@linux1s1s
2019-02-15T13:03:46.000000Z
字数 5854
阅读 2316
Java 反射基础
Java 2015-11
Java 反射的基本概念这里不做赘述,直接上Demo。
Person类
package com.linroid.refact.test;public class Person {private int age;private String name;public Person() {}public Person(int age, String name) {this.age = age;this.name = name;}public int getAge() {return age;}public void setAge(int age) {this.age = age;}public String getName() {return name;}public void setName(String name) {this.name = name;}}
PersonSub子类
package com.linroid.refact.test;public class PersonSub extends Person implements Refector {public PersonSub() {super();}@Overridepublic void refector() {System.out.println("This refector method come from PersonSub.refector()");}}
Refector接口
package com.linroid.refact.test;public interface Refector {public void refector();}
测试用例CommonCase类
package com.linroid.refact.test;import java.lang.reflect.Constructor;import java.lang.reflect.Field;import java.lang.reflect.InvocationTargetException;import java.lang.reflect.Method;import java.lang.reflect.Modifier;public class CommonCase {public static void main(String[] args) {showPackageAndName();System.out.println("===============================================");obtainClassRefine();System.out.println("===============================================");newInstanceWithNoParam();System.out.println("===============================================");newInstanceWithParam();System.out.println("===============================================");modifiedDeclaredField();System.out.println("===============================================");useDeclaredMethod();System.out.println("===============================================");showObjectInfo();}// 通过一个对象获得完整的包名和类名,从这个demo中可以得出所有类的实例其实就是Class的实例private static void showPackageAndName() {Person person = new Person();System.out.println(person.getClass().getName());}// 通过完整包名直接获得实例,推荐使用这种方式private static Class<?> obtainClassRefine(String packageName) {if (packageName == null || packageName.isEmpty()) {return null;}Class<?> person = null;try {person = Class.forName(packageName);} catch (Exception e) {e.printStackTrace();}System.out.println("类名称: " + person.getName());return person;}private static Class<?> obtainClassRefine() {return obtainClassRefine("com.linroid.refact.test.Person");}// 接下来获得了Class实例以后,就要初始化这个实例private static void newInstanceWithNoParam() {Class<?> classPerson = obtainClassRefine();Person person = null;if (classPerson != null) {// 由于这里不能带参数,所以你要实例化的这个类Person,一定要有无参构造函数 ,如果没有无参数的构造器,就一定会抛异常try {person = (Person) classPerson.newInstance();person.setAge(20);person.setName("Nacy");System.out.println("Persion: name is " + person.getName() + " age is " + person.getAge());} catch (InstantiationException e) {e.printStackTrace();} catch (IllegalAccessException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}}// 接着上面的例子,如果没有无参数构造器,会发生什么,该如何应对?private static void newInstanceWithParam() {Class<?> classPerson = obtainClassRefine();Person person1 = null;Person person2 = null;if (classPerson != null) {// 仅仅获取Public构造器,其他包权限、private权限以及protected权限不能获取。换句话说,如果是非Public权限的构造器,通过下面这种反射办法是不能解决问题Constructor<?