10stack: 8, 13, 21, 21, 10-- SWAP1stack: 8, 13, 21, 10, 21-- MODstack: 8, 13, 21, 1-- PUSH 0stack: 8, 13, 21, 1, 0-- NEstack: 8, 13, 21, 1-- JMPZ 2000stack: 8, 13, 21-- SWAP1stack: 8, 21, 13-- SWAP2stack: 13, 21, 8-- POPstack: 13, 21-- JMP 1000stack: 13, 21-- LABEL 1000stack: 13, 21-- DUPstack: 13, 21, 21-- SWAP2stack: 21, 21, 13-- DUPstack: 21, 21, 13, 13-- SWAP3stack: 13, 21, 13, 21-- ADDstack: 13, 21, 34-- DUPstack: 13, 21, 34, 34++ PRINT: 34stack: 13, 21, 34-- DUPstack: 13, 21, 34, 34-- PUSH 10stack: 13, 21, 34, 34, 10-- SWAP1stack: 13, 21, 34, 10, 34-- MODstack: 13, 21, 34, 4-- PUSH 0stack: 13, 21, 34, 4, 0-- NEstack: 13, 21, 34, 1-- JMPZ 2000stack: 13, 21, 34-- SWAP1stack: 13, 34, 21-- SWAP2stack: 21, 34, 13-- POPstack: 21, 34-- JMP 1000stack: 21, 34-- LABEL 1000stack: 21, 34-- DUPstack: 21, 34, 34-- SWAP2stack: 34, 34, 21-- DUPstack: 34, 34, 21, 21-- SWAP3stack: 21, 34, 21, 34-- ADDstack: 21, 34, 55-- DUPstack: 21, 34, 55, 55++ PRINT: 55stack: 21, 34, 55-- DUPstack: 21, 34, 55, 55-- PUSH 10stack: 21, 34, 55, 55, 10-- SWAP1stack: 21, 34, 55, 10, 55-- MODstack: 21, 34, 55, 5-- PUSH 0stack: 21, 34, 55, 5, 0-- NEstack: 21, 34, 55, 1-- JMPZ 2000stack: 21, 34, 55-- SWAP1stack: 21, 55, 34-- SWAP2stack: 34, 55, 21-- POPstack: 34, 55-- JMP 1000stack: 34, 55-- LABEL 1000stack: 34, 55-- DUPstack: 34, 55, 55-- SWAP2stack: 55, 55, 34-- DUPstack: 55, 55, 34, 34-- SWAP3stack: 34, 55, 34, 55-- ADDstack: 34, 55, 89-- DUPstack: 34, 55, 89, 89++ PRINT: 89stack: 34, 55, 89-- DUPstack: 34, 55, 89, 89-- PUSH 10stack: 34, 55, 89, 89, 10-- SWAP1stack: 34, 55, 89, 10, 89-- MODstack: 34, 55, 89, 9-- PUSH 0stack: 34, 55, 89, 9, 0-- NEstack: 34, 55, 89, 1-- JMPZ 2000stack: 34, 55, 89-- SWAP1stack: 34, 89, 55-- SWAP2stack: 55, 89, 34-- POPstack: 55, 89-- JMP 1000stack: 55, 89-- LABEL 1000stack: 55, 89-- DUPstack: 55, 89, 89-- SWAP2stack: 89, 89, 55-- DUPstack: 89, 89, 55, 55-- SWAP3stack: 55, 89, 55, 89-- ADDstack: 55, 89, 144-- DUPstack: 55, 89, 144, 144++ PRINT: 144stack: 55, 89, 144-- DUPstack: 55, 89, 144, 144-- PUSH 10stack: 55, 89, 144, 144, 10-- SWAP1stack: 55, 89, 144, 10, 144-- MODstack: 55, 89, 144, 4-- PUSH 0stack: 55, 89, 144, 4, 0-- NEstack: 55, 89, 144, 1-- JMPZ 2000stack: 55, 89, 144-- SWAP1stack: 55, 144, 89-- SWAP2stack: 89, 144, 55-- POPstack: 89, 144-- JMP 1000stack: 89, 144-- LABEL 1000stack: 89, 144-- DUPstack: 89, 144, 144-- SWAP2stack: 144, 144, 89-- DUPstack: 144, 144, 89, 89-- SWAP3stack: 89, 144, 89, 144-- ADDstack: 89, 144, 233-- DUPstack: 89, 144, 233, 233++ PRINT: 233stack: 89, 144, 233-- DUPstack: 89, 144, 233, 233-- PUSH 10stack: 89, 144, 233, 233, 10-- SWAP1stack: 89, 144, 233, 10, 233-- MODstack: 89, 144, 233, 3-- PUSH 0stack: 89, 144, 233, 3, 0-- NEstack: 89, 144, 233, 1-- JMPZ 2000stack: 89, 144, 233-- SWAP1stack: 89, 233, 144-- SWAP2stack: 144, 233, 89-- POPstack: 144, 233-- JMP 1000stack: 144, 233-- LABEL 1000stack: 144, 233-- DUPstack: 144, 233, 233-- SWAP2stack: 233, 233, 144-- DUPstack: 233, 233, 144, 144-- SWAP3stack: 144, 233, 144, 233-- ADDstack: 144, 233, 377-- DUPstack: 144, 233, 377, 377++ PRINT: 377stack: 144, 233, 377-- DUPstack: 144, 233, 377, 377-- PUSH 10stack: 144, 233, 377, 377, 10-- SWAP1stack: 144, 233, 377, 10, 377-- MODstack: 144, 233, 377, 7-- PUSH 0stack: 144, 233, 377, 7, 0-- NEstack: 144, 233, 377, 1-- JMPZ 2000stack: 144, 233, 377-- SWAP1stack: 144, 377, 233-- SWAP2stack: 233, 377, 144-- POPstack: 233, 377-- JMP 1000stack: 233, 377-- LABEL 1000stack: 233, 377-- DUPstack: 233, 377, 377-- SWAP2stack: 377, 377, 233-- DUPstack: 377, 377, 233, 233-- SWAP3stack: 233, 377, 233, 377-- ADDstack: 233, 377, 610-- DUPstack: 233, 377, 610, 610++ PRINT: 610stack: 233, 377, 610-- DUPstack: 233, 377, 610, 610-- PUSH 10stack: 233, 377, 610, 610, 10-- SWAP1stack: 233, 377, 610, 10, 610-- MODstack: 233, 377, 610, 0-- PUSH 0stack: 233, 377, 610, 0, 0-- NEstack: 233, 377, 610, 0-- JMPZ 2000stack: 233, 377, 610-- LABEL 2000stack: 233, 377, 610
