@Dmaxiya
2018-08-18T13:06:27.000000Z
字数 7522
阅读 1417
Codeforces Round #504 (Div. 1 + Div. 2)
Codeforces
Contests 链接:Codeforces Round #504 (Div. 1 + Div. 2)
过题数:3
排名:1013/7459
A. Single Wildcard Pattern Matching
题意
给定两个字符串 和 ,长度分别为 和 , 串中最多含有一个
*通配符,通配符可以用任意字符串(也可能为空)替换,问能否将其中的通配符用某个字符串替换后,使 与 串相等。
输入
第一行为两个整数 ,第二行为一个长度为 的字符串 ,第三行为一个长度为 的字符串 , 串中只含有小写字母与最多一个
*字符, 串只包含小写字母。
输出
如果 串可以转化为 串,则输出 ,否则输出 。
样例
| 输入 |
|---|
| 6 10 code*s codeforces |
| 输出 |
| YES |
| 提示 |
将 * 改为 force 就可以令两个字符串相等。 |
| 输入 |
|---|
| 6 5 vk*cup vkcup |
| 输出 |
| YES |
| 提示 |
用空串代替 * 就可以令两个字符串相等。 |
| 输入 |
|---|
| 1 1 v k |
| 输出 |
| NO |
| 提示 |
| 两个字符串不相等,故答案为 。 |
| 输入 |
|---|
| 9 6 gfgf*gfgf gfgfgf |
| 输出 |
| NO |
| 提示 |
不论用什么字符串替换 * 都无法使两个字符串相等。 |
题解
如果 串不包含通配符,直接用 比较,否则从前往后、从后往前与 串进行比较,记录 串的分隔位,如果 串的
*之前与 的公共前缀与*之后与 的公共后缀不相交,就输出 ,否则输出 。
过题代码
#include <iostream>#include <cstdio>#include <cstdlib>#include <cstring>#include <climits>#include <cmath>#include <string>#include <vector>#include <list>#include <queue>#include <stack>#include <map>#include <set>#include <functional>#include <algorithm>using namespace std;#define LL long longconst int maxn = 200000 + 100;int n, m;char s[maxn], t[maxn];int main() {#ifdef Dmaxiyafreopen("test.txt", "r", stdin);// freopen("10.out", "w", stdout);#endif // Dmaxiyawhile(scanf("%d%d", &n, &m) != EOF) {int l, r;int tl, tr;bool flag = false;scanf("%s%s", s, t);for(int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {if(s[i] == '*') {flag = true;l = i - 1;r = i + 1;}}if(!flag) {if(strcmp(s, t) == 0) {printf("YES\n");} else {printf("NO\n");}continue;}tl = -1;tr = m;for(int i = 0; i <= l; ++i) {if(s[i] != t[i]) {flag = false;break;}tl = i;}for(int i = 1; n - i >= r; ++i) {if(s[n - i] != t[m - i]) {flag = false;break;}tr = m - i;}if(flag) {if(tl < tr) {printf("YES\n");} else {printf("NO\n");}} else {printf("NO\n");}}return 0;}
B. Pair of Toys
题意
有 个玩具,第 个玩具的价格为 ,问有多少对玩具 ,它们的价值和等于 ,其中 和 被认为是相同的玩具对。
输入
输入只包含两个整数 。
输出
输出满足条件的玩具对数。
样例
| 输入 |
|---|
| 8 5 |
| 输出 |
| 2 |
| 提示 |
| 和 都是合法的选择。 |
| 输入 |
|---|
| 8 15 |
| 输出 |
| 1 |
| 提示 |
| 只有 是合法的选择。 |
| 输入 |
|---|
| 7 20 |
| 输出 |
| 0 |
| 提示 |
| 到 中所有数字相加都不能达到 ,因此答案为 。 |
| 输入 |
|---|
