@ybtang21c
2021-11-15T01:47:47.000000Z
字数 27342
阅读 2133
4.4 矩阵的奇异值分解
高等工程数学 讲义 2021
4.4.1 奇异值
引理 设 ,则
证明思路:设 是齐次方程组 的非零解.
- 于是 .
- 进而可知 ,即 是 的非零解.
- 反之,设 是 的非零解.
- 显然 也是 的非零解.
- 综上, 和 同解,故 .
- 同理可证 .
引理 设 ,,则
- 推论 对任意的 成立.
引理的证明思路
- .
- 初等变换不改变矩阵的行列式,故:
- .
- .
- 故 .
引理 设 ,则 和 的特征值均非负。
证明思路:设 .- 于是 .
- 由此可知 .
- 同理可证 的特征值均非负.
推论 设 ,则 和 有相同的正特征值.
证明思路:.- 这意味着 和 有相同的非零特征值.
- 和 特征值均非负,故二者必有相同的正特征值.
- 该推论说明: 和 最多只是零特征值的个数不同.
讨论: 设
- 若 ,则必有 .
- 由 可知 也是 的特征值.
- 由此不难看出 和 有相同的正特征值.
- 若 ,即 .
- 因为 和 同解,故 .
- 零向量不能作为特征向量,故此时由 无法推出 也是 的特征值.
奇异值
设 , 的特征值为 ,则
称为 的 奇异值 (Singular Value).
- 注: 与 虽然特征值个数可能不同,但有完全一致的正特征值. 为了统一表述,在很多场合,奇异值特指正奇异值.
例 求 的奇异值.
提示:.- .
- 的特征值: .
- 的奇异值: .
例 求 的奇异值.
提示
- 的特征值: .
- 的奇异值: .
另一种解法
- 的特征值: .
- 因为 和 有相同的正特征值, 而 是 阶方阵,故 的全部特征值为 .
- 的奇异值: .
4.4.2 奇异值分解
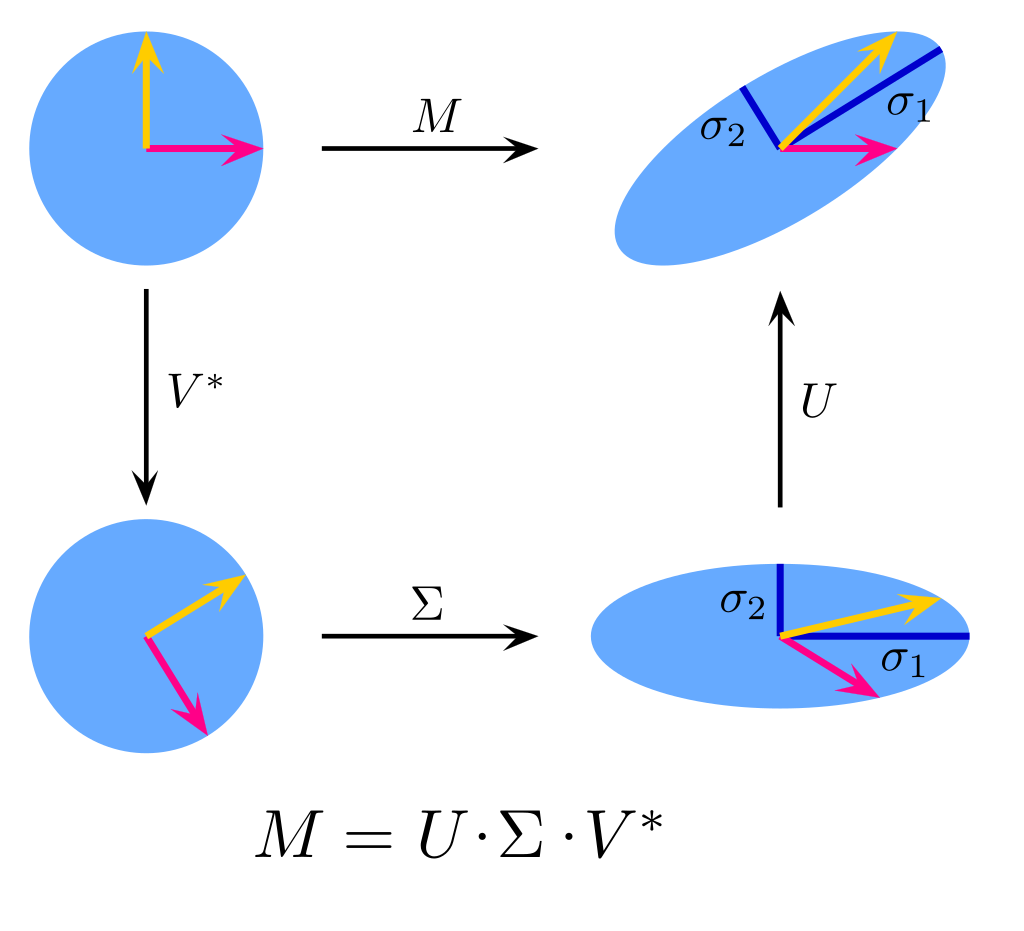
设 , ,则存在 阶酉矩阵 和 阶酉矩阵 ,使得
- 其中 , 是 的正(非零)奇异值.
- 上式称为 的 奇异值分解(Singular Value Decomposition,简称 SVD)
证明思路:
- ,故 有 个正特征值.
- 设 的所有特征值为 .
