@Team
2018-05-24T04:37:56.000000Z
字数 20180
阅读 2933
SSD源码解析
薛坤军
一.本文主要内容
SSD理论总结(SSD: Single Shot MultiBox Detector)
- Model
-
SSD模型采用VGG16作为基础网络结构(base network),在base network 之后添加了额外的网络结构,如下图所示:
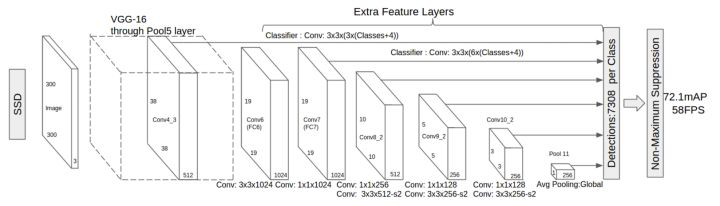
-
1. Multi-scale feature maps for detection
在base network(VGG16的前5层)之后添加了额外的卷基层,具体利用astrous算法将fc6和fc7层转化为两个卷积层,再额外增加3个卷基层(Conv:1*1+Conv:3*3)和一个平均池化层(Avg Pooling,论文中是一个Conv:1*1+Conv:3*3,具有相同作用);
这里我们在网络的所有特征图上应用3*3卷积进行预测,来自较低层的预测有助于处理较小的物体。因为低层的feature map的感受野较小。这意味着可以通过使用与感受野大小相似的feature map来处理大小不同的对象,即达到多尺度特征图检测的目的;
关键代码解析:
#部分初始化参数class SSDNet(object):"""Implementation of the SSD VGG-based 300 network.The default features layers with 300x300 image input are:多尺度feature map检测位置conv4 ==> 38 x 38conv7 ==> 19 x 19conv8 ==> 10 x 10conv9 ==> 5 x 5conv10 ==> 3 x 3conv11 ==> 1 x 1The default image size used to train this network is 300x300."""default_params = SSDParams(img_shape=(300, 300),#输入图像尺寸num_classes=21,#类别数量,20+1(背景)no_annotation_label=21,#多尺度feature map检测位置feat_layers=['block4', 'block7', 'block8', 'block9', 'block10', 'block11'],#feature map尺寸feat_shapes=[(38, 38), (19, 19), (10, 10), (5, 5), (3, 3), (1, 1)],#最低层、最高层default box大小,可根据需要进行修改anchor_size_bounds=[0.15, 0.90],#anchor_size_bounds=[0.20, 0.90],(原论文中的值)#default box大小anchor_sizes=[(21., 45.),(45., 99.),(99., 153.),(153., 207.),(207., 261.),(261., 315.)],# anchor_sizes=[(30., 60.),# (60., 111.),# (111., 162.),# (162., 213.),# (213., 264.),# (264., 315.)],#default box的长宽比例anchor_ratios=[[2, .5],[2, .5, 3, 1./3],[2, .5, 3, 1./3],[2, .5, 3, 1./3],[2, .5],[2, .5]],#default box中心位置间隔anchor_steps=[8, 16, 32, 64, 100, 300],anchor_offset=0.5,#补偿阈值#该特征图是否进行正则化,大于0正则化normalizations=[20, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1],prior_scaling=[0.1, 0.1, 0.2, 0.2])#定义SSD网络结构def ssd_net(input,num_classes=SSDNet.default_params.num_classes,feat_layers=SSDNet.default_params.feat_layers,anchor_sizes=SSDNet.default_params.anchor_sizes,anchor_ratios=SSDNet.default_params.anchor_ratios,normalizations=SSDNet.default_params.normalizations,is_training=True,dropout_keep_prob=0.5,prediction_fn=slim.softmax,reuse=None,scope='ssd_300_vgg'):"""SSD net definition."""# End_points collect relevant activations for external use.#存储每层feature map的输出结果end_points = {}with tf.variable_scope(scope, 'ssd_300_vgg', [inputs], reuse=reuse):# ========Original VGG-16 blocks========net = slim.repeat(input, 2, slim.conv2d, 64, [3, 3], scope='conv1')end_points['block1'] = netnet = slim.max_pool2d(net, [2, 2], scope='pool1', padding='SAME')# Block 2.net = slim.repeat(net, 2, slim.conv2d, 128, [3, 3], scope='conv2')end_points['block2'] = netnet = slim.max_pool2d(net, [2, 2], scope='pool2', padding='SAME')# Block 3.net = slim.repeat(net, 3, slim.conv2d, 256, [3, 3], scope='conv3')end_points['block3'] = netnet = slim.max_pool2d(net, [2, 2], scope='pool3', padding='SAME')# Block 4.net = slim.repeat(net, 3, slim.conv2d, 512, [3, 3], scope='conv4')#第一个用于预测的feature map,shape为(batch_size, 38, 38, 512)end_points['block4'] = netnet = slim.max_pool2d(net, [2, 2], scope='pool4', padding='SAME')# Block 5.net = slim.repeat(net, 3, slim.conv2d, 512, [3, 3], scope='conv5')end_points['block5'] = netnet = slim.max_pool2d(net, [3, 3], stride=1, scope='pool5', padding='SAME')# Additional SSD blocks.# Block 6: let's dilate the hell out of it!net = slim.conv2d(net, 1024, [3, 3], rate=6, scope='conv6')end_points['block6'] = netnet = tf.layers.dropout(net, rate=dropout_keep_prob, training=is_training)# Block 7: 1x1 conv. Because the fuck.net = slim.conv2d(net, 1024, [1, 1], scope='conv7')#第二个用于预测的feature map,shape为(batch_size, 19, 19, 1024)end_points['block7'] = netnet = tf.layers.dropout(net, rate=dropout_keep_prob, training=is_training)# Block 8/9/10/11: 1x1 and 3x3 convolutions stride 2 (except lasts)end_point = 'block8'with tf.variable_scope(end_point):net = slim.conv2d(net, 256, [1, 1], scope='conv1x1')net = custom_layers.pad2d(net, pad=(1, 1))net = slim.conv2d(net, 512, [3, 3], stride=2, scope='conv3x3', padding='VALID')#第三个用于预测的feature map,shape为(batch_size, 10, 10, 512)end_points[end_point] = netend_point = 'block9'with tf.variable_scope(end_point):net = slim.conv2d(net, 128, [1, 1], scope='conv1x1')net = custom_layers.pad2d(net, pad=(1, 1))net = slim.conv2d(net, 256, [3, 3], stride=2, scope='conv3x3', padding='VALID')#第四个用于预测的feature map,shape为(batch_size, 5, 5, 256)end_points[end_point] = netend_point = 'block10'with tf.variable_scope(end_point):net = slim.conv2d(net, 128, [1, 1], scope='conv1x1')net = slim.conv2d(net, 256, [3, 3], scope='conv3x3', padding='VALID')#第五个用于预测的feature map,shape为(batch_size, 3, 3, 256)end_points[end_point] = netend_point = 'block11'with tf.variable_scope(end_point):net = slim.conv2d(net, 128, [1, 1], scope='conv1x1')net = slim.conv2d(net, 256, [3, 3], scope='conv3x3', padding='VALID')#第六个用于预测的feature map,shape为(batch_size, 1, 1, 256)end_points[end_point] = net# Prediction and localisations layers.predictions = []logits = []localisations = []for i, layer in enumerate(feat_layers):with tf.variable_scope(layer + '_box'):#预测bbox的位置(相对于default box的偏移)以及类别p, l = ssd_multibox_layer(end_points[layer],num_classes,anchor_sizes[i],anchor_ratios[i],normalizations[i])#softmaxpredictions.append(prediction_fn(p))#类别概率logits.append(p)#bbox相对于default box的偏移localisations.append(l)return predictions, localisations, logits, end_pointsssd_net.default_image_size = 300
-
