@Yano
2018-12-01T02:34:53.000000Z
字数 3113
阅读 3625
Thrift RPC 框架分析
Java
前言
工作中用到Thrift,一直想深入研究一下。今天这篇博客以提问的方式,分析Thrift的源码。文章部分参考自:Thrift源码分析。
本来计划的题目是:「Thrift RPC 源码分析」,可是写了两个小时才发现,我根本没有贴出多少源码……因为我是在公司项目源码中直接分析的,又不能直接贴在博客中,遂放弃 o_0
Thrift 有什么特点?
- 基于二进制的高性能的编解码框架
- 基于NIO的底层通信
- 相对简单的服务调用模型
- 使用IDL支持跨平台调用
Thrift 的整体架构?
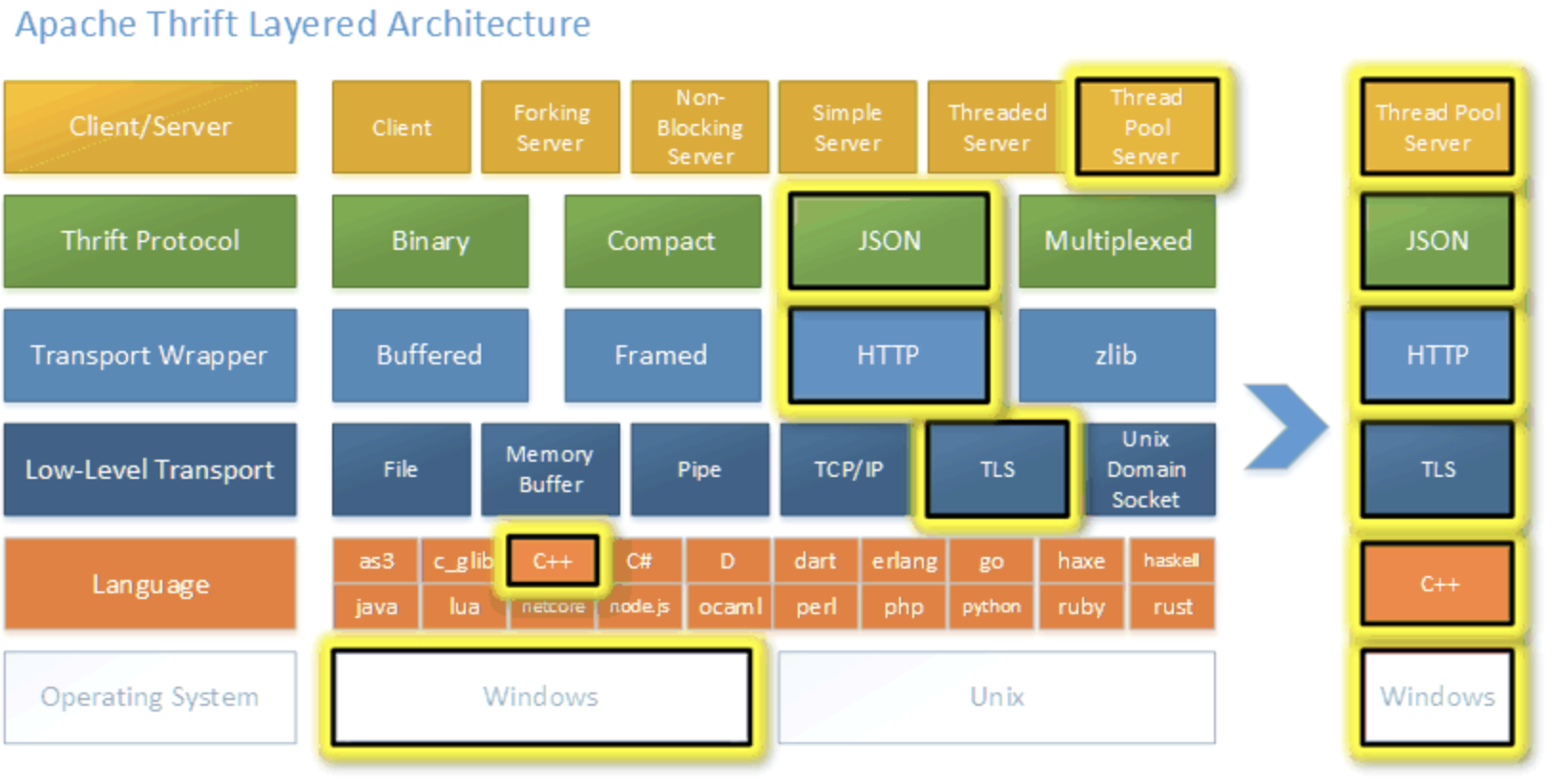
官方文档 Apache Thrift - Concepts详细说明了Thrift的架构:
Thrift network stack
+-------------------------------------------+| Server || (single-threaded, event-driven etc) |+-------------------------------------------+| Processor || (compiler generated) |+-------------------------------------------+| Protocol || (JSON, compact etc) |+-------------------------------------------+| Transport || (raw TCP, HTTP etc) |+-------------------------------------------+
Transport
The Transport layer provides a simple abstraction for reading/writing from/to the network. This enables Thrift to decouple the underlying transport from the rest of the system (serialization/deserialization, for instance).
Transport layer提供了一个从网络IO读写的简单抽象,可以使Thrift与底层解耦。
Transport接口有:
- open
- close
- read
- write
