@Dmaxiya
2018-08-17T02:25:50.000000Z
字数 6881
阅读 1394
Codeforces Round #416 (Div. 2)
Codeforces
Contests 链接:Codeforces Round #416 (Div. 2)
过题数:2
排名:1199/10439
A. Vladik and Courtesy
题意
和 分别有 个糖果, 先给 个糖果, 再给 个糖果 ,以此类推,直到 某一个人无法给出正确数量的糖果为止,他们都不会给出自己所收到的糖果。问谁会是第一个无法给出正确数量的糖果。
输入
输入包含两个整数 。
输出
输出第一个无法给出正确数量糖果的人。
样例
| 输入 | 输出 | 提示 |
|---|---|---|
| 1 1 | Valera | 每次糖果数量变化如图: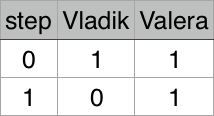 |
| 7 6 | Vladik | 每次糖果数量变化如图: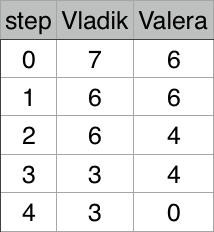 |
题解
由于 ,所以给出的糖果数量的和是平方增长的,所以可以直接按题意模拟,最多只要模拟到 次左右就可以得到结果。
过题代码
#include <iostream>#include <cstdio>#include <cstdlib>#include <cmath>#include <climits>#include <cstring>#include <string>#include <vector>#include <list>#include <queue>#include <stack>#include <map>#include <set>#include <bitset>#include <algorithm>#include <functional>#include <iomanip>using namespace std;#define LL long longint a[10];int main() {#ifdef LOCALfreopen("test.txt", "r", stdin);// freopen("out.txt", "w", stdout);#endif // LOCALios::sync_with_stdio(false);while(scanf("%d%d", &a[0], &a[1]) != EOF) {int who = 0;for(int i = 1; i < 100000; ++i) {if(a[who] < i) {break;} else {a[who] -= i;who = 1 - who;}}if(who == 0) {printf("Vladik\n");} else {printf("Valera\n");}}return 0;}
B. Vladik and Complicated Book
题意
给定一个 的排列,有 次操作,每次操作将区间 上的数字进行从小到大排序,问第 个数字排序前后是否在原位,每次操作结束后都将序列还原成初始状态。
输入
第一行有两个整数 ,第二行有 个整数,为 的排列,接下去 行,每行三个整数 ,表示对区间 上的数字进行排序后,询问第 个数字的位置是否在原位。
输出
对于每次询问,如果第 个数字的位置在原位,则输出 ,否则输出 。
样例
| 输入 | 输出 | 提示 |
|---|---|---|
| 5 5 5 4 3 2 1 1 5 3 1 3 1 2 4 3 4 4 4 2 5 3 |
Yes No Yes Yes No |
对于每次排序的结果: 1 2 3 4 5(第 个数字在原位) 3 4 5 2 1(第 个数字不在原位) 5 2 3 4 1(第 个数字在原位) 5 4 3 2 1(第 个数字在原位) 5 1 2 3 4(第 个数字不在原位) |
| 6 5 1 4 3 2 5 6 2 4 3 1 6 2 4 5 4 1 3 3 2 6 3 |
Yes No Yes No Yes |
题解
对于每次询问,判断第 个数字是否恰好比区间 内的 个数字大,如果是,说明排序前后 的位置不变,否则输出 。
过题代码
#include <iostream>#include <cstdio>#include <cstdlib>#include <cmath>#include <climits>#include <cstring>#include <string>#include <vector>#include <list>#include <queue>#include <stack>#include <map>#include <set>#include <bitset>#include <algorithm>#include <functional>#include <iomanip>using namespace std;#define LL long longconst int maxn = 10000 + 100;int n, m, l, r, x;int num[maxn];int main() {#ifdef LOCALfreopen("test.txt", "r", stdin);// freopen("out.txt", "w", stdout);#endif // LOCALios::sync_with_stdio(false);while(scanf("%d%d", &n, &m) != EOF) {for(int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) {scanf("%d", &num[i]);}for(int i = 0; i < m; ++i) {scanf("%d%d%d", &l, &r, &x);int cnt = 0;for(int j = l; j <= r; ++j) {if(num[j] < num[x]) {++cnt;}}if(l + cnt == x) {printf("Yes\n");} else {printf("No\n");}}}return 0;}
