@richey
2020-09-17T15:36:55.000000Z
字数 4814
阅读 1908
微型计算机技术应用讲义10-python基础(2)
python 讲义
1.最简单的python程序
# coding=utf8print "hello world!\r\n"
2.语法
2.1 缩进(严格缩进4个空格)
def fun1():print "你好!\r\n"fun1()
2.2 数据类型
-list列表
def fun1():print "你好!\r\n"fun1()l=[1,2,5,6,8]print lprint l[3]for item in l:print item
-元组
ython的元组与列表类似,不同之处在于元组的元素不能修改。元组使用小括号,列表使用方括号。
tup1 = ('physics', 'chemistry', 1997, 2000);tup2 = (1, 2, 3, 4, 5 );tup3 = "a", "b", "c", "d";print tup1print tup2print tup3
-字典dict
bdict = {'name':'allen', 'age':'40'}for key in bdict.keys():print keyprint bdict[key]
2.3 if、for、while、break
3 twisted异步网络通信库
3.1 介绍
参考:http://blog.csdn.net/hanhuili/article/details/9389433
Twisted是用Python实现的基于事件驱动的网络引擎框架。Twisted支持许多常见的传输及应用层协议,包括TCP、UDP、SSL/TLS、HTTP、IMAP、SSH、IRC以及FTP。Twisted对于其支持的所有协议都带有客户端和服务器实现,同时附带有基于命令行的工具,使得配置和部署产品级的Twisted应用变得非常方便。
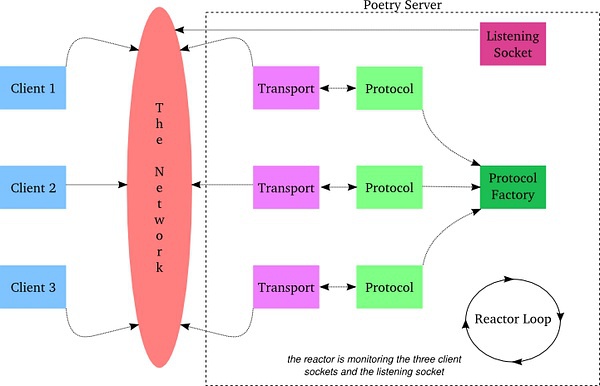
3.2 Reactor
Reactor是事件管理器,用于注册、注销事件,运行事件循环,当事件发生时调用回调函数处理。Reactor可以感知网络、文件系统以及定时器事件。它等待然后处理这些事件,从特定于平台的行为中抽象出来,并提供统一的接口,使得在网络协议栈的任何位置对事件做出响应都变得简单。
关于reactor有下面几个结论:
Twisted的reactor只有通过调用reactor.run()来启动。
reactor循环是在其开始的进程中运行,也就是运行在主进程中。
一旦启动,就会一直运行下去。reactor就会在程序的控制下(或者具体在一个启动它的线程的控制下)。reactor循环并不会消耗任何CPU的资源。并不需要显式的创建reactor,只需要引入就OK了。
3.3 Transports
Transports代表网络中两个通信结点之间的连接。Transports负责描述连接的细节,比如连接是面向流式的还是面向数据报的,流控以及可靠性。TCP、UDP和Unix套接字可作为transports的例子。它们被设计为“满足最小功能单元,同时具有最大程度的可复用性”,而且从协议实现中分离出来,这让许多协议可以采用相同类型的传输。Transports实现了ITransports接口,它包含如下的方法:
write 以非阻塞的方式按顺序依次将数据写到物理连接上
writeSequence 将一个字符串列表写到物理连接上
loseConnection 将所有挂起的数据写入,然后关闭连接
getPeer 取得连接中对端的地址信息
getHost 取得连接中本端的地址信息
将transports从协议中分离出来也使得对这两个层次的测试变得更加简单。可以通过简单地写入一个字符串来模拟传输,用这种方式来检查。
3.4 Protocols
Protocols描述了如何以异步的方式处理网络中的事件。HTTP、DNS以及IMAP是应用层协议中的例子。Protocols实现了IProtocol接口,它包含如下的方法:
makeConnection 在transport对象和服务器之间建立一条连接
connectionMade 连接建立起来后调用
dataReceived 接收数据时调用
connectionLost 关闭连接时调用
3.5 Factory
切确的说,它取名不太好,应该叫做FactoryOfProtocals,即协议工厂(也就是工厂模式),用来管理协议对象实例的。
4 串口收发数据
# coding=utf8import sysimport reif sys.platform == 'win32':from twisted.internet import win32eventreactorwin32eventreactor.install()from twisted.internet import defer, threadsfrom twisted.internet.serialport import SerialPortfrom twisted.internet import protocol,task, reactor, errorfrom twisted.protocols.basic import LineReceiverfrom twisted.python import log, usageclass GasSim(LineReceiver):def __init__(self):self._lc1 = task.LoopingCall(self.sendCmd)self._lc1.start(3,False)def sendCmd(self):self.sendLine("@01c100001".encode('utf-8'))def lineReceived(self, line):line = line.decode('utf-8')print(line)if(re.match('@\d{2}\D\w{4}\d{2}',line)):if(line[3] == 'D'):print ('接收到1条命令!\r\n')tmpstr = "当前电压值=%.3f" % (int(line[4:8],16)/1000.0)print (tmpstr)if __name__ == '__main__':s = SerialPort(GasSim(), 'COM2', reactor, baudrate=9600)reactor.run()
5. socket网络数据通信