| 1000000000000 1000000000001 |
| 输出 |
| 500000000000 |
| 提示 |
| 我们可以选择 ,总共有 对整数。 |
题解
先确定所有可选数字的右边界 ,再确定其左边界 ,其中满足条件的整数对数为
过题代码
#include <iostream>#include <cstdio>#include <cstdlib>#include <cstring>#include <climits>#include <cmath>#include <string>#include <vector>#include <list>#include <queue>#include <stack>#include <map>#include <set>#include <functional>#include <algorithm>using namespace std;#define LL long longLL n, k;int main() {#ifdef Dmaxiyafreopen("test.txt", "r", stdin);// freopen("10.out", "w", stdout);#endif // Dmaxiyawhile(scanf("%I64d%I64d", &n, &k) != EOF) {LL R = min(k - 1, n);LL L = max(1LL, k - R);if(L >= R) {printf("0\n");continue;}printf("%I64d\n", (R - L + 1) / 2);}return 0;}
C. Bracket Subsequence
题意
给定一个长度为 的合法括号序列,其中的左右括号能完全匹配,要求从中找到一个长度为 的合法括号子序列。
输入
第一行为两个整数 ,其中 和 都是偶数,第二行为一个长度为 的字符串,字符串保证是一个合法的括号序列。
输出
输出长度为 的合法括号子序列。
样例
| 输入 |
|---|
6 4()(()) |
| 输出 |
()() |
| 输入 |
|---|
8 8(()(())) |
| 输出 |
(()(())) |
题解
用栈模拟括号匹配的过程,其中弹出栈的必然是合法的括号序列,将弹出栈的括号下标标记,当弹出栈的括号个数达到 时,将所有标记的括号输出。
过题代码
#include <iostream>#include <cstdio>#include <cstdlib>#include <cstring>#include <climits>#include <cmath>#include <string>#include <vector>#include <list>#include <queue>#include <stack>#include <map>#include <set>#include <functional>#include <algorithm>using namespace std;#define LL long longconst int maxn = 200000 + 100;int n, k, top;char str[maxn];bool vis[maxn];int sta[maxn];int main() {#ifdef Dmaxiyafreopen("test.txt", "r", stdin);// freopen("10.out", "w", stdout);#endif // Dmaxiyawhile(scanf("%d%d", &n, &k) != EOF) {top = 0;memset(vis, 0, sizeof(vis));scanf("%s", str);for(int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {if(str[i] == '(') {sta[top++] = i;} else {--top;vis[sta[top]] = true;vis[i] = true;k -= 2;if(k == 0) {break;}}}for(int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {if(vis[i]) {printf("%c", str[i]);}}printf("\n");}return 0;}
D. Array Restoration
题意
有一个长度为 的序列,可以对这 个序列进行 次操作,第 次操作选择一个区间 ,将这个区间内的所有数字用 替换,每个位置上的数字至少被一个区间覆盖,最后将这个序列中的某几个数字改为 。现在题目给出最终的序列,问是否存在合法的 次操作,能够得到给出的序列,求 次操作后(将序列某些数字变为 之前)的序列。
输入
第一行为两个整数 ,第二行为 个整数 。
输出
如果给出的序列无法从上面的操作中得到,输出 ,否则在第一行输出 ,第二行输出 次操作之后的 个整数。
样例
| 输入 |
|---|
