@Dmaxiya
2020-12-12T07:19:20.000000Z
字数 6906
阅读 1391
Educational Codeforces Round 48
Codeforces
Contests 链接:Educational Codeforces Round 48
过题数:4
排名:269/7643
A. Death Note
题意
有一本死亡笔记,这本死亡笔记有无穷多页,每一页能够写下 行名字,死亡笔记要求从第 天到第 天,每天都要在笔记本上写下 行名字,死亡笔记只有在写到最后一行的时候才会翻页,问第 天会翻多少页。
输入
第一行包含两个整数 ,第二行为 个整数 。
输出
输出 个整数 , 表示第 天翻页的次数。
样例
| 输入 | 输出 | 提示 |
|---|---|---|
| 3 5 3 7 9 |
0 2 1 | 死亡笔记上每一页的名字为:, 每一个中括号的内容是每一页的名字,其中的数字 表示第 天需要写下的名字。 |
| 4 20 10 9 19 2 |
0 0 1 1 | |
| 1 100 99 |
0 |
题解
记录写的行数,按照题意模拟。
过题代码
#include <iostream>#include <cstdio>#include <cstdlib>#include <cmath>#include <climits>#include <cstring>#include <string>#include <vector>#include <list>#include <queue>#include <stack>#include <map>#include <set>#include <bitset>#include <algorithm>#include <functional>#include <iomanip>using namespace std;#define LL long longLL n, m, now, cnt, page;int main() {#ifdef Dmaxiyafreopen("test.txt", "r", stdin);// freopen("out.txt", "w", stdout);#endif // Dmaxiyaios::sync_with_stdio(false);while(scanf("%I64d%I64d", &n, &m) != EOF) {now = 0;for(int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) {if(i != 1) {printf(" ");}scanf("%I64d", &page);if(page >= m - now) {page -= m - now;printf("%I64d", page / m + 1);now = page % m;} else {now += page;printf("0");}}printf("\n");}return 0;}
B. Segment Occurrences
题意
给定两个字符串:长度为 的 串和长度为 的 串,有 次询问,每次询问一个区间 ,表示询问在 串的 子串内, 字符串在这个子串内出现的次数,下标从 开始。
输入
第一行包含 个整数 ,第二行为一个长度为 的字符串 ,第三行为一个长度为 的字符串 ,字符串 和 都只包含小写字母,接下去 行每行两个整数 。
输出
对于每次询问都输出一个答案。
样例
| 输入 | 输出 | 提示 |
|---|---|---|
| 10 3 4 codeforces for 1 3 3 10 5 6 5 7 |
0 1 0 1 |
三次询问的子串分别为 "cod", "deforces", "fo" 和 "for"。 |
| 15 2 3 abacabadabacaba ba 1 15 3 4 2 14 |
4 0 3 |
|
| 3 5 2 aaa baaab 1 3 1 1 |
0 0 |
题解
预处理所有区间 内的答案, 输出。
过题代码
#include <iostream>#include <cstdio>#include <cstdlib>#include <cmath>#include <climits>#include <cstring>#include <string>#include <vector>#include <list>#include <queue>#include <stack>#include <map>#include <set>#include <bitset>#include <algorithm>#include <functional>#include <iomanip>using namespace std;#define LL long longconst int maxn = 1000 + 100;int n, m, q, l, r;int ans[maxn][maxn];int Next[maxn];char str1[maxn], str2[maxn];void get_next(char *s) {Next[1] = 0;int j = 0;for(int i = 2; s[i]; ++i) {while(j > 0 && s[i] != s[j + 1]) {j = Next[j];}if(s[i] == s[j + 1]) {++j;}Next[i] = j;}}int main() {#ifdef Dmaxiyafreopen("test.txt", "r", stdin);// freopen("out.txt", "w", stdout);#endif // Dmaxiyaios::sync_with_stdio(false);while(scanf("%d%d%d", &n, &m, &q) != EOF) {scanf("%s%s", str1 + 1, str2 + 1);get_next(str2);for(int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) {int j = 0;int ret = 0;for(int ii = i; str1[ii]; ++ii) {while(j > 0 && str1[ii] != str2[j + 1]) {j = Next[j];}if(str1[ii] == str2[j + 1]) {++j;}if(str2[j + 1] == '\0') {++ret;j = Next[j];}ans[i][ii] = ret;}}while(q--) {scanf("%d%d", &l, &r);printf("%d\n", ans[l][r]);}}return 0;}