测试使用的是tf-1.1.0版本,使用300*300的图片feature map的shape和预期不一样,因此在源码中做了改动,即在max_pool添加参数padding='SAME'。
-
2. Convolutional predictors for detection
- 每一个用于预测的特征层(base network之后的feature map),使用一系列 convolutional filters,产生一系列固定大小(即每个特征图预测的尺度是固定的)的 predictions。对于一个 m×n,具有 p 通道的feature map,使用的convolutional filters 是 3×3 的 kernels。预测default box的类别和偏移位置;
- YOLO 则是用一个全连接层来代替这里的卷积层,全连接层导致输入大小必须固定;
- 关键代码分析:
##在特征图上进行预测(偏移位置,类别概率)"""inpouts:['block4', 'block7', 'block8', 'block9', 'block10', 'block11']num_classes:21sizes:[(21.,45.),(45.,99.),(99.,153.), (153.,207.),(207.,261.),(261.,315.)]ratios:[[2, .5],[2, .5, 3, 1./3],[2, .5, 3, 1./3],[2, .5, 3, 1./3],[2, .5],[2,.5]]参数一一对应"""def ssd_multibox_layer(inputs,num_classes,sizes,ratios=[1],normalization=-1,bn_normalization=False):"""Construct a multibox layer, return a class and localization predictions."""net = inputs#正则化if normalization > 0:net = custom_layers.l2_normalization(net, scaling=True)# Number of anchors.#此feature map每个位置对应的default box个数#len(size)表示长宽比例为1的的个数#len(ratios)表示其它长宽比例num_anchors = len(sizes) + len(ratios)# Location.#位置num_loc_pred = num_anchors * 4#卷积预测器,为每个bbox预测位置"""输出:(batch_size, 38, 38,num_loc_pred)(batch_size, 19, 19,num_loc_pred)(batch_size, 10, 10,num_loc_pred)(batch_size, 5, 5,num_loc_pred)(batch_size, 3, 3,num_loc_pred)(batch_size, 1, 1,num_loc_pred)"""loc_pred = slim.conv2d(net, num_loc_pred, [3, 3], activation_fn=None,scope='conv_loc')loc_pred = custom_layers.channel_to_last(loc_pred)loc_pred = tf.reshape(loc_pred,tensor_shape(loc_pred, 4)[:-1]+[num_anchors, 4])# Class prediction.#卷积预测器,为每个bbox预测类别num_cls_pred = num_anchors * num_classescls_pred = slim.conv2d(net,num_cls_pred,[3, 3],activation_fn=None,scope='conv_cls')cls_pred = custom_layers.channel_to_last(cls_pred)cls_pred = tf.reshape(cls_pred,tensor_shape(cls_pred, 4)[:-1]+[num_anchors, num_classes])return cls_pred, loc_pred
-
3. Default boxes and aspect ratios(长宽比)
-
- 在每一个用于预测的feature map上得到default boxes,default boxes的数量、尺寸、长宽比由网络结构固定而固定;
-
- 关键代码解析:
#为特征每个feature map生成固定的default boxdef ssd_anchor_one_layer(img_shape,feat_shape,sizes,ratios,step,offset=0.5,dtype=np.float32):"""Computer SSD default anchor boxes for one feature layer.Determine the relative position grid of the centers, and the relativewidth and height.Arguments:feat_shape: Feature shape, used for computing relative position grids;size: Absolute reference sizes;ratios: Ratios to use on these features;img_shape: Image shape, used for computing height, width relatively to theformer;offset: Grid offset.Return:y, x, h, w: Relative x and y grids, and height and width."""# Compute the position grid: simple way.# y, x = np.mgrid[0:feat_shape[0], 0:feat_shape[1]]# y = (y.astype(dtype) + offset) / feat_shape[0]# x = (x.astype(dtype) + offset) / feat_shape[1]# Weird SSD-Caffe computation using steps values...