| 4 3 1 0 2 3 |
| 输出 |
| YES 1 2 2 3 |
| 提示 |
| 将 用 替换也是合法的,但是用 替换是不合法的。 |
| 输入 |
|---|
| 3 10 10 10 10 |
| 输出 |
| YES 10 10 10 |
| 提示 |
| 不论前 次操作是怎么样,第 次操作是选择区间 即可。 |
| 输入 |
|---|
| 5 6 6 5 6 2 2 |
| 输出 |
| NO |
| 提示 |
| 由于第 次操作必须在第 次操作之前,所以不可能先将区间 更新为 之后再将区间 更新为 。 |
| 输入 |
|---|
| 3 5 0 0 0 |
| 输出 |
| YES 5 4 2 |
| 提示 |
| 有许多种操作对于 而言都是合法的。 |
题解
由于数字大的一定比数字小的后更新,所以每个数字出现的左端点与右端点之间的数字不能小于它自身,可以用线段树维护最小值,从 到 询问第 个数字出现的左端点 与右端点 ,如果在查询区间最小值时遇到 的情况,就向下将 更新为当前数字再进行查询。记得首先查询序列内是否有数字 ,如果没有数字 就将其中任意一个 修改为 ,如果无法修改则直接输出 。所有询问与更新结束后,如果序列中仍含有 ,就将所有 赋值为 。
过题代码
#include <iostream>#include <cstdio>#include <cstdlib>#include <cstring>#include <climits>#include <cmath>#include <string>#include <vector>#include <list>#include <queue>#include <stack>#include <map>#include <set>#include <functional>#include <algorithm>using namespace std;#define LL long longconst int maxn = 200000 + 100;int n, q;int num[maxn], L[maxn], R[maxn];int Min[maxn << 2];void push_up(int rt) {Min[rt] = min(Min[rt << 1], Min[rt << 1 | 1]);}void build(int l, int r, int rt) {if(l == r) {Min[rt] = num[l];return ;}int m = (l + r) >> 1;build(l, m, rt << 1);build(m + 1, r, rt << 1 | 1);push_up(rt);}void update(int x, int l, int r, int rt) {if(l == r) {Min[rt] = x;num[l] = x;return ;}int m = (l + r) >> 1;if(Min[rt << 1] == 0) {update(x, l, m, rt << 1);}if(Min[rt << 1 | 1] == 0) {update(x, m + 1, r, rt << 1 | 1);}push_up(rt);}int query(int L, int R, int x, int l, int r, int rt) {if(L <= l && r <= R) {if(Min[rt] == 0) {update(x, l, r, rt);}return Min[rt];}int m = (l + r) >> 1;int ret = INT_MAX;if(L <= m) {ret = min(ret, query(L, R, x, l, m, rt << 1));}if(m < R) {ret = min(ret, query(L, R, x, m + 1, r, rt << 1 | 1));}push_up(rt);return ret;}int main() {#ifdef Dmaxiyafreopen("test.txt", "r", stdin);// freopen("10.out", "w", stdout);#endif // Dmaxiyawhile(scanf("%d%d", &n, &q) != EOF) {for(int i = 0; i <= q; ++i) {L[i] = n + 1;R[i] = 0;}for(int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) {scanf("%d", &num[i]);L[num[i]] = min(L[num[i]], i);R[num[i]] = max(R[num[i]], i);}if(L[q] > R[q]) {if(L[0] != n + 1) {num[L[0]] = q;L[q] = R[q] = L[0];} else {printf("NO\n");continue;}}build(1, n, 