@BruceWang
2018-01-03T09:16:36.000000Z
字数 10943
阅读 1838
Jupter numpy pandas matplot 笔记
This is my first jupyter notes
NumpyPandasMatplot
1+2
3
def f(x,y,z):return (x+y)/za = 5b=6c=7.5
import numpy as npdata = np.random.rand(2,11)print(data)
[[ 0.67577294 0.194396 0.5525098 0.04609985 0.14534381 0.93533033
0.32043392 0.0807357 0.46490533 0.89414549 0.260932 ]
[ 0.78801884 0.25585532 0.99597803 0.09019288 0.58768134 0.0815639
0.18691377 0.60306836 0.80131033 0.63986103 0.2780275 ]]
type(data), data.shape
(numpy.ndarray, (2, 11))
data.dtype
dtype('float64')
data.dtype
dtype('float64')
second part
data1 = [23,3,4.45,5,3,5,0]
arr1 = np.array(data1)
arr1
array([ 23. , 3. , 4.45, 5. , 3. , 5. , 0. ])
arr1.shapearr1.reshape(1,7)arr1.shape
(7,)
arr1.dtype
dtype('float64')
np.zeros(10)
array([ 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0.])
np.zeros((3,4))
array([[ 0., 0., 0., 0.],
[ 0., 0., 0., 0.],
[ 0., 0., 0., 0.]])
a = _
a.shape
(3, 4)
np.empty((2,3))
array([[ 23. , 3. , 4.45],
[ 5. , 3. , 5. ]])
np.empty((3,4,5))
array([[[ 1.00999541e-311, 1.00997906e-311, 1.00997961e-311,
1.00997851e-311, 1.00997844e-311],
[ 1.00997838e-311, 1.00997751e-311, 1.00997963e-311,
1.00997838e-311, 1.00997751e-311],
[ 1.00997768e-311, 1.00997961e-311, 1.00997758e-311,
1.00997758e-311, 1.00997768e-311],
[ 1.00997758e-311, 1.00997967e-311, 1.00997939e-311,
1.00997961e-311, 1.00997751e-311]],
[[ 1.00997846e-311, 1.00997865e-311, 1.00997766e-311,
1.00997838e-311, 1.00997751e-311],
[ 1.00997768e-311, 1.00997865e-311, 1.00997852e-311,
1.00997838e-311, 1.00997758e-311],
[ 1.00997758e-311, 1.00997838e-311, 1.00997852e-311,
1.00997865e-311, 1.00997766e-311],
[ 1.00997766e-311, 1.00997865e-311, 1.00997766e-311,
1.00997768e-311, 1.00997766e-311]],
[[ 1.00997865e-311, 1.00997768e-311, 1.00997768e-311,
1.00997749e-311, 1.00997766e-311],
[ 1.00997766e-311, 1.00997768e-311, 1.00997768e-311,
1.00997963e-311, 1.00997963e-311],
[ 1.00997963e-311, 9.21088093e-315, 1.00997964e-311,
9.21088710e-315, 1.00997964e-311],
[ 9.21088093e-315, 9.21088093e-315, 1.00997962e-311,
1.00997963e-311, 9.21088093e-315]]])
a = _print(a.shape)print(a)
(3, 4, 5)
[[[ 1.00999541e-311 1.00997906e-311 1.00997961e-311 1.00997851e-311
1.00997844e-311]
[ 1.00997838e-311 1.00997751e-311 1.00997963e-311 1.00997838e-311
1.00997751e-311]
[ 1.00997768e-311 1.00997961e-311 1.00997758e-311 1.00997758e-311
1.00997768e-311]
[ 1.00997758e-311 1.00997967e-311 1.00997939e-311 1.00997961e-311
1.00997751e-311]]
[[ 1.00997846e-311 1.00997865e-311 1.00997766e-311 1.00997838e-311
1.00997751e-311]
[ 1.00997768e-311 1.00997865e-311 1.00997852e-311 1.00997838e-311
1.00997758e-311]
[ 1.00997758e-311 1.00997838e-311 1.00997852e-311 1.00997865e-311
1.00997766e-311]
[ 1.00997766e-311 1.00997865e-311 1.00997766e-311 1.00997768e-311
1.00997766e-311]]
[[ 1.00997865e-311 1.00997768e-311 1.00997768e-311 1.00997749e-311
1.00997766e-311]
[ 1.00997766e-311 1.00997768e-311 1.00997768e-311 1.00997963e-311
1.00997963e-311]
[ 1.00997963e-311 9.21088093e-315 1.00997964e-311 9.21088710e-315
1.00997964e-311]
[ 9.21088093e-315 9.21088093e-315 1.00997962e-311 1.00997963e-311
9.21088093e-315]]]
np.arange(21)
array([ 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15, 16,
17, 18, 19, 20])
np.arange(21)
array([ 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15, 16,
17, 18, 19, 20])
array: 将数据转化成ndarray
asarray:将数据转换成ndarray
arange:产生的是一个ndarray,而array产生的是list
arr1 = np.arange(12, dtype=np.float64)print(arr1)
[ 0. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11.]
print(arr1.dtype)type(arr1)
float64
numpy.ndarray
np.arange(12,dtype=np.float64)
array([ 0., 1., 2., 3., 4., 5., 6., 7., 8., 9., 10.,
11.])
np.eye(5)
array([[ 1., 0., 0., 0., 0.],
[ 0., 1., 0., 0., 0.],
[ 0., 0., 1., 0., 0.],
[ 0., 0., 0., 1., 0.],
[ 0., 0., 0., 0., 1.]])
向量化的数组运算比纯python同等程度的运算要快很多。
一个简单的例子,假设我们想要评价函数sqrt(x^2 + y^2)
np.meshgrid函数取两个1维的数组,产生一个2位的矩阵,对应于所有两个数组中(x, y)的组合:
import numpy as np
在进行书中的内容之前,先举个例子说明meshgrid的效果。meshgrid函数用两个坐标轴上的点在平面上画网格。
用法:
- [X,Y]=meshgrid(x,y)
- [X,Y]=meshgrid(x)与[X,Y]=meshgrid(x,x)是等同的
- [X,Y,Z]=meshgrid(x,y,z)生成三维数组,可用来计算三变量的函数和绘制三维立体图
这里,主要
以
- [X,Y]=meshgrid(x,y)为例,来对该函数进行介绍。
- [X,Y] = meshgrid(x,y) 将向量x和y定义的区域转换成矩阵X和Y,其中矩阵X的行向量是向量x的简单复制,而矩阵Y的列向量是向量y的简单复制(注:下面代码中X和Y均是数组,在文中统一称为矩阵了)。
假设x是长度为m的向量,y是长度为n的向量,则最终生成的矩阵X和Y的维度都是 nm (注意不是mn)。
m,n = (5,3)x = np.linspace(0,1,m)y = np.linspace(0,1,n)X,Y = np.meshgrid(x,y)x
array([ 0. , 0.25, 0.5 , 0.75, 1. ])
y
array([ 0. , 0.5, 1. ])
x
array([ 0. , 0.25, 0.5 , 0.75, 1. ])
X
array([[ 0. , 0.25, 0.5 , 0.75, 1. ],
[ 0. , 0.25, 0.5 , 0.75, 1. ],
[ 0. , 0.25, 0.5 , 0.75, 1. ]])
X.shape
(3, 5)
Y
array([[ 0. , 0. , 0. , 0. , 0. ],
[ 0.5, 0.5, 0.5, 0.5, 0.5],
[ 1. , 1. , 1. , 1. , 1. ]])
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt%matplotlib inlineplt.style.use('ggplot')plt.plot(X,Y, maker='*', color='blue', linestyle='none')
------------------------------------------------------------------------
AttributeError Traceback (most recent call last)
<ipython-input-74-2621aaa0e2ee> in <module>()
4 plt.style.use('ggplot')
5
----> 6 plt.plot(X,Y, maker='*', color='blue', linestyle='none')
C:\Anaconda3\lib\site-packages\matplotlib\pyplot.py in plot(*args, **kwargs)
3159 ax.hold(hold)
3160 try:
-> 3161 ret = ax.plot(*args, **kwargs)
3162 finally:
3163 ax.hold(washold)
C:\Anaconda3\lib\site-packages\matplotlib\__init__.py in inner(ax, *args, **kwargs)
1816 warnings.warn(msg % (label_namer, func.__name__),
1817 RuntimeWarning, stacklevel=2)
-> 1818 return func(ax, *args, **kwargs)
1819 pre_doc = inner.__doc__
1820 if pre_doc is None:
C:\Anaconda3\lib\site-packages\matplotlib\axes\_axes.py in plot(self, *args, **kwargs)
1380 kwargs = cbook.normalize_kwargs(kwargs, _alias_map)
1381
-> 1382 for line in self._get_lines(*args, **kwargs):
