@Yano
2016-12-15T06:18:45.000000Z
字数 4467
阅读 3332
Google Protocol Buffers 数据交换协议
协议
protobuf 简介
protobuf是什么
protobuf(Protocol Buffers)是Google推出的一个结构化数据交换协议,用于传递自定义的消息格式,可用于同一台机器的进程间、不同设备进程间的数据传递。protobuf是一种语言无关、平台无关、高效、扩展性良好的语言,提供了一种将结构化数据进行序列化和反序列化的方法。
相对于XML,protobuf的体积更小、速度更快、使用更简单。我们仅需要定义一次数据结构,就可以很轻松地使用生成的代码读/写数据,而且这些数据结构是向后兼容的。
官方网站
https://developers.google.com/protocol-buffers/
protobuf的优劣
为什么不使用XML?
相对于XML来说,Protocol buffers在序列化结构化数据上,具有非常明显的优势:
- 更加简单
- 体积减小3~10倍
- 速度提高20~100倍
- 更清晰
- 生成的数据结构代码,更容易使用
如果要生成一个具有name和email的person实例,XML做法如下:
<person><name>John Doe</name><email>jdoe@example.com</email></person>
使用protocol:
# Textual representation of a protocol buffer.# This is *not* the binary format used on the wire.person {name: "John Doe"email: "jdoe@example.com"}
当此消息被编码为二进制格式时,长度大概是28字节,解析时间为100~200ns。在去除所有空格后,XML版本也至少为69字节,解析时间长达5000~10000ns。
同时,使用protocol buffer更简单:
cout << "Name: " << person.name() << endl;cout << "E-mail: " << person.email() << endl;
使用XML的代码:
cout << "Name: "<< person.getElementsByTagName("name")->item(0)->innerText()<< endl;cout << "E-mail: "<< person.getElementsByTagName("email")->item(0)->innerText()<< endl;
相对于JSON来说,protobuf也有明显的优势:
- 更好的前后数据版本兼容性
- 提供了验证机制,更容易被扩展
- 不同语言间互操作性更好
protobuf也有一些缺点,并不是适合所有场景。
- 二进制编码和传输,可读性差
- 编码和解码依赖额外的库,不能在浏览器、JS中直接使用
- 缺乏自描述
如何使用protobuf
- 定义
.proto文件 - 编译protocol buffer
- 使用Java protocol buffer API 读写数据
下面是通过Java使用protobuf的官方示例:https://developers.google.com/protocol-buffers/docs/javatutorial ,并在此基础上进行了简化。
定义.proto文件
定义需要序列化的数据结构,为message中的每一个变量设置名称和类型。下面
package tutorial;option java_package = "yano";option java_outer_classname = "AddressBookProtos";message Person {required string name = 1;required int32 id = 2;optional string email = 3;enum PhoneType {MOBILE = 0;HOME = 1;WORK = 2;}message PhoneNumber {required string number = 1;optional PhoneType type = 2 [default = HOME];}repeated PhoneNumber phone = 4;}message AddressBook {repeated Person person = 1;}
- package:防止不同工程中的命名冲突;生成Java的proto时,如果没有指定java_package,包名默认为package
- java_package:包名
- java_outer_classname:定义生成Java代码的文件名(类名);如果没有指定,会将proto文件变成驼峰形式:默认会将
my_proto.proto生成MyProto的类文件。
定义字段时,我们使用了required、optional、repeated三个关键字。这些关键字表示对字段的约束,分别表示:
- required-非空约束。如果字段值为空,会被认为是uninitialized,并抛出异常。
- optional-可选。表示字段可以赋值,也可以不赋值。不赋值时,将会使用默认值。
- repeated-可重复次数。表示字段可以重复使用的次数,重复顺序会被保存在protobuf中,可以将其理解为一个数组。
proto文件中的其它格式,在此不作介绍,详细内容可以参考官方文档。
编译protocol buffer
现在我们有了一个.proto文件,接下来就需要将生成class文件,我们可以通过这个class文件读写AddressBook的消息。
