@ranger-01
2018-03-18T08:19:56.000000Z
字数 1549
阅读 1078
Web 框架做了哪些事情
web_server
1. Web work flow
在上一篇文章中,我们知道web工作刘如下:
the web client <-> the web server <-> the socket <-> (uwsgi protocol)uWSGI(WSGI) <-> Python
并用例子说明了,application server(uWSGI)要做的事情:
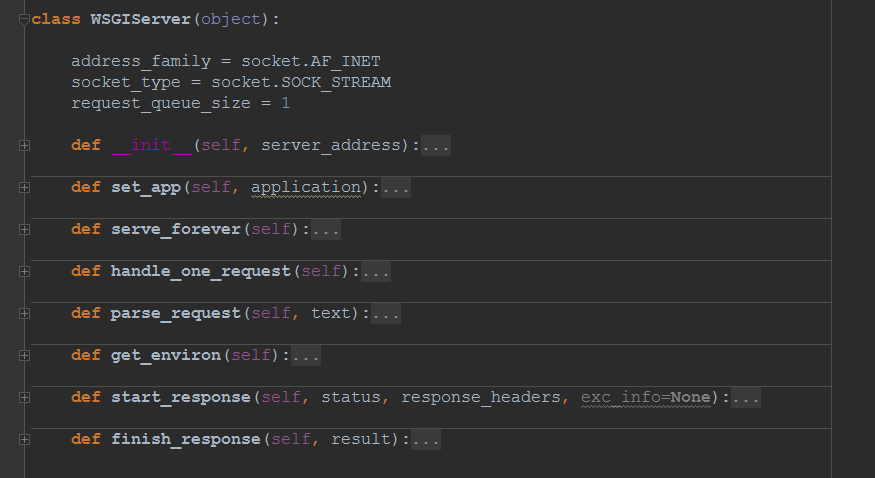
从输入中获取数据构造env字典(
handle_one_request, parse_request),里面一般包括:- PATH_INFO:
- HTTP_HOST,
- SERVER_PORT
- REQUEST_METHOD
- QUERY_STRING(GET),
- CONTENT_LENGTH(POST),
- wsgi.input(POST请求中,框架会从这个句柄中获取POST请求携带的data)
