@RunZhi
2016-09-15T14:53:07.000000Z
字数 10269
阅读 3704
基本运算,求逆,求离散对数实现
密码学 编程 代数
前言
GF称为伽罗瓦域,又称有限域.定义详见Galois field.本文讨论GF(2^8)下加减乘除,求逆和离散对数的程序实现。
环境信息
操作系统:ubuntu 14.04
编程语言:C++
编译器:g++
各个运算的实现
以下介绍GF(2^8)各个部分实现细节。
相关定义
由于要多次使用字节类型,因此在本头文件中作一个宏定义
#define u8 unsigned char
由于会设计到简单的多项式除法,因此用一个结构体保存作除后得到的商和余数.
struct quorem{u8 first; // quotientu8 next; // remainderquorem(u8 i, u8 j){ first = i ; next = j; }};
为方便使用,定义一个类以表达GF(2^8)元素
class GF_eight{// additioninline friend GF_eight operator+(const GF_eight& i, const GF_eight& j);// subtractioninline friend GF_eight operator-(const GF_eight& i, const GF_eight& j);// multiplicationfriend GF_eight operator*(const GF_eight& i, const GF_eight& j);// divisionfriend GF_eight operator/(const GF_eight& i, const GF_eight& j);public:// ConstructorGF_eight(u8 V = 0){this->Value = V;}GF_eight(const GF_eight& V){this->Value = V.Value;}// return valueu8 getValue() const { return this->Value; }// Set the Valuevoid setValue(u8 V) { this->Value = V;}// Check if it is a generator of GF(2^8)bool is_gen() const;// Obtain the inverse elementGF_eight inverse() const;//Obtain the g^nGF_eight power(u8 n) const;//Obtain the dlog based gGF_eight log(const GF_eight& g) const;private:u8 Value;};
其中声明了暂时已实现的元素的操作.private域中的Value是实际保存的值.
加法与减法
中的元素可以看为一个位向量.由于系数是模2的,因此可以把加法看为异或,同样减法也是异或.
inline GF_eight operator+(const GF_eight& i, const GF_eight& j){return GF_eight(i.Value ^ j.Value);}inline GF_eight operator-(const GF_eight& i, const GF_eight& j){return GF_eight(i.Value ^ j.Value);}
乘法
稍微麻烦一点的是乘法,实际上执行乘法运算的话只需要按照我们平时的多项式乘法,其中注意模2,乘出来后得到的多项式还要模去的模多项式:
但这样执行似乎太慢了,我们可以考虑一下更快的乘法.
首先:在中代表零元素.因此有
但是这个有什么用呢?我们可以考虑一下如下运算
根据分配律,我们可以把它写成:
很显然,非常容易算,那么呢?还要按先乘后模吗?不需要,我们来看看怎么计算更好.
(这里用了群的结合律)
首先,移位一次:
既然是,那似乎应该继续移位一次。但我们先不这么做.注意,我们知道了:.它等价于:
因此,
至此,我们计算出了,接下来继续计算也是相同的办法.
基于这样的思想,写出的程序
GF_eight operator*(const GF_eight& i, const GF_eight& j){u8 lowest_bit = 0x01;u8 highest_bit = 0x80;u8 temp_j = j.Value;u8 temp_res = i.Value;u8 res = 0;u8 flag;if ( temp_j & lowest_bit )res = temp_res;temp_j >>= 1;while( temp_j != 0 ){flag = temp_res & highest_bit;temp_res <<= 1;// Plus 27 if b_8 == 1( flag == 1 )if( flag )temp_res ^= XXX;/* test codeprintf("%x\n",temp_res);*/if(temp_j & lowest_bit)res ^= temp_res;temp_j >>= 1;}return GF_eight(res);}
注意:程序执行并不严格按照我之前的例子,但思想是一样的。
求逆
在讲如何实现除法之前,首先要考虑求逆.因为我们不能进行普通的多项式除法,因为这是在模下的运算。而求了逆,除法也不过是一个乘法罢了.