- flush
除了Transport接口,还有一个ServerTransport,用来在server端创建请求的连接。
- open
- listen
- accept
- close
Protocol
Protocol定义了传输数据的序列化、反序列化机制(JSON、XML、binary、compact binary等)。
Protocol的接口如下:
writeMessageBegin(name, type, seq)writeMessageEnd()writeStructBegin(name)writeStructEnd()writeFieldBegin(name, type, id)writeFieldEnd()writeFieldStop()writeMapBegin(ktype, vtype, size)writeMapEnd()writeListBegin(etype, size)writeListEnd()writeSetBegin(etype, size)writeSetEnd()writeBool(bool)writeByte(byte)writeI16(i16)writeI32(i32)writeI64(i64)writeDouble(double)writeString(string)name, type, seq = readMessageBegin()readMessageEnd()name = readStructBegin()readStructEnd()name, type, id = readFieldBegin()readFieldEnd()k, v, size = readMapBegin()readMapEnd()etype, size = readListBegin()readListEnd()etype, size = readSetBegin()readSetEnd()bool = readBool()byte = readByte()i16 = readI16()i32 = readI32()i64 = readI64()double = readDouble()string = readString()
Processor
Processor封装了读取输入流、写入输出流的能力,其中输入流、输出流都是Protocol的对象。接口很简单:
interface TProcessor {bool process(TProtocol in, TProtocol out) throws TException}
其中用户需要实现TProcessor接口。
Thrift 的源码实现?