C. Vladik and Memorable Trip
题意
有 个人在火车站排队,每个人都有自己的目的地 ,列车长想要将这些乘客分到不同的车厢,他必须选择队列中连续的一段,让这些人进入到同一个车厢,如果想去城市 的人进入了一个车厢,那么队列中所有想去城市 的人都必须和那个人在同一个车厢内。同一个车厢内乘客的舒适度等于车厢内所有不同目的地的异或值,整列火车的舒适度等于每一节车厢的舒适度的和。
现在列车长想要找到一种能使整列火车舒适度最高的分配车厢的方案,注意他不必让所有人都上车。
输入
第一行为一个整数 ,第二行有 个整数 ,表示 位乘客想去的目的地编号,以及排队的顺序(从 到 )。
输出
输出最大的舒适度。
样例
| 输入 | 输出 | 提示 |
|---|---|---|
| 6 4 4 2 5 2 3 |
14 | 最优的选择为 ,舒适度为 |
| 9 5 1 3 1 5 2 4 2 5 |
9 | 最优的选择为 ,舒适度为 |
题解
首先 处理出所有合法的区间,对于每个终点 ,找到对应合法区间的起点 以及区间异或值 ,如果终点 不是一个合法区间的终点,则将 设为 ,接着从前往后 ,设 表示以 为结尾的序列的最大的舒适度,于是有下面的递推式:
过题代码
#include <iostream>#include <cstdio>#include <cstdlib>#include <cmath>#include <climits>#include <cstring>#include <string>#include <vector>#include <list>#include <queue>#include <stack>#include <map>#include <set>#include <bitset>#include <algorithm>#include <functional>#include <iomanip>using namespace std;typedef long long LL;const int maxn = 5000 + 100;int n;int num[maxn];int Begin[maxn], cnt[maxn], cnttmp[maxn], Xor[maxn], dp[maxn];bool vis[maxn];void Init(int Index) {int ccnt = 0;Xor[Index] = 0;memset(vis, 0, sizeof(vis));memcpy(cnttmp, cnt, sizeof(cnt));for(int i = Index; i > 0; --i) {if(!vis[num[i]]) {Xor[Index] ^= num[i];vis[num[i]] = true;++ccnt;}--cnttmp[num[i]];if(cnttmp[num[i]] == 0) {--ccnt;}if(ccnt == 0) {Begin[Index] = i;return ;}}}int main() {#ifdef Dmaxiyafreopen("test.txt", "r", stdin);// freopen("test1.out", "w", stdout);#endif // Dmaxiyaios::sync_with_stdio(false);while(scanf("%d", &n) != EOF) {memset(cnt, 0, sizeof(cnt));memset(Begin, 0, sizeof(Begin));for(int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) {scanf("%d", &num[i]);++cnt[num[i]];}for(int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) {Init(i);}for(int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) {if(Begin[i] != 0) {dp[i] = max(dp[i - 1], dp[Begin[i] - 1] + Xor[i]);} else {dp[i] = dp[i - 1];}}printf("%d\n", dp[n]);}return 0;}
D. Vladik and Favorite Game
题意
很喜欢玩一个游戏,这个游戏是在一个 的迷宫里从初始位置 走到终点,迷宫用一字符表示,所有字符只包含:
'.':一般的位置,玩家可以站在这里,数据保证 为'.';'F':终点,数据保证只有一个终点,且一定存在一条从 到'F'的路线;'*':危险的位置,如果玩家走到这里,则游戏失败。现在玩家可以按下
'U','D','L','R'四个按钮,每按下一个按钮,都将会返回一个坐标,如果走向的方向是边界,则玩家的坐标不会改变,如果走向的方向是安全的,则会返回这个坐标,如果走向的方向是一个'*',则会返回 ,游戏立即结束。
有趣的是,在这个游戏中,上下和左右两个相对的方向可能会被颠倒,如果玩家输入'U'可能会返回一个往下走的坐标,现在玩家要在 步内到达终点,请输出玩家的移动步骤。
输入
初始输入第一行包含两个整数 ,接下去 行每行 个字符,字符只包含
'.'、'*'、'F'。后续输出将根据玩家的输入决定。
输出
每次输出
'U','D','L','R'四个字符中的一个占一行,表示要按下的按钮,每输出一行应及时清空输出缓冲区。
样例
| 输入 | 输出 |
|---|---|