由于是一个域,它对乘法运算构成一个交换群。我们可以参考数论里的EGCD算法(扩展欧几里德算法)进行求逆。
EGCD算法由于需要的篇幅不小,因此讲解请参考欧几里德算法与扩展欧几里德算法。注意,这个网站上虽然说的是上的EGCD算法,但是实际上,只要把域元素替换为,把相应的运算进行修改,对相应的变量类型进行一定的修改,得到的新算法就是适用于的EGCD算法.如果你看不懂这句话,那真的需要学点代数了。
求逆的代码在此:
GF_eight GF_eight::inverse() const{// Deal with the trivial casesif( this->Value == 0){printf("Zero element doesn't have inverse!\n");return GF_eight(0);}if( this->Value == 1)return GF_eight(1);// Using Extended Algorithmu8 r1 = 0x8D;u8 r2 = this->Value;u8 r3 = 0;u8 v1 = 1;u8 v2 = 0;u8 v3 = 0;u8 w1 = 0;u8 w2 = 1;u8 w3 = 0;u8 q = 0;quorem p(0,0);GF_eight temp(0);// Because we use the byte to implement poly_div. So we must// deal with the highest bit of the 0x11B before using EGCD.// The division is actually the same as the usual division. I just do some operation explicitly( Because we are just allowed to implement in bytes.)p = poly_div(r1, r2);q = p.first;r3 = p.next;r3 <<= 1;r3 ^= 1;q <<= 1;p = poly_div(r3, r2);q ^= p.first;r3 = p.next;/* test codeprintf("q:%x\n",q);printf("r3:%x\n",r3);printf("v:%x\n",v3);printf("w:%x\n\n",w3);getchar();*/r1 = r2;r2 = r3;v1 = 0;v2 = 1;w1 = 1;w2 = q;// Using EGCDwhile(1){//Obtain the quotient and remainderp = poly_div(r1, r2);q = p.first;r3 = p.next;if( r3 == 0 ) break;// The multiplication must be token in GF(2^8)temp = GF_eight(q) * GF_eight(v2);v3 = v1 ^ (temp.getValue());temp = GF_eight(q) * GF_eight(w2);w3 = w1 ^ (temp.getValue());/* test codeprintf("q:%x\n",q);printf("r1:%x\n",r1);printf("r2:%x\n",r2);printf("r3:%x\n",r3);printf("v:%x\n",v3);printf("w:%x\n\n",w3);getchar();*/r1 = r2;r2 = r3;v1 = v2;v2 = v3;w1 = w2;w2 = w3;}return GF_eight((u8)w2);
代码很长,我并不擅长写很简洁的代码。。。关于代码的部分解释,我想注释里面已经说了。这里的代码用到了函数poly_div,这个函数的声明为:
static quorem poly_div(u8 ii, u8 jj)
声明为static是因为这个函数只是用于辅助求逆运算的,没必要被用在外面。这个函数完成的是两个字节变量的多项式除法运算 ,并把得到的商和余数保存到结构体quorem中。注意,我们执行的是普通的多项式除法。
除法
完成了求逆之后,就可以直接进行除法运算了:
GF_eight operator/(const GF_eight& i, const GF_eight& j){GF_eight temp = j.inverse();return i * temp;}
求离散对数
求离散对数的一种很普通的方法就是逐个穷尽进行寻找。但我们实际上可以做得精细一些.可以使用碰撞法
碰撞法的描述可参考:An Introduction to Mathematical Cryptography 的page80, Proposition 2.22:
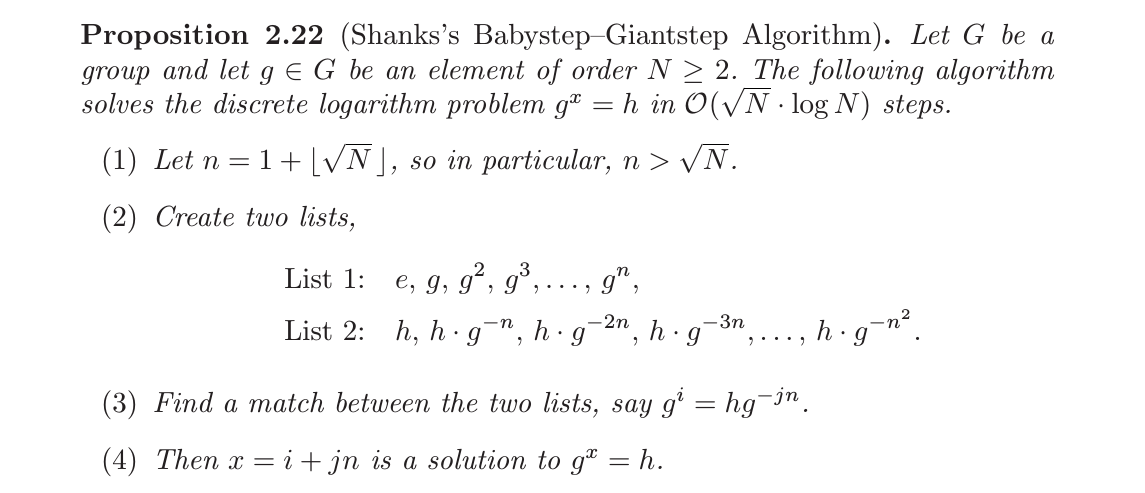
这个算法正确性的证明显然不适合放在这篇文章这里,有想法的人可以自行搜索上面说的电子书进行学习。
同样地,这个原始的算法也是解决的离散对数的,但还是那句话,代数告诉我们这个算法可以移植到.
具体实现代码如下:
GF_eight GF_eight::log(const GF_eight_pack::GF_eight &g) const{if( !g.is_gen() ){printf("The input is not a generator!\n");return 0;}GF_eight temp(1);GF_eight h(this->Value);// Using the simple algorithm:Collision method to solve g^x = hint N = 255;int n = sqrt(N)+1;// list for finding Collisionu8 list[256];memset(list, 0, 256);// Computing g^0,g^1,...,g^n and record the index iu8 i = 0;do{list[temp.getValue()] = i;temp = temp * g;i++;}while( i <= n );temp = temp.inverse(); // temp = g^-(n+1)temp = temp * g; // temp = g^-ni = 0;u8 j = 0;do{i = list[h.getValue()];if( i != 0)break;list[h.getValue()] = j;h = h * temp;j++;}while( j <= n );return i + (j*n);}
这段代码里面包含了两个辅助函数 is_gen 和 power.它们一个是判断某元素是否是生成元,另一个是快速幂运算。它们的代码请参考后面的完整代码.
完整代码
/**********************************************************************************FileName: gf.hpp*Author: RunzhiZeng*Version: 3.1*Date: 16-09-12*Description:Implementation of add, sub, mul, div, inv and dlog of GF(2^8)*Others:For Computer Security course*History:1. 16-09-12 V3.0:Implement the add, sub, mul and some other miscellaneous functions.2. 16-09-13 V3.1:Implement the inv, div and dlog function,also including the power and poly div functions.**********************************************************************************/#ifndef _GF_H_#define _GF_H_#include<cstdio>#include<cmath>#include<cstring>namespace GF_eight_pack{#define u8 unsigned char// x^8const u8 XXX = 0x1B;// Struct used to save quotient and remainderstruct quorem{u8 first; // quotientu8 next; // remainderquorem(u8 i, u8 j){ first = i ; next = j; }};class GF_eight{// additioninline friend GF_eight operator+(const GF_eight& i, const GF_eight& j);// subtractioninline friend GF_eight operator-(const GF_eight& i, const GF_eight& j);// multiplicationfriend GF_eight operator*(const GF_eight& i, const GF_eight& j);// divisionfriend GF_eight operator/(const GF_eight& i, const GF_eight& j);public:// ConstructorGF_eight(u8 V = 0){this->Value = V;}GF_eight(const GF_eight& V){this->Value = V.Value;}// return valueu8 getValue() const { return this->Value; }// Set the Valuevoid setValue(u8 V) { this->Value = V;}// Check if it is a generator of GF(2^8)bool is_gen() const;// Obtain the inverse elementGF_eight inverse() const;//Obtain the g^nGF_eight power(u8 n) const;//Obtain the dlog based gGF_eight log(const GF_eight& g) const;private:u8 Value;};inline GF_eight operator+(const GF_eight& i, const GF_eight& j){return GF_eight(i.Value ^ j.Value);}inline GF_eight operator-(const GF_eight& i, const GF_eight& j){return GF_eight(i.Value ^ j.Value);}GF_eight operator*(const GF_eight& i, const GF_eight& j){u8 lowest_bit = 0x01;u8 highest_bit = 0x80;u8 temp_j = j.Value;u8 temp_res = i.Value;u8 res = 0;u8 flag;if ( temp_j & lowest_bit )res = temp_res;temp_j >>= 1;while( temp_j != 0 ){flag = temp_res & highest_bit;temp_res <<= 1;// Plus 27 if b_8 == 1( flag == 1 )if( flag )temp_res ^= XXX;/* test codeprintf("%x\n",temp_res);*/if(temp_j & lowest_bit)res ^= temp_res;temp_j >>= 1;}return GF_eight(res);}GF_eight operator/(const GF_eight& i, const GF_eight& j){GF_eight temp = j.inverse();return i * temp;}////////////* Auxiliary functions for finding inverse*///////////////////// Auxiliary function for poly_div// Check if i's degree is equal to j'sstatic inline bool equal_degree(u8 i, u8 j){return ((i ^ j) < i && (i ^ j) < j);}// Poly division in GF(2^n). n equals to 8 in this functionstatic quorem poly_div(u8 ii, u8 jj){u8 shift = 0;u8 temp = 1;u8 res = 0;// Trival Caseif( jj == 0 ){printf("Error divisor\n");return quorem(0, 0);}if( ii == 0 )return quorem(0, jj);if( jj == 1 )return quorem(ii, 0);// When ii's degree is larger or equal to jj's degreeu8 temp_j = jj;res = 0;while( equal_degree(ii, jj) || ii > jj ){temp_j = jj;// Right shift the divisor until the divisor's degree is equal to the dividend'swhile(!equal_degree(ii, temp_j)){shift++;temp_j <<= 1;}/* test codeprintf("%x\n",temp_j);*/temp <<= shift;ii ^= temp_j;res ^= temp;shift = 0;temp = 1;}return quorem(res, ii);}/////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////// Finding inverse using EGCDGF_eight GF_eight::inverse() const{// Deal with the trivial casesif( this->Value == 0){printf("Zero element doesn't have inverse!\n");return GF_eight(0);}if( this->Value == 1)return GF_eight(1);// Using Extended Algorithmu8 r1 = 0x8D;u8 r2 = this->Value;u8 r3 = 0;u8 v1 = 1;u8 v2 = 0;u8 v3 = 0;u8 w1 = 0;u8 w2 = 1;u8 w3 = 0;u8 q = 0;quorem p(0,0);GF_eight temp(0);// Because we use the byte to implement poly_div. So we must// deal with the highest bit of the 0x11B before using EGCD.// The division is actually the same as the usual division. I just do some operation explicitly( Because we are just allowed to implement in bytes.)p = poly_div(r1, r2);q = p.first;r3 = p.next;r3 <<= 1;r3 ^= 1;q <<= 1;p = poly_div(r3, r2);q ^= p.first;r3 = p.next;/* test codeprintf("q:%x\n",q);printf("r3:%x\n",r3);printf("v:%x\n",v3);printf("w:%x\n\n",w3);getchar();*/r1 = r2;r2 = r3;v1 = 0;v2 = 1;w1 = 1;w2 = q;// Using EGCDwhile(1){//Obtain the quotient and remainderp = poly_div(r1, r2);q = p.first;r3 = p.next;if( r3 == 0 ) break;// The multiplication must be token in GF(2^8)temp = GF_eight(q) * GF_eight(v2);v3 = v1 ^ (temp.getValue());temp = GF_eight(q) * GF_eight(w2);w3 = w1 ^ (temp.getValue());/* test codeprintf("q:%x\n",q);printf("r1:%x\n",r1);printf("r2:%x\n",r2);printf("r3:%x\n",r3);printf("v:%x\n",v3);printf("w:%x\n\n",w3);getchar();*/r1 = r2;r2 = r3;v1 = v2;v2 = v3;w1 = w2;w2 = w3;}return GF_eight((u8)w2);}bool GF_eight::is_gen() const{GF_eight g(this->Value);u8 cnt = 0;while( g.Value != 1 ){g = g * (*this);cnt = cnt + 1;if ( cnt == 254)return true;}return false;}GF_eight GF_eight::log(const GF_eight_pack::GF_eight &g) const{if( !g.is_gen() ){printf("The input is not a generator!\n");return 0;}GF_eight temp(1);GF_eight h(this->Value);// Using the simple algorithm:Collision method to solve g^x = hint N = 255;int n = sqrt(N)+1;// list for finding Collisionu8 list[256];memset(list, 0, 256);// Computing g^0,g^1,...,g^n and record the index iu8 i = 0;do{list[temp.getValue()] = i;temp = temp * g;i++;}while( i <= n );temp = temp.inverse(); // temp = g^-(n+1)temp = temp * g; // temp = g^-ni = 0;u8 j = 0;do{i = list[h.getValue()];if( i != 0)break;list[h.getValue()] = j;h = h * temp;j++;}while( j <= n );return i + (j*n);}// Quick powerGF_eight GF_eight::power(u8 n) const{GF_eight res(1);GF_eight a(this->Value);while( n > 0){if ( n & 1 )res = res * a;n >>= 1;a = a * a;}return res;}#undef u8}#endif /* _GF_H_ */