1383 self.add_line(line)
1384 lines.append(line)
C:\Anaconda3\lib\site-packages\matplotlib\axes\_base.py in _grab_next_args(self, *args, **kwargs)
379 return
380 if len(remaining) <= 3:
--> 381 for seg in self._plot_args(remaining, kwargs):
382 yield seg
383 return
C:\Anaconda3\lib\site-packages\matplotlib\axes\_base.py in _plot_args(self, tup, kwargs)
367 ncx, ncy = x.shape[1], y.shape[1]
368 for j in xrange(max(ncx, ncy)):
--> 369 seg = func(x[:, j % ncx], y[:, j % ncy], kw, kwargs)
370 ret.append(seg)
371 return ret
C:\Anaconda3\lib\site-packages\matplotlib\axes\_base.py in _makeline(self, x, y, kw, kwargs)
274 default_dict = self._getdefaults(None, kw)
275 self._setdefaults(default_dict, kw)
--> 276 seg = mlines.Line2D(x, y, **kw)
277 return seg
278
C:\Anaconda3\lib\site-packages\matplotlib\lines.py in __init__(self, xdata, ydata, linewidth, linestyle, color, marker, markersize, markeredgewidth, markeredgecolor, markerfacecolor, markerfacecoloralt, fillstyle, antialiased, dash_capstyle, solid_capstyle, dash_joinstyle, solid_joinstyle, pickradius, drawstyle, markevery, **kwargs)
378 # update kwargs before updating data to give the caller a
379 # chance to init axes (and hence unit support)
--> 380 self.update(kwargs)
381 self.pickradius = pickradius
382 self.ind_offset = 0
C:\Anaconda3\lib\site-packages\matplotlib\artist.py in update(self, props)
857 func = getattr(self, 'set_' + k, None)
858 if func is None or not six.callable(func):
--> 859 raise AttributeError('Unknown property %s' % k)
860 func(v)
861 changed = True
AttributeError: Unknown property maker
z = [i for i in zip(X.flat, Y.flat)]zlen(z)
15
points = np.arange(-5,5,0.01)
points = np.arange(-5,5,0.01)xs,ys = np.meshgrid(points, points)xs,ys
(array([[-5. , -4.99, -4.98, ..., 4.97, 4.98, 4.99],
[-5. , -4.99, -4.98, ..., 4.97, 4.98, 4.99],
[-5. , -4.99, -4.98, ..., 4.97, 4.98, 4.99],
...,
[-5. , -4.99, -4.98, ..., 4.97, 4.98, 4.99],
[-5. , -4.99, -4.98, ..., 4.97, 4.98, 4.99],
[-5. , -4.99, -4.98, ..., 4.97, 4.98, 4.99]]),
array([[-5. , -5. , -5. , ..., -5. , -5. , -5. ],
[-4.99, -4.99, -4.99, ..., -4.99, -4.99, -4.99],
[-4.98, -4.98, -4.98, ..., -4.98, -4.98, -4.98],
...,
[ 4.97, 4.97, 4.97, ..., 4.97, 4.97, 4.97],
[ 4.98, 4.98, 4.98, ..., 4.98, 4.98, 4.98],
[ 4.99, 4.99, 4.99, ..., 4.99, 4.99, 4.99]]))
z = np.sqrt(xs ** 2 + ys ** 2)z
array([[ 7.07106781, 7.06400028, 7.05693985, ..., 7.04988652,
7.05693985, 7.06400028],
[ 7.06400028, 7.05692568, 7.04985815, ..., 7.04279774,
7.04985815, 7.05692568],
[ 7.05693985, 7.04985815, 7.04278354, ..., 7.03571603,
7.04278354, 7.04985815],
...,
[ 7.04988652, 7.04279774, 7.03571603, ..., 7.0286414 ,
7.03571603, 7.04279774],
[ 7.05693985, 7.04985815, 7.04278354, ..., 7.03571603,
7.04278354, 7.04985815],
[ 7.06400028, 7.05692568, 7.04985815, ..., 7.04279774,
7.04985815, 7.05692568]])
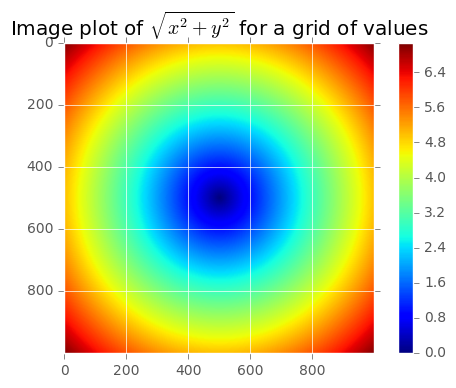
plt.imshow(z);plt.colorbar()plt.title("Image plot of $\sqrt{x^2+y^2}$ for a grid of values")
<matplotlib.text.Text at 0x1dbfb43e7f0>
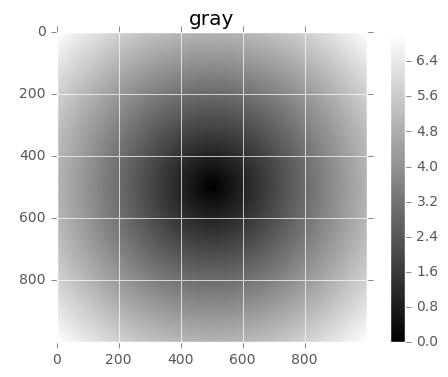
plt.imshow(z,cmap=plt.cm.gray); plt.colorbar()plt.title("gray")
<matplotlib.text.Text at 0x1db84940390>
xarr = np.arange(10)yarr = np.arange(10, 20)cond = np.array([True,False, True,False,False, True,False,False, True, True])
np.where中第二个和第三个参数不用必须是数组。
where在数据分析中一个典型的用法是基于一个数组,产生一个新的数组值。假设我们有一个随机数字生成的矩阵,我们想要把所有的正数变为2,所有的负数变为-2。
用where的话会非常简单:
result = [x if c else y for x,y,c in zip(xarr,yarr,cond)]result
[0, 11, 2, 13, 14, 5, 16, 17, 8, 9]
result = np.where(cond, xarr, yarr)result
array([ 0, 11, 2, 13, 14, 5, 16, 17, 8, 9])
假设我们有一个随机数字生成的矩阵,我们想要把所有的正数变为2,所有的负数变为-2。
用where的话会非常简单
arr = np.random.randn(4,4)arr
array([[-1.7249151 , 0.47436864, 1.25594568, -0.50147823],
[ 0.32329558, 0.70147251, -0.84606626, -0.81102393],
[ 0.56334907, -0.87781646, -1.29420612, -0.882093 ],
[-2.05570648, -0.60100428, -0.43001513, -0.18520691]])
arr>0
array([[False, True, True, False],
[ True, True, False, False],
[ True, False, False, False],
[False, False, False, False]], dtype=bool)
np.where(arr>0, 2,-2)
array([[-2, 2, 2, -2],
[ 2, 2, -2, -2],
[ 2, -2, -2, -2],
[-2, -2, -2, -2]])
np.where(arr>0, 2, arr)
array([[-1.7249151 , 2. , 2. , -0.50147823],
[ 2. , 2. , -0.84606626, -0.81102393],
[ 2. , -0.87781646, -1.29420612, -0.882093 ],
[-2.05570648, -0.60100428, -0.43001513, -0.18520691]])
np.where(arr>0, -2, 2)
array([[ 2, -2, -2, 2],
[-2, -2, 2, 2],
[-2, 2, 2, 2],
[ 2, 2, 2, 2]])
数学和统计方法
一些能计算统计值的数学函数能基于整个数组,或者沿着一个轴,可以使用aggregatios 降维, 比如sum,mean, and std。
下面是一些aggregate statistics (汇总统计)
arr = np.random.randn(5,4)arr
array([[-0.69958443, -2.46355531, 0.19856965, 1.29106598],
[ 0.46347983, 0.33712368, -1.09018919, -0.21548269],
[ 0.29535286, -1.39083895, -0.09018223, -0.2594519 ],
[ 0.90665136, -0.44205849, -0.16239346, 0.31531549],
[ 0.49731548, 1.08907863, -1.52806488, -0.5010424 ]])
arr.mean()
-0.17244454806253073
np.mean(arr)
-0.17244454806253073
arr.sum()
-3.4488909612506147
arr.mean(axis=1)
array([-0.41837603, -0.12626709, -0.36128006, 0.15437873, -0.11067829])
arr.sum(axis=0)
array([ 1.46321511, -2.87025044, -2.67226011, 0.63040448])
我是过度线--------------------------------------
arr = np.array([0,2,3,4,4,5,66])
arr.cumsum()
array([ 0, 2, 5, 9, 13, 18, 84], dtype=int32)
上面的计算是一个累加的结果,0+2 = 2, 2+3=5...
np.cumsum?
arr = np.array([[23,4,4],[3,5,4,],[42,5,3]])arr
array([[23, 4, 4],
[ 3, 5, 4],
[42, 5, 3]])
arr.cumsum(axis=0)
array([[23, 4, 4],
[26, 9, 8],
[68, 14, 11]], dtype=int32)
arr.cumsum(axis=1)
array([[23, 27, 31],
[ 3, 8, 12],
[42, 47, 50]], dtype=int32)
arr = np.random.randn(100)(arr>0).sum()
55
有其他两个办法,any和all, 对于布尔数组特别有用,any 检测数组中只要有一个Ture就返回,就是Ture, 而all,检测数组中所有都是True,才返回True
bools = np.array([False, False, True, True])
bools.any()
True
bools.all()
False
Sorting(排序)
np.random.randn?
arr = np.random.randn(6)arr
array([ 0.3934821 , 0.95045695, 0.08114809, 0.71009844, -0.58873837,
-0.39691479])
arr
array([ 0.3934821 , 0.95045695, 0.08114809, 0.71009844, -0.58873837,
-0.39691479])
arr.sort()arr
array([-0.58873837, -0.39691479, 0.08114809, 0.3934821 , 0.71009844,
0.95045695])
arr = np.random.randn(5,3)arr
array([[ 2.09807311, 0.76233307, 0.50202059],
[-1.72025055, -0.16630714, -1.47464429],
[ 2.82788532, -1.25434574, 0.97145056],
[ 0.58417455, 0.51401424, -0.4251397 ],
[ 0.89538709, 1.15031466, -0.66813715]])
arr.sort()arr
array([[ 0.50202059, 0.76233307, 2.09807311],
[-1.72025055, -1.47464429, -0.16630714],
[-1.25434574, 0.97145056, 2.82788532],
[-0.4251397 , 0.51401424, 0.58417455],
[-0.66813715, 0.89538709, 1.15031466]])
arr.sort(0)arr
array([[-1.72025055, -1.47464429, -0.16630714],
[-1.25434574, 0.51401424, 0.58417455],
[-0.66813715, 0.76233307, 1.15031466],
[-0.4251397 , 0.89538709, 2.09807311],
[ 0.50202059, 0.97145056, 2.82788532]])
