@w460461339
2018-09-17T06:03:22.000000Z
字数 9747
阅读 2822
生成对抗网络:CGAN,InfoGAN
MachineLearning
1、CGAN
这个真的是好简单呃…但是效果出奇的好。
https://blog.csdn.net/liuxiao214/article/details/73485333
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/44170959
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/25542274
1.1 基本思想
传统GAN,特别是生成器,在生成的时候,往往会生成很多随机的内容(毕竟输入就是个随机向量,还想怎么样)。现在人们想通过给生成器一定的约束,让它能够在生成的时候有一点规律。
放到公式里,就是这样:
传统GAN
CGAN
即,我们需要求在给定条件y的情况下,D和G的最优解。
那么y是什么呢:
1、对于生成器而言,就是这次你希望生成器生成的内容满足一个什么样的条件。
在之前有的例子是生成二次元萌妹的,没有任何约束的时候,生成的都是随机的妹子;但是CGAN中,如果你让y=‘金发碧眼’,那么生成的所有妹子都是金发碧眼。
2、对于判别器而言,在没有y之前,只需要判断这个是生成数据还是真实数据。但是现在,生成器起到了一点分类器的作用:
2.1 对于真实数据,他不仅要判断这是一个真实数据,还需要判断这个真实数据是不是满足输入条件y。
2.2 对于生成数据,他要在输入约束y的条件下,去判断这个x是不是生成数据。
1.2 网络结构
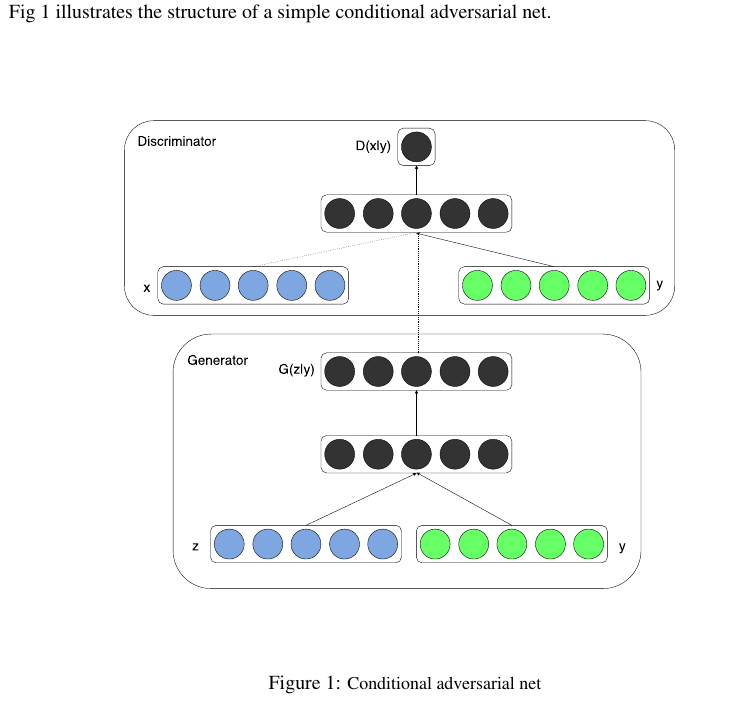
这个图也许不够清楚,那么看看下面这个:
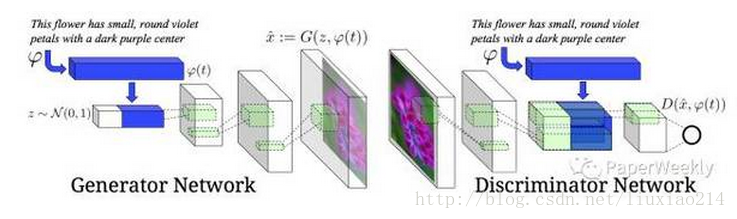
网上的文章说的很少,我一开始还以为是没人看,结果是太简单了。
什么条件概率啥的,放到网络里,就是无脑拼接= -。
1.3 改进策略
感觉CGAN和InfoGAN就是除了随机噪声外,还加入一些隐变量,然后通过一些办法,让隐变量起作用。
当然,为了让模型更好的训练,作者还加入了一些调优策略。
1)针对判别器改进。之前说了判别器需要判断图像是真实还是生成,以及是否满足描述,而原来我们的数据只有两种: a. 真实数据+正确label;b. 生成数据+正确label。现在,作者还加入了:c. 真实数据+错误label。通过这样的方式,来加速判别器的训练和收敛。
2)其实我感觉针对判别器的这一套改进才是重点。若是对输入的label内容没有任何的使用,它的效果不会很好(或者直接丢给你一个和原始GAN一样的网络也不是不行)。但是由于在判别器中,我们加入了对LABEL的判断,尤其是对【真实数据+错误label】数据的加入,令整个网络能够学习并使用这个附加内容。
3)针对生成器改进。这里就是用扩展数据集的方式,设一个文字描述是,另一个文字描述是,我们可以得到他们的一个内插值。其中。这样的内插实际上是得到了两个文字描述的某种“中间态”,为我们增加了样本数量。
1.4 搭建网络
算来算去,这是我写的第一个GAN,先上效果图:(左边是初始状态,右边CPU跑了1000轮)

下面代码静下心来看看,应该很好看懂,不想静心的话,可以直接看看训练部分,弄清楚每个输入数据的格式,shape,就能够大概明白整个流程。
代码:
# load datafrom tensorflow.examples.tutorials.mnist import input_data# 把mnist数据放在MNIST_data下就好mnist = input_data.read_data_sets('MNIST_data',one_hot=True)OUTPUT_DIR='samples'if not os.path.exists(OUTPUT_DIR):os.mkdir(OUTPUT_DIR)tf.reset_default_graph()X = tf.placeholder(dtype=tf.float32, shape=[None, HEIGHT, WIDTH, 1], name='X')y_label = tf.placeholder(dtype=tf.float32, shape=[None, HEIGHT, WIDTH, LABEL], name='y_label')noise = tf.placeholder(dtype=tf.float32, shape=[None, z_dim], name='noise')y_noise = tf.placeholder(dtype=tf.float32, shape=[None, LABEL], name='y_noise')is_training = tf.placeholder(dtype=tf.bool, name='is_training')def lrelu(x,leak=0.2):return tf.maximum(x,leak*x)def sigmoid_cross_entropy_with_logits(x,y):return tf.nn.sigmoid_cross_entropy_with_logits(logits=x,labels=y)# discriminatordef discriminator(image,label,reuse=None,is_training=is_training):momentum=0.9with tf.variable_scope('discriminator',reuse=reuse):# 把输入图像和condition进行拼接 【无脑拼接】h0 = tf.concat([image,label],axis=3)h0 = tf.layers.conv2d(h0,kernel_size=5,filters=64,strides=2,padding='same')h0 = lrelu(h0)# 对于batch_norm,训练的时候需要,推断的时候就不需要。