>[] constructor = classPerson.getConstructors();if (constructor.length >= 2) {try {person1 = (Person) constructor[0].newInstance();person1.setAge(21);person1.setName("Gracy");person2 = (Person) constructor[1].newInstance(22, "Brala");System.out.println("Persion: name is " + person1.getName() + " age is " + person1.getAge());System.out.println("Persion: name is " + person2.getName() + " age is " + person2.getAge());} catch (InstantiationException e) {e.printStackTrace();} catch (IllegalAccessException e) {e.printStackTrace();} catch (IllegalArgumentException e) {e.printStackTrace();} catch (InvocationTargetException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}}}// 获得构造器以后可以构造实例,在构造实例的同时会初始化成员变量,如果不满意,也可以直接通过反射获取成员变量,然后直接赋值改变即可private static void modifiedDeclaredField() {Class<?> classPerson = obtainClassRefine();Person person = null;if (classPerson != null) {try {person = (Person) classPerson.newInstance();Field name = classPerson.getDeclaredField("name");if (name != null) {name.setAccessible(true);name.set(person, "Durk");}Field age = classPerson.getDeclaredField("age");if (age != null) {age.setAccessible(true);age.set(person, 12);}System.out.println("Persion: name is " + person.getName() + " age is " + person.getAge());} catch (NoSuchFieldException e) {e.printStackTrace();} catch (SecurityException e) {e.printStackTrace();} catch (InstantiationException e1) {e1.printStackTrace();} catch (IllegalAccessException e1) {e1.printStackTrace();}}}// 接下来看看反射最有用处的地方,通过Java反射机制调用类方法private static void useDeclaredMethod() {Class<?> classPerson = obtainClassRefine("com.linroid.refact.test.PersonSub");Person person = null;if (classPerson != null) {try {person = (Person) classPerson.newInstance();Method refector = classPerson.getMethod("refector");if (refector != null) {refector.invoke(person);}} catch (InstantiationException e) {e.printStackTrace();} catch (IllegalAccessException e) {e.printStackTrace();} catch (NoSuchMethodException | SecurityException e) {e.printStackTrace();} catch (IllegalArgumentException | InvocationTargetException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}}// 获取类的基本信息,比如继承的接口,父类,函数信息,成员信息,类型等private static void showObjectInfo() {Class<?> classPerson = obtainClassRefine("com.linroid.refact.test.PersonSub");if (classPerson != null) {// 获取父类名Class<?> superClass = classPerson.getSuperclass();System.out.println("Persion: Super class name is " + superClass.getName());// 获取类的成员变量Field[] fields = classPerson.getFields();int fieldSize = 0;if (fields != null && (fieldSize = fields.length) > 0) {for (int i = 0; i < fieldSize; i++) {System.out.println("类中的成员: " + fields[i]);}}// 获取类的方法Method[] methods = classPerson.getDeclaredMethods();int methodSize = 0;if (methods != null & (methodSize = methods.length) > 0) {for (int i = 0; i < methodSize; i++) {System.out.println("函数名:" + methods[i].getName());System.out.println("函数返回类型:" + methods[i].getReturnType());System.out.println("函数访问修饰符:" + Modifier.toString(methods[i].getModifiers()));System.out.println("函数代码写法: " + methods[i]);}}// 获取类实现的接口, 是不是看到多重继承的影子了\(^o^)/~Class<?>[] implementsClass = classPerson.getInterfaces();int implementsSize = 0;if (implementsClass != null && (implementsSize = implementsClass.length) > 0) {for (int i = 0; i < implementsSize; i++) {System.out.println("实现的接口类名: " + implementsClass[i].getName());}}}}}
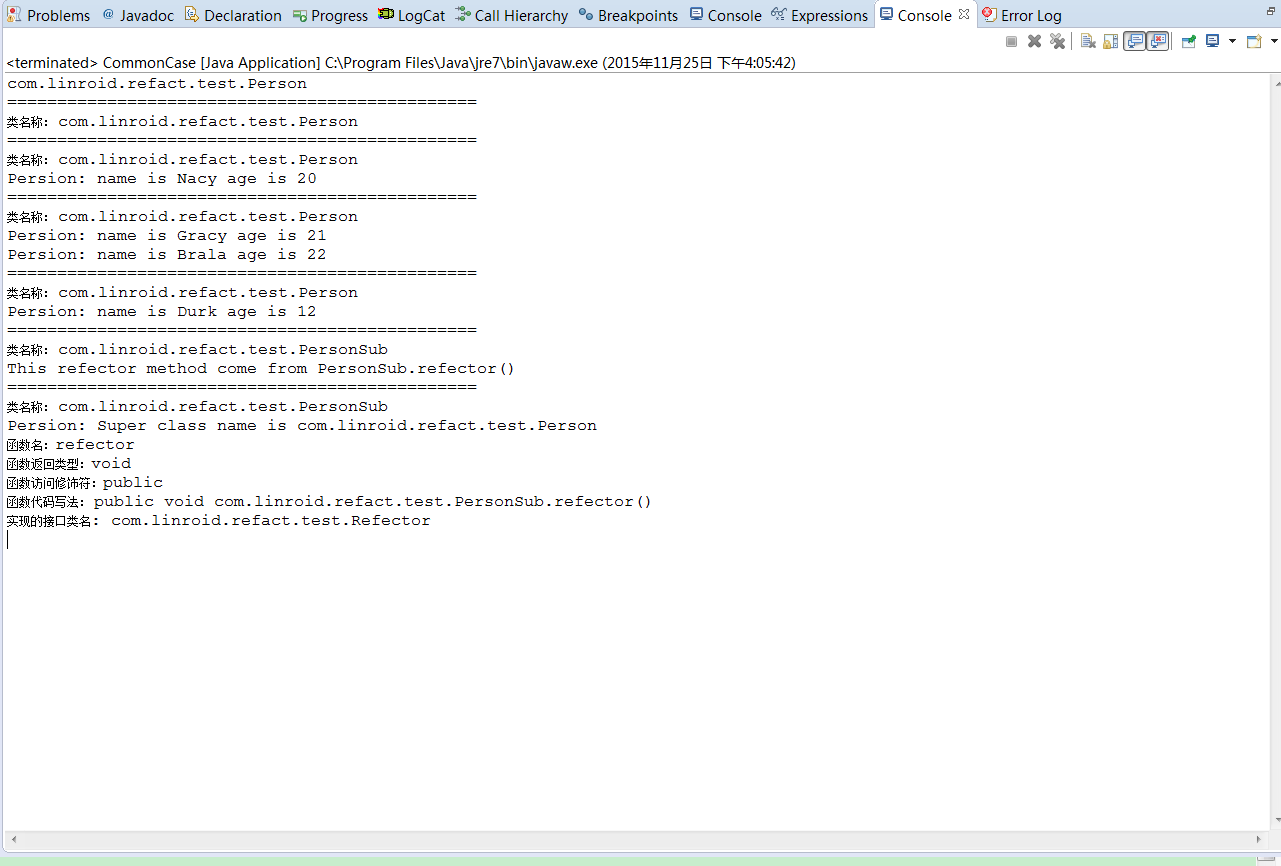
运行结果