# coding: utf-8import reimport datetimeimport timeimport jsonimport redisfrom twisted.internet import reactor, task, protocolfrom twisted.internet import defer, threadsfrom twisted.internet.protocol import Protocol, error, Factoryfrom twisted.protocols.basic import LineReceiverr = redis.Redis(host='127.0.0.1',port=6379,db=0)def getCurrentStrTime():return time.strftime("%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S", time.localtime())class GasServerProtocol(LineReceiver):def __init__(self, factory):self.id = ''self.factory = factorydef connectionMade(self):print(("[%s]: %s连接到服务器端。" %(getCurrentStrTime(), self.transport.getPeer())))self.sendLine("$99'".encode('utf-8'))def connectionLost(self, reason):if self.id in self.factory.clients:del self.factory.clients[self.id]print("[%s]:ID %s 下线" % (getCurrentStrTime(), self.id))print(("[%s]: %s断开了连接,原因是%s" %(getCurrentStrTime(),self.transport.getPeer(),reason)))def lineReceived(self, data):data = data.decode('utf-8')tmpstr = ("[%s]: 收到数据 %s") % (getCurrentStrTime(), data)print(tmpstr)if(re.match("\$\d{2}\$", data)):self.id = str(data[1:3])dicttmp = {}dicttmp['handle'] = selfdicttmp['timestamp'] = time.time()self.factory.clients[self.id] = dicttmpprint("[%s]:ID %s 注册成功" % (getCurrentStrTime(), self.id))if(re.match('@\d{2}\D\w{4}\d{2}',data)):if(data[3] == 'D'):print('接收到1条命令!\r\n')volttmp = (int(data[4:8],16)/1000.0)tmpstr = "当前电压值=%.3f" % volttmpprint(tmpstr)dicttmp = {}dicttmp['collecttime'] = getCurrentStrTime()dicttmp['volt'] = volttmpdicttmp['id'] = self.idr.set(self.id, json.dumps(dicttmp))print(r.get(self.id))class GasServerFactory(Factory):def __init__(self):self.clients = {} # maps clients ids to GasServerProtocol instancesself._lc = task.LoopingCall(self.send_to_clients)self._lc.start(3,now=False)def buildProtocol(self, addr):return GasServerProtocol(self)def send_to_clients(self):for client_addr in self.clients :self.clients[client_addr]['handle'].sendLine('hello!'.encode('utf-8'))def startMoniter():print("[%s]启动监控服务" % getCurrentStrTime())cf = GasServerFactory()reactor.listenTCP(8234, cf)reactor.run()def stopMoniter():print("[%s]停止监控服务" % getCurrentStrTime())try:reactor.crash()except RuntimeError:return defer.fail()else:return defer.succeed(None)startMoniter()