1);bool flag = true;for(int i = q; i >= 1; --i) {if(L[i] > R[i]) {continue;}if(query(L[i], R[i], i, 1, n, 1) < i) {flag = false;break;}}if(!flag) {printf("NO\n");continue;}printf("YES\n");for(int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) {if(i != 1) {printf(" ");}if(num[i] == 0) {printf("1");} else {printf("%d", num[i]);}}printf("\n");}return 0;}
E. Down or Right
题意
这是一道交互题,有一个 的网格,其中有一些网格是可以行走的,而有一些是无法行走的,在可以行走的网格中,下一步只能往右或下两个方向移动到下一格可以行走的网格中,但是我们并不知道这个网格哪些格子是可以行走的那些无法行走。 要从 点走到 点,每次可以询问他从 点是否能到达 点, 将会回答 或者 ,且每次询问 与 的哈密顿距离不能小于 ,最终输出从 到 的合法行走方案。询问的次数不能超过 。
输入
第一次输入为一个整数 ,后面的输入为 或者 ,取决于输出的询问。
输出
如果为询问,则按照 的格式询问,如果已经可以求得路径,则第一个字符为
!,空一格之后,输出 个字符,第 个字符为D表示第 步需要往下走,为R表示需要往右走。
样例
| 输入 |
|---|
| 4 YES NO YES YES |
| 输出 |
? 1 1 4 4 ? 1 2 4 3 ? 4 1 4 4 ? 1 4 4 4 ! RDRRDD |
| 提示 |
网格中的可行走方格与不可行走方格如下图: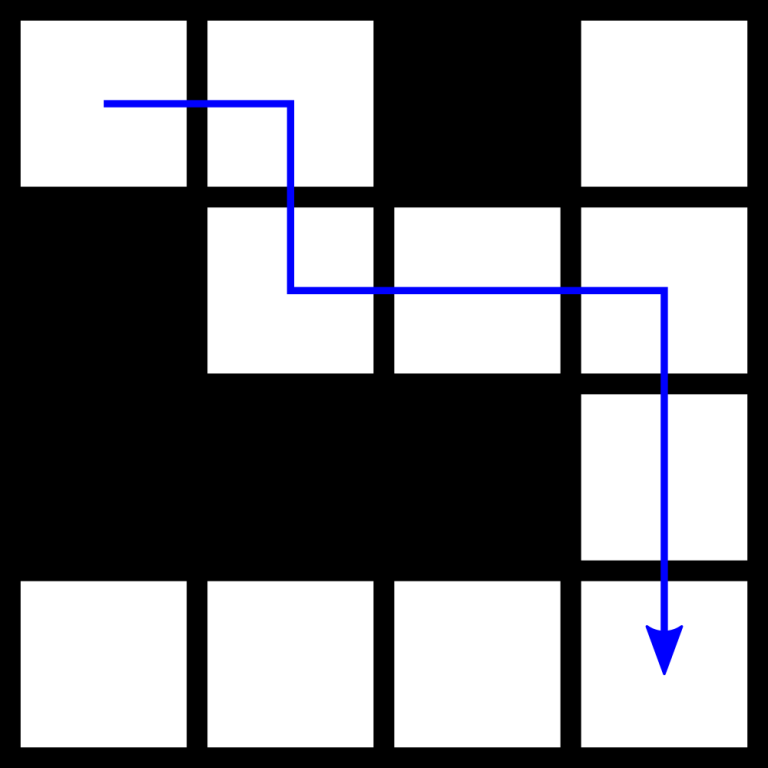 |
题解
如果“左上的点”表示与点 的哈密顿距离不大于 的所有点,“右下的点”表示与点 的哈密顿距离不大于 的点,则先从 开始询问左上的点是否能到达 ,能往右就尽量往右走,再从 开始询问 能否到达右下的点,能往上就尽量往上,最后这两条路径一定会重合于某一点 ,其中 。
过题代码
#include <iostream>#include <cstdio>#include <cstdlib>#include <cstring>#include <climits>#include <cmath>#include <string>#include <vector>#include <list>#include <queue>#include <stack>#include <map>#include <set>#include <functional>#include <algorithm>using namespace std;#define LL long longconst int maxn = 20000 + 100;int n, cntl, cntr;char ret[10];char ansl[maxn], ansr[maxn];int dis(int x1, int y1, int x2, int y2) {return abs(x1 - x2) + abs(y1 - y2);}int main() {#ifdef Dmaxiya// freopen("test.txt", "r", stdin);// freopen("10.out", "w", stdout);#endif // Dmaxiyascanf("%d", &n);int x = 1, y = 1;while(dis(1, 1, x, y + 1) <= n - 1) {int xx = x;int yy = y + 1;printf("? %d %d %d %d\n", xx, yy, n, n);fflush(stdout);scanf("%s", ret);if(ret[0] == 'Y') {ansl[cntl++] = 'R';++y;} else {ansl[cntl++] = 'D';++x;}}x = y = n;while(dis(x - 1, y, n, n) <= n - 1) {int xx = x - 1;int yy = y;printf("? %d %d %d %d\n", 1, 1, xx, yy);fflush(stdout);scanf("%s", ret);if(ret[0] == 'Y') {ansr[cntr++] = 'D';--x;} else {ansr[cntr++] = 'R';--y;}}ansl[cntl] = '\0';printf("! %s", ansl);for(int i = cntr - 1; i >= 0; --i) {printf("%c", ansr[i]);}printf("\n");fflush(stdout);return 0;}
