@Dmaxiya
2020-12-12T07:30:42.000000Z
字数 9661
阅读 1355
Codeforces Round #420 (Div. 2)
Codeforces
Contests 链接:Codeforces Round #420 (Div. 2)
过题数:3
排名:1308/9135
A. Okabe and Future Gadget Laboratory
题意
给定一个 的矩阵,如果一个矩阵是好的,那么这个矩阵中所有不等于 的数字 ,等于第 行中的某个数字加上第 列的某个数字的和。判断给出的矩阵是否是一个好的矩阵。
输入
第一行为一个整数 ,接下去 行,每行 个整数,其中第 行第 列的数字 满足 。
输出
如果这个矩阵是好的,则输出 ,否则输出 ,大小写任意。
样例
| 输入 | 输出 | 提示 |
|---|---|---|
| 3 1 1 2 2 3 1 6 4 1 |
Yes | 左下角的数字 是合法的,因为它等于在它上面的 和它右边的 的和,对矩阵中其他不等于 的数字同理,都满足要求,所以这是一个好的矩阵。 |
| 3 1 5 2 1 1 1 1 2 3 |
No | 数字 是非法的,因为它不能等于和它同一行的任何一个数字加上同一列的任何一个数字的和, 所以这个矩阵是不好的矩阵。 |
题解
按照题意判断。
过题代码
#include <iostream>#include <cstdio>#include <cstdlib>#include <cmath>#include <climits>#include <cstring>#include <string>#include <vector>#include <list>#include <queue>#include <stack>#include <map>#include <set>#include <bitset>#include <algorithm>#include <functional>#include <iomanip>using namespace std;typedef long long LL;const int maxn = 100;int n;int num[maxn][maxn];bool judge(int x, int y) {for(int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) {for(int j = 1; j <= n; ++j) {if(num[x][j] + num[i][y] == num[x][y]) {return true;}}}return false;}int main() {#ifdef Dmaxiyafreopen("test.txt", "r", stdin);// freopen("test1.out", "w", stdout);#endif // Dmaxiyaios::sync_with_stdio(false);while(scanf("%d", &n) != EOF) {for(int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) {for(int j = 1; j <= n; ++j) {scanf("%d", &num[i][j]);}}bool flag = true;for(int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) {for(int j = 1; j <= n; ++j) {if(num[i][j] != 1 && !judge(i, j)) {flag = false;}}}if(flag) {printf("Yes\n");} else {printf("No\n");}}return 0;}
B. Okabe and Banana Trees
题意
用平面直角坐标系表示一个雨林,在这个雨林里的每个非负整数坐标点 处,都有一棵香蕉树,上面有 个香蕉,现在 打算在直线 下框定一个矩形,在这个矩形内采集香蕉,他每次选矩形,先在 轴上选择一个长度 ,然后做直线 ,过与斜线的交点做 轴的垂线 ,在范围 内采集所有的香蕉。注意这个矩形可以是退化的,它可以是一条线甚至一个点。
输入
第一行为两个整数 和 ,数据保证答案不超过 。
输出
输出 能采集的所有香蕉数量。
样例
| 输入 | 输出 | 提示 |
|---|---|---|
| 1 5 | 30 | 最优的选择香蕉范围如下: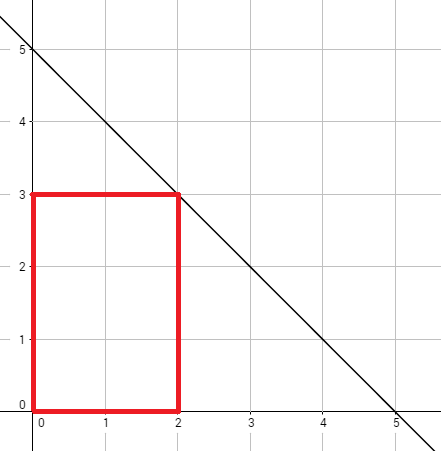 |
| 2 3 | 25 |
题解
的最大值为 ,枚举 很可能超时,可以通过枚举 来计算获得香蕉的最大数量,对于每一个矩形 ,计算收获的香蕉数量,就是对 方向做 ,且每一行应该被计算 次,在 方向上的计算同理。
过题代码