TTransport
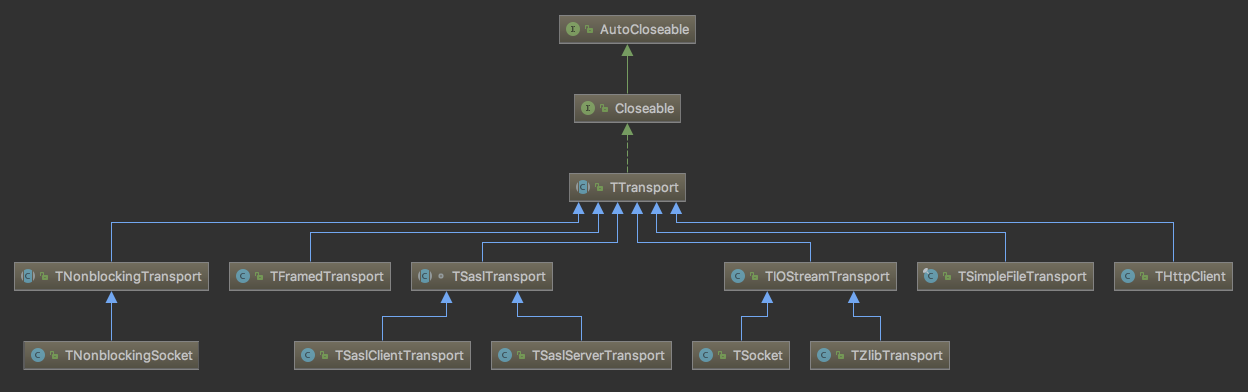
TTransport有很多实现,其中最重要的就是TFramedTransport。
客户端的实际使用:
TSocket socket = new TSocket(host, port);socket.setTimeout(timeout);TTransport transport = new TFramedTransport(socket);TProtocol protocol = new TCompactProtocol(transport);transport.open();
TProtocol
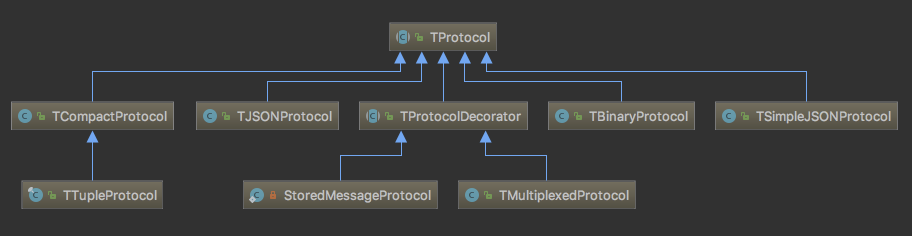
Thrift主要支持的协议有:
- JSON
- SimpleJSON
- Binary
- Compact Binary
其中Binary协议的序列化、反序列化,可以参考我的另一篇文章:Thrift 对象序列化、反序列化-字节数组分析。
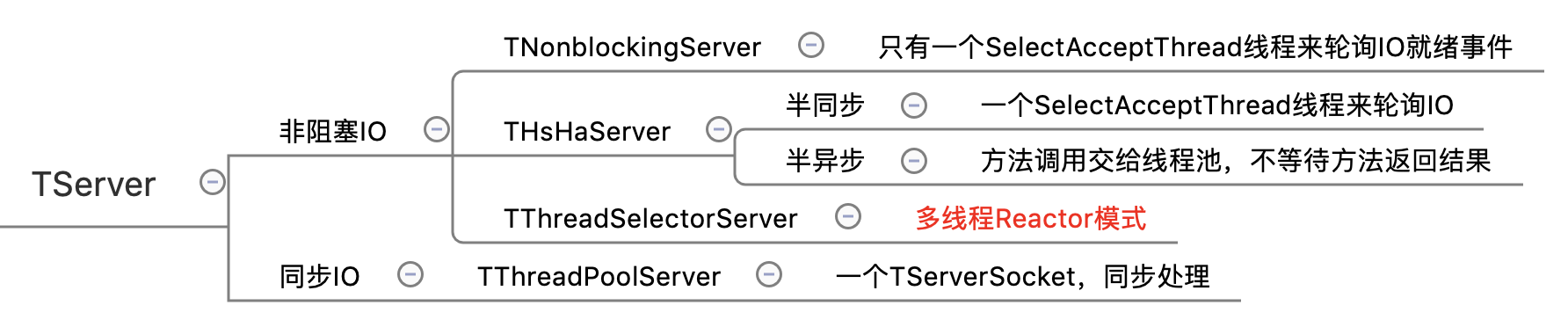
TServer
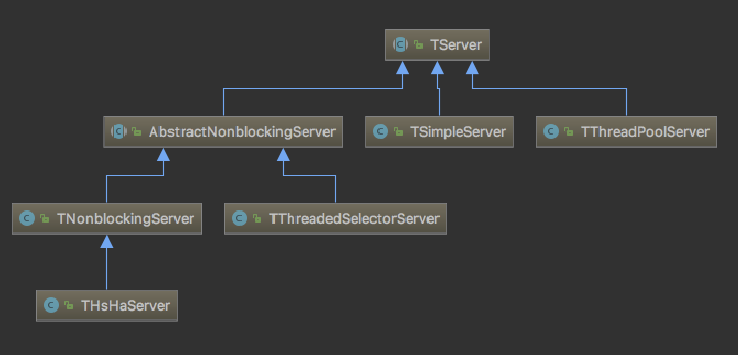
解释起来太麻烦,还是直接贴思维导图吧,更直观 0_o
TServerTransport
TServerTransport作为服务器的Acceptor抽象,来监听端口,创建客户端Socket连接。
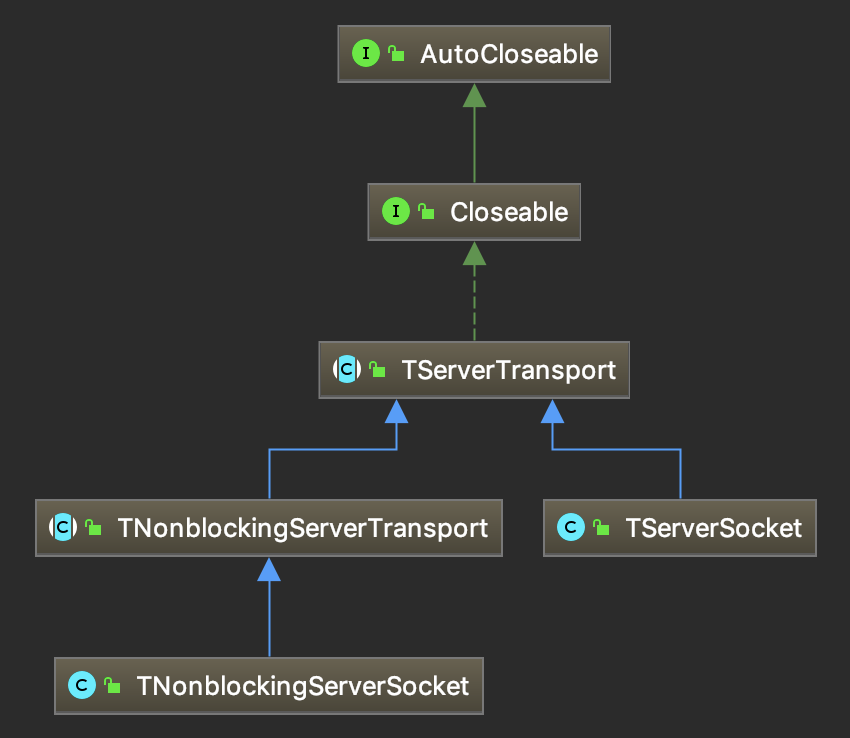
