@Arbalest-Laevatain
2018-12-28T03:23:32.000000Z
字数 966
阅读 733
快速排序测试
未分类
测试代码
#include <iostream>#include "Sort.h"using namespace std;/*快速排序*/int flag01 = 0; //全局变量,来计数//一次划分函数int Part(RcdType rcd[], int low, int high){rcd[0] = rcd[low];while (low<high){while (low < high && rcd[high].key >= rcd[0].key)high--;rcd[low] = rcd[high];while (low < high && rcd[low].key <= rcd[0].key)low++;rcd[high] = rcd[low];}//此时low即为划分后枢轴应该在的位置rcd[low] = rcd[0];flag01++;return low;}void QSort(RcdType rcd[], int s, int t){int mid;//枢轴位置if (s <= 0 || t <= 0)return;else if (s<t){mid = Part(rcd, s, t);QSort(rcd, mid+1, t);QSort(rcd, s, mid-1);}}int QSort_num(){return flag01;}void out(RcdType rcd[],int n){for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)cout << rcd[i].key<<" ";cout << endl;}RcdType rcd[10] = {0,9,8,7,6,5,4,3,2,1};RcdType rcd1[10] = { 0,6,8,7,5,9,4,3,2,1 };RcdType rcd2[10] = { 0,3,8,7,6,9,5,4,2,1 };int main(){out(rcd1,10);QSort(rcd1, 1, 10 - 1);out(rcd1, 10);cout << QSort_num() << endl;flag01 = 0;out(rcd2, 10);QSort(rcd2, 1, 10 - 1);out(rcd2, 10);cout << QSort_num() << endl;return 0;}
测试结果
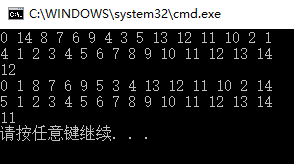
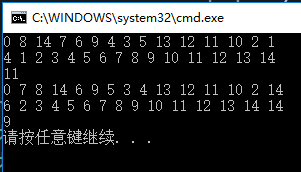
有上面两次测试可见,当枢轴的值接近于待排序列的中位数时,快速排序性能较好。
为避免枢轴的值为最小最大值,可以前、后、中间三个记录的大小居中的记录为枢轴