#include <iostream>#include <cstdio>#include <cstdlib>#include <cmath>#include <climits>#include <cstring>#include <string>#include <vector>#include <list>#include <queue>#include <stack>#include <map>#include <set>#include <bitset>#include <algorithm>#include <functional>#include <iomanip>using namespace std;typedef long long LL;LL m, b, ans;int main() {#ifdef Dmaxiyafreopen("test.txt", "r", stdin);// freopen("test1.out", "w", stdout);#endif // Dmaxiyaios::sync_with_stdio(false);while(scanf("%I64d%I64d", &m, &b) != EOF) {ans = 0;for(LL y = 0; y <= b; ++y) {LL x = (b - y) * m;ans = max(ans, (1 + x) * x / 2 * (y + 1) + (1 + y) * y / 2 * (x + 1));}printf("%I64d\n", ans);}return 0;}
C. Okabe and Boxes
题意
在指挥 将 箱子搬来搬去, 要做的事情只有两种:一种是将编号为 的箱子累到顶部,一种是将顶部的箱子取下来。 是一个控制狂,他想让 每次从顶部取下来的箱子都要按照 的顺序,当然如果累箱子的顺序是任意的, 就无法正确地完成任务,所以 就趁 休息的时候(两次发布任务的间隙)调整箱子的顺序,问 最少需要调整多少次就能完成 的任务?
输入
第一行为一个整数 ,表示箱子的数量,接下去 行为 的命令,每条命令要么是 "add x",表示将编号为 的箱子累到顶部,要么是 "remove",表示要将顶部的箱子搬下来,数据保证每个 都不相等,且在第 条 "remove" 命令之前,箱子 一定出现在之前的 "add x" 命令中。
输出
输出 需要调整的最少的次数。
样例
| 输入 | 输出 | 提示 |
|---|---|---|
| 3 add 1 remove add 2 add 3 remove remove |
1 | 应该在 "add 3" 的命令后调整所有箱子的位置。 |
| 7 add 3 add 2 add 1 remove add 4 remove remove remove add 6 add 7 add 5 remove remove remove |
2 | 应该在 "add 4" 和 "add 7" 的命令之后调整箱子的位置。 |
题解
可以用一个栈来模拟这个过程,为了让调整的次数最少,就是在每次 "remove" 的时候检查栈顶元素是否符合要求,实际上不必对栈内所有元素进行排序,只要“假设”对栈内的元素排序即可,当每次需要对栈内元素进行调整时,如果栈顶元素不符合要求,就清空栈,表示对栈内元素进行调整,这样“栈为空”就表示栈内元素已经被调整过,一定是符合要求的。
过题代码
#include <iostream>#include <cstdio>#include <cstdlib>#include <cmath>#include <climits>#include <cstring>#include <string>#include <vector>#include <list>#include <queue>#include <stack>#include <map>#include <set>#include <bitset>#include <algorithm>#include <functional>#include <iomanip>using namespace std;typedef long long LL;const int maxn = 300000 + 100;int n, top, x, ans, num;int sta[maxn];char command[20];int main() {#ifdef Dmaxiyafreopen("test.txt", "r", stdin);// freopen("test1.out", "w", stdout);#endif // Dmaxiyaios::sync_with_stdio(false);while(scanf("%d", &n) != EOF) {ans = top = num = 0;for(int i = 0; i < n * 2; ++i) {scanf("%s", command);if(command[0] == 'a') {scanf("%d", &x);sta[top++] = x;} else {++num;if(top != 0) {if(sta[top - 1] != num) {++ans;top = 0;} else {--top;}}}}printf("%d\n", ans);}return 0;}
D. Okabe and City
题意
在一个 的网格街道上,有一些路口有路灯,而其他的路口则没有路灯。 最开始在左上角的路口,他想要到达右下角的 路口,他每次只能从一个路口移动到相邻的路口。为了安全,他只能走在有灯的地方,如果有些地方没有灯,他可以每次可以花 元钱照亮任意一整条街道(照亮任意一行或者任意一列的所有路口),他只能站在本来就是亮着的路口付钱,并且当他离开那条被他照亮的街道时,那条街道就会立即变暗,问他最少要付多少钱才能到达路口 。