C. Vasya And The Mushrooms
题意
在一个 的网格内,每一格都有一个蘑菇,第一行第 格内的蘑菇每分钟长大 ,第二行第 格内的蘑菇每分钟长大 , 从第 行第 列的网格开始走起,每分钟都只能往相邻网格内移动,每一格蘑菇都必须经过一次(不能多于一次),最后不必回到初始位置,问如何规划路线才能使 收获的蘑菇最多。
输入
第一行包含一个整数 ,第二行为 个整数 ,第三行为 个整数 ,其中
输出
输出最大能够收获的蘑菇数量。
样例
| 输入 | 输出 | 提示 |
|---|---|---|
| 3 1 2 3 6 5 4 |
70 | 最优的路线如下: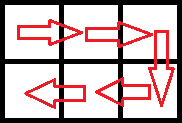 最后收获的蘑菇为: |
| 3 1 1000 10000 10 100 100000 |
543210 | 最优的路线如下: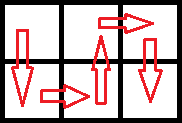 最后收获的蘑菇为: |
题解
由于每个网格都必须经过一次,所以从左上角开始的路线只有两类:“” 折返以及在某一次往右时停止折返,一直往右直到最后一格,然后返回,一般的情况如下(也可能在第二行一直往右,到最后从第一行返回):
因此就是枚举中断往返开始一直往右的点,取最大值,在枚举中间点的时候,每次都需要 地求出贡献,首先用 预处理出 “” 走法的每个点的系数(从左上角点按照“下上右”的顺序 就可以得到):
然后从右往左递推一下后半段(先往右到最后,再往左回来的部分)的贡献,首先假设到某个点 的时候的系数为 ,则后面接着所有点的系数为:
继续算从第 个点开始右转的贡献:
其中 为第 个点上面第二张系数图中对应的系数,对比上一张系数图可以发现,从第 列到第 列所有的系数贡献都减 ,而从第 到第 列的贡献需要根据 的位置进行计算,因此就可以从 到 递推得到从任何一列开始右转的贡献,最终 地枚举转折点取最大值就能得到答案。
过题代码
#include <iostream>#include <cstdio>#include <cstdlib>#include <cmath>#include <climits>#include <cstring>#include <string>#include <vector>#include <list>#include <queue>#include <stack>#include <map>#include <set>#include <bitset>#include <algorithm>#include <functional>#include <iomanip>using namespace std;#define LL long longconst int maxn = 300000 + 100;int n;bool vis[2][maxn];LL num[2][maxn], c[2][maxn], L[2][maxn], R[2][maxn];LL sum[maxn];const int dir[3][2] = {1, 0, -1, 0, 0, 1};bool in(int x, int y) {return x >= 0 && x < 2 && y >= 0 && y < n;}void dfs(int x, int y, LL cc) {vis[x][y] = true;c[x][y] = cc;for(int i = 0; i < 3; ++i) {int xx = x + dir[i][0];int yy = y + dir[i][1];if(in(xx, yy) && !vis[xx][yy]) {L[xx][yy] = L[x][y] + cc * num[x][y];dfs(xx, yy, cc + 1);}}}int main() {#ifdef Dmaxiyafreopen("test.txt", "r", stdin);// freopen("out.txt", "w", stdout);#endif // Dmaxiyaios::sync_with_stdio(false);while(scanf("%d", &n) != EOF) {memset(sum, 0, sizeof(sum));for(int i = 0; i < 2; ++i) {for(int j = 0; j < n; ++j) {scanf("%I64d", &num[i][j]);sum[j] += num[i][j];vis[i][j] = false;R[i][j] = 0;}}for(int i = n - 2; i >= 0; --i) {sum[i] += sum[i + 1];}dfs(0, 0, 0);int Begin_up, Begin_down;if(n % 2 == 0) {Begin_up = n - 2;LL cc = c[0][n - 2];R[0][n - 2] = cc * num[0][n - 2] + (cc + 1) * num[0][n - 1] + (cc + 2) * num[1][n - 1] + (cc + 3) * num[1][n - 2];Begin_down = n - 1;cc = c[1][n - 1];R[1][n - 1] = cc * num[1][n - 1] + (cc + 1) * num[0][n - 1];} else {Begin_up = n - 1;LL cc = c[0][n - 1];R[0][n - 1] = cc * num[0][n - 1] + (cc + 1) * num[1][n - 1];Begin_down = n - 2;cc = c[1][n - 2];R[1][n - 2] = cc * num[1][n - 2] + (cc + 1) * num[1][n - 1] + (cc + 2) * num[0][n - 1] + (cc + 3) * num[0][n - 2];}for(int i = Begin_up; i - 2 >= 0; i -= 2) {LL cc = c[0][i - 2];R[0][i - 2] = R[0][i] - sum[i] * 2;R[0][i - 2] += cc * num[0][i - 2] + (cc + 1) * num[0][i - 1];cc += (n - i) * 2 + 2;R[0][i - 2] += cc * num[1][i - 1] + (cc + 1) * num[1][i - 2];}for(int i = Begin_down; i - 2 >= 0; i -= 2) {LL cc = c[1][i - 2];R[1][i - 2] = R[1][i] - sum[i] * 2;R[1][i - 2] += cc * num[1][i - 2] + (cc + 1) * num[1][i - 1];cc += (n - i) * 2 + 2;R[1][i - 2] += cc * num[0][i - 1] + (cc + 1) * num[0][i - 2];}LL aans = 0;for(int i = 0; i < 2; ++i) {for(int j = 0; j < n; ++j) {if((i + j) % 2 == 0) {aans = max(aans, L[i][j] + R[i][j]);}}}printf("%I64d\n", aans);}return 0;}
D. Vasya And The Matrix
题意
构造一个 行 列的矩阵,要求构造矩阵的每一行的异或值为 ,每一列的异或值为 。
输入
第一行包含两个整数 ,第二行有 个整数 ,第三行有 个整数 。
输出
如果可以构造出满足条件的矩阵,第一行输出一个 ,接着输出一个 的矩阵,要求矩阵的每一格元素 ,否则输出 。
样例
| 输入 | 输出 |
|---|---|
| 2 3 2 9 5 3 13 |
YES 3 4 5 6 7 8 |
| 3 3 1 7 6 2 15 12 |
NO |
题解
前 行 列都填 ,最后一行的前 列分别填上 ,最后一列的前 行分别填上 ,最后根据异或的运算规则,分别从行和列的异或结果计算出第 行第 列的值,如果两次计算得到的值相等,则可以构造出满足条件的矩阵,否则输出 。
过题代码
#include <iostream>#include <cstdio>#include <cstdlib>#include <cmath>#include <climits>#include <cstring>#include <string>#include <vector>#include <list>#include <queue>#include <stack>#include <map>#include <set>#include <bitset>#include <algorithm>#include <functional>#include <iomanip>using namespace std;#define LL long longconst int maxn = 100 + 100;int n, m;int a[maxn], b[maxn];int ans[maxn][maxn];int main() {#ifdef LOCALfreopen("test.txt", "r", stdin);// freopen("out.txt", "w", stdout);#endif // LOCALios::sync_with_stdio(false);while(scanf("%d%d", &n, &m) != EOF) {for(int i = 1; i < n; ++i) {for(int j = 1; j < m; ++j) {ans[i][j] = 0;}}for(int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) {scanf("%d", a + i);ans[i][m] = a[i];}for(int i = 1; i <= m; ++i) {scanf("%d", b + i);ans[n][i] = b[i];}int tmp = 0;for(int i = 1; i < n; ++i) {tmp ^= ans[i][m];}ans[n][m] = tmp ^ ans[n][m];tmp = 0;for(int i = 1; i <= m; ++i) {tmp ^= ans[n][i];}if(tmp == a[n]) {printf("YES\n");for(int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) {for(int j = 1; j <= m; ++j) {if(j != 1) {printf(" ");}printf("%d", ans[i][j]);}printf("\n");}} else {printf("NO\n");}}return 0;}




