@iStarLee
2019-08-13T05:46:21.000000Z
字数 13304
阅读 1093
GlobalPlanner —— A*算法
navigation
Reference
1 Introduction
1.1 常见路径搜索算法
- Dijkstra
保证是是最短路径,只要所有的边都有一个非负的cost - Heuristic Approaches (启发式算法 eg: 最佳优先搜索BFS)
基于贪心策略,能够评估(称为启发式的)任意结点到目标点的代价,它比Dijkstra算法快的多,因为它用了一个启发式函数(heuristic function)快速地导向目标结点。 - A*
1968年发明的A*算法就是把启发式方法(heuristic approaches)如BFS,和常规方法如Dijsktra算法结合在一起的算法。有点不同的是,类似BFS的启发式方法经常给出一个近似解而不是保证最佳解。然而,尽管A*基于无法保证最佳解的启发式方法,A*却能保证找到一条最短路径。
1.2 A*的一个简单描述
在凹型障碍物的例子中,A*找到一条和Dijkstra算法一样好的路径:
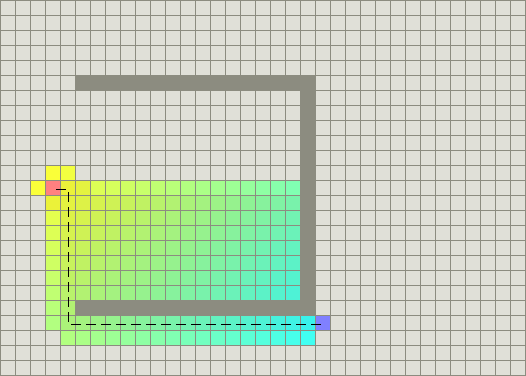
成功的秘决在于,它把Dijkstra算法(靠近初始点的结点)和BFS算法(靠近目标点的结点)的信息块结合起来。在讨论A*的标准术语中
- g(n)表示从初始结点到任意结点n的代价
- h(n)表示从结点n到目标点的启发式评估代价(heuristic estimated cost)。
在上图中,
- yellow(h)表示远离目标的结点
- teal(g)表示远离初始点的结点。
当从初始点向目标点移动时,A*权衡这两者。每次进行主循环时,它检查f(n)最小的结点n,其中f(n) = g(n) + h(n)。
2 启发式算法
启发式函数h(n)告诉A*从任意结点n到目标结点的最小代价评估值。
2.1 A*对启发式函数的使用
启发式函数可以控制A*的行为:
- 一种极端情况,如果h(n)是0,则只有g(n)起作用,此时A*演变成Dijkstra算法,这保证能找到最短路径。
- 如果h(n)经常都比从n移动到目标的实际代价小(或者相等),则A*保证能找到一条最短路径。h(n)越小,A*扩展的结点越多,运行就得越慢。
- 如果h(n)精确地等于从n移动到目标的代价,则A*将会仅仅寻找最佳路径而不扩展别的任何结点,这会运行得非常快。尽管这不可能在所有情况下发生,你仍可以在一些特殊情况下让它们精确地相等(译者:指让h(n)精确地等于实际值)。只要提供完美的信息,A*会运行得很完美,认识这一点很好。
- 如果h(n)有时比从n移动到目标的实际代价高,则A*不能保证找到一条最短路径,但它运行得更快。
- 另一种极端情况,如果h(n)比g(n)大很多,则只有h(n)起作用,A*演变成BFS算法。
所以我们得到一个很有趣的情况,那就是我们可以决定我们想要从A*中获得什么。理想情况下(注:原文为At exactly the right point),我们想最快地得到最短路径。如果我们的目标太低,我们仍会得到最短路径,不过速度变慢了;如果我们的目标太高,那我们就放弃了最短路径,但A*运行得更快。
A*的这个特性非常有用。例如,你会发现在某些情况下,你希望得到一条好的路径("good" path)而不是一条完美的路径("perfect" path)。为了权衡g(n)和h(n),你可以修改任意一个。
在学术上,如果启发式函数值是对实际代价的低估,A*算法被称为简单的A算法(原文为simply A)。然而,我继续称之为A*,因为在实现上是一样的,并且在游戏编程领域并不区别A和A*。
2.2 速度还是精确度?
