@pastqing
2016-04-14T05:27:03.000000Z
字数 6817
阅读 2784
Java集合框架——List(一)
java java-collection-framwork
一、ArrayList源码分析(JDK7)
ArrayList内部维护了一个动态的Object数组,ArrayList的动态增删就是对这个对组的动态的增加和删除。
1、ArrayList构造以及初始化
- ArrayList实例变量
//ArrayList默认容量private static final int DEFAULT_CAPACITY = 10;//默认空的Object数组, 用于定义空的ArrayListprivate static final Object[] EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA = {};//ArrayList存放存放元素的Object数组private transient Object[] elementData;//ArrayList中元素的数量private int size;
ArrayList构造函数
- 无参构造函数: 即构造一个空的Object[]
public ArrayList() {super();this.elementData = EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA;}
- 指定容量大小构造:
public ArrayList(int initialCapacity) {super();if (initialCapacity < 0)throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal Capacity: "+initialCapacity);this.elementData = new Object[initialCapacity];}
- 指定某一实现Collection接口的集合构造:
public ArrayList(Collection<? extends E> c) {elementData = c.toArray();size = elementData.length;// c.toArray might (incorrectly) not return Object[] (see 6260652)if (elementData.getClass() != Object[].class)elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, size, Object[].class);}
这里也说明了Collection的作用, java-collection-framwork设计Collection接口而不是直接使用List,Set等接口的原因。
2、ArrayList的容量分配机制
- ArrayList的容量上限: ArrayList容量是有上限的,理论允许分配
Integer.Max_VALUE - 8大小的容量。但是能分配多少还跟堆栈设置有关, 需要设置VM参数
private static final int MAX_ARRAY_SIZE = Integer.MAX_VALUE - 8;
- 调用Add方法时扩容规则
public boolean add(E e) {ensureCapacityInternal(size + 1); // Increments modCount!!elementData[size++] = e;return true;}
ensureCapacityInternal(int)方法实际上确定一个最小扩容大小。
private void ensureCapacityInternal(int minCapacity) {if (elementData == EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA) {minCapacity = Math.max(DEFAULT_CAPACITY, minCapacity);}ensureExplicitCapacity(minCapacity);}
private void ensureExplicitCapacity(int minCapacity) {modCount++;// overflow-conscious codeif (minCapacity - elementData.length > 0)grow(minCapacity);}
- 关于modCount: modCount定义在抽象类AbstratList中, 源码的注释基本说明了它的用处:在使用迭代器遍历的时候,用来检查列表中的元素是否发生结构性变化(列表元素数量发生改变的一个计数)了,主要在多线程环境下需要使用,防止一个线程正在迭代遍历,另一个线程修改了这个列表的结构。
This field is used by the iterator and list iterator implementation returned by the iterator and listIterator methods.If the value of this field changes unexpectedly, the iterator (or list iterator) will throw a ConcurrentModificationException in response to the next, remove, previous, set or add operations.This provides fail-fast behavior, rather than non-deterministic behavior in the face of concurrent modification during iteration.
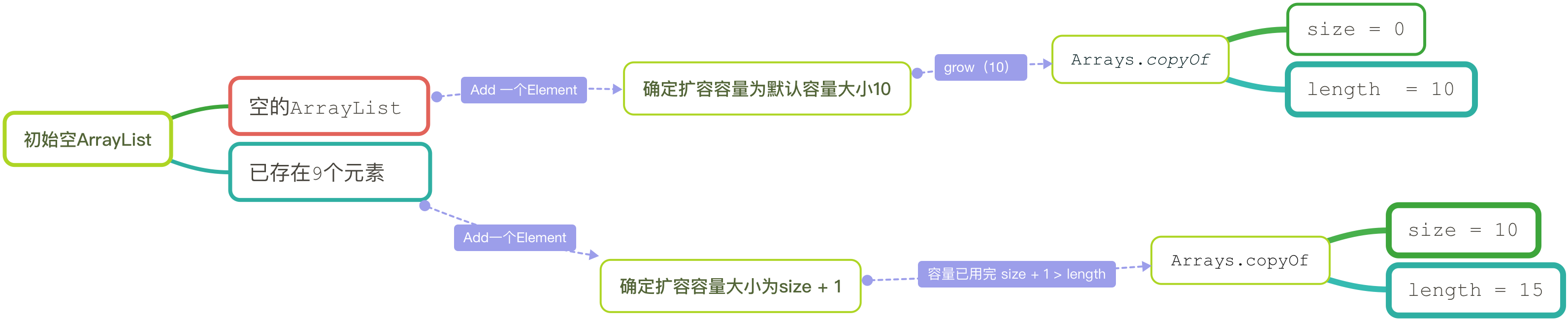
grow方法为真正的扩容方法
private void grow(int minCapacity) {// overflow-conscious codeint oldCapacity = elementData.length;int newCapacity = oldCapacity + (oldCapacity >> 1);if (newCapacity - minCapacity < 0)newCapacity = minCapacity;if (newCapacity - MAX_ARRAY_SIZE > 0)newCapacity = hugeCapacity(minCapacity);// minCapacity is usually close to size, so this is a win:elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, newCapacity);}
其中对大容量扩容多少还有个hugeCapacity方法
private static int hugeCapacity(int minCapacity) {if (minCapacity < 0) // overflowthrow new OutOfMemoryError();return (minCapacity > MAX_ARRAY_SIZE) ?Integer.MAX_VALUE :MAX_ARRAY_SIZE;}
- 总结:
- 每次扩容都会伴随着数组的复制操作, 因此一次给定恰当的容量会提高一点性能。
- 下图是我归纳的整个扩容流程:
二、ArrayList迭代器
ArrayList的迭代器主要有两种Itr和ListItr, 但是在jDK1.8中还添加了一个ArrayListSpliterator, 下面分别学一下Itr和ListItr的源码分析。
1、Itr:只能向后遍历
