@Dmaxiya
2018-08-17T02:25:38.000000Z
字数 7661
阅读 1392
Codeforces Round #490 (Div. 3)
Codeforces
Contests 链接:Codeforces Round #490 (Div. 3)
过题数:5
排名:125/7615
A. Mishka and Contest
题意
给出 个问题的难度等级序列, 只能解决难度等级不大于 的问题,她每次解决问题都是从序列的前面或者后面选一个问题,如果她可以解决这个问题,那么这个问题就会从序列中删掉,她将会重复这个操作,直到她无法解决任何问题为止,问题她最多能解决多少问题。
输入
第一行为两个整数 和 ,第二行有 个整数 ,表示问题的难度。
输出
输出 能解决的最多的问题数。
样例
| 输入 | 输出 | 提示 |
|---|---|---|
| 8 4 4 2 3 1 5 1 6 4 |
5 | 可以按照 [4,2,3,1,5,1,6,4][2,3,1,5,1,6,4] [2,3,1,5,1,6][3,1,5,1,6][1,5,1,6][5,1,6] 的顺序最多解决 个问题。 |
| 5 2 3 1 2 1 3 |
0 | 由于序列两端的问题难度都大于 ,所以 无法解决任何问题。 |
| 5 100 12 34 55 43 21 |
5 | 可以解决所有问题。 |
题解
先判断序列中是否有大于 的项,如果没有则直接输出 ,否则从两端找到最多的不大于 的数字个数相加。
过题代码
#include <iostream>#include <cstdio>#include <cstdlib>#include <cmath>#include <climits>#include <cstring>#include <string>#include <vector>#include <list>#include <queue>#include <stack>#include <map>#include <set>#include <bitset>#include <algorithm>#include <functional>#include <iomanip>using namespace std;typedef long long LL;const int maxn = 200;int n, k;int num[maxn];int main() {#ifdef Dmaxiyafreopen("test.txt", "r", stdin);// freopen("test1.out", "w", stdout);#endif // Dmaxiyaios::sync_with_stdio(false);while(scanf("%d%d", &n, &k) != EOF) {bool flag = true;for(int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) {scanf("%d", &num[i]);if(num[i] > k) {flag = false;}}if(flag) {printf("%d\n", n);continue;}int cnt = 0;for(int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) {if(num[i] > k) {break;}++cnt;}for(int i = n; i >= 1; --i) {if(num[i] > k) {break;}++cnt;}printf("%d\n", cnt);}return 0;}
B. Reversing Encryption
题意
对一个长度为 的字符串,从 到 枚举 的所有因数 ,将字符串在区间 上的所有字符反转,将得到一个新的字符串,如:"codeforces""secrofedoc""orcesfedoc""rocesfedoc""rocesfedoc"。
现在给出进行以上操作之后的字符串,输出原字符串。
输入
第一行为一个整数 ,第二行为一个长度为 的字符串 , 仅包含小写字符。
输出
输出原字符串。
样例
| 输入 | 输出 |
|---|---|
| 10 rocesfedoc |
codeforces |
| 16 plmaetwoxesisiht |
thisisexampletwo |
| 1 z |
z |
题解
从 到 枚举所有 的因数 ,将区间 内的所有字符反转,就能得到原字符串。
过题代码
#include <iostream>#include <cstdio>#include <cstdlib>#include <cmath>#include <climits>#include <cstring>#include <string>#include <vector>#include <list>#include <queue>#include <stack>#include <map>#include <set>#include <bitset>#include <algorithm>#include <functional>#include <iomanip>using namespace std;typedef long long LL;const int maxn = 100 + 100;int n;char str[maxn];void Reverse(int Index) {for(int i = 1; i <= Index / 2; ++i) {swap(str[i], str[Index - i + 1]);}}int main() {#ifdef Dmaxiyafreopen("test.txt", "r", stdin);// freopen("test1.out", "w", stdout);#endif // Dmaxiyaios::sync_with_stdio(false);while(scanf("%d", &n) != EOF) {scanf("%s", str + 1);for(int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) {if(n % i == 0) {Reverse(i);}}printf("%s\n", str + 1);}return 0;}
C. Alphabetic Removals
题意
给出一个长度为 的只包含小写字符的字符串 ,输出对 进行 次以下操作后的字符串:
- 如果字符串内含有字符 'a',则删掉最左边的那个 'a',否则进入下一步;
- 如果字符串内含有字符 'b',则删掉最左边的那个 'b',否则进入下一步;
- 如果字符串内有 'z',则删掉最左边的 'z'。
输入
第一行为两个整数 和 ,第二行为一个字符串 。
输出
输出经过 次删除字符的操作的字符串。
样例
| 输入 | 输出 |
|---|---|
| 15 3 cccaabababaccbc |
cccbbabaccbc |
| 15 9 cccaabababaccbc |
cccccc |
| 1 1 u |
题解
先统计每个字符出现的次数,然后根据 计算出每个字符要删除多少次,然后 跑一遍整个字符串,每跑到一个字符就判断这个字符是否需要删除,如果需要删除就将该字符需要删除的次数减一,否则输出这个字符。
过题代码
#include <iostream>#include <cstdio>#include <cstdlib>#include <cmath>#include <climits>#include <cstring>#include <string>#include <vector>#include <list>#include <queue>#include <stack>#include <map>#include <set>#include <bitset>#include <algorithm>#include <functional>#include <iomanip>using namespace std;typedef long long LL;const int maxn = 400000 + 100;int n, k;char str[maxn];int cnt[30], Del[30];int main() {#ifdef Dmaxiyafreopen("test.txt", "r", stdin);// freopen("test1.out", "w", stdout);#endif // Dmaxiyaios::sync_with_stdio(false);while(scanf("%d%d", &n, &k) != EOF) {memset(cnt, 0, sizeof(cnt));memset(Del, 0, sizeof(Del));scanf("%s", str);for(int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {++cnt[str[i] - 'a'];}int Index = 0;while(k > 0) {if(k > cnt[Index]) {Del[Index] = cnt[Index];k -= cnt[Index];++Index;} else {Del[Index] = k;break;}}for(int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {if(Del[str[i] - 'a'] <= 0) {putchar(str[i]);}--Del[str[i] - 'a'];}printf("\n");}return 0;}
D. Equalize the Remainders
题意
给定两个整数 和 ,保证 为整数,以及 个整数的序列 , 表示序列中对 取模等于 的数字个数。
现在你可以对这个序列进行修改,每次修改可以将序列中的某个数字 ,问最少需要多少次修改,能够使得 ,并输出修改后的序列。
输入
第一行为两个整数 和 ,数据保证 ,第二行为 个整数 。
输出
第一行输出要使 的最少修改次数,第二行为 个整数,表示修改后的序列,如果有多解,输出任意一组,输出要保证每个数字都不应超过 。
样例
| 输入 | 输出 |
|---|---|
| 6 3 3 2 0 6 10 12 |
3 3 2 0 7 10 14 |
| 4 2 0 1 2 3 |
0 0 1 2 3 |
题解
这题整体的思路就是贪心,如果 大于 个,将其中多出来的数字转化成离他“最近”的 小于 的数字。
思路很好想,就是代码的实现上如果没想清楚的话可能会写得很复杂,我的写法是这样的:用一个 数组来存,第 个 存的是所有的对 取模等于 的数字的下标,然后一直调整 中的数字个数,直到所有 的大小都等于 为止,调整的方法是:用一个 来跑 数组的那个 ,同时用一个队列,如果第 个 的 大于 ,就把第 个 后面的元素放入队列,如果第 个 的 小于 ,就把队首元素弹出,放到这个 后面,并将这个元素弹出队列, 的跑法是 。
过题代码
#include <iostream>#include <cstdio>#include <cstdlib>#include <cmath>#include <climits>#include <cstring>#include <string>#include <vector>#include <list>#include <queue>#include <stack>#include <map>#include <set>#include <bitset>#include <algorithm>#include <functional>#include <iomanip>using namespace std;typedef long long LL;const int maxn = 200000 + 100;int n, m;int num[maxn];vector<int> G[maxn];queue<int> que;bool vis[maxn];int main() {#ifdef Dmaxiyafreopen("test.txt", "r", stdin);// freopen("test1.out", "w", stdout);#endif // Dmaxiyaios::sync_with_stdio(false);while(scanf("%d%d", &n, &m) != EOF) {for(int i = 0; i < m; ++i) {G[i].clear();vis[i] = false;}int k = n / m;for(int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) {scanf("%d", &num[i]);G[num[i] % m].push_back(i);}int cnt = 0;int Index = 0;while(cnt < m) {while((int)G[Index].size() > k) {que.push(G[Index].back());G[Index].pop_back();}while((int)G[Index].size() < k && !que.empty()) {int tmp = que.front();que.pop();G[Index].push_back(tmp);}if((int)G[Index].size() == k && !vis[Index]) {vis[Index] = true;++cnt;}Index = (Index + 1) % m;}LL ans = 0;for(int i = 0; i < m; ++i) {int len = G[i].size();for(int j = 0; j < len; ++j) {int Index = G[i][j];int d = ((i - (num[Index] % m)) % m + m) % m;ans += d;num[Index] += d;}}printf("%I64d\n", ans);for(int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) {if(i != 1) {printf(" ");}printf("%d", num[i]);}printf("\n");}return 0;}
E. Reachability from the Capital
题意
在一个 个节点、 条边的有向图上,问最少要添加多少条有向边,使节点 能到达所有节点。
输入
第一行包含三个整数 ,接下来 行每行两个数字 ,表示在有向图上有一条从节点 指向 的边。
输出
输出要让节点 能够到达其他点需要添加的最少的有向边的数量。
样例
| 输入 | 输出 | 提示 |
|---|---|---|
| 9 9 1 1 2 1 3 2 3 1 5 5 6 6 1 1 8 9 8 7 1 |
3 | 有向图如图所示: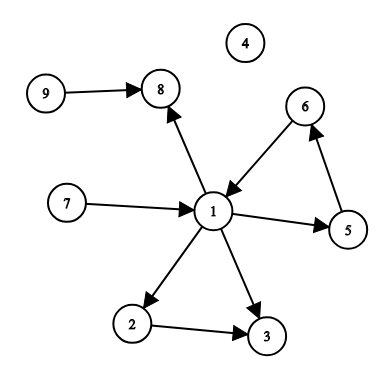 可以添加这三条有向边:,让节点 能到达其他所有节点, 且 是最少需要添加的有向边的数量。 |
| 5 4 5 1 2 2 3 3 4 4 1 |
1 | 有向图如图所示: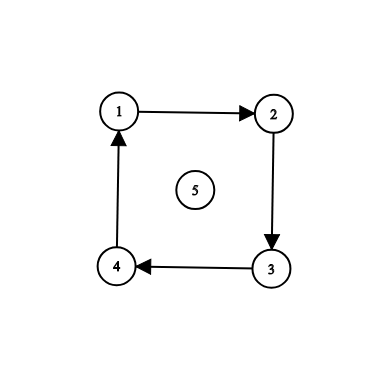 你可以添加 中的任意一条有向边,使 能到达 其他所有节点。 |
题解
先对整张图做 缩点,统计新图上入度为 且 的节点数量。
过题代码
#include <iostream>#include <cstdio>#include <cstdlib>#include <cmath>#include <climits>#include <cstring>#include <string>#include <vector>#include <list>#include <queue>#include <stack>#include <map>#include <set>#include <bitset>#include <algorithm>#include <functional>#include <iomanip>using namespace std;typedef long long LL;const int maxn = 5000 + 100;int n, m, u, v, s, ans;int top, bcnt, dcnt;int sta[maxn], dfn[maxn], low[maxn], belong[maxn], deg[maxn];bool ins[maxn];vector<int> G[maxn];void dfs(int x) {dfn[x] = low[x] = ++dcnt;ins[x] = true;sta[top++] = x;int len = G[x].size();for(int i = 0; i < len; ++i) {int pos = G[x][i];if(dfn[pos] == 0) {dfs(pos);low[x] = min(low[x], low[pos]);} else if(ins[pos]) {low[x] = min(low[x], dfn[pos]);}}if(dfn[x] == low[x]) {++bcnt;int pos;do {pos = sta[--top];ins[pos] = false;belong[pos] = bcnt;} while(pos != x);}}void Tarjan() {bcnt = top = dcnt = 0;memset(dfn, 0, sizeof(dfn));memset(ins, 0, sizeof(ins));for(int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) {if(dfn[i] == 0) {dfs(i);}}for(int i = 1; i <= bcnt; ++i) {deg[i] = 0;}for(int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) {int len = G[i].size();for(int j = 0; j < len; ++j) {int pos = G[i][j];int u = belong[i];int v = belong[pos];if(u != v) {++deg[v];}}}}int main() {#ifdef Dmaxiyafreopen("test.txt", "r", stdin);// freopen("test1.out", "w", stdout);#endif // Dmaxiyaios::sync_with_stdio(false);while(scanf("%d%d%d", &n, &m, &s) != EOF) {for(int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) {G[i].clear();}for(int i = 0; i < m; ++i) {scanf("%d%d", &u, &v);G[u].push_back(v);}Tarjan();ans = 0;for(int i = 1; i <= bcnt; ++i) {if(belong[s] != i && deg[i] == 0) {++ans;}}printf("%d\n", ans);}return 0;}