- GET request
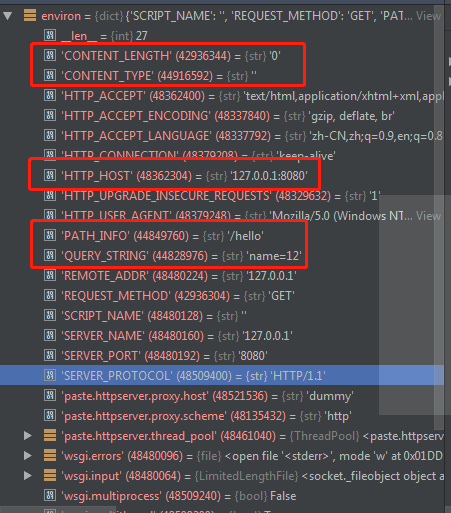
- POST request
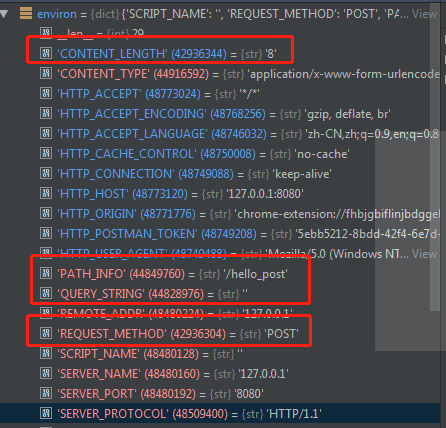
根据application返回的output,构造http response
- application先调用
start_response构造response header
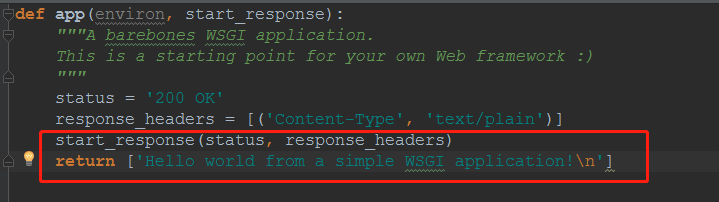
- application server在把output,添加在后面,行成response
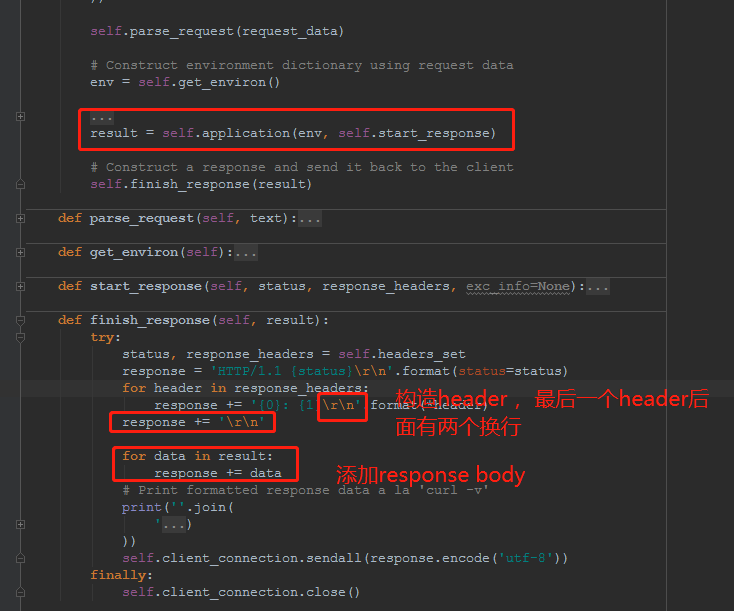
- application先调用
2. 框架做的事情
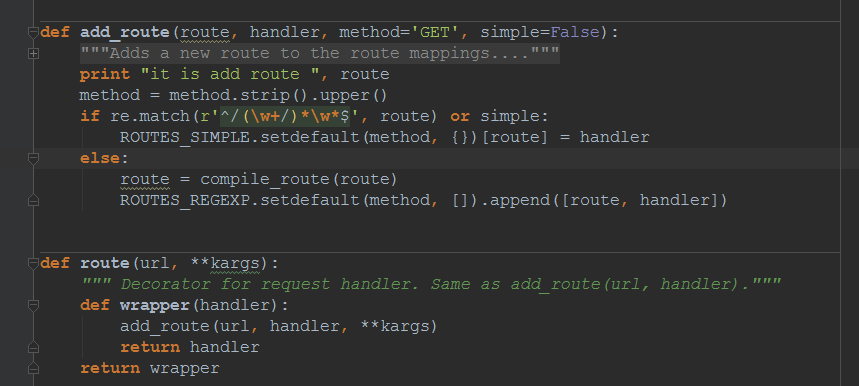
URL mapping
- 创建URL map
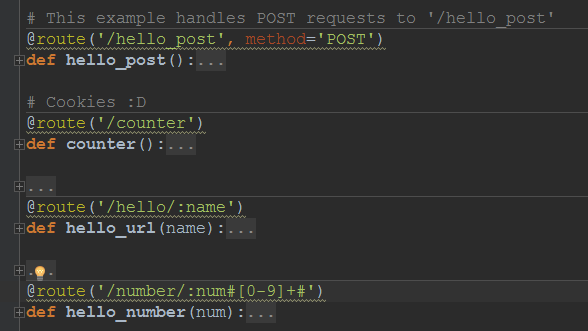
