@Dmaxiya
2018-08-17T02:16:19.000000Z
字数 4439
阅读 1516
Codeforces Round #472 (Div. 1)
Codeforces
Contests 链接:Codeforces Round #472 (Div. 1)
过题数:3
排名:253/1066
A. Mystical Mosaic
题意
最初有一个 的网格,每个方格的颜色最初都是白色的,每次操作可以选择一些行与一些列,将这些行和列的交点上的方格都涂上黑色,每一个行与列在所有操作中只能被选择一次,给定最终的网格,问能否通过有限次合法的操作得到最终网格。
输入
第一行包括两个整数 ,接下去 行每行为一个长度为 的字符串,字符串只包含
.和#,.表示最终该方格颜色为白色,#表示最终该方格为黑色。
输出
如果可以通过有限次合法的操作得到最终的网格,就输出 ,否则输出 ,大小写任意。
样例
| 输入 |
|---|
5 8.#.#..#......#...#.#..#.#.#....#.....#.. |
| 输出 |
| Yes |
| 提示 |
该网格可以通过以下三次操作得到: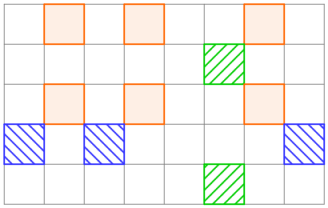 |
| 输入 |
|---|
5 5..#....#..#####..#....#.. |
| 输出 |
| No |
| 提示 |
| 为了得到中间的一行,第一次操作必须选择第 行与所有列,这样其它列在后面的操作中就无法再被选择,因此其他行的黑色方块就无法被涂上黑色。 |
| 输入 |
|---|
5 9........##..........##.#..........#.....#.#.# |
| 输出 |
| No |
题解
可以发现,在一次操作中,所有被操作行得到的字符串都是完全相同的,因此我们可以将所有字符串都放入到一个 中,在已经被去重的所有字符串中,同一列只能出现最多一个黑色方格,如果出现多于 个的黑色网格,则说明两次操作选择了同一列。
过题代码
#include <iostream>#include <cstdio>#include <cstdlib>#include <cmath>#include <climits>#include <cstring>#include <string>#include <vector>#include <list>#include <queue>#include <stack>#include <map>#include <set>#include <bitset>#include <algorithm>#include <functional>#include <iomanip>using namespace std;#define LL long longconst int maxn = 100;int n, m;string str[maxn];string tmp;set<string> st;set<string>::iterator it;int cnt[maxn];int main() {#ifdef LOCALfreopen("test.txt", "r", stdin);// freopen("test1.out", "w", stdout);#endif // LOCALios::sync_with_stdio(false);while(cin >> n >> m) {st.clear();memset(cnt, 0, sizeof(cnt));for(int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {cin >> str[i];st.insert(str[i]);}for(it = st.begin(); it != st.end(); ++it) {tmp = *it;int len = tmp.length();for(int i = 0; i < len; ++i) {if(tmp[i] == '#') {++cnt[i];}}}bool flag = true;for(int i = 0; i < m; ++i) {if(cnt[i] > 1) {flag = false;break;}}if(flag) {cout << "Yes\n";} else {cout << "No\n";}}return 0;}
B. Three-level Laser
题意
一个原子的电子可以处在 个不同的能级 上,若某个电子的基态能级为 ,每当电子吸收 的能量后,电子将跃迁到能级 ,接着电子将跃迁到一个低于 的能级 并释放出能量为 的光子,最后回到基态 并损失 的能量,跃迁过程中必然有 。由于某些限制,电子吸收的能量不能超过 ,设能量的利用率为 ,问在所有情况下,最大的能量利用率。
输入
第一行包含两个整数 ,第二行包含 个整数 。
输出
如果无法找到 个合法的能级提供跃迁,则输出 ,否则输出可能的最大能量利用率 ,误差在 内均认为答案正确。
样例
| 输入 |
|---|
| 4 4 1 3 5 7 |
| 输出 |
| 0.5 |
| 提示 |
| 选择 分别为 ,则能量利用率为 。 |
| 输入 |
|---|
| 10 8 10 13 15 16 17 19 20 22 24 25 |
| 输出 |
| 0.875 |
| 提示 |
| 选择能级 ,能量利用率为 |
| 输入 |
|---|
| 3 1 2 5 10 |
| 输出 |
| -1 |
题解
对于每一个能级 ,找到最大的能跃迁到的能级 ,并选择 ,这样就能得到最大的能量利用率,如果所有的 到 之间不存在可以跃迁的能级,则输出 。
过题代码