private class Itr implements Iterator<E> {int cursor; // index of next element to returnint lastRet = -1; // index of last element returned; -1 if no such//expectedModCount 是modCount的一个副本int expectedModCount = modCount;public boolean hasNext() {return cursor != size;}@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")public E next() {checkForComodification();//记录当前位置int i = cursor;if (i >= size)throw new NoSuchElementException();Object[] elementData = ArrayList.this.elementData;if (i >= elementData.length)throw new ConcurrentModificationException();//下一个元素的位置cursor = i + 1;return (E) elementData[lastRet = i];}//使用迭代器的remove方法public void remove() {if (lastRet < 0)throw new IllegalStateException();checkForComodification();try {//注意内部类调用外部类的方式ArrayList.this.remove(lastRet);//remove之后需要重新调整各个指针的位置cursor = lastRet;lastRet = -1;expectedModCount = modCount;} catch (IndexOutOfBoundsException ex) {throw new ConcurrentModificationException();}}final void checkForComodification() {if (modCount != expectedModCount)throw new ConcurrentModificationException();}}
- 从源码中可以看出Itr迭代器是向前迭代器, 它提供了一个
next方法用于获取ArrayList中的元素。 checkForComodification是java-collection-framwork中的一种fail-fast的错误检测机制。在多线程环境下对同一个集合操作,就可能触发fail-fast机制, 抛出ConcurrentModificationException异常。Itr迭代器定义了一个
expectedModCount记录modCount副本。在ArrayList执行改变结构的操作的时候例如Add, remove, clear方法时modCount的值会改变。通过Itr源码可以看出调用
next和remove方法会触发fail-fast检查。此时如果在遍历该集合时, 存在其他线程正在执行改变该集合结构的操作时就会发生异常。
2、ListItr:支持向前和向后遍历,下面看看ListItr的源码:
private class ListItr extends Itr implements ListIterator<E> {ListItr(int index) {super();cursor = index;}public boolean hasPrevious() {return cursor != 0;}public int nextIndex() {return cursor;}public int previousIndex() {return cursor - 1;}@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")public E previous() {checkForComodification();//arrayList前一个元素的位置int i = cursor - 1;if (i < 0)throw new NoSuchElementException();Object[] elementData = ArrayList.this.elementData;if (i >= elementData.length)throw new ConcurrentModificationException();cursor = i;return (E) elementData[lastRet = i];}//该迭代器中添加了set方法public void set(E e) {if (lastRet < 0)throw new IllegalStateException();checkForComodification();try {ArrayList.this.set(lastRet, e);} catch (IndexOutOfBoundsException ex) {throw new ConcurrentModificationException();}}//该迭代器添加了add方法public void add(E e) {checkForComodification();try {int i = cursor;ArrayList.this.add(i, e);//重新标记指针位置cursor = i + 1;lastRet = -1;expectedModCount = modCount;} catch (IndexOutOfBoundsException ex) {throw new ConcurrentModificationException();}}}
- ListItr的实现基本与Itr一致, 添加了可以先前遍历的方法以及
add与set方法。
3、使用java.util.concurrent中的CopyOnWriteArrayList解决fast-fail问题
CopyOnWriteArrayList是线程安全的, 具体看一下它的add方法源码:
public boolean add(E e) {final ReentrantLock lock = this.lock;lock.lock();try {Object[] elements = getArray();int len = elements.length;Object[] newElements = Arrays.copyOf(elements, len + 1);newElements[len] = e;setArray(newElements);return true;} finally {lock.unlock();}}
- CopyOnWriteArrayList就是写时复制的ArrayList。当开始写数据的操作时候, Arrays.copyOf一个新的数组, 这样不会影响读操作。
- 这样的代价就是会损耗内存, 带来性能的问题。CopyOnWriteArrayList写的时候在内存中生成一个副本对象, 同时原来的对象仍然存在。
- CopyOnWriteArrayList无法保证数据实时的一致, 只能保证结果的一致。适用于并发下读多写少得场景, 例如缓存。
三、ArrayList的其他方法源码:
- 一个私有方法
batchRemove(Collection<?>c, boolean complement), 即批量移除操作
private boolean batchRemove(Collection<?> c, boolean complement) {//下面会提到使用final的原因final Object[] elementData = this.elementData;int r = 0, w = 0;boolean modified = false;try {//遍历List中的元素,进行验证for (; r < size; r++)if (c.contains(elementData[r]) == complement)elementData[w++] = elementData[r];} finally {//try中如果出现异常,则保证数据一致性执行下面的copy操作if (r != size) {System.arraycopy(elementData, r,elementData, w,size - r);w += size - r;}//清理无用的元素, 通知GC回收if (w != size) {// clear to let GC do its workfor (int i = w; i < size; i++)elementData[i] = null;modCount += size - w;size = w;modified = true;}}return modified;}
- final修饰的变量指的是同一个引用, 为了后面保持数据的一致性。
此方法,想保留Collection c中的元素时, complement值为true; 想移除c中的元素时, complement值为false。这样就分别变成了
retainAll和removeAll方法。swap:交换arrayList中的某两个位置的