速度和精确度之间的选择前不是静态的。你可以基于CPU的速度、用于路径搜索的时间片数、地图上物体(units)的数量、物体的重要性、组(group)的大小、难度或者其他任何因素来进行动态的选择。取得动态的折衷的一个方法是,建立一个启发式函数用于假定通过一个网格空间的最小代价是1,然后建立一个代价函数(cost function)用于测量(scales):
- 如果是0,则改进后的代价函数的值总是1。这种情况下,地形代价被完全忽略,A*工作变成简单地判断一个网格可否通过。
- 如果是1,则最初的代价函数将起作用,然后你得到了A*的所有优点。
- 你可以设置的值为0到1的任意值。
速度和精确度之间的选择并不是全局的。在地图上的某些区域,精确度是重要的,你可以基于此进行动态选择。
在安全区域,可以考虑不寻找精确的最短路径而取近似路径,因此寻路快;但在危险区域,逃跑的安全性和逃跑速度是重要的,即路径的精确度是重要的,因此可以多花点时间用于寻找精确路径。
2.3 衡量单位
A*计算f(n) = g(n) + h(n)。为了对这两个值进行相加,这两个值必须使用相同的衡量单位。如果g(n)用小时来衡量而h(n)用米来衡量,那么A*将会认为g或者h太大或者太小,因而你将不能得到正确的路径,同时你的A*算法将运行得更慢。
2.4 精确的启发式函数
如果你的启发式函数精确地等于实际最佳路径(optimal path),如下一部分的图中所示,你会看到此时A*扩展的结点将非常少。A*算法内部发生的事情是:在每一结点它都计算f(n) = g(n) + h(n)。当h(n)精确地和g(n)匹配(译者注:原文为match)时,f(n)的值在沿着该路径时将不会改变。不在正确路径(right path)上的所有结点的f值均大于正确路径上的f值(译者注:正确路径在这里应该是指最短路径)。如果已经有较低f值的结点,A*将不考虑f值较高的结点,因此它肯定不会偏离最短路径。
2.4.1 预计算的精确启发式函数
构造精确启发函数的一种方法是预先计算任意一对结点之间最短路径的长度。在许多游戏的地图中这并不可行。然后,有几种方法可以近似模拟这种启发函数:
- Fit a coarse grid on top of the fine grid. Precompute the shortest path between any pair of coarse grid locations.
- Precompute the shortest path between any pair of waypoints. This is a generalization of the coarse grid approach.
(译者:此处不好翻译,暂时保留原文)
然后添加一个启发函数h’用于评估从任意位置到达邻近导航点(waypoints)的代价。(如果愿意,后者也可以通过预计算得到。)最终的启发式函数可以是:
或者如果你希望一个更好但是更昂贵的启发式函数,则分别用靠近结点和目标的所有的w1,w2对对上式进行求值。(译者注:原文为or if you want a better but more expensive heuristic, evaluate the above with all pairs w1, w2 that are close to the node and the goal, respectively.)
