@adamhand
2019-03-04T01:21:17.000000Z
字数 12535
阅读 1252
leetcode之mysql题解
176. Second Highest Salary
Write a SQL query to get the second highest salary from the Employee table.
+----+--------+| Id | Salary |+----+--------+| 1 | 100 || 2 | 200 || 3 | 300 |+----+--------+
For example, given the above Employee table, the query should return 200 as the second highest salary. If there is no second highest salary, then the query should return null.
+---------------------+| SecondHighestSalary |+---------------------+| 200 |+---------------------+
需要注意对查询条件为null这种情况的处理。下面给出建表、插入数据和选择语句。
create table Employee(Id bigint not null primary key auto_increment,Salary bigint not null)engine=InnoDB;insert into Employee (Id,Salary)values(1,100),(2,200),(3,300);selectifnull((select distinct Salaryfrom Employeeorder by Salary desclimit 1 offset 1),null)as SecondHighestSalary;
ifnull()(expr1,expr2)函数的含义是:如果第一个参数不为空,则返回第一个参数,否则返回第二个参数。
196. Delete Duplicate Emails
题目描述:
Write a SQL query to delete all duplicate email entries in a table named Person, keeping only unique emails based on its smallest Id.
+----+------------------+| Id | Email |+----+------------------+| 1 | john@example.com || 2 | bob@example.com || 3 | john@example.com |+----+------------------+
Id is the primary key column for this table.For example, after running your query, the above Person table should have the following rows:
+----+------------------+| Id | Email |+----+------------------+| 1 | john@example.com || 2 | bob@example.com |+----+------------------+
Note:Your output is the whole Person table after executing your sql. Use delete statement.
思路:
这个题可以使用cross join来解决。cross join其实就是笛卡尔积,执行cross join时会将两个表相乘。它的写法有:
SELECT * FROM table1 CROSS JOIN table2SELECT * FROM table1,table2
比如,有一个Person表和一个Employee表,它们的结构分别如下:
# Person+----+------------------+| Id | Email |+----+------------------+| 1 | john@example.com || 2 | bob@example.com || 3 | john@example.com |+----+------------------+#Employee+----+--------+| Id | Salary |+----+--------+| 1 | 100 || 2 | 200 || 3 | 300 |+----+--------+
当执行
select* from Employee e, Person p;
时的结果如下:
+----+--------+----+------------------+| Id | Salary | Id | Email |+----+--------+----+------------------+| 1 | 100 | 1 | john@example.com || 2 | 200 | 1 | john@example.com || 3 | 300 | 1 | john@example.com || 1 | 100 | 2 | bob@example.com || 2 | 200 | 2 | bob@example.com || 3 | 300 | 2 | bob@example.com || 1 | 100 | 3 | john@example.com || 2 | 200 | 3 | john@example.com || 3 | 300 | 3 | john@example.com |+----+--------+----+------------------+
可以看到,最终得到的表结构是将前一个表的每一行分别和后一个表的第一行、第二行...连接形成的。
对于本题而言,就可以按照如下语句选择出合适的行:
SELECT p1.*FROM Person p1,Person p2WHEREp1.Email = p2.Email AND p1.Id > p2.Id;
将select语句替换成delete语句就可以了:
delete p1 from Person p1,Person p2wherep1.Email = p2.Email and p1.Id > p2.Id;
最后附上建表和插入语句:
drop table if exists Person;create table Person(Id tinyint not null primary key auto_increment,Email varchar(30) not null)engine=InnoDB;insert into Person (Id, Email)values(1,'john@example.com'),(2,'bob@example.com'),(3,'john@example.com');
mysql中的join小结
join称为连接,连接的主要作用是根据两个或多个表中的列之间的关系,获取存在于不同表中的数据。连接可以分为以下几类:
- 内连接:在
mysql中以关键字inner join表示 - 外连接
- 左外连接:在
mysql中以关键字left join表示 - 右外连接:在
mysql中以关键字rign join表示
- 左外连接:在
- 交叉连接:在
mysql中以关键字cross join表示,在mysql中,交叉连接和内连接功能等价 - 全连接:
mysql没有具体的关键字来表示,但是可以通过union关键字实现;oracle提供了full join关键字完成这一功能。
下面通过具体的例子来分析。假如有两个表t1和t2,建表和插入语句如下:
drop table if exists t1;create table t1(id tinyint not null primary key auto_increment,name varchar(30) not null,description varchar(255) default null)engine=InnoDB;create table t2 like t1;insert into t1 values(1,'林丹','获得12奥运会冠军'),(2,'李宗伟','获得12奥运会亚军'),(3,'谌龙','获得12奥运会季军');insert into t2 values(1,'谌龙','获得16奥运会冠军'),(2,'李宗伟','获得16奥运会亚军'),(3,'安赛龙','获得16奥运会季军');
两个表的结构分别如下:
表
t1 表
t2 交叉连接(cross join)
cross join指的就是两个表的笛卡尔积。上面说了,在Mysql中,Cross Join 和 Inner Join 是等价的,但是在标准SQL中,它们并不等价,Inner Join 用于带有on表达式的连接,反之用Cross Join。
以下几种方式均可以产生笛卡尔积:
select * from t1 cross join t2;select * from t1 inner join t2;select * from t1 join t2;select * from t1,t2;select * from t1 nature join t2;select * from t1 natura join t2;
产生的结果集为:
内连接(inner join)
通过上面的可以看到,内连接和交叉连接在mysql中的效果是一样的。但是内连接一般会配合on一起使用,用于在结果选出符合某个条件的记录,即两个表的交集。
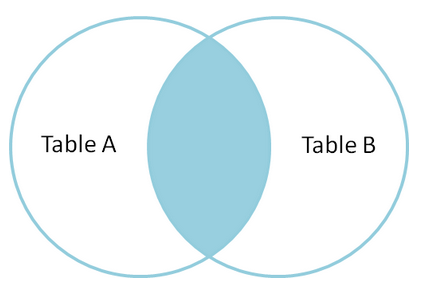
下面的语句是在cross join集中选择name字段相等的记录。
select * from t1 inner join t2 on t1.name=t2.name;
产生的结果集如下:
下面的语句是只在t1中选择,而不是在cross join集中。tt1和tt2是交叉表中左右两个表的名字。
select tt1.*fromt1 tt1inner joint2 tt2on tt1.name=tt2.name;# 不取实例,和上面语句的结果一样select t1.*fromt1inner joint2on t1.name=t2.name;
产生的结果集如下:
左外连接(left join)
从左表产生一套完整的记录,还有右边匹配的记录,如果没有匹配就包含null。
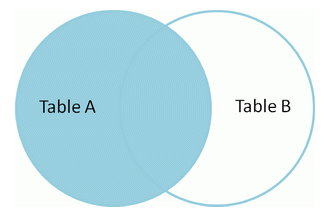
select *fromt1 tt1left joint2 tt2 on tt1.name=tt2.name;
产生的结果集如下:
只查询左表的数据,不包含右表的,使用where 限制右表key为null。
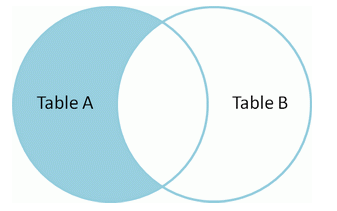
select *fromt1 tt1left joint2 tt2on tt1.name=tt2.namewhere tt2.name is null;
产生的结果集如下:
右外连接(right join)
从右表产生一套完整的记录,还有左边匹配的记录,如果没有匹配就包含null。和上述左连接类似。
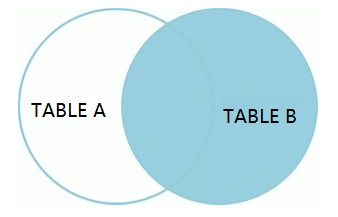
需要注意的是,左连接表1、表2等价于右连接表2、表1。
#这两个语句等价select * from t2 right join t1 using(name);select * from t1 left join t2 using(name);
产生的结果集如下:
只查询右表的数据,不包含左表的,使用where 限制右表key为null。
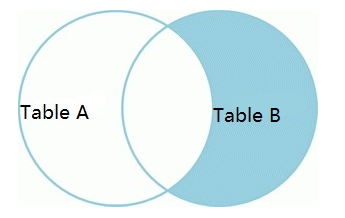
select *fromt1 tt1right joint2 tt2on tt1.name=tt2.namewhere tt1.name is null;
产生的结果集如下:
全连接(full join)
使用union语句实现全连接。
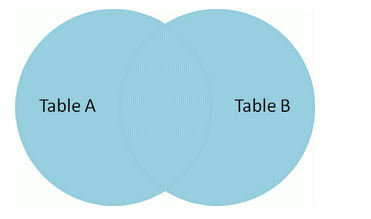
select *fromt1left joint2on t1.name=t2.nameunionselect *fromt1right joint2on t1.name=t2.name;
产生的结果集如下:
求差集
两表的全连接中除去重合的部分,即两张表分别的特有部分的合集。
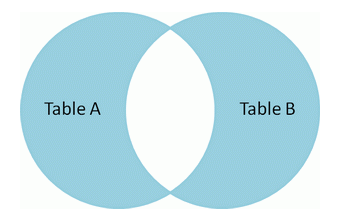
select *fromt1left joint2on t1.name=t2.namewhere t2.name is nullunionselect *fromt1right joint2on t1.name=t2.namewhere t1.name is null;
产生的结果集如下:
参考
MySQL的join关键字详解
MySQL之join语句
MySQL的JOIN用法
MySQL的Join使用
197. Rising Temperature
描述:
Given a Weather table, write a SQL query to find all dates' Ids with higher temperature compared to its previous (yesterday's) dates.
+---------+------------------+------------------+| Id(INT) | RecordDate(DATE) | Temperature(INT) |+---------+------------------+------------------+| 1 | 2015-01-01 | 10 || 2 | 2015-01-02 | 25 || 3 | 2015-01-03 | 20 || 4 | 2015-01-04 | 30 |+---------+------------------+------------------+For example, return the following Ids for the above Weather table:
+----+| Id |+----+| 2 || 4 |+----+
思路:
使用inner join。下面使用到的TO_DAYS函数返回一个天数: 从年份0开始的天数。
比如SELECT TO_DAYS(‘1997-10-07′);的结果Wie729669,就是从0年开始 到1997年10月7号之间的天数。
SELECT t1.IdFROMWeather t1INNER JOINWeather t2ON TO_DAYS(t1.RecordDate) = TO_DAYS(t2.RecordDate) + 1WHERE t1.Temperature > t2.Temperature;
还可以使用datediff()函数。它的语法为DATEDIFF(date1,date2)。比如SELECT DATEDIFF('2008-12-30','2008-12-29') AS DiffDate的结果为1。
selectw1.Id as 'id'fromWeather w1inner joinWeather w2on datediff(w1.RecordDate, w2.RecordDate)=1where w1.Temperature > w2.Temperature;
627. Swap Salary
描述:
Given a table salary, such as the one below, that has m=male and f=female values. Swap all f and m values (i.e., change all f values to m and vice versa) with a single update query and no intermediate temp table.
For example:
| id | name | sex | salary ||----|------|-----|--------|| 1 | A | m | 2500 || 2 | B | f | 1500 || 3 | C | m | 5500 || 4 | D | f | 500 |
After running your query, the above salary table should have the following rows:
| id | name | sex | salary ||----|------|-----|--------|| 1 | A | f | 2500 || 2 | B | m | 1500 || 3 | C | f | 5500 || 4 | D | m | 500 |
思路:
可以使用case-when-else语句。
UPDATE salarySET sex = (CASE WHEN sex = 'm'THEN 'f'ELSE 'm'END);
还可以使用if语句。
UPDATE salary SET sex = IF(sex = 'm', 'f', 'm')
case语句小结
case 具有两种格式:
- 简单
case函数:将某个表达式与一组简单表达式进行比较以确定结果。 case搜索函数:计算一组布尔表达式以确定结果。
# 简单case函数case input_expressionwhen when_expression_1 thenresult_expression_1when when_expression_2 thenresult_expression_2elseelse_result_expressionend# case搜索函数casewhen Boolean_expression_1 thenresult_expression_1when Boolean_expression_2 thenresult_expression_2elseelse_result_expressionend
下面举个例子,首先建立casetest表并插入语句,建表语句和插入数据语句如下:
drop table if exists casetest;create table casetest(id tinyint not null primary key auto_increment,name varchar(30) not null,gender varchar(13) not null,birthday date not null)engine=InnoDB;insert into casetest values(1,'Bob','male','1895-03-26'),(2,'Alice','female','1999-3-10'),(3,'Tom','male','1995-02-21'),(4,'Jerry','male','1885-03-14'),(5,'Dog','female','1996-05-23');
表的结构如下:
+----+-------+--------+------------+| id | name | gender | birthday |+----+-------+--------+------------+| 1 | Bob | male | 1895-03-26 || 2 | Alice | female | 1999-03-10 || 3 | Tom | male | 1995-02-21 || 4 | Jerry | male | 1885-03-14 || 5 | Dog | female | 1996-05-23 |+----+-------+--------+------------+
使用简单case函数进行选择
select *,casewhen birthday<'1981' then 'old'when birthday>'1988' then 'yong'else 'ok' end yornfrom casetest;
结果集如下:
| id | name | gender | birthday | YORN |+----+-------+--------+------------+------+| 1 | Bob | male | 1895-03-26 | old || 2 | Alice | female | 1999-03-10 | yong || 3 | Tom | male | 1995-02-21 | yong || 4 | Jerry | male | 1885-03-14 | old || 5 | Dog | female | 1996-05-23 | yong |+----+-------+--------+------------+------+
使用case搜索函数进行选择
select *,case namewhen 'Bob' then 'old'when 'Alice' then 'yong'when 'Tom' then 'old'else 'ok' end yornfrom casetest;
结果集如下:
+----+-------+--------+------------+------+| id | name | gender | birthday | YORN |+----+-------+--------+------------+------+| 1 | Bob | male | 1895-03-26 | old || 2 | Alice | female | 1999-03-10 | yong || 3 | Tom | male | 1995-02-21 | old || 4 | Jerry | male | 1885-03-14 | ok || 5 | Dog | female | 1996-05-23 | ok |+----+-------+--------+------------+------+
使用cas搜索函数进行更新
下面语句的功能是将表中的male和female互换。
update casetestset gender = (case genderwhen 'male' then 'female'else 'male'end);
之后使用select进行选择,结果集如下:
+----+-------+--------+------------+| id | name | gender | birthday |+----+-------+--------+------------+| 1 | Bob | female | 1895-03-26 || 2 | Alice | male | 1999-03-10 || 3 | Tom | female | 1995-02-21 || 4 | Jerry | female | 1885-03-14 || 5 | Dog | male | 1996-05-23 |+----+-------+--------+------------+
if语句小结
基本语法为:
IF(condition, value_if_true, value_if_false)
IF函数根据条件的结果为true或false,返回第一个值,或第二个值。例子如下。
select *,if(gender='male',1,2) as gender_id from casetest;+----+-------+--------+------------+-----------+| id | name | gender | birthday | gender_id |+----+-------+--------+------------+-----------+| 1 | Bob | female | 1895-03-26 | 2 || 2 | Alice | male | 1999-03-10 | 1 || 3 | Tom | female | 1995-02-21 | 2 || 4 | Jerry | female | 1885-03-14 | 2 || 5 | Dog | male | 1996-05-23 | 1 |+----+-------+--------+------------+-----------+
184. Department Highest Salary
描述:
The Employee table holds all employees. Every employee has an Id, a salary, and there is also a column for the department Id.
+----+-------+--------+--------------+| Id | Name | Salary | DepartmentId |+----+-------+--------+--------------+| 1 | Joe | 70000 | 1 || 2 | Henry | 80000 | 2 || 3 | Sam | 60000 | 2 || 4 | Max | 90000 | 1 |+----+-------+--------+--------------+
The Department table holds all departments of the company.
+----+----------+| Id | Name |+----+----------+| 1 | IT || 2 | Sales |+----+----------+Write a SQL query to find employees who have the highest salary in each of the departments. For the above tables, Max has the highest salary in the IT department and Henry has the highest salary in the Sales department.+------------+----------+--------+| Department | Employee | Salary |+------------+----------+--------+| IT | Max | 90000 || Sales | Henry | 80000 |+------------+----------+--------+
思路:可以使用group by和in来操作。先给出建表语句和插入行的语句:
drop table if exists employee;create table employee(id tinyint not null primary key auto_increment,name varchar(30) not null,salary int not null,departmentid tinyint not null)engine=InnoDB;drop if exists department;create table department(id tinyint not null primary key auto_increment,name varchar(30) not null)engine=InnoDB;insert into employee values(1,'Joe',70000,1),(2,'Henry',80000,2),(3,'Sam',60000,2),(4,'Max',90000,1);insert into department values(1,'IT'),(2,'Sales');
使用
selectdepartmentid as departmentid,max(salary) as maxsalaryfromemployeegroup by departmentid;
可以查找到如下结果集:
+--------------+-----------+| departmentid | maxsalary |+--------------+-----------+| 1 | 90000 || 2 | 80000 |+--------------+-----------+
将这个结果集作为in的一部分,可以得到最终语句:
selectdepartment.name as Department,employee.name as Employee,employee.salary as Salaryfromemployeejoindepartment on employee.departmentid=department.idwhere(employee.departmentid, salary) in(selectdepartmentid, max(salary)fromemployee group by departmentid);
178. Rank Scores
Write a SQL query to rank scores. If there is a tie between two scores, both should have the same ranking. Note that after a tie, the next ranking number should be the next consecutive integer value. In other words, there should be no "holes" between ranks.+----+-------+| Id | Score |+----+-------+| 1 | 3.50 || 2 | 3.65 || 3 | 4.00 || 4 | 3.85 || 5 | 4.00 || 6 | 3.65 |+----+-------+For example, given the above Scores table, your query should generate the following report (order by highest score):+-------+------+| Score | Rank |+-------+------+| 4.00 | 1 || 4.00 | 1 || 3.85 | 2 || 3.65 | 3 || 3.65 | 3 || 3.50 | 4 |+-------+------+
先给出建表语句:
drop table if exists scores;create table scores(id int not null primary key auto_increment,score float not null)engine=InnoDB;insert into scores values(1,3.50),(2,3.65),(3,4.00),(4,3.85),(5,4.00),(6,3.65);
解法:
select score,(select count(distinct score) from scores where score>=s.score) as `rank`from scores s order by score desc;
分析:这个语句中有4个score,先不看中间嵌套的select语句,这个语句的主干是:select score from scores s order by score desc;,所以,第一个score是属于表s的;而第二个和第三个score是数据中间嵌套的select语句的,这样这个语句就分解清楚了,搜索结果包括两列:第一列:分数;第二列:大于等于此分数的分数值的不重复个数;按分数降序排列。
180. Consecutive Numbers
Write a SQL query to find all numbers that appear at least three times consecutively.+----+-----+| Id | Num |+----+-----+| 1 | 1 || 2 | 1 || 3 | 1 || 4 | 2 || 5 | 1 || 6 | 2 || 7 | 2 |+----+-----+For example, given the above Logs table, 1 is the only number that appears consecutively for at least three times.+-----------------+| ConsecutiveNums |+-----------------+| 1 |+-----------------+
思路,还是用join。一个join走天下。使用
select *fromlogs l1,logs l2,logs l3wherel1.id=l2.id-1and l2.id=l3.id-1and l1.num=l2.numand l2.num=l3.num;
语句之后的结果如下:
+----+-----+----+-----+----+-----+| id | num | id | num | id | num |+----+-----+----+-----+----+-----+| 1 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 3 | 1 |+----+-----+----+-----+----+-----+
将上面的语句稍微改变一下就得到该题的结果:
select distinct l1.num as `ConsecutiveNums`fromlogs l1,logs l2,logs l3wherel1.id=l2.id-1and l2.id=l3.id-1and l1.num=l2.numand l2.num=l3.num;