输入
第一行为三个整数 ,接下去 行每行两个整数 。数据保证所有的 都不相同,且一定包含 。
输出
如果他不可能到达路口 ,就输出 ,否则输出他需要付的最少的费用。
样例
| 输入 | 输出 | 提示 |
|---|---|---|
| 4 4 5 1 1 2 1 2 3 3 3 4 3 |
2 | 他可以经过 , 这样他只需要在 和 两条路上点亮街道。 |
| 5 5 4 1 1 2 1 3 1 3 2 |
-1 | |
| 2 2 4 1 1 1 2 2 1 2 2 |
0 | |
| 5 5 4 1 1 2 2 3 3 4 4 |
3 | 他可以经过 ,这样他只需要在 、 和 三条道路上点亮街道。 |
题解
这题可以这样计算花费:如果两个点相邻,他们之间的花费就为 ,如果两个点的水平/竖直距离在 以内, 就可以通过照亮一条街道到达另一个点,这时候它们之间的花费就为 。注意如果点 没有路灯,就假设点 为终点且这一点是亮着的。在这样的图上跑一遍最短路就能得到答案。
过题代码
#include <iostream>#include <cstdio>#include <cstdlib>#include <cmath>#include <climits>#include <cstring>#include <string>#include <vector>#include <list>#include <queue>#include <stack>#include <map>#include <set>#include <bitset>#include <algorithm>#include <functional>#include <iomanip>using namespace std;typedef long long LL;const int maxn = 10000 + 100;const int INF = 100000000;struct Node {int x, y;int dis;Node() {}Node(int xx, int yy, int d) {x = xx;y = yy;dis = d;}};bool operator==(const Node &a, const Node &b) {return a.x == b.x && a.y == b.y;}bool operator<(const Node &a, const Node &b) {return a.dis > b.dis;}int n, m, k, Begin, End;Node node[maxn];priority_queue<Node> que;int dij() {while(!que.empty()) {que.pop();}node[Begin].dis = 0;que.push(node[Begin]);while(!que.empty()) {Node tmp = que.top();que.pop();if(tmp == node[End]) {return tmp.dis;}for(int i = 1; i <= k; ++i) {int dx = abs(node[i].x - tmp.x);int dy = abs(node[i].y - tmp.y);int d = INF;if(dx + dy == 1) {d = 0;} else if(dx <= 2 || dy <= 2) {d = 1;}if(d + tmp.dis < node[i].dis) {node[i].dis = d + tmp.dis;que.push(node[i]);}}}return -1;}int main() {#ifdef Dmaxiyafreopen("test.txt", "r", stdin);// freopen("test1.out", "w", stdout);#endif // Dmaxiyaios::sync_with_stdio(false);while(scanf("%d%d%d", &n, &m, &k) != EOF) {End = 0;for(int i = 1; i <= k; ++i) {node[i].dis = INF;scanf("%d%d", &node[i].x, &node[i].y);if(node[i].x == 1 && node[i].y == 1) {Begin = i;}if(node[i].x == n && node[i].y == m) {End = i;}}if(End == 0) {++n;++m;++k;node[k].x = n;node[k].y = m;node[k].dis = INF;End = k;}printf("%d\n", dij());}return 0;}
E. Okabe and El Psy Kongroo
题意
想要在一个平面直角坐标系表示的地图上从 走到 ,当他处在 时,他可以走到 ,他想知道如果在躲避所有的监视的情况下从起点走到终点,总共有多少种走法。
为了躲避监视,他必须走在 条平行于 轴的线段下方,这些线段用三个整数表示:, 分别表示线段的起点和终点, 且对于所有的 ,。输出所有可能的路线的方案数对 取模后的结果。
输入
第一行包含两个整数 和 ,接下去 行每行三个整数 ,数据保证满足题给条件。
输出
输出所有合法的方案数对 取模后的结果。
样例
| 输入 | 输出 | 提示 |
|---|---|---|
| 1 3 0 3 3 |
4 | 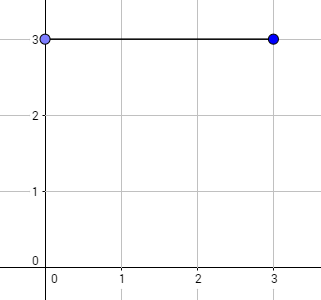 四种可能的走法是: |
| 2 6 0 3 0 3 10 2 |
4 |  四种可能的走法是: |
题解
如果不考虑数据范围,这题就是一个 。
从走路的方式很容易看出,如果设走到坐标 的走法为 ,则:
其中任何一项的纵坐标超过 ,其值都为 。由于 的范围是 ,这题可以将每一个横坐标对应的所有点看作是一个状态,那么对于每一段(注意这里每一段对应的都是不同的矩阵)的状态转移方程就是:
可以得出矩阵:
于是走 步就相当于将这个矩阵的 次幂乘上 的初始值,所以 就可以用矩阵快速幂求得。
最后两个细节上的问题,一个是在两段的分界线上, 值不同应当将两个 值中最小的那个 值以上的所有状态都设为 。另一个是算法的时间复杂度,显然被分的段数越多, 的取值范围越大,算法的时间复杂度也越高,整体的时间复杂度大概为 ,庆幸 才 , 也只在 左右。
过题代码
#include <iostream>#include <cstdio>#include <cstdlib>#include <cmath>#include <sstream>#include <cstring>#include <string>#include <vector>#include <list>#include <queue>#include <stack>#include <map>#include <set>#include <algorithm>using namespace std;#define LL long longconst int maxn = 16;const LL MOD = 1000000007;struct Matrix {int Size;LL num[maxn][maxn];Matrix() {}Matrix(int s) {Size = s;}void Init() {for(int i = 0; i < Size; ++i) {for(int j = 0; j < Size; ++j) {if(i == j) {num[i][j] = 1;} else {num[i][j] = 0;}}}}void Set(int s) {Size = s;memset(num, 0, sizeof(num));for(int i = 0; i < Size; ++i) {for(int j = i - 1; j <= i + 1; ++j) {if(j >= 0 && j < Size) {num[i][j] = 1;}}}}const Matrix& operator*=(const Matrix &m) {Matrix ans(Size);for(int i = 0; i < Size; ++i) {for(int j = 0; j < Size; ++j) {ans.num[i][j] = 0;for(int k = 0; k < Size; ++k) {ans.num[i][j] = (ans.num[i][j] + num[i][k] * m.num[k][j] % MOD) % MOD;}}}memcpy(num, ans.num, sizeof(ans.num));return (*this);}void Pow(LL n) {Matrix ans(Size);for(ans.Init(); n != 0; n >>= 1) {if((n & 1) == 1) {ans *= (*this);}(*this) *= (*this);}memcpy(num, ans.num, sizeof(num));}};LL N, K, a, b, c, Ans[2][maxn], now;Matrix tmp;void setZero(LL *num, int n) {for(int i = n + 1; i < maxn; ++i) {num[i] = 0;}}int main() {#ifdef Dmaxiyafreopen("test.txt", "r", stdin);#endif // Dmaxiyaios::sync_with_stdio(false);while(scanf("%I64d%I64d", &N, &K) != EOF) {now = 0;Ans[now][0] = 1;while(N--) {scanf("%I64d%I64d%I64d", &a, &b, &c);if(a < K) {if(b > K) {b = K;}setZero(Ans[now], c);tmp.Set(c + 1);tmp.Pow(b - a);for(int i = 0; i <= c; ++i) {Ans[!now][i] = 0;for(int j = 0; j <= c; ++j) {Ans[!now][i] = (Ans[!now][i] + tmp.num[i][j] * Ans[now][j] % MOD) % MOD;}}now = !now;setZero(Ans[now], c);}}printf("%I64d\n", Ans[now][0]);}return 0;}