2.4.2 线性精确启发式算法
在特殊情况下,你可以不通过预计算而让启发式函数很精确。如果你有一个不存在障碍物和slow地形,那么从初始点到目标的最短路径应该是一条直线。
如果你正使用简单的启发式函数(我们不知道地图上的障碍物),则它应该和精确的启发式函数相符合(译者注:原文为match)。如果不是这样,则你会遇到衡量单位的问题,或者你所选择的启发函数类型的问题。
2.5 网格地图中的启发式算法
在网格地图中,有一些众所周知的启发式函数。
2.5.1 曼哈顿距离
标准的启发式函数是曼哈顿距离(Manhattan distance)。考虑你的代价函数并找到从一个位置移动到邻近位置的最小代价D,因此,我的游戏中的启发式函数应该是曼哈顿距离的D倍:
// 曼哈顿距离H(n) = D * (abs ( n.x – goal.x ) + abs ( n.y – goal.y ) )
你应该使用符合你的代价函数的衡量单位。
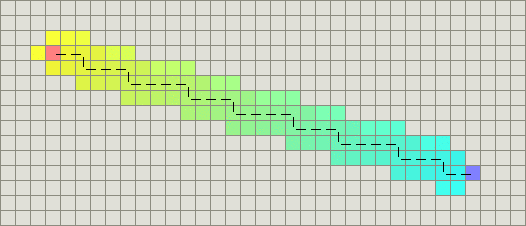
曼哈顿距离又称为出租车距离,曼哈顿距离不是距离不变量,当坐标轴变动时,点间的距离就会不同
2.5.2 对角线距离
如果在你的地图中你允许对角运动那么你需要一个不同的启发函数。(4 east, 4 north)的曼哈顿距离将变成8*D。然而,你可以简单地移动(4 northeast)代替,所以启发函数应该是4*D。这个函数使用对角线,假设直线和对角线的代价都是D:
// 对角线距离h(n) = D * max(abs(n.x - goal.x), abs(n.y - goal.y))
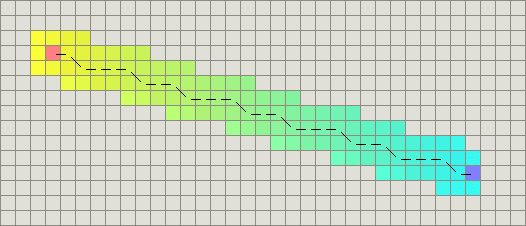
如果对角线运动的代价不是D,但类似于D2 = sqrt(2) *D,则上面的启发函数不准确。你需要一些更准确(原文为sophisticated)的东西:
// 计算h_diagonal(n):沿着斜线可以移动的步数h_diagonal(n) = min(abs(n.x - goal.x), abs(n.y - goal.y))// h_straight(n):曼哈顿距离h_straight(n) = (abs(n.x - goal.x) + abs(n.y - goal.y))// 然后合并这两项,让所有的斜线步都乘以D2,剩下的所有直线步(注意这里是曼哈顿距离的步数减去2倍的斜线步数)都乘以Dh(n) = D2 * h_diagonal(n) + D * (h_straight(n) - 2*h_diagonal(n)))
2.5.3 欧几里得距离
如果你的单位可以沿着任意角度移动(而不是网格方向),那么你也许应该使用直线距离:
h(n) = D * sqrt((n.x-goal.x)^2 + (n.y-goal.y)^2)
然而,如果是这样的话,直接使用A*时将会遇到麻烦,因为代价函数g不会match启发函数h。因为欧几里得距离比曼哈顿距离和对角线距离都短,你仍可以得到最短路径,不过A*将运行得更久一些:
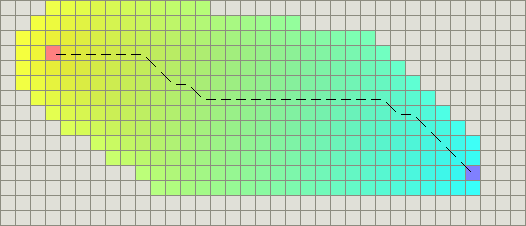
2.5.4 平方后的欧几里得距离
我曾经看到一些A*的网页,其中提到让你通过使用距离的平方而避免欧几里得距离中昂贵的平方根运算:
// THIS is wrong!h(n) = D * ((n.x-goal.x)^2 + (n.y-goal.y)^2)
不要这样做!这明显地导致衡量单位的问题。当A*计算f(n) = g(n) + h(n),距离的平方将比g的代价大很多,并且你会因为启发式函数评估值过高而停止。对于更长的距离,这样做会靠近g(n)的极端情况而不再计算任何东西,A*退化成BFS:
2.5.5 Breaking ties
2.5.6 区域搜索
如果你想搜索邻近目标的任意不确定结点,而不是某个特定的结点,你应该建立一个启发函数h’(x),使得h’(x)为h1(x), h2(x), h3(x)。。。的最小值,而这些h1, h2, h3是邻近结点的启发函数。然而,一种更快的方法是让A*仅搜索目标区域的中心。一旦你从OPEN集合中取得任意一个邻近目标的结点,你就可以停止搜索并建立一条路径了。
3 Implementation notes
3.1 算法流程
3.1.1 基本概念总结
- 启发式搜索:启发式搜索就是在状态空间中的搜索对每一个搜索的位置进行评估,得到最好的位置,再从这个位置进行搜索直到目标。这样可以省略大量无畏的搜索路径,提到了效率。在启发式搜索中,对位置的估价是十分重要的。采用了不同的估价可以有不同的效果。
- 估价函数:从当前节点移动到目标节点的预估费用;这个估计就是启发式的。在寻路问题和迷宫问题中,我们通常用曼哈顿(manhattan)估价函数(下文有介绍)预估费用。
- start:路径规划的起始点,也是机器人当前位置或初始位置A
- goal:路径规划的终点,也是机器人想要到达的位置B
- g_score:当前点到沿着start点A产生的路径到A点的移动耗费
- h_score:不考虑不可通过区域,当前点到goal点B的理论移动耗费
- f_score:g_score+h_score,通常也写为F=G+H
- 开启列表openset:寻路过程中的待检索节点列表
- 关闭列表closeset:不需要再次检索的节点列表
- 追溯表comeFrom:存储父子节点关系的列表,用于追溯生成路径。
3.1.2 算法解析
算法流程参看的是geeksforgeeks,这个上面的是英文写的,但是都比较浅显,非常容易理解。
// A* Search Algorithm1. Initialize the open list2. Initialize the closed listput the starting node on the openlist (you can leave its f at zero)3. while the open list is not emptya) find the node with the least f onthe open list, call it "q"b) pop q off the open listc) generate q's 8 successors and set theirparents to qd) for each successori) if successor is the goal, stop searchsuccessor.g = q.g + distance betweensuccessor and qsuccessor.h = distance from goal tosuccessor (This can be done using manyways, we will discuss three heuristics-Manhattan, Diagonal and EuclideanHeuristics)successor.f = successor.g + successor.hii) if a node with the same position assuccessor is in the OPEN list which has alower f than successor, skip this successoriii) if a node with the same position assuccessor is in the CLOSED list which hasa lower f than successor, skip this successorotherwise, add the node to the open listend (for loop)e) push q on the closed listend (while loop)
