@Dmaxiya
2019-01-16T11:14:12.000000Z
字数 7570
阅读 1523
Codeforces Round #532 (Div. 2)
Codeforces
Contests 链接:Codeforces Round #532 (Div. 2)
过题数:3
排名:579/5142
A. Roman and Browser
题意
最开始打开了 个网页,所有网页要么是个测试网页,要么是一个社交网页,现在他打算每隔 个网页就关闭一个网页,要使得这两种网页的差的绝对值最大,求最大值。
输入
第一行为两个整数 ,第二行为 个整数,第 个整数为 表示第 个网页的类型是社交网页,为 表示第 个网页是测试网页。
输出
输出所求答案。
样例
| 输入 |
|---|
| 4 2 1 1 -1 1 |
| 输出 |
| 2 |
| 提示 |
| 可以关闭第 个和第 个网页,这样最后就只剩下测试网页,因此两种网页的个数差的绝对值为 。 |
| 输入 |
|---|
| 14 3 -1 1 -1 -1 1 -1 -1 1 -1 -1 1 -1 -1 1 |
| 输出 |
| 9 |
| 提示 |
| 我们可以关闭所有的社交网页。 |
题解
将所有下标对 取模后,统计两种网页的数量,从 到 枚举取最大值。
过题代码
#include <cstdio>#include <cstdlib>#include <cstring>#include <cmath>#include <cfloat>#include <climits>#include <iostream>#include <string>#include <vector>#include <list>#include <queue>#include <stack>#include <map>#include <set>#include <algorithm>#include <bitset>#include <sstream>using namespace std;#define LL long longconst int maxn = 100 + 100;int n, k;int sum[2];int cnt[maxn][2];int num[maxn];int main() {#ifdef Dmaxiyafreopen("test.txt", "r", stdin);#endif // Dmaxiyaios::sync_with_stdio(false);while(scanf("%d%d", &n, &k) != EOF) {memset(cnt, 0, sizeof(cnt));memset(sum, 0, sizeof(sum));for(int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {scanf("%d", &num[i]);if(num[i] == 1) {++sum[0];++cnt[i % k][0];} else {++sum[1];++cnt[i % k][1];}}int ans = 0;for(int i = 0; i < k; ++i) {ans = max(ans, abs((sum[0] - cnt[i][0]) - (sum[1] - cnt[i][1])));}printf("%d\n", ans);}return 0;}
B. Build a Contest
题意
举办一场比赛需要 道难度不同的题目,每道题目的难度用 到 的数字来表示, 依次出了 题,每当他出一道题,就会把这道题放到题库中,如果题库中所有的题目足够办一场比赛,就会立即选出难度为 到 的题目来举办比赛,并将这些题目从题库中删去。每当 出一道题,问是否会立即举办一场比赛。初始题库为空。
输入
第一行为两个整数 ,第二行为 个整数 ,表示每次出题的难度。
输出
输出一个长度为 的 串,如果出第 道题后会立即举办一场比赛,则第 位为
1,否则为0。
样例
| 输入 |
|---|
| 3 11 2 3 1 2 2 2 3 2 2 3 1 |
| 输出 |
| 00100000001 |
| 输入 |
|---|
| 4 8 4 1 3 3 2 3 3 3 |
| 输出 |
| 00001000 |
题解
统计 到 的所有难度的题目出现的次数 ,以及所有 出现的次数,若 出现的次数达到举办一次比赛的条件,则开始举办一场比赛。
过题代码
#include <cstdio>#include <cstdlib>#include <cstring>#include <cmath>#include <cfloat>#include <climits>#include <iostream>#include <string>#include <vector>#include <list>#include <queue>#include <stack>#include <map>#include <set>#include <algorithm>#include <bitset>#include <sstream>using namespace std;#define LL long longconst int maxn = 100000 + 100;int n, m, x;int cnt[maxn], ccnt[maxn];int main() {#ifdef Dmaxiyafreopen("test.txt", "r", stdin);#endif // Dmaxiyaios::sync_with_stdio(false);while(scanf("%d%d", &n, &m) != EOF) {memset(cnt, 0, sizeof(cnt));memset(ccnt, 0, sizeof(ccnt));ccnt[0] = n;int tmp = 0;for(int i = 1; i <= m; ++i) {scanf("%d", &x);--ccnt[cnt[x]];if(ccnt[tmp] == 0) {printf("1");++tmp;} else {printf("0");}++cnt[x];++ccnt[cnt[x]];}printf("\n");}return 0;}
C. NN and the Optical Illusion
题意
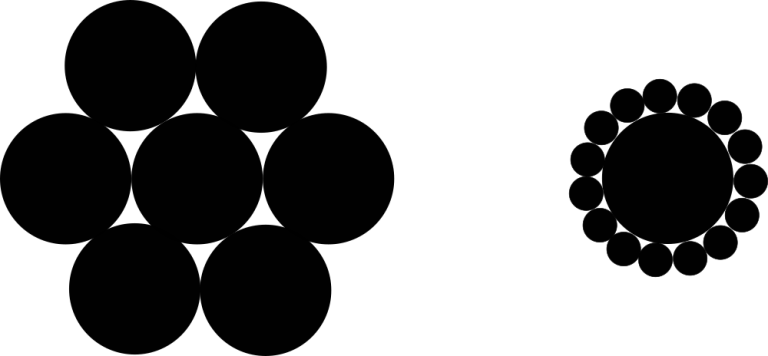
给定中间一个圆的半径 ,要求在圆外有 个圆与其相切,且这 个圆中任意相邻的两个圆也相切,如下图:
输入
输入为两个数字 。
输出
输出一个实数 ,为 个外切圆的半径,误差在 内即认为答案正确。
样例
| 输入 |
|---|
| 3 1 |
| 输出 |
| 6.4641016 |
| 输入 |
|---|
| 6 1 |
| 输出 |
| 1.0000000 |
| 输入 |
|---|
| 100 100 |
| 输出 |
| 3.2429391 |
题解
将 个圆的圆心连线,就可以得到一个正 边形,边长为 ,将多边形上相邻的两个顶点与中心圆心连线,可以得到一个等腰三角形,腰长为 ,顶角为 ,可以由余弦定理得到一个一元二次方程,该方程的其中一个解就是答案。
过题代码
#include <cstdio>#include <cstdlib>#include <cstring>#include <cmath>#include <cfloat>#include <climits>#include <iostream>#include <string>#include <vector>#include <list>#include <queue>#include <stack>#include <map>#include <set>#include <algorithm>#include <bitset>#include <sstream>using namespace std;#define LL long longconst double PI = acos(-1.0);double n, r;int main() {#ifdef Dmaxiyafreopen("test.txt", "r", stdin);#endif // Dmaxiyaios::sync_with_stdio(false);while(scanf("%lf%lf", &n, &r) != EOF) {double theta = 2 * PI / n;double t = 1 - cos(theta);double a = t - 2;double b = 2 * t * r;double c = t * r * r;double ans = (-b - sqrt(b * b - 4 * a * c)) / 2 / a;printf("%.10f\n", ans);}return 0;}
D. Dasha and Chess
题意
在一个大小为 的棋盘上,有 个黑棋,你有一个白棋,所有棋子互不重叠,你和黑棋轮流移动棋子,你每次可以向周围八个方向移动到不与任何一个黑棋重叠的一格,黑棋可以选择任意一个棋子将这个棋子放在任意一个不与其他棋子重叠的位置上,一旦白棋与任何一个黑棋在同一行或同一列,则白棋获胜,如果在 个回合之内白棋没有获胜,则黑棋获胜。
输入
初始输入 行整数,每行两个整数 ,第一行为白棋坐标,接下去 行为黑棋坐标,数据保证初始情况下白棋不会立即获胜。后面的输入,将在每次输出后给出,每次输入三个整数,若输入为 ,表示将第 个黑棋移动到 ,若为 表示白棋获胜,白棋获胜后应立即结束程序,不能有多余的输出。若为 则会返回 。
输出
每次输出一个坐标,表示白棋将移动到的位置,每次移动必须保证合法。
样例
| 输入 |
|---|
| 前 行:https://pastebin.com/qQCTXgKP 1 700 800 2 1 2 <...> -1 -1 -1 |
| 输出 |
| 999 998 999 997 <...> 999 26 |
| 提示 |
| 程序不保证将会按样例中的输入来执行。 |
题解
先将白棋移动到最中间,然后统计此时黑棋的分布,以 为原点,将棋盘分为四个象限,任选三个象限的黑棋个数的总和至少为 个,往这三个象限中间的那个象限的一角移动,最多需要 步,在这个过程中,白棋会扫过这三个象限所有位置,而黑棋最多也只能将 个黑棋移出这三个象限,剩下的一个黑棋必定会被白棋扫到。
过题代码
#include <cstdio>#include <cstdlib>#include <cstring>#include <cmath>#include <cfloat>#include <climits>#include <iostream>#include <string>#include <vector>#include <list>#include <queue>#include <stack>#include <map>#include <set>#include <algorithm>#include <bitset>#include <sstream>using namespace std;#define LL long longconst int maxn = 1000 + 100;struct Node {int x, y;};int k;int cnt[4];Node s, tmp;Node node[maxn];bool vis[maxn][maxn];const int End[4][2] = {999, 999, 999, 1, 1, 999, 1, 1};int sign(int x) {if(x == 0) {return 0;}return x > 0? 1: -1;}int Move(int dx, int dy) {Node t;t.x = s.x + dx;t.y = s.y + dy;if(vis[t.x][t.y]) {printf("%d %d", t.x, s.y);fflush(stdout);return 0;}s = t;printf("%d %d\n", s.x, s.y);fflush(stdout);scanf("%d%d%d", &k, &tmp.x, &tmp.y);if(k == -1) {return 0;}vis[node[k].x][node[k].y] = false;node[k] = tmp;vis[node[k].x][node[k].y] = true;return 1;}int main() {#ifdef Dmaxiyafreopen("test.txt", "r", stdin);#endif // Dmaxiyaios::sync_with_stdio(false);scanf("%d%d", &s.x, &s.y);for(int i = 1; i <= 666; ++i) {scanf("%d%d", &node[i].x, &node[i].y);vis[node[i].x][node[i].y] = true;}while(s.x != 500 || s.y != 500) {int flag = Move(sign(500 - s.x), sign(500 - s.y));if(flag == 0) {return 0;}}for(int i = 1; i <= 999; ++i) {for(int j = 1; j <= 999; ++j) {if(!vis[i][j]) {continue;}++cnt[i / 500 * 2 + j / 500];}}for(int i = 0; i < 4; ++i) {cnt[i] = 666 - cnt[i];if(cnt[i] >= 500) {while(s.x != End[i][0] || s.y != End[i][1]) {int flag = Move(sign(End[i][0] - s.x), sign(End[i][1] - s.y));if(flag == 0) {return 0;}}}}return 0;}
E. Andrew and Taxi
题意
给定一个 个节点 条边的有向图,每条边都有一个权重,要求将其中的一些边反向,使这张图中不存在环,代价为所有被反向的边的权重最大值。要求用最小的代价,使这张图成为一个 ,并输出方案。
输入
第一行为两个整数 ,接下去 行每行三个整数 ,表示第 条边从节点 指向 ,权重为 。
输出
第一行输出两个整数,第一个整数为最小代价,第二个整数 为需要反向的边的数量,第二行为 个整数,每个整数表示需要反向的边的下标。
样例
| 输入 |
|---|
| 5 6 2 1 1 5 2 6 2 3 2 3 4 3 4 5 5 1 5 4 |
| 输出 |
| 2 2 1 3 |
| 输入 |
|---|
| 5 7 2 1 5 3 2 3 1 3 3 2 4 1 4 3 5 5 4 1 1 5 3 |
| 输出 |
| 3 3 3 4 7 |
题解
先二分最小代价,每次二分忽略所有权重小于等于代价的边,判断剩余的边是否存在环。得到最小代价后,对整张图跑一遍得到拓扑序,最后将每条边中,拓扑序大的指向小的边反向,就能得到一张有向无环图。
过题代码
#include <cstdio>#include <cstdlib>#include <cstring>#include <cmath>#include <cfloat>#include <climits>#include <iostream>#include <string>#include <vector>#include <list>#include <queue>#include <stack>#include <map>#include <set>#include <algorithm>#include <bitset>#include <sstream>using namespace std;#define LL long longconst int maxn = 100000 + 100;struct Node {int Index, pos, dis;Node() {}Node(int I, int p, int d) {Index = I;pos = p;dis = d;}};int n, m, u, v, c, ans, cnt;int deg[maxn], num[maxn], Index[maxn], aans[maxn];vector<Node> G[maxn];queue<int> que;bool topsort(int up) {cnt = 0;while(!que.empty()) {int x = que.front();que.pop();num[cnt++] = x;int len = G[x].size();for(int i = 0; i < len; ++i) {if(G[x][i].dis <= up) {continue;}int pos = G[x][i].pos;--deg[pos];if(deg[pos] == 0) {que.push(pos);}}}for(int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) {if(deg[i] != 0) {return false;}}return true;}bool judge(int up) {memset(deg + 1, 0, sizeof(int) * n);for(int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) {int len = G[i].size();for(int j = 0; j < len; ++j) {if(G[i][j].dis <= up) {continue;}++deg[G[i][j].pos];}}for(int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) {if(deg[i] == 0) {que.push(i);}}return topsort(up);}int main() {#ifdef Dmaxiyafreopen("test.txt", "r", stdin);#endif // Dmaxiyaios::sync_with_stdio(false);while(scanf("%d%d", &n, &m) != EOF) {for(int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) {G[i].clear();}for(int i = 1; i <= m; ++i) {scanf("%d%d%d", &u, &v, &c);G[u].push_back(Node(i, v, c));}int high = 1000000000;int low = -1;int mid;while(high - low > 1) {mid = (high + low) >> 1;if(judge(mid)) {high = mid;} else {low = mid;}}ans = high;judge(ans);for(int i = 0; i < cnt; ++i) {Index[num[i]] = i;}cnt = 0;for(int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) {int len = G[i].size();for(int j = 0; j < len; ++j) {int pos = G[i][j].pos;if(Index[pos] < Index[i]) {aans[cnt++] = G[i][j].Index;}}}printf("%d %d\n", ans, cnt);for(int i = 0; i < cnt; ++i) {if(i != 0) {printf(" ");}printf("%d", aans[i]);}printf("\n");}return 0;}