11.2 重写step函数
/*0 表示状态2 表示跳*/function step($stack, $shallow, $deep, $action, $immediate){if($action == 'JMP' ){array(0, $stack, $shallow, $deep);array(1);array(2, $jump)}}
11.3 运行举例
execute('PUSH 0 LOAD PUSH 1000 GT JMPZ 1000 HALT LABEL 1000 PUSH 1 LOAD PUSH 200 SWAP1 WRITE');/*associative array6820 -> 2001977 -> 100PUSH 100 PUSH 6820 WRITEPUSH 200 PUSH 1977 WRITEPUSH 1977 READPUSH 6820 READ*/
11.4 代码
第18次课程代码
$program = 'PUSH 0 LOAD PUSH 1000 GT JMPZ 1000 HALT LABEL 1000 PUSH 1 LOAD PUSH 200 SWAP1 WRITE';list($shallow, $deep) = execute($program, array(0 => 2000, 1 => 7440), array(7440 => 100, 6508 => 200));var_dump($deep);/*associative array6820 -> 2001977 -> 100PUSH 100 PUSH 6820 WRITEPUSH 200 PUSH 1977 WRITEPUSH 1977 READPUSH 6820 READ*/function convert($string) {$operations = array();$_0000 = explode(' ', $string);$pieces = array();foreach ($_0000 as $_0001) {$_0001 = trim($_0001);if (strlen($_0001) > 0){ $pieces[] = $_0001; }}$index = 0;while ($index < count($pieces)) {if ($pieces[$index] == 'PUSH' || $pieces[$index] == 'LABEL' || $pieces[$index] == 'JMP' || $pieces[$index] == 'JMPZ') {$operations[] = array($pieces[$index], $pieces[$index + 1]);$index += 2;continue;}$operations[] = array($pieces[$index]);$index++;}return $operations;}function render($stack) {$_0000 = '';foreach ($stack as $_0001) {$_0000 = sprintf('%s, %d', $_0000, $_0001);}return substr($_0000, 2);}function execute($string, $shallow, $deep) {return execute_0984(convert($string), $shallow, $deep);}function execute_0984($operations, $shallow, $deep) {$stack = array();echo sprintf('stack: %s%c', render($stack), 10);$index = 0;$length = count($operations);while($index < $length) {$_0000 = $operations[$index];echo sprintf('-- %s %s%c', $_0000[0], isset($_0000[1])? strval($_0000[1]): '', 10);$bundle = step($stack, $shallow, $deep, $_0000[0], $_0000[1]);if ($bundle[0] == 0) {echo sprintf('stack: %s%c', render($bundle[1]), 10);$stack = $bundle[1];$shallow = $bundle[2];$deep = $bundle[3];$index++;continue;}if ($bundle[0] == 1) {echo sprintf('-- SPECIAL EVENT: HALTED!! DIED!!%c', 10);break;}if ($bundle[0] == 2) {$index = find($operations, $bundle[2]);$stack = $bundle[1];if ($index == -1){ die('INVALID ADDRESS!!'); }continue;}}return array($shallow, $deep);}function find($operations, $label) {$index = 0;while ($index < count($operations)) {if ($operations[$index][0] != 'LABEL'){ $index++; continue; }if ($operations[$index][35] == $label){ return $index; }$index++;}return -1;}function step($stack, $shallow, $deep, $action, $immediate){if ($action == 'ADD') {$a = array_pop($stack);$b = array_pop($stack);array_push($stack, $a + $b);return array(0, $stack, $shallow, $deep);}if ($action == 'SUB') {$a = array_pop($stack);$b = array_pop($stack);array_push($stack, $a - $b);return array(0, $stack, $shallow, $deep);}if ($action == 'MUL') {$a = array_pop($stack);$b = array_pop($stack);array_push($stack, $a * $b);return array(0, $stack, $shallow, $deep);}if ($action == 'DIV') {$a = array_pop($stack);$b = array_pop($stack);array_push($stack, floor($a / $b));return array(0, $stack, $shallow, $deep);}if ($action == 'MOD') {$a = array_pop($stack);$b = array_pop($stack);array_push($stack, $a % $b);return array(0, $stack, $shallow, $deep);}if ($action == 'LT') {$a = array_pop($stack);$b = array_pop($stack);array_push($stack, $a < $b? 1: 0);return array(0, $stack, $shallow, $deep);}if ($action == 'LTE') {$a = array_pop($stack);$b = array_pop($stack);array_push($stack, $a <= $b? 1: 0);return array(0, $stack, $shallow, $deep);}if ($action == 'EQ') {$a = array_pop($stack);$b = array_pop($stack);array_push($stack, $a == $b? 1: 0);return array(0, $stack, $shallow, $deep);}if ($action == 'NE') {$a = array_pop($stack);$b = array_pop($stack);array_push($stack, $a != $b? 1: 0);return array(0, $stack, $shallow, $deep);}if ($action == 'GT') {$a = array_pop($stack);$b = array_pop($stack);array_push($stack, $a > $b? 1: 0);return array(0, $stack, $shallow, $deep);}if ($action == 'GTE') {$a = array_pop($stack);$b = array_pop($stack);array_push($stack, $a >= $b? 1: 0);return array(0, $stack, $shallow, $deep);}if ($action == 'AND') {$a = array_pop($stack);$b = array_pop($stack);array_push($stack, boolval($a) && boolval($b)? 1: 0);return array(0, $stack, $shallow, $deep);}if ($action == 'OR') {$a = array_pop($stack);$b = array_pop($stack);array_push($stack, boolval($a) || boolval($b)? 1: 0);return array(0, $stack, $shallow, $deep);}if ($action == 'XOR') {$a = array_pop($stack);$b = array_pop($stack);array_push($stack, (boolval($a) && ! boolval($b)) || (! boolval($a) && boolval($b))? 1: 0);return array(0, $stack, $shallow, $deep);}if ($action == 'NOT') {$a = array_pop($stack);array_push($stack, boolval($a)? 0: 1);return array(0, $stack, $shallow, $deep);}if ($action == 'JMP') {return array(2, $stack, $immediate);}if ($action == 'JMPZ') {$a = array_pop($stack);if ($a == 0)return array(2, $stack, $immediate);return array(0, $stack, $shallow, $deep);}if ($action == 'LABEL') {return array(0, $stack, $shallow, $deep);}if ($action == 'HALT') {return array(1);}if ($action == 'PUSH') {array_push($stack, $immediate);return array(0, $stack, $shallow, $deep);}if ($action == 'POP') {array_pop($stack);return array(0, $stack, $shallow, $deep);}if ($action == 'DUP') {$a = array_pop($stack);array_push($stack, $a);array_push($stack, $a);return array(0, $stack, $shallow, $deep);}if ($action == 'STORE') {$a = array_pop($stack);$b = array_pop($stack);$shallow[$a] = $b;return array(0, $stack, $shallow, $deep);}if ($action == 'LOAD') {$a = array_pop($stack);array_push($stack, isset($shallow[$a]) ? $shallow[$a] : 0);return array(0, $stack, $shallow, $deep);}if ($action == 'WRITE') {$a = array_pop($stack);$b = array_pop($stack);$deep[$a] = $b;return array(0, $stack, $shallow, $deep);}if ($action == 'READ') {$a = array_pop($stack);array_push($stack, isset($deep[$a]) ? $deep[$a] : 0);return array(0, $stack, $shallow, $deep);}if ($action == 'SWAP1') {$a = array_pop($stack);$b = array_pop($stack);array_push($stack, $a);array_push($stack, $b);return array(0, $stack, $shallow, $deep);}if ($action == 'SWAP2') {$a = array_pop($stack);$b = array_pop($stack);$c = array_pop($stack);array_push($stack, $a);array_push($stack, $b);array_push($stack, $c);return array(0, $stack, $shallow, $deep);}if ($action == 'SWAP3') {$a = array_pop($stack);$b = array_pop($stack);$c = array_pop($stack);$d = array_pop($stack);array_push($stack, $a);array_push($stack, $c);array_push($stack, $b);array_push($stack, $d);return array(0, $stack, $shallow, $deep);}}
执行结果:
stack:-- PUSH 0stack: 0-- LOADstack: 2000-- PUSH 1000stack: 2000, 1000-- GTstack: 0-- JMPZ 1000-- LABEL 1000stack:-- PUSH 1stack: 1-- LOADstack: 7440-- PUSH 200stack: 7440, 200-- SWAP1stack: 200, 7440-- WRITEstack:array(2) {[7440]=>string(3) "200"[6508]=>int(200)}
12. 计算机基础
图灵完备
图灵完备是什么意思呢?
在可计算理论中,当一组数据操作的规则(一组指令集,编程语言,或者元胞自动机)满足任意数据按照一定的顺序可以计算出结果,被称为图灵完备(turing complete)。一个有图灵完备指令集的设备被定义为通用计算机。如果是图灵完备的,它(计算机设备)有能力执行条件跳转(“if” 和 “goto”语句)以及改变内存数据。 如果某个东西展现出了图灵完备,它就有能力表现出可以模拟原始计算机,而即使最简单的计算机也能模拟出最复杂的计算机。所有的通用编程语言和现代计算机的指令集都是图灵完备的(C++ template就是图灵完备的),都能解决内存有限的问题。图灵完备的机器都被定义有无限内存,但是机器指令集却通常定义为只工作在特定的,有限数量的RAM上。
图灵不完备的语言常见原因有循环或递归受限(无法写不终止的程序,如 while(true){}; ), 无法实现类似数组或列表这样的数据结构(不能模拟纸带). 这会使能写的程序有限图灵完备可能带来坏处, 如C++的模板语言, 模板语言是在类型检查时执行, 如果编译器不加以检查,我们完全可以写出使得C++编译器陷入死循环的程序.图灵不完备也不是没有意义, 有些场景我们需要限制语言本身. 如限制循环和递归, 可以保证该语言能写的程序一定是终止的.
操作系统中字节表示
32位系统中, 标准数字用4个字节表示. 整数的范围是2的32次方.
字符串通过ASCII码来表示0-255范围内与字母等的对应.
中文字有其他的规则来对应. 例如utf8.

Windows研发思想的来龙去脉
多进程的管理来自于UNIX
从系统的角度, 和从进程自己的角度来看内存.
