@songlaf
2016-05-30T13:47:23.000000Z
字数 4969
阅读 721
Nginx安装手册
Linux
一) nginx安装环境
#gccyum install gcc-c++#PCRE PCRE(Perl Compatible Regular Expressions)是一个Perl库,包括 perl 兼容的正则表达式库。nginx的http模块使用pcre来解析正则表达式,所以需要在linux上安装pcre库。yum install -y pcre pcre-devel#zlib库提供了很多种压缩和解压缩的方式,nginx使用zlib对http包的内容进行gzip,所以需要在linux上安装zlib库。yum install -y zlib zlib-devel#OpenSSL 是一个强大的安全套接字层密码库,囊括主要的密码算法、常用的密钥和证书封装管理功能及SSL协议,并提供丰富的应用程序供测试或其它目的使用。nginx不仅支持http协议,还支持https(即在ssl协议上传输http),所以需要在linux安装openssl库。yum install -y openssl openssl-devel
二) 编译安装
#将nginx-1.8.0.tar.gz拷贝至linux服务器。#解压:tar -zxvf nginx-1.8.0.tar.gzcd nginx-1.8.0#修改配置参数./configure --help查询详细参数(参考本教程附录部分:nginx编译参数)参数设置如下:./configure \--prefix=/usr/local/nginx \--pid-path=/var/run/nginx/nginx.pid \--lock-path=/var/lock/nginx.lock \--error-log-path=/var/log/nginx/error.log \--http-log-path=/var/log/nginx/access.log \--with-http_gzip_static_module \--http-client-body-temp-path=/var/temp/nginx/client \--http-proxy-temp-path=/var/temp/nginx/proxy \--http-fastcgi-temp-path=/var/temp/nginx/fastcgi \--http-uwsgi-temp-path=/var/temp/nginx/uwsgi \--http-scgi-temp-path=/var/temp/nginx/scgi注意:上边将临时文件目录指定为/var/temp/nginx,需要在/var下创建temp及nginx目录编译安装makemake install
安装成功查看安装目录 :
三)nginx相关命令
#启动nginxcd /usr/local/nginx/sbin/./nginx
查询nginx进程:
ps aux|grep nginx#15098是nginx主进程的进程id,15099是nginx工作进程的进程id

注意:执行./nginx启动nginx,这里可以-c指定加载的nginx配置文件,如下:
./nginx -c /usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf
如果不指定-c,nginx在启动时默认加载conf/nginx.conf文件,此文件的地址也可以在编译安装nginx时指定./configure的参数(--conf-path= 指向配置文件(nginx.conf))
4 停止nginx
方式1,快速停止:
cd /usr/local/nginx/sbin
./nginx -s stop
此方式相当于先查出nginx进程id再使用kill命令强制杀掉进程。
方式2,完整停止(建议使用):
cd /usr/local/nginx/sbin
./nginx -s quit
此方式停止步骤是待nginx进程处理任务完毕进行停止。
5 重启nginx
方式1,先停止再启动(建议使用):
对nginx进行重启相当于先停止nginx再启动nginx,即先执行停止命令再执行启动命令。
如下:
./nginx -s quit
./nginx
方式2,重新加载配置文件:
当nginx的配置文件nginx.conf修改后,要想让配置生效需要重启nginx,使用-s reload不用先停止nginx再启动nginx即可将配置信息在nginx中生效,如下:
./nginx -s reload
6 测试
nginx安装成功,启动nginx,即可访问虚拟机上的nginx:

到这说明nginx上安装成功。
7 开机自启动nginx
7.1 编写shell脚本
这里使用的是编写shell脚本的方式来处理
vi /etc/init.d/nginx (输入下面的代码)
!/bin/bash
nginx Startup script for the Nginx HTTP Server
it is v.0.0.2 version.
chkconfig: - 85 15
description: Nginx is a high-performance web and proxy server.
It has a lot of features, but it's not for everyone.
processname: nginx
pidfile: /var/run/nginx.pid
config: /usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf
nginxd=/usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx
nginx_config=/usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf
nginx_pid=/var/run/nginx.pid
RETVAL=0
prog="nginx"
Source function library.
. /etc/rc.d/init.d/functions
Source networking configuration.
. /etc/sysconfig/network
Check that networking is up.
