@windmelon
2018-11-11T16:50:21.000000Z
字数 4959
阅读 2610
CSAPP:binarybomb(一)
csapp实验 逆向工程
binarybomb简介
binarybomb是csapp系列实验中的一个,涉及到大量汇编代码。实验给定一个可执行文件和源代码,但是源代码中没有函数实现细节,需要我们反汇编成汇编代码后,阅读并理解代码细节,使得输入字符串让程序中的函数能正确运行,否则炸弹爆炸,故名二进制炸弹。
整个实验有48个bomb,主要是为了使每个小组都分到不同的炸弹,这里以bomb9为例进行分析讲解
第一步:阅读源码
FILE *infile;int main(int argc, char *argv[]){char *input;/* Note to self: remember to port this bomb to Windows and put a* fantastic GUI on it. *//* When run with no arguments, the bomb reads its input lines* from standard input. */if (argc == 1) {infile = stdin;}/* When run with one argument <file>, the bomb reads from <file>* until EOF, and then switches to standard input. Thus, as you* defuse each phase, you can add its defusing string to <file> and* avoid having to retype it. */else if (argc == 2) {if (!(infile = fopen(argv[1], "r"))) {printf("%s: Error: Couldn't open %s\n", argv[0], argv[1]);exit(8);}}/* You can't call the bomb with more than 1 command line argument. */else {printf("Usage: %s [<input_file>]\n", argv[0]);exit(8);}/* Do all sorts of secret stuff that makes the bomb harder to defuse. */initialize_bomb();printf("Welcome to my fiendish little bomb. You have 6 phases with\n");printf("which to blow yourself up. Have a nice day!\n");/* Hmm... Six phases must be more secure than one phase! */input = read_line(); /* Get input */phase_1(input); /* Run the phase */phase_defused(); /* Drat! They figured it out!* Let me know how they did it. */printf("Phase 1 defused. How about the next one?\n");/* The second phase is harder. No one will ever figure out* how to defuse this... */input = read_line();phase_2(input);phase_defused();printf("That's number 2. Keep going!\n");/* I guess this is too easy so far. Some more complex code will* confuse people. */input = read_line();phase_3(input);phase_defused();printf("Halfway there!\n");/* Oh yeah? Well, how good is your math? Try on this saucy problem! */input = read_line();phase_4(input);phase_defused();printf("So you got that one. Try this one.\n");/* Round and 'round in memory we go, where we stop, the bomb blows! */input = read_line();phase_5(input);phase_defused();printf("Good work! On to the next...\n");/* This phase will never be used, since no one will get past the* earlier ones. But just in case, make this one extra hard. */input = read_line();phase_6(input);phase_defused();/* Wow, they got it! But isn't something... missing? Perhaps* something they overlooked? Mua ha ha ha ha! */return 0;}
可以看到总共有六个input,对应六个phase_x(),input正确之后调用phase_defused(),意味着炸弹解除。那么我们需要分析的就是phase_1()、phase_2()、phase_3()、phase_4()、phase_5()、phase_6()这六个函数