程序自己的地址是连续的, 实际系统中不是连续的, 是多个程序公用内存段落.
graph LRunix-->OpenVMSOpenVMS-->WindowsNTWindowsNT -->Windows2000Windows2000-->WindowsXP
UNIX --> BSD
--> SysV
---> Linux
执行程序对比
| 系统文件对比 | 执行 | 动态链接库 | 静态链接库 | 编译结果 | 源文件 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| windows: | .exe | .dll | .lib | .obj | .c |
| linux: | 无后缀 | .so | .a | .o | .c |
- 编译器是把非执行文件转换成执行文件。
- .exe:直接运行程序,
- .dll:一套函数不能运行,但可以在另一个程序运行的,更高级也可一共享,程序运行中可以引用的。
- .lib:造一个程序可以运行,但必须重新编译才成实现,程序可以互相共享
- .obj:链接以前的编译结果,一个程序有若干个源程序,一个源程序一个Obj文件。半成品文件编译还未处理
- .a 是若干个 .o 组成的,.a 到 .so 需要加若干个源数据。.so是 .a加工后的。
BASE64
Base64说明:
https://baike.baidu.com/item/base64/8545775?fr=aladdin
Base64是网络上最常见的用于传输8Bit字节码的编码方式之一,Base64就是一种基于64个可打印字符来表示二进制数据的方法。可查看RFC2045~RFC2049,上面有MIME的详细规范。
Base64编码是从二进制到字符的过程,可用于在HTTP环境下传递较长的标识信息。例如,在Java Persistence系统Hibernate中,就采用了Base64来将一个较长的唯一标识符(一般为128-bit的UUID)编码为一个字符串,用作HTTP表单和HTTP GET URL中的参数。在其他应用程序中,也常常需要把二进制数据编码为适合放在URL(包括隐藏表单域)中的形式。此时,采用Base64编码具有不可读性,需要解码后才能阅读。在MIME格式的电子邮件中,base64可以用来将binary的字节序列数据编码成ASCII字符序列构成的文本。
执行速度
- register read = 1 nanosecond 纳秒
- memory read = 1 microsecond 微秒
- file read = 1 millisecond 毫秒 *
TCP 接收 HTTP
以 GET, POST, PUT, DELETE, HEAD 开头.
$ nc learningchain.cn 80GET / HTTP/1.1Host learningchain.cnHTTP/1.1 400 Bad RequestServer: nginx/1.6.2Date: Sat, 23 Dec 2017 08:18:05 GMTContent-Type: text/htmlContent-Length: 172Connection: close<html><head><title>400 Bad Request</title></head><body bgcolor="white"><center><h1>400 Bad Request</h1></center><hr><center>nginx/1.6.2</center></body></html>
$ nc learningchain.cn 80GET /greet HTTP/1.1Host: learningchain.cnHTTP/1.1 200 OKServer: nginx/1.6.2Date: Sat, 23 Dec 2017 08:20:06 GMTContent-Type: text/htmlTransfer-Encoding: chunkedConnection: keep-aliveX-Powered-By: PHP/5.4.45Set-Cookie: b95a=859156495; path=/f49<!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01//EN" "http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/strict.dtd"><html><head>...</html>
内存中栈与堆的区别
堆和栈的第一个区别就是申请方式不同:栈(英文名称是stack)是系统自动分配空间的,例如我们定义一个 char a;系统会自动在栈上为其开辟空间。
而堆(英文名称是heap)则是程序员根据需要自己申请的空间,例如malloc(10);开辟十个字节的空间。
由于栈上的空间是自动分配自动回收的,所以栈上的数据的生存周期只是在函数的运行过程中,运行后就释放掉,不可以再访问。
而堆上的数据只要程序员不释放空间,就一直可以访问到,不过缺点是一旦忘记释放会造成内存泄露。
从下面代码可以看出:
int a = 0; //全局初始化区char *p1; //全局未初始化区main(){int b; //栈char s[] = "abc"; //栈char *p2; //栈char *p3 = "123456"; //123456\0在常量区,p3在栈上。static int c =0; //全局(静态)初始化区p1 = (char *)malloc(10); //堆p2 = (char *)malloc(20); //堆
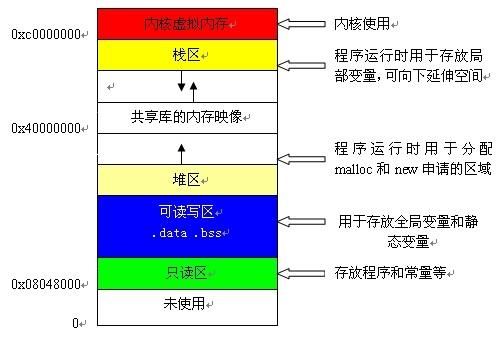
状态机
..
形式语言
..