- 因为 是 Hermite 矩阵,故存在 阶酉矩阵 ,使得 是对角阵.
- .
- 其中 .
- 记 , 的列向量为单位正交特征向量.
- 记 .
- .
- 记 .
- 由 可知 是 中两两正交的单位向量.
- 将 扩张为标准正交基 .
- 记 ,则 .
- .
- 以上即为 的奇异值分解.
4.4.3 奇异值分解的求解
- 求 的特征值以及对应单位正交特征向量:
- .
- .
- 记 , , , ,令 .
- 将 的列向量扩张成 的标准正交基 ,令 .
例 求 的奇异值分解.
提示:.- ,故 的特征值为 .
- 由 ,解得 关于 的特征向量 .
- 由 解得 关于 的特征向量 .
- 令 , ,
- .
- 将 的列向量 扩张成 中的标准正交基:
- 设 ,满足
- 解之得 .
- 令
- 综上, 的奇异值分解为:
-
- .
注:
设 的 SVD 为
- 的列向量是方阵 的标准正交特征向量.
- 显然 的 SVD 为 .
- 由此可知 的列向量是 的标准正交特征向量.
- 问:是否可以以此为基础得到一个求解 和 的新方法?
例 求 的奇异值分解.
提示
- .
- ,故 的特征值为 .
- 由 解得 关于 的单位特征向量 .
- 由 解得 关于 的单位特征向量 .
- 令 .
- 又 的所有特征值 .
- 由 解得 关于特征值 的单位特征向量 .
- 由 解得 关于特征值 的单位特征向量 .
- 由 解得 关于特征值 的单位正交特征向量
- 令 .
问题出在哪里?
- 若取 关于 的单位特征向量为 ,再令 ,则
- 标准正交特征向量组不具有唯一性,如果随意进行选择,可能导致得不到正确的 SVD
4.4.4 奇异值分解的应用
最小二乘问题(Least Squares Problem)数据/图像压缩(Data/Image Compression)潜在语义索引(Latent Semantic Indexing)
最小二乘问题
设 , ,求 ,使得
- 设 的奇异值分解为 ,于是
- .
- 令 ,则上式可化为 .
- 关于 的求解:
- 是酉矩阵,不改变向量的长度(2-范数).
- 故由 可知必有 .
- 记 ,进而
- .
- 显然 时 最小,进而由此解出 .
- 最后,由 ,得到 ,即为所求的最小二乘解.
数据压缩
矩阵 包含 个数据,可否使用尽可能少的数据来表示(或逼近) ?
- 通常情况下,可以用 来度量 中数据的
冗余度(Redundancy) - 例 若 ,则必存在 和 ,使得 .
- 上式意味着,用 个独立的数据就能够完全表示 .
例 一幅图像可以对应于一个矩阵 ,其中 表示坐标 处的点的像素值(或灰度).
- 设 的 SVD 为 .
- 记 , 不难发现,存储 只需要 个数据.
- 当图像尺寸特别大时,可以考虑用 来近似 ,达到节省存储空间的目的.
- 此时图像 压缩比 可定义为 .
潜在语义索引(Latent Semantic Indexing, LSI)[1]
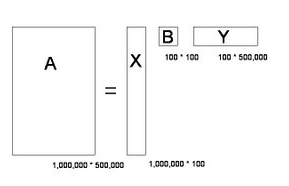
例 一百万篇文章和五十万个不同词汇的关联可以描述为一个 的矩阵
- 如图 SVD 后,所需的存储量仅为原来的
三千分之一. - 的每列对应一个
主题,列中元素代表每篇文章与之的相关性. - 的每行也对应与以上相同的某个
主题,行中元素代表每个单词与之的相关性. - 的对角元代表主题的
重要性.
以 为例[2]
- 红点表示单词,蓝点表示文档.
- 通过 SVD 得到的关联性可以用来完成词和文档的
聚类(Clustering). - 利用并行算法已可以高效地完成 SVD.

小结
- SVD
- 奇异值的定义与性质
- SVD 的求解
- SVD 的应用
SVD[3]
A brief history of SVD[4]
The singular value decomposition was originally developed by differential geometers, who wished to determine whether a real bilinear form could be made equal to another by independent orthogonal transformations of the two spaces it acts on. Eugenio Beltrami and Camille Jordan discovered independently, in 1873 and 1874 respectively, that the singular values of the bilinear forms, represented as a matrix, form a complete set of invariants for bilinear forms under orthogonal substitutions. James Joseph Sylvester also arrived at the singular value decomposition for real square matrices in 1889, apparently independently of both Beltrami and Jordan. Sylvester called the singular values the canonical multipliers of the matrix A. The fourth mathematician to discover the singular value decomposition independently is Autonne in 1915, who arrived at it via the polar decomposition. The first proof of the singular value decomposition for rectangular and complex matrices seems to be by Carl Eckart and Gale J. Young in 1936; they saw it as a generalization of the principal axis transformation for Hermitian matrices.
Practical methods for computing the SVD date back to Kogbetliantz in 1954, 1955 and Hestenes in 1958, resembling closely the Jacobi eigenvalue algorithm, which uses plane rotations or Givens rotations. However, these were replaced by the method of Gene Golub and William Kahan published in 1965, which uses Householder transformations or reflections. In 1970, Golub and Christian Reinsch published a variant of the Golub/Kahan algorithm[5] that is still the one most-used today.