- TNonblockingServerTransport和TNonblockingServerSocket作为非阻塞IO的Acceptor,封装了ServerSocketChannel
- TServerSocket作为阻塞同步IO的Acceptor,封装了ServerSocket
其他 RPC 框架有哪些?
- rpcx: 基于Go的服务治理的rpc框架、客户端支持跨语言
- grpc: Google 出品的跨语言rpc框架,很弱的(实验性的)负载均衡, 测试使用的是grpc-go
- go std rpc: Go标准库的rpc, 不支持跨语言(jsonrpc支持json rpc 1.0)
- thrift: 跨语言的rpc框架,facebook贡献
- dubbo: 国内较早开源的服务治理的Java rpc框架,虽然在阿里巴巴内部竞争中落败于HSF,沉寂了几年,但是在国内得到了广泛的应用,目前dubbo项目又获得了支持,并且dubbo 3.0也开始开发
- motan: 微博内部使用的rpc框架,底层支持java,生态圈往service mesh发展以支持多语言
- hprose: 国内开发人员开发的一个跨语言的rpc框架,非服务治理但是性能高效
- twirp: twitch.tv刚刚开源的一个restful风格的rpc框架
- go-micro: Go语言的一个服务治理rpc框架, 在测试中发现性能不太好,所以没有继续测试,相关的测试代码已在github库中
- go kit:
- 腾讯 Tars:腾讯公司的rpc框架
- 百度 brpc: 百度公司的rpc框架
- spring cloud:
