@zzzc18
2017-09-02T12:14:42.000000Z
字数 3616
阅读 1755
bzoj4017 小Q的无敌异或
bzoj BIT
Link:http://www.lydsy.com/JudgeOnline/problem.php?id=4017
题意:有一个长度为 的数列,求其
以及
Solution
对于第一个子问题,按位计算贡献,即计算ans能加多少个
首先我们计算一下前缀异或和
注:以下就以某一位来讨论
我们维护两个值, 的个数以及 的个数
令当前已经计算了 个值的贡献,要计算 的贡献
如果 处前缀异或和这一位是 则贡献要加上先前 的个数,否则要加上 的个数 (显然,想要使对最终答案的贡献为 ,之前一定是 或者 )
最后ans直接加上 即可
第一问就解决了,时间复杂度
第二个子问题:
答案是异或和,我们不妨按位来考虑,看什么时候会使 的某一位变成
显然,由异或的性质可知,第 位 有奇数个 出现时,最终答案的第 位才为
形式化的,我们有
此时这题复杂度已经比纯暴力好了非常多,对于每一个 统计出所有满足上式的 的个数,但仍然很高
不过由上面的操作统计先前满足条件的个数,想到可以使用树状数组或线段树来维护, 查询
上述式子可以进一步展开,
可以用树状数组分别查询
代码里会看到查询三个值,很诡异,原因见下图
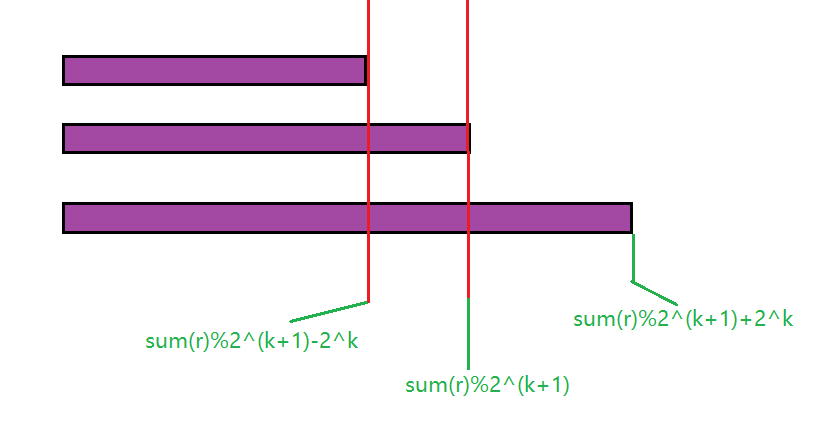
由之前推的两个式子可知,两条红线之间夹的是不可取的地方,我们需要左右两边的值,如果用BIT存奇偶性,查找三个绿色处的前缀,异或起来就可以了(中间部分有两遍异或,相当与不存在)
最后,每一位统计最终的奇偶性,若为奇数,则
ps: 等价于 //二进制考虑一下
First Code(奇偶性):
#include<cstdio>#include<cstring>#include<algorithm>#define LL long long#define MAXN 100010#define MOD 998244353using namespace std;LL n;LL sum[MAXN];LL xsum[MAXN];LL p[MAXN];LL ans;bool tree[MAXN];int lowbit(int x){return (x)&(-x);}void change(LL pos){pos++;if(pos==0)return;LL i;for(i=pos;i<=n+1;i+=lowbit(i))tree[i]^=1;}LL getnum(LL pos){LL re=0;LL i;pos++;for(i=pos;i;i-=lowbit(i))re^=tree[i];return re;}LL getloc(LL x){LL l=0,r=n;LL ans=-1;while(l<=r){LL mid=(l+r)>>1;if(p[mid]<=x){l=mid+1;ans=mid;}elser=mid-1;}return ans;}void solve1(){LL k;LL i;LL cnt[2];for(k=0;k<=30;k++){cnt[0]=cnt[1]=0;LL tmp=0;for(i=0;i<=n;i++){bool tt=xsum[i]&(1<<k);tmp+=cnt[tt^1];cnt[tt]++;}ans += (1<<k) * tmp%MOD;ans%=MOD;}printf("%lld ",ans);}void solve2(){ans=0;LL i,k;for(k = 0;(1LL << k) <= sum[n];k++){LL tmp=0;for(i=0;i<=n;i++)p[i] = sum[i] & ((1LL << (k+1)) - 1);sort(p,p+n+1);memset(tree,0,sizeof(tree));for(i=0;i<=n;i++){LL now = sum[i] & ((1LL << (k + 1)) - 1);//printf("%lld %lld\n",now,getloc(now));LL t1=getnum(getloc(now-(1LL<<k)));LL t2=getnum(getloc(now+(1LL<<k)));LL t3=getnum(getloc(now));change(getloc(now));//printf("--%lld %lld %lld\n",now-(1LL<<k),now+(1LL<<k),now);//printf("::%lld %lld %lld\n",t1,t2,t3);tmp^=t1^t2^t3;}if(tmp)ans |= (1LL<<k);}printf("%lld\n",ans);}int main(){scanf("%lld",&n);LL i;LL x;for(i=1;i<=n;i++){scanf("%lld",&x);xsum[i]=xsum[i-1]^x;sum[i]=sum[i-1]+x;}solve1();solve2();return 0;}
Second Code(统计个数):
#include<cstdio>#include<cstring>#include<algorithm>#define LL long long#define MAXN 100010#define MOD 998244353using namespace std;LL n;LL sum[MAXN];LL xsum[MAXN];LL p[MAXN];LL ans;int tree[MAXN];int lowbit(int x){return (x)&(-x);}void change(LL pos,int v){pos++;if(pos==0)return;LL i;for(i=pos;i<=n+1;i+=lowbit(i))tree[i]+=v;}LL getnum(LL pos){LL re=0;LL i;pos++;for(i=pos;i;i-=lowbit(i))re+=tree[i];return re;}LL getloc(LL x){LL l=0,r=n;LL ans=-1;while(l<=r){LL mid=(l+r)>>1;if(p[mid]<=x){l=mid+1;ans=mid;}elser=mid-1;}return ans;}void solve1(){LL k;LL i;LL cnt[2];for(k=0;k<=30;k++){cnt[0]=cnt[1]=0;LL tmp=0;for(i=0;i<=n;i++){bool tt=xsum[i]&(1<<k);tmp+=cnt[tt^1];cnt[tt]++;}ans += (1<<k) * tmp%MOD;ans%=MOD;}printf("%lld ",ans);}void solve2(){ans=0;LL i,k;for(k = 0;(1LL << k) <= sum[n];k++){LL tmp=0;for(i=0;i<=n;i++)p[i] = sum[i] & ((1LL << (k+1)) - 1);sort(p,p+n+1);memset(tree,0,sizeof(tree));for(i=0;i<=n;i++){LL now = sum[i] & ((1LL << (k + 1)) - 1);change(getloc(now),1);LL t1=getnum(getloc(now-(1LL<<k)));LL t2=getnum(getloc(now+(1LL<<k)));LL t3=getnum(getloc(now));tmp+=t1+t2-t3;}if(tmp%2)ans |= (1LL<<k);}printf("%lld\n",ans);}int main(){scanf("%lld",&n);LL i;LL x;for(i=1;i<=n;i++){scanf("%lld",&x);xsum[i]=xsum[i-1]^x;sum[i]=sum[i-1]+x;}solve1();solve2();return 0;}