h1 = tf.layers.conv2d(h0,kernel_size=5,filters=128,strides=2,padding='same')h1 = lrelu(tf.contrib.layers.batch_norm(h1,is_training=is_training,decay=momentum))h2 = tf.layers.conv2d(h1,kernel_size=5,filters=256,strides=2,padding='same')h2 = lrelu(tf.contrib.layers.batch_norm(h2,is_training=is_training,decay=momentum))h3 = tf.layers.conv2d(h2,kernel_size=5,filters=512,strides=2,padding='same')h3 = lrelu(tf.contrib.layers.batch_norm(h3,is_training=is_training,decay=momentum))# 最后一层输出拉平+全连接,没有用FCN。h4 = tf.contrib.layers.flatten(h3)h4 = tf.layers.dense(h4,units=1)# h4是一个batch_size*1的向量吧return tf.nn.sigmoid(h4),h4# generatordef generator(z,label,is_training=is_training):momentum=0.9with tf.variable_scope('generator',reuse=None):d =3z = tf.concat([z,label],axis=1)h0 = tf.layers.dense(z,units=d*d*512)h0 = tf.reshape(h0,shape=[-1,d,d,512])h0 = tf.nn.relu(tf.contrib.layers.batch_norm(h0,is_training=is_training,decay=momentum))h1 = tf.layers.conv2d_transpose(h0,kernel_size=5,filters=256,strides=2,padding='same')h1 = tf.nn.relu(tf.contrib.layers.batch_norm(h1,is_training=is_training,decay=momentum))h2 = tf.layers.conv2d_transpose(h1,kernel_size=5,filters=128,strides=2,padding='same')h2 = tf.nn.relu(tf.contrib.layers.batch_norm(h2,is_training=is_training,decay=momentum))h3 = tf.layers.conv2d_transpose(h2,kernel_size=5,filters=64,strides=2,padding='same')h3 = tf.nn.relu(tf.contrib.layers.batch_norm(h3,is_training=is_training,decay=momentum))h4 = tf.layers.conv2d_transpose(h3,kernel_size=5,filters=1,strides=1,padding='valid',activation=tf.nn.tanh,name='g')return h4# loss# 1、拿到生成的生成内容g = generator(noise, y_noise)# 2、用真实数据训练判别器d_real, d_real_logits = discriminator(X, y_label)# 3、用生成数据训练判别器d_fake, d_fake_logits = discriminator(g, y_label, reuse=True)# 喵喵喵???vars_g = [var for var in tf.trainable_variables() if var.name.startswith('generator')]vars_d = [var for var in tf.trainable_variables() if var.name.startswith('discriminator')]# 4、通过判别器拿到V(G,D)中第一项loss_d_real=tf.reduce_mean(sigmoid_cross_entropy_with_logits(d_real_logits,tf.ones_like(d_real)))# 5、通过判别器拿到V(G,D)中第二项loss_d_fake=tf.reduce_mean(sigmoid_cross_entropy_with_logits(d_fake_logits,tf.zeros_like(d_fake)))# 6、通过判别器定义生成器的lossloss_g=tf.reduce_mean(sigmoid_cross_entropy_with_logits(d_fake_logits,tf.ones_like(d_fake)))# 7、组合得到判别器的lossloss_d=loss_d_fake+loss_d_real# optimizerupdate_ops = tf.get_collection(tf.GraphKeys.UPDATE_OPS)with tf.control_dependencies(update_ops):optimizer_d = tf.train.AdamOptimizer(learning_rate=0.0002,beta1=0.5).minimize(loss_d,var_list=vars_d)optimizer_g = tf.train.AdamOptimizer(learning_rate=0.0002,beta1=0.5).minimize(loss_g,var_list=vars_g)# 就是为了方便看结果,和模型没关系def montage(images):if isinstance(images,list):images = np.array(images)img_h = images.shape[1]img_w = images.shape[2]n_plots = int(np.ceil(np.sqrt(images.shape[0])))m = np.ones((images.shape[1]*n_plots+n_plots+1,images.shape[2]*n_plots+n_plots+1))*0.5for i in range(n_plots):for j in range(n_plots):this_filter = i*n_plots+jif this_filter < images.shape[0]:this_img = images[this_filter]m[1 + i + i * img_h:1 + i + (i + 1) * img_h,1 + j + j * img_w:1 + j + (j + 1) * img_w] = this_imgreturn msess=tf.Session()sess.run(tf.global_variables_initializer())z_samples = np.random.uniform(-1.0,1.0,[batch_size,z_dim]).astype(np.float32)y_samples = np.zeros([batch_size,LABEL])for i in range(LABEL):for j in range(LABEL):y_samples[i*LABEL+j,i]=1samples=[]loss={'d':[],'g':[]}import time'''batch_size=100z_dim=100WIDTH=28HEIGHT=28LABEL=10'''for i in tqdm(range(60000)):# 0、generator每次也就100个输入,每个输入为长100的向量n = np.random.uniform(-1.0,1.0,[batch_size,z_dim]).astype(np.float32)# 1、拿到的训练集图片,像素值已经被归一化到0~1之间batch,label=mnist.train.next_batch(batch_size=batch_size)# 1.1 从batch_size,784 reshape到 batch_size,28,28; 最后那个1表示channelbatch = np.reshape(batch,[batch_size,HEIGHT,WIDTH,1])# 1.2 将0~1的图像像素值变成-1~1之间,满足tanh的要求。batch = (batch-0.5)*2yn = np.copy(label)# 2、能够理解这么做是为了在判别器中将label和图片接在一起,只是这种做法有点迷= -# label从 batch,1,1,LABEL_LEN的张量,变成,batch,28,28,LABEL_LEN的张量y1 = np.reshape(label,[batch_size,1,1,LABEL])y1 = y1*np.ones([batch_size,HEIGHT,WIDTH,LABEL])# 3、先跑一下loss,保存loss结果,为了后面画图用d_ls,g_ls = sess.run([loss_d,loss_g],feed_dict={X:batch,noise:n,y_label:y1,y_noise:yn,is_training:True})loss['d'].append(d_ls)loss['g'].append(g_ls)# 4、真正训练在这里,基本就是判别器训练一次,生成器训练2次。# 4.1 其实可以这么理解,训练一次判别器,需要真实数据(batch),以及生成器生成的数据。# 4.2 而生成器一次就只生成batch_size大小的数据。# 4.3 因此判别器一次训练,所使用的数据量,是判别器的两倍,所以训练一次判别器,需要训练两次生成器。sess.run(optimizer_d,feed_dict={X: batch, noise: n, y_label: y1,y_noise: yn, is_training: True})sess.run(optimizer_g, feed_dict={X: batch, noise: n, y_label: y1,y_noise: yn, is_training: True})sess.run(optimizer_g, feed_dict={X: batch, noise: n, y_label: y1,y_noise: yn, is_training: True})if i % 1000 == 0:print(i, d_ls, g_ls)# 5、每次到了节点,把这个时刻生成器生成的内容输出一下。gen_imgs = sess.run(g, feed_dict={noise: z_samples, y_noise: y_samples,is_training: False})# 6、生成器输出的图像,像素在-1~1之间,现在需要把它们转化回0~1之间。gen_imgs = (gen_imgs + 1) / 2# 7、逐个拿一下图片,拼图啥的。