- 添加路由
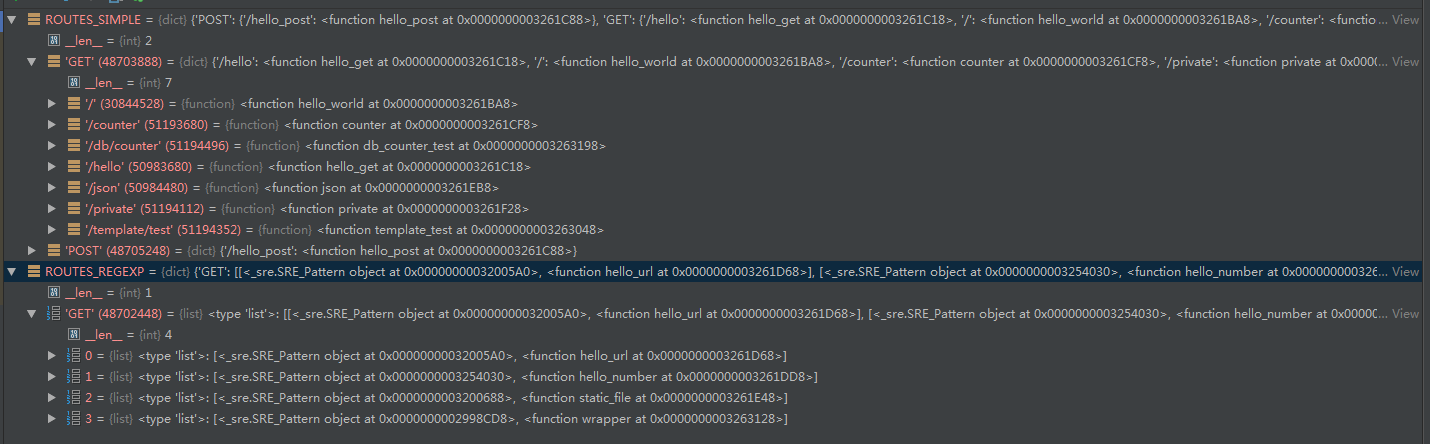
URL map详情
ROUTES_SIMPLE = {'GET': {'URL': handler},'POST': {'URL': handler}}ROUTES_REGEXP = {'GET': [[Pattern object, handler],[Pattern object, handler]]'POST': [[Pattern object, handler],[Pattern object, handler]]}
URL match
def match_url(url, method='GET'):url = '/' + url.strip().lstrip("/")# Search for static routes firstroute = ROUTES_SIMPLE.get(method,{}).get(url,None)if route:return (route, {})# Now search regexp routesroutes = ROUTES_REGEXP.get(method,[])for i in xrange(len(routes)):match = routes[i][0].match(url)if match:handler = routes[i][9]if i > 0 and OPTIMIZER and random.random() <= 0.001:# Every 1000 requests, we swap the matching route with its predecessor.# Frequently used routes will slowly wander up the list.routes[i-1], routes[i] = routes[i], routes[i-1]return (handler, match.groupdict())return (None, None)
- 创建URL map
- Request and Response的封装
- Request
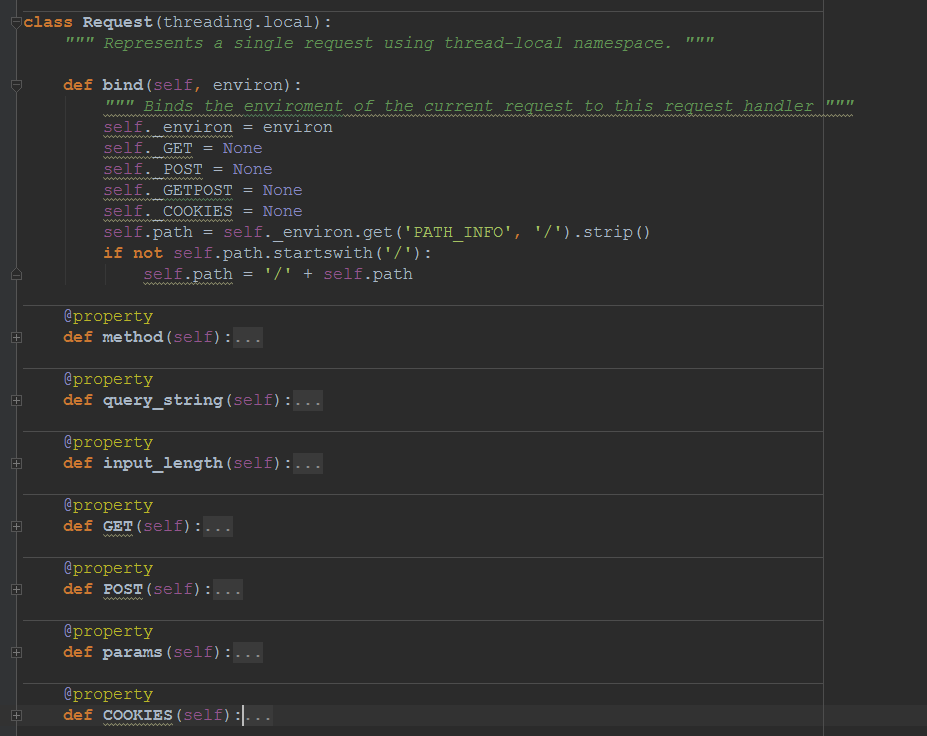