3.2 算法实现
我根据上面的代码理解,修改了一下代码,代码量减少了很多
// A C++ Program to implement A* Search Algorithm#include<bits/stdc++.h>using namespace std;#define ROW 9#define COL 10// Creating a shortcut for int, int pair typetypedef pair<int, int> Pair;// Creating a shortcut for pair<int, pair<int, int>> typetypedef pair<double, pair<int, int>> pPair;// A structure to hold the neccesary parametersstruct cell {// Row and Column index of its parent// Note that 0 <= i <= ROW-1 & 0 <= j <= COL-1int parent_i, parent_j;// f = g + hdouble f, g, h;};// A Utility Function to check whether given cell (row, col)// is a valid cell or not.bool isValid(int row, int col){// Returns true if row number and column number// is in rangereturn (row >= 0) && (row < ROW) &&(col >= 0) && (col < COL);}// A Utility Function to check whether the given cell is// blocked or notbool isUnBlocked(int grid[][COL], int row, int col){// Returns true if the cell is not blocked else falseif (grid[row][col] == 1)return (true);elsereturn (false);}// A Utility Function to check whether destination cell has// been reached or notbool isDestination(int row, int col, Pair dest){if (row == dest.first && col == dest.second)return (true);elsereturn (false);}// A Utility Function to calculate the 'h' heuristics.double calculateHValue(int row, int col, Pair dest){// Return using the distance formulareturn ((double) sqrt((row - dest.first)*(row - dest.first)+ (col - dest.second)*(col - dest.second)));}// A Utility Function to trace the path from the source// to destinationvoid tracePath(cell cellDetails[][COL], Pair dest){printf("\nThe Path is ");int row = dest.first;int col = dest.second;stack<Pair> Path;while (!(cellDetails[row][col].parent_i == row&& cellDetails[row][col].parent_j == col)){Path.push(make_pair(row, col));int temp_row = cellDetails[row][col].parent_i;int temp_col = cellDetails[row][col].parent_j;row = temp_row;col = temp_col;}Path.push(make_pair(row, col));while (!Path.empty()){pair<int, int> p = Path.top();Path.pop();printf("-> (%d,%d) ", p.first, p.second);}return;}// traversing neighborsbool TraversingEightNeighbors(cell cellDetails[][COL], Pair dest,bool closedList[][COL], int grid[][COL],set<pPair> &openList, bool &foundDest, int i, int j){/*Generating all the 8 successor of this cellN.W N N.E\ | /\ | /W----Cell----E/ | \/ | \S.W S S.ECell-->Popped Cell (i, j)N --> North (i-1, j)S --> South (i+1, j)E --> East (i, j+1)W --> West (i, j-1)N.E--> North-East (i-1, j+1)N.W--> North-West (i-1, j-1)S.E--> South-East (i+1, j+1)S.W--> South-West (i+1, j-1)*/vector<pair<int, int>> neighborsIndex = {make_pair(i - 1, j),make_pair(i + 1, j),make_pair(i, j + 1),make_pair(i, j - 1),make_pair(i - 1, j + 1),make_pair(i - 1, j - 1),make_pair(i + 1, j + 1),make_pair(i + 1, j - 1)};for (int ind = 0; ind < neighborsIndex.size(); ++ind){int ni = neighborsIndex[ind].first;int nj = neighborsIndex[ind].second;// Only process this cell if this is a valid oneif (isValid(ni, nj) == true){// If the destination cell is the same as the// current successorif (isDestination(ni, nj, dest) == true){// Set the Parent of the destination cellcellDetails[ni][nj].parent_i = i;cellDetails[ni][nj].parent_j = j;printf("The destination cell is found\n");tracePath(cellDetails, dest);foundDest = true;return true;}// If the successor is already on the closed// list or if it is blocked, then ignore it.// Else do the followingelse if (closedList[ni][nj] == false && isUnBlocked(grid, ni, nj) == true){// To store the 'g', 'h' and 'f' of the 8 successorsdouble gNew = cellDetails[i][j].g + 1.0;double hNew = calculateHValue(ni, nj, dest);double fNew = gNew + hNew;// If it isn’t on the open list, add it to// the open list. Make the current square// the parent of this square. Record the// f, g, and h costs of the square cell// OR// If it is on the open list already, check// to see if this path to that square is better,// using 'f' cost as the measure.if (cellDetails[ni][nj].f == FLT_MAX ||cellDetails[ni][nj].f > fNew){openList.insert(make_pair(fNew, make_pair(ni, nj)));// Update the details of this cellcellDetails[ni][nj].f = fNew;cellDetails[ni][nj].g = gNew;cellDetails[ni][nj].h = hNew;cellDetails[ni][nj].parent_i = i;cellDetails[ni][nj].parent_j = j;}}}}return false;}// A Function to find the shortest path between// a given source cell to a destination cell according// to A* Search Algorithmvoid aStarSearch(int grid[][COL], Pair src, Pair dest){// If the source is out of rangeif (isValid(src.first, src.second) == false){printf("Source is invalid\n");return;}// If the destination is out of rangeif (isValid(dest.first, dest.second) == false){printf("Destination is invalid\n");return;}// Either the source or the destination is blockedif (isUnBlocked(grid, src.first, src.second) == false ||isUnBlocked(grid, dest.first, dest.second) == false){printf("Source or the destination is blocked\n");return;}// If the destination cell is the same as source cellif (isDestination(src.first, src.second, dest) == true){printf("We are already at the destination\n");return;}// Create a closed list and initialise it to false which means// that no cell has been included yet// This closed list is implemented as a boolean 2D arraybool closedList[ROW][COL];memset(closedList, false, sizeof(closedList));// Declare a 2D array of structure to hold the details//of that cellcell cellDetails[ROW][COL];int i, j;for (i = 0; i < ROW; i++){for (j = 0; j < COL; j++){cellDetails[i][j].f = FLT_MAX;cellDetails[i][j].g = FLT_MAX;cellDetails[i][j].h = FLT_MAX;cellDetails[i][j].parent_i = -1;cellDetails[i][j].parent_j = -1;}}// Initialising the parameters of the starting nodei = src.first, j = src.second;cellDetails[i][j].f = 0.0;cellDetails[i][j].g = 0.0;cellDetails[i][j].h = 0.0;cellDetails[i][j].parent_i = i;cellDetails[i][j].parent_j = j;/*Create an open list having information as-<f, <i, j>>where f = g + h,and i, j are the row and column index of that cellNote that 0 <= i <= ROW-1 & 0 <= j <= COL-1This open list is implenented as a set of pair of pair.*/set<pPair> openList;// Put the starting cell on the open list and set its// 'f' as 0openList.insert(make_pair(0.0, make_pair(i, j)));// We set this boolean value as false as initially// the destination is not reached.bool foundDest = false;while (!openList.empty()){// Find the node with the least f on the open listpPair p = *openList.begin();// Remove this vertex from the open listopenList.erase(openList.begin());// Add this vertex to the closed listi = p.second.first;j = p.second.second;closedList[i][j] = true;// if find destination, returnif (TraversingEightNeighbors(cellDetails, dest, closedList, grid,openList, foundDest, i, j))return;}// When the destination cell is not found and the open// list is empty, then we conclude that we failed to// reach the destiantion cell. This may happen when the// there is no way to destination cell (due to blockages)if (foundDest == false)printf("Failed to find the Destination Cell\n");return;}// Driver program to test above functionint main(){/* Description of the Grid-1--> The cell is not blocked0--> The cell is blocked */int grid[ROW][COL] ={{1, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 1, 1, 1},{1, 1, 1, 0, 1, 1, 1, 0, 1, 1},{1, 1, 1, 0, 1, 1, 0, 1, 0, 1},{0, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1},{1, 1, 1, 0, 1, 1, 1, 0, 1, 0},{1, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 1, 0, 0},{1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 1},{1, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 1, 1, 1},{1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1}};// Source is the left-most bottom-most cornerPair src = make_pair(8, 0);// Destination is the left-most top-most cornerPair dest = make_pair(0, 0);aStarSearch(grid, src, dest);return (0);}
3.3 算法总结
- 检查grid某位置是否正确 isValid
- 检查是否碰到了障碍物 isUnBlocked
- 检查是否到达目标位置 isDestination
- 计算h值 calculateHValue 有精确方法和近似方法,我们采用近似方法, geeksforgeeks上面介绍了三种近似方法
- closedList 存储的是不需要再检索的位置,使用bool[ ][ ]存储即可
- openList 存储的是待检索的位置,因为还需要对其进行插入和删除操作,选择合适的数据结构就比较重要,本文选择的是set>>,set的特殊性在于内部是按照一定的元素顺序排列的,所以要想取得f_scrore的最小值对应的元素只需要取出set的第一个元素即可
- cellDetails 记录了parent位置,可以用来回溯路径,一个细节是终点的parentshe设置为
cellDetails[ni][nj].parent_i = i;cellDetails[ni][nj].parent_j = j;
所以回溯路径的判断条件是
//最终row和col会达到初始点的位置while (!(cellDetails[row][col].parent_i == row&& cellDetails[row][col].parent_j == col)){Path.push(make_pair(row, col));int temp_row = cellDetails[row][col].parent_i;int temp_col = cellDetails[row][col].parent_j;row = temp_row;col = temp_col;}