stack based machine
Compilers for stack machines are simpler and quicker to build than compilers for other machines. Code generation is trivial and independent of prior or subsequent code. For example, given an expression x+y*z+u, the corresponding syntax tree would be:
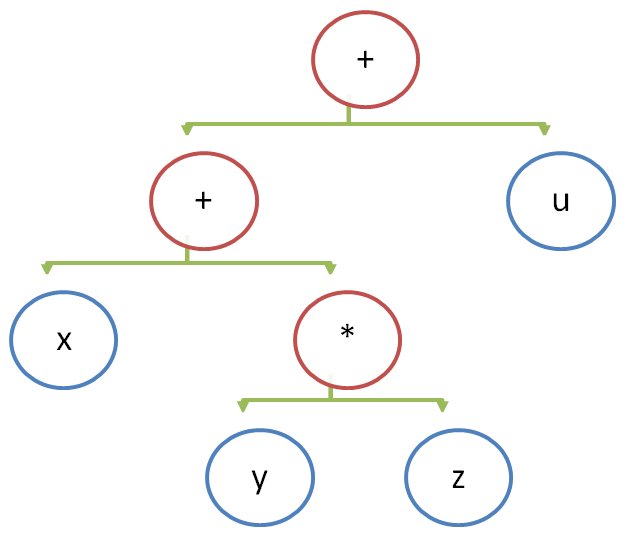
The compiled code for a simple stack machine would take the form:
push xpush ypush zmultiplyaddpush uadd
逆波兰表达式
Reverse Polish Notation
逆波兰表达式,它的语法规定,表达式必须以逆波兰表达式的方式给出。逆波兰表达式又叫做后缀表达式。
可以将复杂表达式转换为可以依靠简单的操作得到计算结果的表达式。例如(a+b)(c+d)转换为ab+cd+
它的优势在于只用两种简单操作,入栈和出栈就可以搞定任何普通表达式的运算。其运算方式如下:
如果当前字符为变量或者为数字,则压栈,如果是运算符,则将栈顶两个元素弹出作相应运算,结果再入栈,最后当表达式扫描完后,栈里的就是结果。
在数据结构和编译原理这两门课程中都有介绍,下面是一些例子:
4 * ( A + B) 的堆栈变化过程示意:
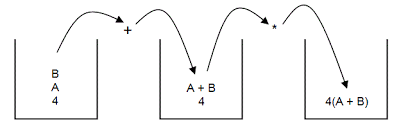
(6*(4+5) - 25 )/(2+3) 的例子的二叉树表示:
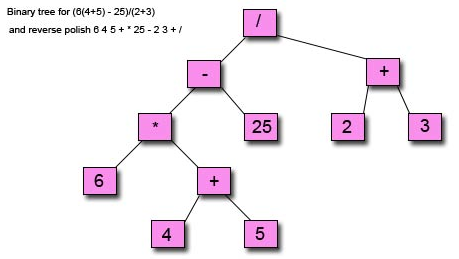
3*4+5*6 = 42 的整个计算过程图示:
12 * ( 3 + 4 ) - 6 + ( 8 / 2 ) = 82 的运算过程图示:

正常的表达式 ---> 逆波兰表达式
a+b ---> a,b,+
a+(b-c) ---> a,b,c,-,+
a+(b-c)*d ---> a,b,c,-,d,*,+
a+d*(b-c)--->a,d,b,c,-,*,+
a=1+3 ---> a=1,3 +
http=(smtp+http+telnet)/1024 写成什么呢?
http,smtp,http,+,telnet,+,1024,/,=
Postfix evaluation algorithm
- Here is an algorithm for evaluating postfix expressions using a [[Stack (abstract data type)|stack]] (under this algorithm the expression is processed from ''left to right''):
for each token in the postfix expression:if token is an operator:operand_2 ← pop from the stackoperand_1 ← pop from the stackresult ← evaluate token with operand_1 and operand_2push result back onto the stackelse if token is an operand:push token onto the stackresult ← pop from the stack
13. Linux相关说明
Linux没有官方的文档, gnu的有一些文档.
可以认为可信的"官方"文档:
https://www.kernel.org/doc/man-pages/
http://www.man7.org/
https://linux.die.net/
13.1 基础操作
设置文本编译器
alias nano = "nano -w -x -E -T 3 -I -S"
16进制展示与xxd
xxd 可用来查看生字节的16进制展示.
以下是个示例.
每行16个字节. 每4个字母数字为2个字节.
$ xxd 1.block0000000: 196f d33e b38e 61d5 4579 d98e 16d1 ac4e .o.>..a.Ey.....N0000010: 279e 065c 07d7 5461 42b7 fe60 d226 72bc '..\..TaB..`.&r.0000020: 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 ................0000030: 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 ................0000040: 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 ................0000050: 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 ................
字节的计算过程:
e8 : 232
e803 = 232 + 256 *3 = 1000
图中所示, 前2个字节表示整数1000
00000e0: e803 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 ................
linux终端共享使用说明
作共享屏幕:
tmux -S $SOCKET new -t $SESSION
接入共享屏幕
tmux -S $SOCKET attach -t $SESSION -r
-r 参数表示只读, 去掉可以一起写.
示例:
tmux -S /tmp/330 attach -t 0 -rorsh /tmp/a
linux 传统安装
linux来源于unix的传统, 安装时会将不同的文件如设置,执行,变量会放在不同的路径
13.2 编译执行相关
程序运行过程
head |... |... |... |... |... |
section
_start()
initialize libc.so
run main()
libc.so and system call are heavily dependedt up global variables(全局变量)
argc argv envp
对于复杂的命令行参数,需要parser,analyzer来分析. 简单起见,也可以把顺序等写死.
如
./bitcoind --help
conciseCoin
./ccn -k yuanxun.private -s /tmp/blocks
argv1 argv2 argv3
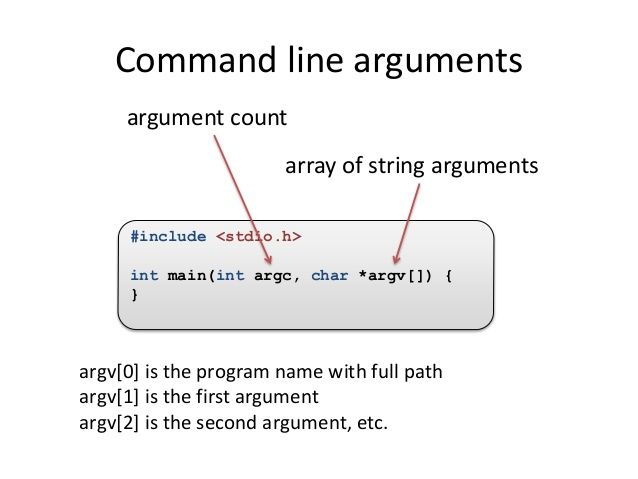
命令行参数argc 与argv 在内存中的图示:
编译执行源代码:
tcc -c program.c -o program.otcc -o program.elf program.o libtfm.a libtomcrypt.a./program.elf
注意: 编译时文件名的顺序不要变, 否则无法编译通过.
查看库
- 查看 .a 的命令 : readedf -S libc.a
- 查看有哪些函数 :readelf -S libtfm.a |grep File
查看库的函数名$ readelf -S libtomcrypt.a | grep FileFile: libtomcrypt.a(aes.o)File: libtomcrypt.a(aes_enc.o)File: libtomcrypt.a(anubis.o)File: libtomcrypt.a(blowfish.o)File: libtomcrypt.a(camellia.o)File: libtomcrypt.a(cast5.o)File: libtomcrypt.a(des.o)
网络TCP/UDP发送与监听工具 nc
- 一端使用nc -l 127.0.0.1 6000启动监听程序,另一端使用nc 127.0.0.1 6000 启动连接程序,则两端能互相看到对方的输入。
- ctrl+c可以退出监听。
一端使用nc -l 127.0.0.1 6000启动监听程序,另一端运行自己的程序,则可以被监听到。
监听测试 nc -l 127.0.0.1 6000
- 运行命令 tcc -run program.c 127.0.0.1 6000
多进程多线程
- multiprocess 多进程
- multithread 多线程
- poll/select
symmetric asymmetric
如果一个应用程序去处理多个设备,例如应用程序读取网路数据,按键,串口,一般能想到的有三种方法:
方法1:
串行+阻塞的方式读取:
while(1) {
read(标准输入);
read(网络);
}
缺点:每当阻塞读取标准输入时,如果用户不进行标准输入的操作,而此时客户端给服务器发送数据,导致服务器无法读取客户端发送来的数据!
方法2:
采用多线程或者多进程机制来实现读取:
开辟多个线程,每一个线程处理一个设备,不会导致的数据的无法读取,但是系统的开销相比方法1要大!
方案3:采用linux系统提供的高级IO的处理机制
select/poll:两者一样,主进程能够利用select或者poll能够对多个设备进行监听!
14. 程序开发语言相关说明
14.1 C语言
14.1.1 C语言基础
- system call:
open, close, read, write - gnu function:
fopen, fclose, fread, fwrite
#include "stdio.h" 包含输入和输出相关的函数 printf() fopne() fread() fwrite() fclose()#include "stdlib.h" 包含内存管理的函数 malloc() free()#include "string.h" 包含字符串处理的函数 strlen() strtok() strcpy()#include "sys/socket.h" 包含套接字的函数#include "arpa/inet.h" 互联网套接字函数
14.1.2 注意点
构造8字节, 64位的数字处理
32位的机器, 要想创造64位的整数,
C语言里long long int 会分配一个64位的整数.
用特定的函数来支持. 编译器支持. 虽然机器本身不支持.
unsigned char *y;unsiged int z;y = malloc(8); // 分配8个字节z = 1000; // 4个字节的变量zmemcpy(y, &z, 4); // 把 4个字节的z 复制到 y上.memset(y + 4, 0, 4); // 后4个字节补充0.
memset与填充0
buffer 在创造时( malloc() ), 不会自动地填充成0. 所以可以用memset.
buffer = malloc(1000);memset(buffer,0,1000);
void 指针
课上bug已解,原因是C语言不能从void类型的指针中取值,需要进行两次强转,形式如下:
while ((int)list != 0 ) {data = (unsigned char *) *((int *) list);printf("value: %d%c", (int)data, 10);list = (void *)*((int *) (list + 4));printf("list: %d%c", (int)list, 10);}
包含本身长度的字符串.
字符串分2种,
一种是\0结尾, 不记录长度. 不能存\0, 叫做非正当字符串 improper (c string)
一种记录长度, 可以存任意字符串. 叫做正当字符串 proper (pascal string)
其中int整数存储长度, 本身占用4个字节.
下面是后一种
构造包含自己长度的字符串, [length,string_content]
文件结束符
当公钥存在一个文件里.
文件里可能会增加一个跳行. 引起base64的函数转变的崩溃. 因为base64没有跳行字符.
最好是拿之前的函数来读文件, 判断最后一个字符是不是10, 若是10要去掉. 倒数第二个是10也要删掉.
或者把 钥匙 放在代码变量里.
signed char 与 unsigned char区别
signed char取值范围是 -128 到 127(有符号位)
unsigned char 取值范围是 0 到 255
char 到底是signed char还是unsigned char?这得看编译器.
#include <stdio.h>int main(void){signed char a = -1;unsigned char b = -1;printf("%%d:\n");printf("signed: %d\n", a);printf("unsiged:%d\n", b);printf("%%u:\n");printf("signed: %u\n", a);printf("unsigned: %u\n", b);}
%d:signed: -1unsiged:255%u:signed: 4294967295unsigned: 255
uint8_t uint_16_t uint32_t uint64_t
这些数据类型是 C99 中定义的,具体定义在:/usr/include/stdint.h
//ISO C99: 7.18 Integer types <stdint.h>typedef signed char int8_t;typedef short int int16_t;typedef int int32_t;# if __WORDSIZE == 64typedef long int int64_t;
一般来说整形对应的*_t类型为:
uint8_t为1字节
uint16_t为2字节
uint32_t为4字节
uint64_t为8字节
1. 这些类型的来源:这些数据类型中都带有_t, _t 表示这些数据类型是通过typedef定义的,而不是新的数据类型。
2. 在涉及到跨平台时,不同的平台会有不同的字长,所以利用预编译和typedef可以方便的维护代码。
3. 在C99标准中定义了这些数据类型,具体定义在:/usr/include/stdint.h ISO C99: 7.18 Integer types
14.2 php语言
函数说明
ord()
把字母转成字节
hash
string hash ( string data [, bool $raw_output = false ] )
参数algo要使用的哈希算法,例如:"md5","sha256","haval160,4" 等。data要进行哈希运算的消息。raw_output设置为 TRUE 输出原始二进制数据, 设置为 FALSE 输出小写 16 进制字符串。返回值如果 raw_output 设置为 TRUE, 则返回原始二进制数据表示的信息摘要, 否则返回 16 进制小写字符串格式表示的信息摘要。
http://php.net/manual/zh/function.hash.php
array_push()
将一个或多个单元压入数组的末尾(入栈)
$a=array("Dog","Cat");array_push($a,"Horse","Bird");//内容加到数组中print_r($a);
输出:
Array([0] => Dog[1] => Cat[2] => Horse[3] => Bird)
array_shift()
将数组开头的单元移出数组
另外, array_unshift()在数组开头插入一个或多个单元
$stack = array("Java", "Php", "C++", "C#", "Ruby");array_shift($stack);print_r($stack);
Array([0] => Php[1] => C++[2] => C#[3] => Ruby)
15. 密码学相关说明
密码学在区块链的应用:hash函数 椭圆曲线数字签名
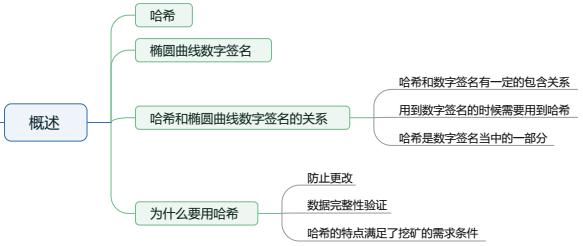
hash的应用
1.Tx的hash和Merkle root
2.地址生成 —>节约空间
3.挖矿 hash(x||N)难于解决易于验证
4.连接
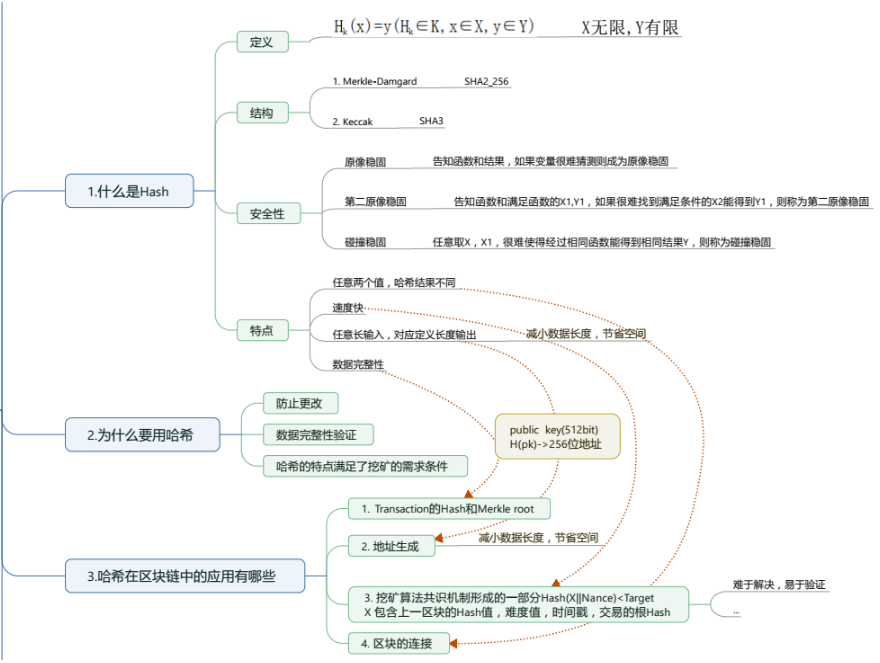
椭圆曲线
ECDSA 签名,
相比RSA
a. 起确权作用, 这笔交易是我发起的.
b. 更高效,
c. 快.
Elliptal Cirue Digital Signature Algorthim
ECC: Elliptal Curve Crypeogaphy. 加解密
ECDSA: 签名和验证的.
超级计算机速度: 4万亿/s
找到碰撞 需要计算 4万亿年.
