@wudawufanfan
2016-10-01T09:56:19.000000Z
字数 5693
阅读 571
The numerical problem in the decays of two types of nucleus
calculation decay nucles
Introduction
A radioactive decay problem involving two types of nuclei,A and B,with populations and .That the type A nuclei decay to form type B nuclei according to the differential equations
while for simplicity.
Now we should solve this system of equations for the numbers of nuclei, and , as functions of time.
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-"""Created on Sat Oct 1 14:44:46 2016@author: 帆帆"""import pylab as plclass uranium_decay:def __init__(self, number_of_nuclei_A = 100, number_of_nuclei_B=0, time_constant = 1, time_of_duration = 5, time_step = 0.05):# unit of time is secondself.n_uranium_A = [number_of_nuclei_A]self.n_uranium_B = [number_of_nuclei_B]self.t = [0]self.tau = time_constantself.dt = time_stepself.time = time_of_durationself.nsteps = int(time_of_duration // time_step + 1)print("Initial number of nuclei A ->", number_of_nuclei_A)print("Initial number of nuclei B->", number_of_nuclei_B)print("Time constant ->", time_constant)print("time step -> ", time_step)print("total time -> ", time_of_duration)def calculate(self):for i in range(self.nsteps):tmpA = self.n_uranium_A[i] + (self.n_uranium_B[i] / self.tau -self.n_uranium_A[i] / self.tau)* self.dttmpB = self.n_uranium_B[i] + (self.n_uranium_A[i] / self.tau -self.n_uranium_B[i] / self.tau)* self.dtself.n_uranium_A.append(tmpA)self.n_uranium_B.append(tmpB)self.t.append(self.t[i] + self.dt)def show_results(self):pl.plot(self.t, self.n_uranium_A)pl.xlabel('time ($s$)')pl.ylabel('Number of Nuclei A')pl.show()pl.plot(self.t, self.n_uranium_B)pl.xlabel('time ($s$)')pl.ylabel('Number of Nuclei B')pl.show()a = uranium_decay()a.calculate()a.show_results()
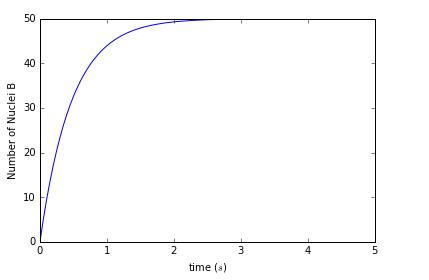
[the two results and the combination]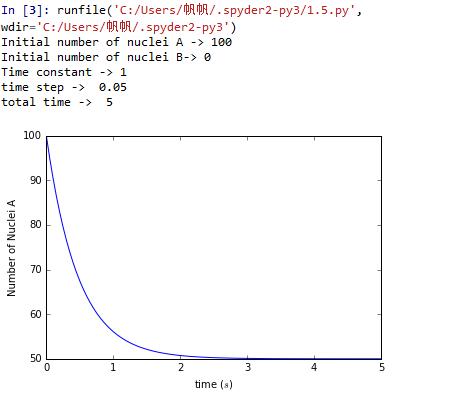
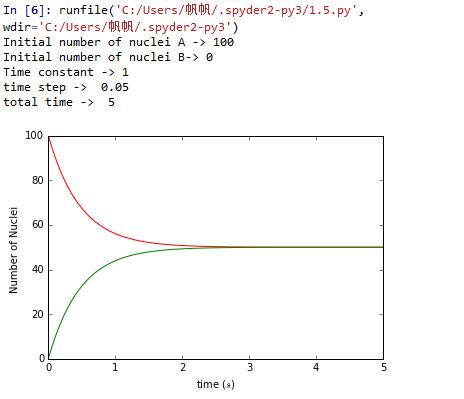
In attacking the radioactive decay problem we were led to treat time as a discrete variable.Such a discretization of time,or space,or both,is a common practice in numerical calculation,and brings up two related questions:
- How do we konw that the errors introduced by this discretencess are negligible
- How do we choose the value of such a step size for a calculation
We know
=
solve this first order differential equations with initial conditions we have
import pylab as plclass uranium_decay:def __init__(self, number_of_nuclei_A = 100, number_of_nuclei_B=0, time_constant = 1, time_of_duration = 5, time_step = 0.05):# unit of time is secondself.n_uranium_A = [number_of_nuclei_A]self.n_uranium_B = [number_of_nuclei_B]self.t = [0]self.tau = time_constantself.dt = time_stepself.time = time_of_durationself.nsteps = int(time_of_duration // time_step + 1)print("Initial number of nuclei A ->", number_of_nuclei_A)print("Initial number of nuclei B->", number_of_nuclei_B)print("Time constant ->", time_constant)print("time step -> ", time_step)print("total time -> ", time_of_duration)def calculate(self):for i in range(self.nsteps):tmpA = self.n_uranium_A[i] + (self.n_uranium_B[i] / self.tau -self.n_uranium_A[i] / self.tau)* self.dttmpB = self.n_uranium_B[i] + (self.n_uranium_A[i] / self.tau -self.n_uranium_B[i] / self.tau)* self.dtself.n_uranium_A.append(tmpA)self.n_uranium_B.append(tmpB)self.t.append(self.t[i] + self.dt)def show_results(self):pl.plot(self.t, self.n_uranium_A,'r')pl.plot(self.t, self.n_uranium_B,'g',)pl.xlabel('time ($s$)')pl.ylabel('Number of Nuclei ')pl.show()import mathclass exact_results_check(uranium_decay):def show_results(self):self.etA = []self.etB = []for i in range(len(self.t)):tempA = 50+50*math.exp(- self.t[i] / self.tau)tempB = 50-50*math.exp(- self.t[i] / self.tau)self.etA.append(tempA)self.etB.append(tempB)pl.plot(self.t, self.etA)pl.plot(self.t, self.etB)pl.plot(self.t, self.n_uranium_A, '*')pl.plot(self.t, self.n_uranium_B, '*')pl.xlabel('time ($s$)')pl.ylabel('Number of Nuclei')pl.xlim(0, self.time)pl.show()a = exact_results_check()a.calculate()a.show_results()
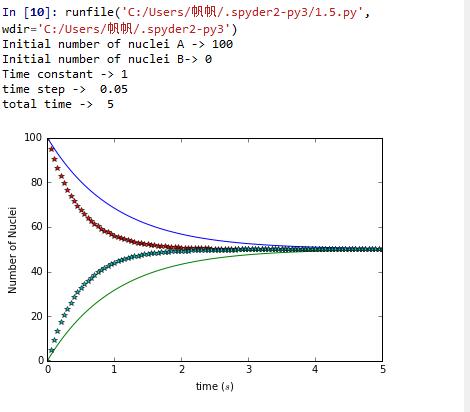
clearly,the simulation results is a bit different from the real result.
Improvement
import pylab as plclass uranium_decay:def __init__(self, number_of_nuclei_A = 100, number_of_nuclei_B=0, time_constant = 1, time_of_duration = 5, time_step = 0.05):# unit of time is secondself.n_uranium_A = [number_of_nuclei_A]self.n_uranium_B = [number_of_nuclei_B]self.t = [0]self.tau = time_constantself.dt = time_stepself.time = time_of_durationself.nsteps = int(time_of_duration // time_step + 1)print("Initial number of nuclei A ->", number_of_nuclei_A)print("Initial number of nuclei B->", number_of_nuclei_B)print("Time constant ->", time_constant)print("time step -> ", time_step)print("total time -> ", time_of_duration)def calculate(self):for i in range(self.nsteps):tmpA = self.n_uranium_A[i] + (self.n_uranium_B[i] / self.tau -self.n_uranium_A[i] / self.tau)* self.dttmpB = self.n_uranium_B[i] + (self.n_uranium_A[i] / self.tau -self.n_uranium_B[i] / self.tau)* self.dtself.n_uranium_A.append(tmpA)self.n_uranium_B.append(tmpB)self.t.append(self.t[i] + self.dt)class diff_step_check(uranium_decay):def show_results(self, style = 'b'):pl.plot(self.t, self.n_uranium_A, style)pl.plot(self.t, self.n_uranium_B, style)pl.xlabel('time ($s$)')pl.ylabel('Number of Nuclei')pl.xlim(0, self.time)from pylab import *b = diff_step_check(number_of_nuclei_A=100,number_of_nuclei_B=0, time_constant=1,time_of_duration = 5, time_step = 0.05)b.calculate()b.show_results()c = diff_step_check(number_of_nuclei_A=100,number_of_nuclei_B=0, time_constant=1,time_of_duration = 5, time_step = 0.0001)c.calculate()c.show_results('r')show()
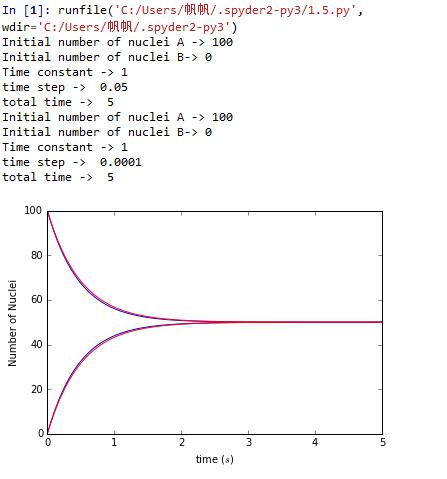
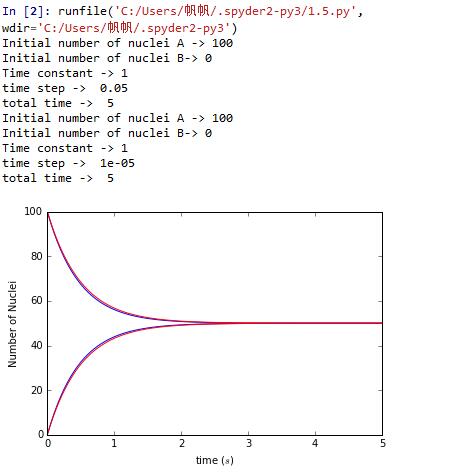
Change the time step didn't change the curve much.But we know this result is different from the real result a lot.So there may be another way to improve the accuracy of numerical results.
Conclusion
The numerical results are consistent with the idea that the system reaches a steady state in which and are constant.d/dt and d/dt vanish as well.
Thanks
Thanks for Caihao's PPT.