- proto编译器下载地址:https://developers.google.com/protocol-buffers/docs/downloads
- 运行编译器,指定proto路径、生成路径、
.proto文件。
protoc -I=$SRC_DIR --java_out=$DST_DIR $SRC_DIR/addressbook.proto
Protocol Buffer API
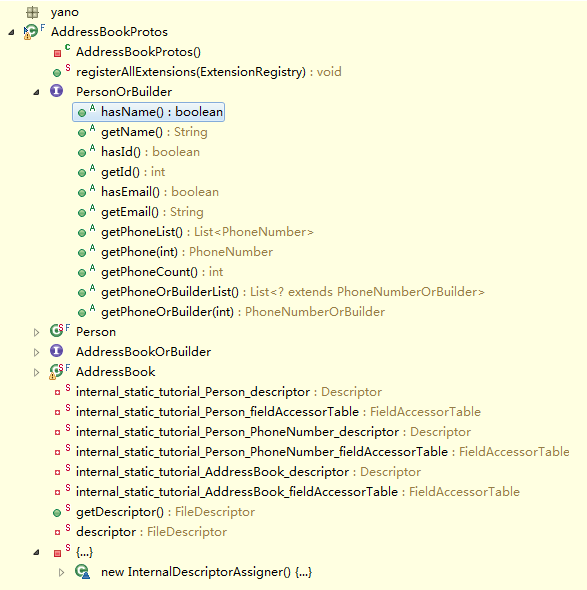
通过proto编译器,addressbook.proto生成了Java类AddressBookProtos.java。每个class都有自己的Builder,用以生成该类的实例。
// required string name = 1;public boolean hasName();public String getName();// required int32 id = 2;public boolean hasId();public int getId();// optional string email = 3;public boolean hasEmail();public String getEmail();// repeated .tutorial.Person.PhoneNumber phone = 4;public List<PhoneNumber> getPhoneList();public int getPhoneCount();public PhoneNumber getPhone(int index);
Person.Builder 除了getters,还有setters方法:
// required string name = 1;public boolean hasName();public java.lang.String getName();public Builder setName(String value);public Builder clearName();// required int32 id = 2;public boolean hasId();public int getId();public Builder setId(int value);public Builder clearId();// optional string email = 3;public boolean hasEmail();public String getEmail();public Builder setEmail(String value);public Builder clearEmail();// repeated .tutorial.Person.PhoneNumber phone = 4;public List<PhoneNumber> getPhoneList();public int getPhoneCount();public PhoneNumber getPhone(int index);public Builder setPhone(int index, PhoneNumber value);public Builder addPhone(PhoneNumber value);public Builder addAllPhone(Iterable<PhoneNumber> value);public Builder clearPhone();
创建一个 Person 实例:
Person john =Person.newBuilder().setId(1234).setName("John Doe").setEmail("jdoe@example.com").addPhone(Person.PhoneNumber.newBuilder().setNumber("555-4321").setType(Person.PhoneType.HOME)).build();
标准消息方法
以下方法能够让我们检查和操作整个message:
- isInitialized():检查required字段是否全部设置
- toString():返回可阅读的格式,在debug时非常有用
- mergeFrom(Message other):将
other的内容合并到该message中,会覆盖相同的字段,对repeated字段会添加 - clear():重置所有字段
解析和序列化
所有的protocol buffer类都有读写二进制的方法:
- byte[] toByteArray():序列化消息并返回包含其原始字节的字节数组
- static Person parseFrom(byte[] data):通过给定的字节数组,解析message
- void writeTo(OutputStream output):序列化消息,并将其写到
OutputStream - static Person parseFrom(InputStream input):从
InputStream中读取并解析message
扩展protobuf
在扩展proto文件时,需要注意以下事项:
- 绝对不能改变已经存在的字段的
tag numbers - 绝对不能添加或删除
required字段 - 可以删除
optional和repeated字段 - 可以添加新的
optional和repeated字段,但是必须使用新的tag numbers
结束语
我的博客:http://www.jianshu.com/users/6835c29fc12a/latest_articles
我的知乎:https://www.zhihu.com/people/liu-jia-yu-58/activities