#以(38*38)的feature map为例生成default box#理解为feature map对应的y轴坐标,x轴坐标"""y的shape(38,38),值为:np.array([[0,0,0,...,0,0,0],[1,1,1,...,1,1,1],......[37,37,37,...,37,37,37]])x的shape(38,38),值为:np.array([[0,1,2,...,35,36,37],[0,1,2,...,35,36,37],......[0,1,2,...,35,36,37]])"""y, x = np.mgrid[0:feat_shape[0], 0:feat_shape[1]]#将feature map的点对应到原始图像上并归一化[0-1]#y = (y + 0.5) * 8/300#x = (x + 0.5) * 8/300#x,y为default box在原始图片中的中心位置,并归一化[0-1]y = (y.astype(dtype) + offset) * step / img_shape[0]x = (x.astype(dtype) + offset) * step / img_shape[1]# Expand dims to support easy broadcasting.#扩展维度,shape为(38,38,1)y = np.expand_dims(y, axis=-1)x = np.expand_dims(x, axis=-1)# Compute relative height and width.# Tries to follow the original implementation of SSD for the order.#anchors的数量#feature map每个点对应的default box 的数量num_anchors = len(sizes) + len(ratios)#default box 的高和宽h = np.zeros((num_anchors, ), dtype=dtype)w = np.zeros((num_anchors, ), dtype=dtype)# Add first anchor boxes with ratio=1.##长宽比例为1的default box,高和宽都为21/300h[0] = sizes[0] / img_shape[0]w[0] = sizes[0] / img_shape[1]di = 1#长宽比例为1的default box额外添加一个尺寸为sqrt(Sk*Sk+1)的default boxif len(sizes) > 1:#宽高都为sqrt(21*45)h[1] = math.sqrt(sizes[0] * sizes[1]) / img_shape[0]w[1] = math.sqrt(sizes[0] * sizes[1]) / img_shape[1]di += 1#剩余长宽比的default boxfor i, r in enumerate(ratios):h[i+di] = sizes[0] / img_shape[0] / math.sqrt(r)w[i+di] = sizes[0] / img_shape[1] * math.sqrt(r)#返回default box的中心位置以及宽和高#y,x的shape为(38,38,1)#h,w的shape为(4,)return y, x, h, wdef ssd_anchors_all_layers(img_shape,#原始图像的shapelayers_shape,#特征图shapeanchor_sizes,#default box尺寸anchor_ratios,#长宽比例anchor_steps,offset=0.5,dtype=np.float32):"""Compute anchor boxes for all feature layers.""""""params:img_shape: (300,300)layers_shape: [(38,38),(19,19),(10,10),(5,5),(3,3),(1,1)]21,45,99,153,207,261anchor_sizes: [(21,45),(45,99),(99,153),(153,207),(207,261),(261,315)]anchor_ratios:[[2,.5],[2,.5,3,1./3],[2,.5,3,1./3],[2,.5,3,1./3],[2,.5],[2,.5]]anchor_steps: [8,16,32,64,100,300]offset: 0.5"""layers_anchors = []#enumerate,python的内置函数返回索引、内容"""即:0,(38,38)1,(19,19)2,(10,10)3,(5,5)4,(3,3)5,(1,1)"""for i, s in enumerate(layers_shape):anchor_bboxes = ssd_anchor_one_layer(img_shape, s,anchor_sizes[i],anchor_ratios[i],anchor_steps[i],offset=offset,dtype=dtype)layers_anchors.append(anchor_bboxes)return layers_anchors
- 训练
-
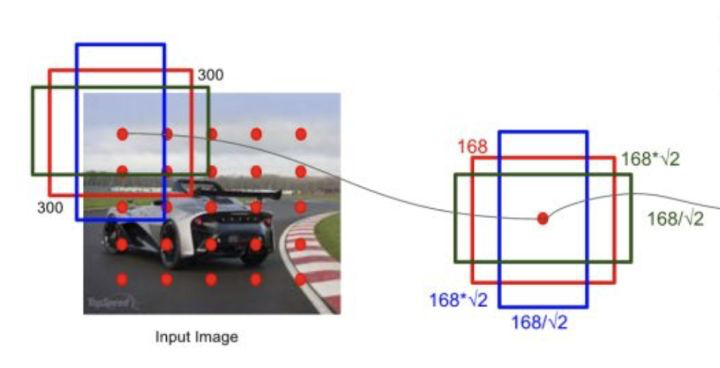
1. 生成default box
- 对每种尺寸的feature map,按照相应的大小(scale)和宽高比例(ratio)在每个点生成固定数量的default box,也就是说,SSD中的default box是由网络结构固定而固定的,如下图(仅仅是为了举例),红色点代表feature map(5*5),每个位置预测3个default box,尺寸为168,宽高比为1,1/2,2,则default box宽高分别为([168,168], [],[ ]);
-
- 生成default box:
- 首先设计出最小和最大default box的尺寸[ ],即越底层的feature map对应的default box尺寸越小(感受野越小,更适合检测小尺寸对象),论文中为[0.2,0.9],上述代码中为[0.15,0.9];
- 每个feature map(由低层到高层)对应的default box的尺寸计算公式为: ,为feature map数量;
- 每个尺寸的default box宽高根据比例值计算,如下所示:
宽:,高:为default box尺寸;
比例为1的默认框,额外添加一个尺寸为的default box;
每个默认框中心设定为为特征图尺寸;
- 生成default box:
-
2. 生成训练数据
- 根据图片的ground truth和default box生成训练数据,关键代码解析如下:
#gt编码函数#labels:gt的类别#bboxes:gt的位置#anchors:default box的位置#num_class:类别数量#no_annotation_label:21#ignore_threshold=0.5,阈值#prior_scaling=[0.1, 0.1, 0.2, 0.2],缩放def tf_ssd_bboxes_encode(labels, bboxes, anchors, num_classes,no_annotation_label, ignore_threshold=0.5,prior_scaling=[0.1, 0.1, 0.2, 0.2],dtype=tf.float32, scope='ssd_bboxes_encode'):"""Encode groundtruth labels and bounding boxes using SSD net anchors.Encoding boxes for all feature layers.Arguments:labels: 1D Tensor(int64) containing groundtruth labels;bboxes: Nx4 Tensor(float) with bboxes relative coordinates;anchors: List of Numpy array with layer anchors;matching_threshold: Threshold for positive match with groundtruth bboxes;prior_scaling: Scaling of encoded coordinates.Return:(target_labels, target_localizations, target_scores):Each element is a list of target Tensors."""with tf.name_scope(scope):target_labels = []target_localizations = []target_scores = []for i, anchors_layer in enumerate(anchors):with tf.name_scope('bboxes_encode_block_%i' % i):#处理每个尺寸的default box(对应一层的feature map),生成训练数据t_labels, t_loc, t_scores = \tf_ssd_bboxes_encode_layer(labels, bboxes,anchors_layer,num_classes,no_annotation_label,ignore_threshold,prior_scaling, dtype)target_labels.append(t_labels)target_localizations.append(t_loc)target_scores.append(t_scores)return target_labels, target_localizations, target_scores
- 处理每个尺寸的default box(对应一层的feature map),生成训练数据,关键代码解析,以shape为(38,38)feature map为例:
-
- 本代码块中对于每一个anchor和所有的gt计算重叠度,anchor的类别为重叠度最高的gt的类别,偏移位置为相对于重叠度最高的gt的偏移位置;
- 给定输入图像以及每个物体的 ground truth,首先找到每个gt对应的default box中重叠度最大的作为(与该ground true box相关的匹配)正样本。然后,在剩下的default box中找到那些与任意一个ground truth box 的 IOU 大于 0.5的default box作为(与该ground true box相关的匹配)正样本。剩余的default box 作为负例样本;
- 一个anchor对应一个gt,而一个gt可能对应多个anchor;
#labels:gt的类别#bboxes:gt的位置#anchors_layer:特定feature map的default box的位置#num_class:类别数量#no_annotation_label:21#ignore_threshold=0.5,阈值#prior_scaling=[0.1, 0.1, 0.2, 0.2],缩放def tf_ssd_bboxes_encode_layer(labels,bboxes,anchors_layer,num_classes,no_annotation_label,ignore_threshold=0.5,prior_scaling=[0.1, 0.1, 0.2, 0.2],dtype=tf.float32):"""Encode groundtruth labels and bounding boxes using SSD anchors fromone layer.Arguments:labels: 1D Tensor(int64) containing groundtruth labels;bboxes: Nx4 Tensor(float) with bboxes relative coordinates;anchors_layer: Numpy array with layer anchors;matching_threshold: Threshold for positive match with groundtruth bboxes;prior_scaling: Scaling of encoded coordinates.Return:(target_labels, target_localizations, target_scores): Target Tensors."""