4 3...**.F*....1 1 1 2 1 3 1 3 2 3 3 3 4 3 4 2 4 1 3 1 |
R L L D U U U R R D |
题解
先对给出的图进行一遍 找到最短路径,然后在第一个安全的地方( 以及路径中的第一个转折点)确定上下、左右是否被颠倒,第一次确认之后,就不必再进行确认,直接交换上下、左右的两个字符即可,后面的直接按照最短路径输出。
过题代码
#include <iostream>#include <cstdio>#include <cstdlib>#include <cmath>#include <climits>#include <cstring>#include <string>#include <vector>#include <list>#include <queue>#include <stack>#include <map>#include <set>#include <bitset>#include <algorithm>#include <functional>#include <iomanip>using namespace std;typedef long long LL;const int maxn = 200;struct Node {int x, y;Node() {}Node(int xx, int yy) {x = xx;y = yy;}};bool operator<(const Node &a, const Node &b) {return (a.x == b.x? a.y < b.y: a.x < b.x);}bool operator==(const Node &a, const Node &b) {return a.x == b.x && a.y == b.y;}Node operator+(const Node &a, const Node &b) {return Node(a.x + b.x, a.y + b.y);}Node operator-(const Node &a, const Node &b) {return Node(a.x - b.x, a.y - b.y);}Node s, f;bool flag[2];int n, m, top;queue<Node> que;map<Node, int> mp;int ans[maxn * maxn];char str[maxn][maxn];bool vis[maxn][maxn];Node pos[maxn * maxn];char dstr[5] = "UDLR";Node pre[maxn][maxn], sta[maxn * maxn];Node dir[4] = {Node(-1, 0), Node(1, 0), Node(0, -1), Node(0, 1)};bool in(const Node &node) {return node.x > 0 && node.x <= n && node.y > 0 && node.y <= m;}void bfs() {memset(vis, 0, sizeof(vis));que.push(s);vis[1][1] = true;while(!que.empty()) {Node tmp = que.front();que.pop();if(tmp == f) {return ;}for(int i = 0; i < 4; ++i) {Node ntmp = tmp + dir[i];if(in(ntmp) && !vis[ntmp.x][ntmp.y] && str[ntmp.x][ntmp.y] != '*') {que.push(ntmp);vis[ntmp.x][ntmp.y] = true;pre[ntmp.x][ntmp.y] = tmp;}}}}int main() {#ifdef Dmaxiya// freopen("test.txt", "r", stdin);// freopen("test1.out", "w", stdout);#endif // Dmaxiyaios::sync_with_stdio(false);s = Node(1, 1);for(int i = 0; i < 4; ++i) {mp[dir[i]] = i;}scanf("%d%d", &n, &m);top = 0;memset(flag, 0, sizeof(flag));for(int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) {scanf("%s", str[i] + 1);for(int j = 1; j <= m; ++j) {if(str[i][j] == 'F') {f = Node(i, j);}}}bfs();while(!(f == s)) {Node ntmp = f;f = pre[ntmp.x][ntmp.y];sta[top++] = ntmp - f;}for(int i = top - 1; i >= 0; --i) {ans[i] = mp[sta[i]];}pos[top] = s;for(int i = top - 1; i >= 0; --i) {printf("%c\n", dstr[ans[i]]);fflush(stdout);scanf("%d %d", &pos[i].x, &pos[i].y);if(!flag[ans[i] >> 1]) {flag[ans[i] >> 1] = true;if(pos[i] == pos[i + 1]) {swap(dstr[ans[i]], dstr[ans[i] ^ 1]);printf("%c\n", dstr[ans[i]]);fflush(stdout);scanf("%d %d", &pos[i].x, &pos[i].y);}}}return 0;}