imgs = [img[:, :, 0] for img in gen_imgs]gen_imgs = montage(imgs)plt.axis('off')plt.imshow(gen_imgs, cmap='gray')imageio.imsave(os.path.join(OUTPUT_DIR, 'sample_%d.jpg' % i), gen_imgs)plt.show()samples.append(gen_imgs)plt.plot(loss['d'], label='Discriminator')plt.plot(loss['g'], label='Generator')plt.legend(loc='upper right')plt.savefig('Loss.png')plt.show()imageio.mimsave(os.path.join(OUTPUT_DIR, 'samples.gif'), samples, fps=5)saver = tf.train.Saver()saver.save(sess, './mnist_cgan', global_step=60000)
使用生成器
import tensorflow as tfimport numpy as npimport matplotlib.pyplot as pltbatch_size = 100z_dim = 100LABEL = 10def montage(images):if isinstance(images, list):images = np.array(images)img_h = images.shape[1]img_w = images.shape[2]n_plots = int(np.ceil(np.sqrt(images.shape[0])))m = np.ones((images.shape[1] * n_plots + n_plots + 1, images.shape[2] * n_plots + n_plots + 1)) * 0.5for i in range(n_plots):for j in range(n_plots):this_filter = i * n_plots + jif this_filter < images.shape[0]:this_img = images[this_filter]m[1 + i + i * img_h:1 + i + (i + 1) * img_h,1 + j + j * img_w:1 + j + (j + 1) * img_w] = this_imgreturn msess = tf.Session()sess.run(tf.global_variables_initializer())saver = tf.train.import_meta_graph('./mnist_cgan-60000.meta')saver.restore(sess, tf.train.latest_checkpoint('./'))graph = tf.get_default_graph()g = graph.get_tensor_by_name('generator/g/Tanh:0')noise = graph.get_tensor_by_name('noise:0')y_noise = graph.get_tensor_by_name('y_noise:0')is_training = graph.get_tensor_by_name('is_training:0')n = np.random.uniform(-1.0, 1.0, [batch_size, z_dim]).astype(np.float32)y_samples = np.zeros([batch_size, LABEL])for i in range(LABEL):for j in range(LABEL):y_samples[i * LABEL + j, i] = 1gen_imgs = sess.run(g, feed_dict={noise: n, y_noise: y_samples, is_training: False})gen_imgs = (gen_imgs + 1) / 2imgs = [img[:, :, 0] for img in gen_imgs]gen_imgs = montage(imgs)plt.axis('off')plt.imshow(gen_imgs, cmap='gray')plt.show()
2、InfoGAN
https://blog.csdn.net/dagekai/article/details/53953513
https://blog.csdn.net/u011699990/article/details/71599067
https://www.jianshu.com/p/b8c34c6f09ad
2.1 基本理论
对于原始的GAN而言,生成器的输入z和输出x之间,是没有什么可解释性的。即,我们不知道什么样的z能够生成什么样的x。
在CGAN中,我们通过给定一个隐向量c,以及让判别器去判断生成/真实图像是否符合描述,来约束生成器的行为。这一定程度上,可以认为是,描述c控制了输出x中的与c相关的特征。
然后,呃,有的大佬或许觉得这样不过瘾吧,说我想控制所有的特征;然而我并不能知道一幅图像有哪些特征。于是,我给一个向量作为隐向量,和GAN网络一起训练,然后可以认为,这个向量的每一维,都描述了图像的某一种特征。
问题:
对于这样的隐向量,我没有办法知道它到底描述的是哪几个特征,因此没办法使用CGAN里面的策略来判断这个隐向量是否生效了。
解决:
隐向量最直接的影响应该是生成器的输出,那么只要判断隐向量和生成器输出之间的互信息,就能够知道隐向量是否起作用了。
最终的COST——function:其中L1是经过优化的互信息下界。

详细推断:

2.2 网络结构
网络的逻辑结构就是这样,具体的结构可以和CGAN差不多。

2.3 具体实现
网上找的一版感觉有点问题= -,之后试试keras版本的。