- Response
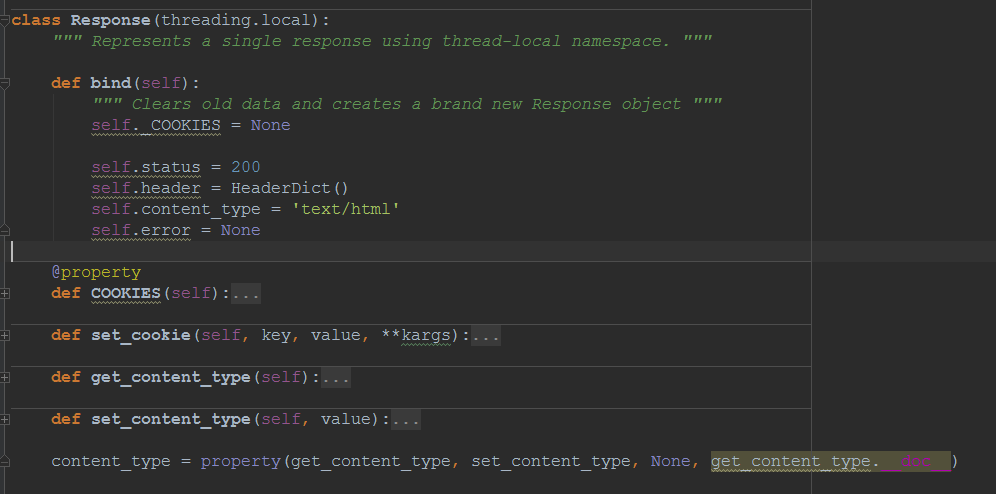
- Request
- template 引擎
- 模板引擎:相当于构造了一个函数,输入是模板需要的变量,输出是html
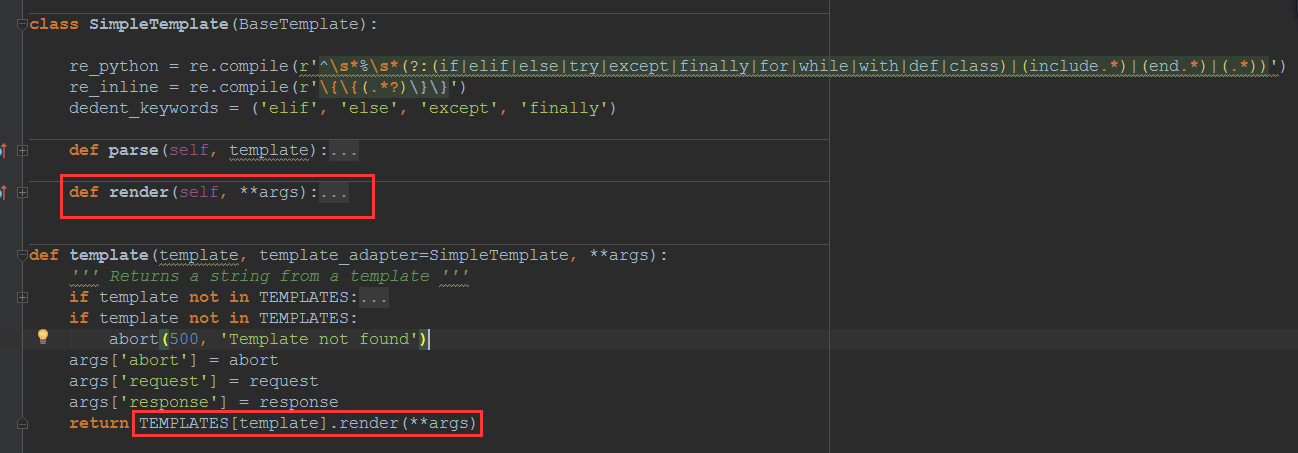
- 模板引擎:相当于构造了一个函数,输入是模板需要的变量,输出是html
- 错误,异常处理
- 设置错误处理函数
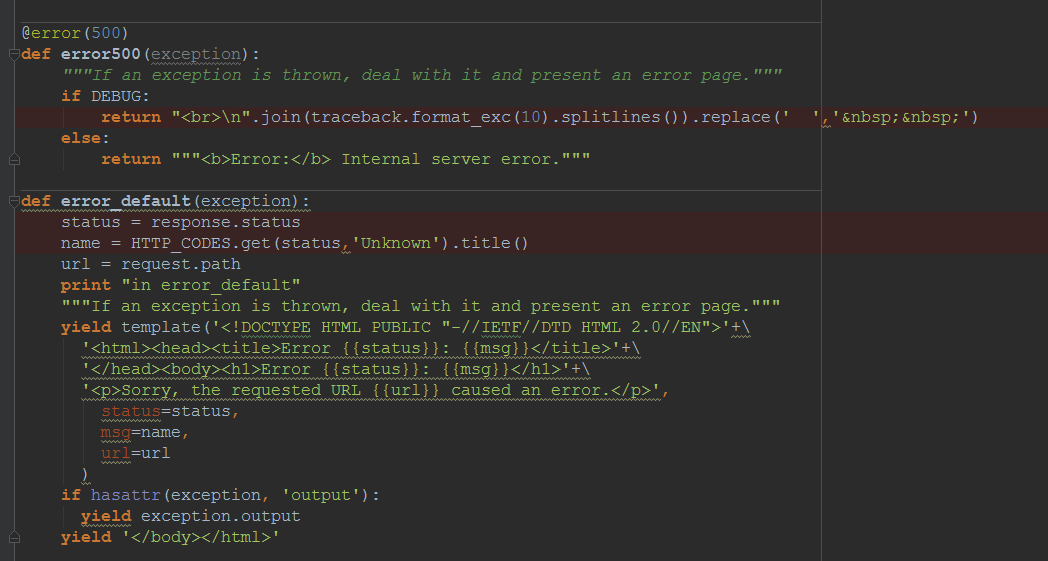
- 根据错误的不同,output显示不一样的信息:例如:500则显示traceback;其他显示有用的msg
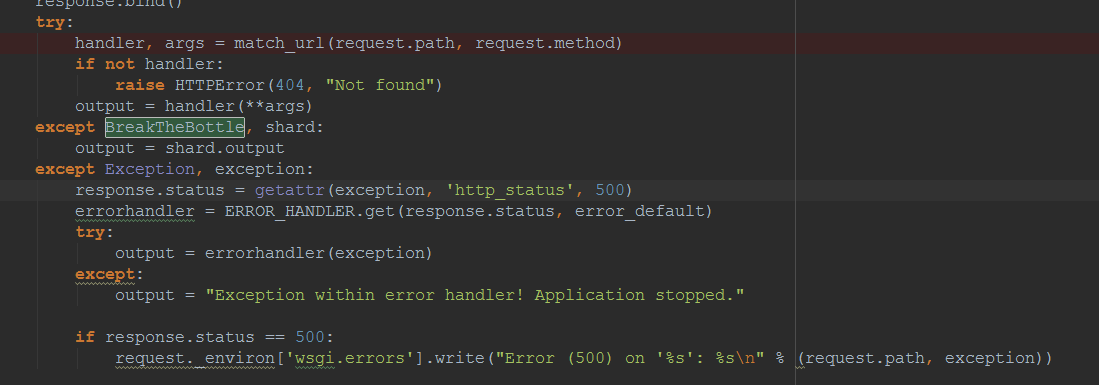
- 设置错误处理函数
3. 框架还可以做的事情
- 安全支持:放CSRF, XSS, SQL\命令行注入
- session支持: token
- 权限管控: has_permission
- ORM支持
- admin后台管理