# Anchors coordinates and volume.#anchors的中心坐标,以及宽高#shape为(38,38,1),(38,38,1),(4,),(4,)yref, xref, href, wref = anchors_layerymin = yref - href / 2.#anchor的下边界,(38,38,4)xmin = xref - wref / 2.#anchor的左边界,(38,38,4)ymax = yref + href / 2.#anchor的上边界,(38,38,4)xmax = xref + wref / 2.#anchor的右边界,(38,38,4)vol_anchors = (xmax - xmin) * (ymax - ymin)#anchor的面积,(38,38,4)# Initialize tensors...#(38,38,4)shape = (yref.shape[0], yref.shape[1], href.size)feat_labels = tf.zeros(shape, dtype=tf.int64)feat_scores = tf.zeros(shape, dtype=dtype)feat_ymin = tf.zeros(shape, dtype=dtype)feat_xmin = tf.zeros(shape, dtype=dtype)feat_ymax = tf.ones(shape, dtype=dtype)feat_xmax = tf.ones(shape, dtype=dtype)#计算jaccard重合度#box存储的是gt的四个边界位置,并且都进行了归一化def jaccard_with_anchors(bbox):"""Compute jaccard score between a box and the anchors."""#获取gt和anchors重合的部分int_ymin = tf.maximum(ymin, bbox[0])int_xmin = tf.maximum(xmin, bbox[1])int_ymax = tf.minimum(ymax, bbox[2])int_xmax = tf.minimum(xmax, bbox[3])h = tf.maximum(int_ymax - int_ymin, 0.)w = tf.maximum(int_xmax - int_xmin, 0.)# Volumes.inter_vol = h * w#计算重叠部分面积union_vol = vol_anchors - inter_vol \+ (bbox[2] - bbox[0]) * (bbox[3] - bbox[1])jaccard = tf.div(inter_vol, union_vol)return jaccard#返回重合度#计算重叠部分面积占anchor面积的比例def intersection_with_anchors(bbox):"""Compute intersection between score a box and the anchors."""int_ymin = tf.maximum(ymin, bbox[0])int_xmin = tf.maximum(xmin, bbox[1])int_ymax = tf.minimum(ymax, bbox[2])int_xmax = tf.minimum(xmax, bbox[3])h = tf.maximum(int_ymax - int_ymin, 0.)w = tf.maximum(int_xmax - int_xmin, 0.)inter_vol = h * wscores = tf.div(inter_vol, vol_anchors)return scores#tf.while_loop的条件def condition(i, feat_labels, feat_scores,feat_ymin, feat_xmin, feat_ymax, feat_xmax):"""Condition: check label index."""#返回I<tf.shape(labels)是否为真r = tf.less(i, tf.shape(labels))return r[0]#tf.while_loop的主体def body(i, feat_labels, feat_scores,feat_ymin, feat_xmin, feat_ymax, feat_xmax):"""Body: update feature labels, scores and bboxes.Follow the original SSD paper for that purpose:- assign values when jaccard > 0.5;- only update if beat the score of other bboxes."""# Jaccard score.#第i个gt的类别和位置label = labels[i]bbox = bboxes[i]#计算gt和每一个anchor的重合度jaccard = jaccard_with_an4chors(bbox)# Mask: check threshold + scores + no annotations + num_classes.#比较两个值的大小来输出对错,大于输出true,shape(38,38,4)#feat_scores存储的是anchor和gt重叠度最高的值mask = tf.greater(jaccard, feat_scores)#mask = tf.logical_and(mask,tf.greater(jaccard,matching_threshold))#逻辑与mask = tf.logical_and(mask, feat_scores > -0.5)mask = tf.logical_and(mask, label < num_classes)imask = tf.cast(mask, tf.int64)fmask = tf.cast(mask, dtype)# Update values using mask.