[ {NETWORKING} = "no" ] && exit 0
[ -xnginxd ] || exit 0
Start nginx daemons functions.
start() {
if [ -e "Starting nginxd -c ?
echo
[ RETVAL = 0 ] && touch /var/lock/subsys/nginx
returnRETVAL
}
Stop nginx daemons functions.
stop() {
echo -n prog: "
killproc ?
echo
[ $RETVAL = 0 ] && rm -f /var/lock/subsys/nginx /var/run/nginx.pid
}
reload nginx service functions.
reload() {
echo -n prog: "
#kill -HUP cat ${nginx_pid}
killproc ?
echo
}
See how we were called.
case "prog
RETVAL="Usage: RETVAL
:wq 保存并退出
7.2 设置文件的访问权限
chmod a+x /etc/init.d/nginx (a+x ==> all user can execute 所有用户可执行)
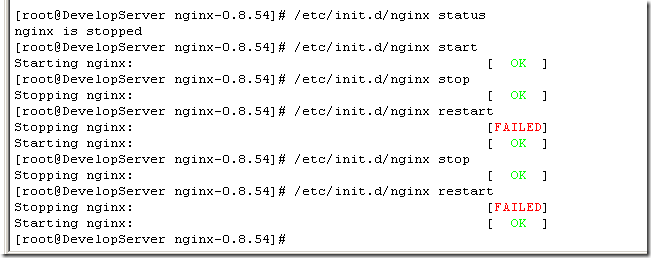
这样在控制台就很容易的操作nginx了:查看Nginx当前状态、启动Nginx、停止Nginx、重启Nginx…
如果修改了nginx的配置文件nginx.conf,也可以使用上面的命令重新加载新的配置文件并运行,可以将此命令加入到rc.local文件中,这样开机的时候nginx就默认启动了
7.3 加入到rc.local文件中
vi /etc/rc.local
加入一行 /etc/init.d/nginx start 保存并退出,下次重启会生效。
配置目录轨迹
1、打开/usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf,找到Server配置处,加入以下内容:
location /soft/ {
root /var/www/; 此处为soft的上一级目录
autoindex on;
autoindex_exact_size off;
autoindex_localtime on;
}
例子,有如下匹配规则:
[plain] view plain copy 在CODE上查看代码片派生到我的代码片
location = / {
#规则A
}
location = /login {
#规则B
}
location ^~ /static/ {
#规则C
}
location ~ .(gif|jpg|png|js|css){
#规则D
}
location ~* \.png {
#规则E
}
location !~ .xhtml{
#规则F
}
location !~* \.xhtml {
#规则G
}
location / {
#规则H
}
那么产生的效果如下:
访问根目录/, 比如http://localhost/ 将匹配规则A
访问 http://localhost/login 将匹配规则B,http://localhost/register 则匹配规则H
访问 http://localhost/static/a.html 将匹配规则C
访问 http://localhost/a.gif, http://localhost/b.jpg 将匹配规则D和规则E,但是规则D顺序优先,规则E不起作用,而 http://localhost/static/c.png 则优先匹配到 规则C
访问 http://localhost/a.PNG 则匹配规则E, 而不会匹配规则D,因为规则E不区分大小写。
访问 http://localhost/a.xhtml 不会匹配规则F和规则G,http://localhost/a.XHTML不会匹配规则G,因为不区分大小写。规则F,规则G属于排除法,符合匹配规则但是不会匹配到,所以想想看实际应用中哪里会用到。
访问 http://localhost/category/id/1111 则最终匹配到规则H,因为以上规则都不匹配,这个时候应该是nginx转发请求给后端应用服务器,比如FastCGI(php),tomcat(jsp),nginx作为方向代理服务器存在。
所以实际使用中,个人觉得至少有三个匹配规则定义,如下:
[plain] view plain copy 在CODE上查看代码片派生到我的代码片
直接匹配网站根,通过域名访问网站首页比较频繁,使用这个会加速处理,官网如是说。
这里是直接转发给后端应用服务器了,也可以是一个静态首页
第一个必选规则
location = / {
proxy_pass http://tomcat:8080/index
}
第二个必选规则是处理静态文件请求,这是nginx作为http服务器的强项
有两种配置模式,目录匹配或后缀匹配,任选其一或搭配使用
location ^~ /static/ {
root /webroot/static/;
}
location ~* .(gif|jpg|jpeg|png|css|js|ico)$ {
root /webroot/res/;
}
第三个规则就是通用规则,用来转发动态请求到后端应用服务器
非静态文件请求就默认是动态请求,自己根据实际把握
毕竟目前的一些框架的流行,带.php,.jsp后缀的情况很少了
location / {
proxy_pass http://tomcat:8080/
}