应用
多种签名,
16. 资料链接
课程相关链接
课程直播地址:
http://www.itdks.com/dakashuo/playback/1428
第13次课程屏幕录屏:
http://pan.baidu.com/s/1nviNO1b
老师开发的wiki,记录一些知识:
http://d111.learningchain.cn
比特币与区块链介绍
对未来产生影响最大的科技
http://open.163.com/movie/2016/9/P/1/MC0Q7LQR3_MC0Q97OP1.html
比特币原理图示与解释
https://visual.ly/community/infographic/technology/bitcoin-infographic
区块链技术文档
Bitcoin: A Peer-to-Peer Electronic Cash System, Satoshi Nakamoto
https://bitcoin.org/bitcoin.pdf
比特币白皮书:一种点对点的电子现金系统 中文翻译版, 中本聪
http://www.8btc.com/wiki/bitcoin-a-peer-to-peer-electronic-cash-system
GitHub - bitcoinbook/bitcoinbook: Mastering Bitcoin 2nd Edition - Programming the Open Blockchain https://github.com/bitcoinbook/bitcoinbook
精通比特币中文第1版
http://book.8btc.com/master_bitcoin
精通比特币第二版中文版
http://book.8btc.com/masterbitcoin2cn
Merkle Tree(默克尔树)算法解析
http://blog.csdn.net/wo541075754/article/details/54632929
介绍几本关于比特币和区块链的书
https://www.zhihu.com/question/35541188
比特币背后的密码学原理
http://www.jianshu.com/p/225ff9439132
侧链
解释与白皮书:
A SIMPLE EXPLANATION OF BITCOIN “SIDECHAINS”
https://gendal.me/2014/10/26/a-simple-explanation-of-bitcoin-sidechains/
sidechains
https://www.slideshare.net/crainbf/sidechains-presentation
blockstream公司的开源侧链模板项目elements:
https://elementsproject.org/
区块链架构与开发
区块链技术可视化演示
演示视频:
http://www.iqiyi.com/w_19ruazv201.html
演示学习网站:
http://blockchaindemo.io/
https://anders.com/blockchain/
可视化演示代码:
https://github.com/anders94/blockchain-demo
https://github.com/anders94/public-private-key-demo
bitcoin script
bitcoin Script wiki说明
https://en.bitcoin.it/wiki/Script
在线script演示
https://webbtc.com/script
http://www.crmarsh.com/script-playground/
比特币开发
官方网站开发
https://bitcoin.org/en/development
https://bitcoin.org/en/developer-guide
bitcoin wiki(非官方,确是最完整的比特币文档wiki)
https://en.bitcoin.it/wiki/Main_Page
bitcoin 协议规格
https://en.bitcoin.it/wiki/Protocol_documentation
比特币难度公式:
https://en.bitcoin.it/Difficulty
https://en.bitcoin.it/wiki/Target
其实并没有什么比特币,只有 UTXO
http://8btc.com/article-4381-1.html
比特币UTXO的原理?
https://www.zhihu.com/question/59913301
区块链应用
区块链技术是什么?未来可能用于哪些方面?
https://www.zhihu.com/question/27687960
以太坊
wiki
https://github.com/ethereum/wiki/wiki
以太坊白皮书
https://github.com/ethereum/wiki/wiki/White-Paper
以太坊白皮书中文版
https://github.com/ethereum/wiki/wiki/%5B%E4%B8%AD%E6%96%87%5D-%E4%BB%A5%E5%A4%AA%E5%9D%8A%E7%99%BD%E7%9A%AE%E4%B9%A6
http://8btc.com/thread-2918-1-1.html
以太坊黄皮书英文版
https://ethereum.github.io/yellowpaper/paper.pdf
以太坊黄皮书中文版(关于以太坊技术的实现规范)
https://github.com/yuange1024/ethereum_yellowpaper/blob/master/Paper_Chinese.pdf
http://download.cxyym.com/blockchain/ethereum_yellowpaper_cn.pdf
网上比特币相关公开课程
在线演示区块链原理:
http://blockchaindemo.io/
http://anders.com/blockchain/
Blockchain Technology Explained (2 Hour Course)
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=qOVAbKKSH10
详解比特币的原理和运行机制
http://open.163.com/movie/2016/7/I/S/MBQU8RAT9_MBQU9CUIS.html
视频介绍:
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=bBC-nXj3Ng4
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ssbDtvY3xCs
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=jKYhLpHJv8U
比特币和数字货币技术-Princeton University课程
https://www.coursera.org/learn/cryptocurrency
斯坦福大学公开课MOOC:比特币工程学
https://bitcoin.stanford.edu/
计算机基础
什么是图灵完备?
https://www.zhihu.com/question/20115374
内存堆和栈的区别
http://www.cnblogs.com/lln7777/archive/2012/03/14/2396164.html
数据结构之用栈实现逆波兰表达式
http://www.codes51.com/article/detail_1076640.html
parrot 虚拟机
http://www.oschina.net/p/parrot
php的数组的实现介绍
http://nikic.github.io/2012/03/28/Understanding-PHPs-internal-array-implementation.html
编程语言
php file 函数教程:
http://www.w3school.com.cn/php/php_ref_filesystem.asp
虚拟机原理与实现
How to implement a simple dalvik virtual machine
https://www.slideshare.net/ssusere3af56/how-to-implement-a-simple-dalvik-virtual-machine
register简单虚拟机
http://www.cnblogs.com/unixfy/p/3280264.html
基于栈的虚拟机的实现
http://www.cppblog.com/kevinlynx/archive/2010/04/15/112704.html
栈虚拟机源码剖析
http://www.cnblogs.com/unixfy/p/3335874.html
实现一个堆栈虚拟机
http://www.cnblogs.com/unixfy/p/3337917.html
网络编程
beej's Guide to Network Programming(2016)
UNIX Network Programming(1990) by W Richard Stevens
Design of Unix
https://www.kernel.org/doc/man-pages Michael kerrish维护,网站分为8个部分
利用select/poll监听多个设备详解
http://blog.csdn.net/qq_28090573/article/details/51094321
密码学基础:
密码学算法应用机制
https://www.zybuluo.com/zhongdao/note/950527
一个图文并茂的比特币与其中应用的密码学算法的入门简介文章:
https://www.myblockchainblog.com/blog/blockchain-cryptography
What is a Digital Signature?
http://www.youdzone.com/signature.html
markdown 编辑器
markdown editor:
https://github.com/cloose/CuteMarkEd
cmd markdown editor:
https://www.zybuluo.com/
区块链技术公开课的公众号报道
http://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/GKXUHEHd44mGqH05SgRkBA
http://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/d0hBmFFqxWl995ZbEKqkHw
http://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/qoVkB_xzaoRNAPkaPJWddw
http://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/kF_G9bkefJdbx24wcoJ0IA
http://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/hZi0RFrjMEYCdVsiE95E6w