#根据imask更新类别,和位置#imask表示本轮anchor和gt重合度之前gt的重合度,1-imask保留之前的结果#更新anchor的类别标签feat_labels = imask * label + (1 - imask) * feat_labels#jaccard返回true对应的值,feat_scores返回false对应的值#更新anchor与gt的重合度,为每个anchor保留重合度最大值feat_scores = tf.where(mask, jaccard, feat_scores)#更新anchor对应的gt(具有最大重合度)feat_ymin = fmask * bbox[0] + (1 - fmask) * feat_yminfeat_xmin = fmask * bbox[1] + (1 - fmask) * feat_xminfeat_ymax = fmask * bbox[2] + (1 - fmask) * feat_ymaxfeat_xmax = fmask * bbox[3] + (1 - fmask) * feat_xmax# Check no annotation label: ignore these anchors...# interscts = intersection_with_anchors(bbox)# mask = tf.logical_and(interscts > ignore_threshold,# label == no_annotation_label)# # Replace scores by -1.# feat_scores = tf.where(mask, -tf.cast(mask, dtype), feat_scores)return [i+1, feat_labels, feat_scores,feat_ymin, feat_xmin, feat_ymax, feat_xmax]# Main loop definition.i = 0[i, feat_labels, feat_scores,feat_ymin, feat_xmin,feat_ymax, feat_xmax] = tf.while_loop(condition, body,[i, feat_labels, feat_scores,feat_ymin, feat_xmin,feat_ymax, feat_xmax])# Transform to center / size.#计算anchor对应的gt的中心位置以及宽和高feat_cy = (feat_ymax + feat_ymin) / 2.feat_cx = (feat_xmax + feat_xmin) / 2.feat_h = feat_ymax - feat_yminfeat_w = feat_xmax - feat_xmin# Encode features.#计算anchor与对应的gt的偏移位置feat_cy = (feat_cy - yref) / href / prior_scaling[0]feat_cx = (feat_cx - xref) / wref / prior_scaling[1]feat_h = tf.log(feat_h / href) / prior_scaling[2]feat_w = tf.log(feat_w / wref) / prior_scaling[3]# Use SSD ordering: x / y / w / h instead of ours.feat_localizations = tf.stack([feat_cx, feat_cy, feat_w, feat_h], axis=-1)#返回每个anchor的类别标签,以及anchor和对应gt的偏移,anchor与对应gt的重合度return feat_labels, feat_localizations, feat_scores
- 3.损失函数
-
SSD损失函数分为两部分:
localization loss(loc)
confidence loss(conf)
-
定义, 表示 第 个 default box 与第 个 ground truth box 相匹配,类别为,若不匹配的话,值为0。
-
训练对象为:
- ,为匹配default box,;
- 为预测框和ground truth box 的 ,定义如下:
-
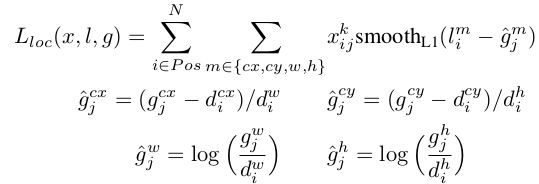
- 为预测框,为ground truth, 为defaultbox,我们对偏移位置进行回归。 为多类别softmax loss,定义如下, 通过交叉验证将设为1 :
-
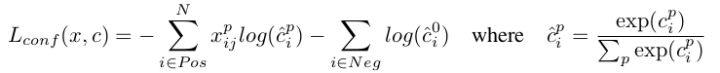
- 关键代码分析:
#SSD损失函数定义#logits:预测的类别#localisations:预测的偏移位置#gclasses:default box相对于gt的类别#glocalisations:default box相对于gt的偏移位置#gscores:default box和gt的重叠度def ssd_losses(logits, localisations,gclasses, glocalisations, gscores,match_threshold=0.5,negative_ratio=3.,alpha=1.,label_smoothing=0.,device='/cpu:0',scope=None):with tf.name_scope(scope, 'ssd_losses'):lshape = tfe.get_shape(logits[0], 5)#类别数量num_classes = lshape[-1]batch_size = lshape[0]# Flatten out all vectors!flogits = []fgclasses = []fgscores = []flocalisations = []fglocalisations = []#处理所有尺寸feature map的预测结果#(38,38),(19,19),(10,10),(5,5),(3,3),(1,1)for i in range(len(logits)):#预测的类别(38*38*4, 21)flogits.append(tf.reshape(logits[i], [-1, num_classes]))#真实类别(38*38*4)fgclasses.append(tf.reshape(gclasses[i], [-1]))#重叠度(38*38*4)fgscores.append(tf.reshape(gscores[i], [-1]))#预测偏移位置,(38*38*4, 4)flocalisations.append(tf.reshape(localisations[i], [-1, 4]))#真实偏移位置,(38*38*4, 4)fglocalisations.append(tf.reshape(glocalisations[i], [-1, 4]))# And concat the crap!logits = tf.concat(flogits, axis=0)gclasses = tf.concat(fgclasses, axis=0)gscores = tf.concat(fgscores, axis=0)localisations = tf.concat(flocalisations, axis=0)glocalisations = tf.concat(fglocalisations, axis=0)dtype = logits.dtype# Compute positive matching mask...#获取重叠度>0.5的default box个数,即损失函数中的N,正例样本位置pmask = gscores > match_thresholdfpmask = tf.cast(pmask, dtype)n_positives = tf.reduce_sum(fpmask)# Hard negative mining...no_classes = tf.cast(pmask, tf.int32)#将输出类别对应的softmaxpredictions = slim.softmax(logits)#逻辑与,获得负类样本的位置nmask = tf.logical_and(tf.logical_not(pmask),gscores > -0.5)fnmask = tf.cast(nmask, dtype)#获得负例样本对应的概率nvalues = tf.where(nmask,predictions[:, 0],1. - fnmask)nvalues_flat = tf.reshape(nvalues, [-1])# Number of negative entries to select.#负例样本数目,保证正负样本数目为1:3max_neg_entries = tf.cast(tf.reduce_sum(fnmask), tf.int32)n_neg = tf.cast(negative_ratio * n_positives, tf.int32)+batch_sizen_neg = tf.minimum(n_neg, max_neg_entries)val, idxes = tf.nn.top_k(-nvalues_flat, k=n_neg)max_hard_pred = -val[-1]# Final negative mask.nmask = tf.logical_and(nmask, nvalues < max_hard_pred)fnmask = tf.cast(nmask, dtype)# Add cross-entropy loss.#正样本概率损失函数with tf.name_scope('cross_entropy_pos'):loss = tf.nn.sparse_softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits(logits=logits,labels=gclasses)loss = tf.div(tf.reduce_sum(loss * fpmask),batch_size, name='value')tf.losses.add_loss(loss)#负样本概率损失函数with tf.name_scope('cross_entropy_neg'):loss = tf.nn.sparse_softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits(logits=logits,labels=no_classes)loss = tf.div(tf.reduce_sum(loss * fnmask),batch_size, name='value')tf.losses.add_loss(loss)# Add localization loss: smooth L1, L2, ...#位置损失函数with tf.name_scope('localization'):# Weights Tensor: positive mask + random negative.weights = tf.expand_dims(alpha * fpmask, axis=-1)loss = custom_layers.abs_smooth(localisations - glocalisations)loss = tf.div(tf.reduce_sum(loss * weights),batch_size,name='value')tf.losses.add_loss(loss)
-
4. Hard Negative Mining
- 绝大多数的default box都是负例样本,导致正负样本不平衡,训练时采用Hard Negative Mining策略(使正负样本比例为1:3)来平衡正负样本比例。
总结
- 本文总结论文中的关键点,并对关键源码进行分析。在读完论文之后有很多不明确的地方,阅读了源码之后,豁然开朗
- 本文主要讲解了SSD的多尺度特征图检测、default box的生成、训练数据预处理、目标函数。