#include <iostream>#include <cstdio>#include <cstdlib>#include <cmath>#include <climits>#include <cstring>#include <string>#include <vector>#include <list>#include <queue>#include <stack>#include <map>#include <set>#include <bitset>#include <algorithm>#include <functional>#include <iomanip>using namespace std;#define LL long longconst int maxn = 100000 + 100;int n, U;int num[maxn];int *it;double ans;int main() {#ifdef LOCALfreopen("test.txt", "r", stdin);// freopen("test1.out", "w", stdout);#endif // LOCALios::sync_with_stdio(false);while(scanf("%d%d", &n, &U) != EOF) {ans = 0;for(int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {scanf("%d", &num[i]);}bool flag = false;for(int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {it = upper_bound(num, num + n, num[i] + U);if(it - (num + i) >= 3) {flag = true;--it;ans = max(ans, (double)(*it - num[i + 1]) / (*it - num[i]));}}if(flag) {printf("%.10f\n", ans);} else {printf("-1\n");}}return 0;}
C. Riverside Curio
题意
打算观察一条河的水位 天,每天他都在水平面处做一个标记,水的涨落不会将之前的标记冲走,每天他都会记录下严格在水平面上方的标记数量 ,如果记严格在水平面下方的标记数为 ,求 的最小值。
输入
第一行为一个整数 ,第二行为 个整数 。
输出
输出最小的 的值。
样例
| 输入 |
|---|
| 6 0 1 0 3 0 2 |
| 输出 |
| 6 |
| 提示 |
最优的水平面的涨落情况如下: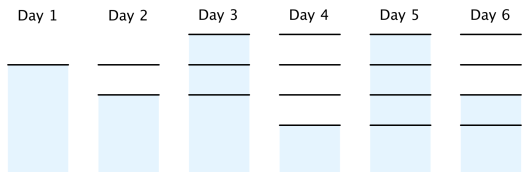 注意第 天必须要打上 个新的标记,否则无法保证第 天在水平面上方出现 个标记。 |
| 输入 |
|---|
| 5 0 1 2 1 2 |
| 输出 |
| 1 |
| 提示 |
最优的水平面的涨落情况如下: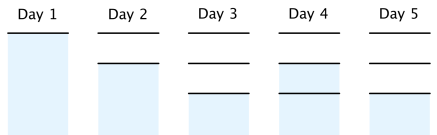 |
| 输入 |
|---|
| 5 0 1 1 2 2 |
| 输出 |
| 0 |
题解
首先找到最大的 ,在这一天之后不再生成新的标记,这样可以使得在这一天之后的 的值最小,这一天之后的 的和为 ,在这一天之前,只要计算出每一天最少的标记数即可,我们从第 天往前枚举 ,设总的标记数为 ,如果在第 天之前的最大值小于 ,那么第 天的标记就可以认为是新画上的,将 减一,继续往前枚举,每天在水平面下方的标记数为 。
过题代码
#include <iostream>#include <cstdio>#include <cstdlib>#include <cmath>#include <climits>#include <cstring>#include <string>#include <vector>#include <list>#include <queue>#include <stack>#include <map>#include <set>#include <bitset>#include <algorithm>#include <functional>#include <iomanip>using namespace std;#define LL long longconst int maxn = 100000 + 100;int n, tot;LL ans;int num[maxn], Max[maxn];int main() {#ifdef LOCALfreopen("test.txt", "r", stdin);// freopen("test1.out", "w", stdout);#endif // LOCALios::sync_with_stdio(false);while(scanf("%d", &n) != EOF) {ans = 0;tot = 0;int Index = 1;for(int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) {scanf("%d", &num[i]);if(num[i] > num[Index]) {Index = i;}}tot = num[Index];Max[0] = 0;for(int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) {Max[i] = max(Max[i - 1], num[i]);}for(int i = Index + 1; i <= n; ++i) {ans += num[Index] - num[i];}for(int i = Index; i >= 1; --i) {ans += tot - num[i];if(Max[i - 1] < tot) {--tot;}}printf("%I64d\n", ans);}return 0;}