第二步:反汇编,破译出函数的细节
我们用objdump对可执行文件进行反汇编,对每个函数单独进行分析
phase_1()
08048b80 <phase_1>:8048b80: 55 push %ebp8048b81: 89 e5 mov %esp,%ebp8048b83: 83 ec 08 sub $0x8,%esp8048b86: c7 44 24 04 98 99 04 movl $0x8049998,0x4(%esp)8048b8d: 088048b8e: 8b 45 08 mov 0x8(%ebp),%eax8048b91: 89 04 24 mov %eax,(%esp)8048b94: e8 3a 05 00 00 call 80490d3 <strings_not_equal>8048b99: 85 c0 test %eax,%eax8048b9b: 74 05 je 8048ba2 <phase_1+0x22>8048b9d: e8 f8 0a 00 00 call 804969a <explode_bomb>8048ba2: c9 leave8048ba3: c3 ret
看到7行把%ebp+0x8位置存放的东西赋给%eax,我们知道这个位置存的是函数的第一个参数,即input,然后把%eax存到%esp指向的位置,即栈顶(之前做的时候不知道这一步为了什么,实际上是为了把input作为参数传入<strings_not_equal>),然后调用<strings_not_equal>,紧跟着
test %eax,%eaxje 8048ba2 <phase_1+0x22>call 804969a <explode_bomb>
意思是如果%eax里面的内容不为0就调用<explode_bomb>,那么我们就需要知道<strings_not_equal>干了什么
080490d3 <strings_not_equal>:80490d3: 55 push %ebp80490d4: 89 e5 mov %esp,%ebp80490d6: 53 push %ebx80490d7: 83 ec 18 sub $0x18,%esp80490da: 8b 45 08 mov 0x8(%ebp),%eax80490dd: 89 04 24 mov %eax,(%esp)80490e0: e8 c4 ff ff ff call 80490a9 <string_length>80490e5: 89 c3 mov %eax,%ebx80490e7: 8b 45 0c mov 0xc(%ebp),%eax80490ea: 89 04 24 mov %eax,(%esp)80490ed: e8 b7 ff ff ff call 80490a9 <string_length>80490f2: 39 c3 cmp %eax,%ebx80490f4: 74 09 je 80490ff <strings_not_equal+0x2c>80490f6: c7 45 e8 01 00 00 00 movl $0x1,-0x18(%ebp)80490fd: eb 3e jmp 804913d <strings_not_equal+0x6a>80490ff: 8b 45 08 mov 0x8(%ebp),%eax8049102: 89 45 f4 mov %eax,-0xc(%ebp)8049105: 8b 45 0c mov 0xc(%ebp),%eax8049108: 89 45 f8 mov %eax,-0x8(%ebp)804910b: eb 1f jmp 804912c <strings_not_equal+0x59>804910d: 8b 45 f4 mov -0xc(%ebp),%eax8049110: 0f b6 10 movzbl (%eax),%edx8049113: 8b 45 f8 mov -0x8(%ebp),%eax8049116: 0f b6 00 movzbl (%eax),%eax8049119: 38 c2 cmp %al,%dl804911b: 74 09 je 8049126 <strings_not_equal+0x53>804911d: c7 45 e8 01 00 00 00 movl $0x1,-0x18(%ebp)8049124: eb 17 jmp 804913d <strings_not_equal+0x6a>8049126: ff 45 f4 incl -0xc(%ebp)8049129: ff 45 f8 incl -0x8(%ebp)804912c: 8b 45 f4 mov -0xc(%ebp),%eax804912f: 0f b6 00 movzbl (%eax),%eax8049132: 84 c0 test %al,%al8049134: 75 d7 jne 804910d <strings_not_equal+0x3a>8049136: c7 45 e8 00 00 00 00 movl $0x0,-0x18(%ebp)804913d: 8b 45 e8 mov -0x18(%ebp),%eax8049140: 83 c4 18 add $0x18,%esp8049143: 5b pop %ebx8049144: 5d pop %ebp8049145: c3 ret
代码看起来很长,我们一步一步分析
函数主题功能从第6行开始
mov 0x8(%ebp),%eax将第一个参数赋给%eax
mov %eax,(%esp)call 80490a9 <string_length>
接着把%eax内容作为参数传给<string_length>,这里我们可以根据函数名直接大胆猜测<string_length>函数为计算字符串长度,我们可以在gdb里验证一下
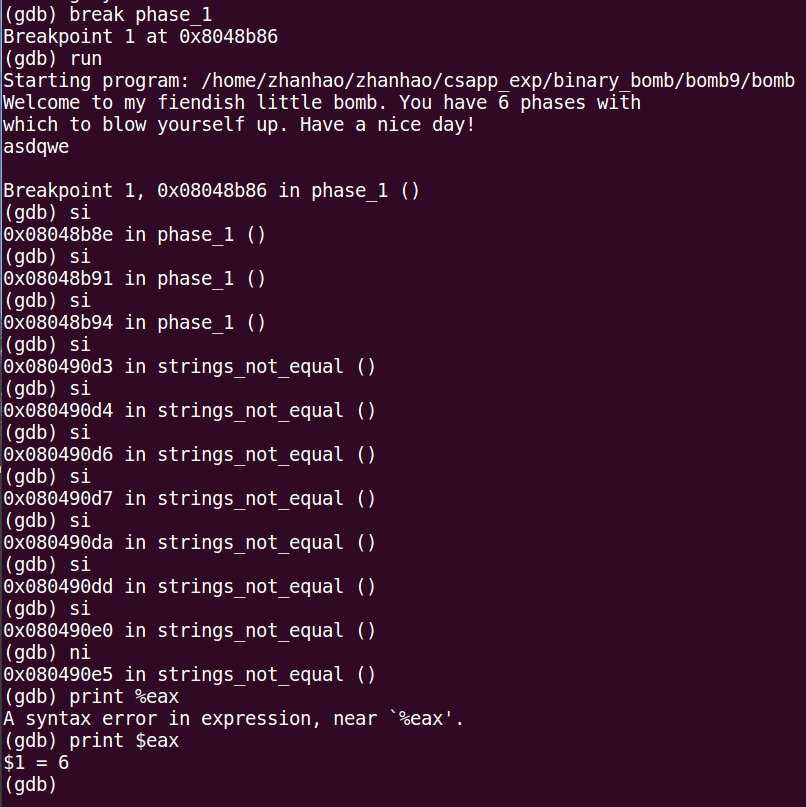
我们输入字符串asdqwe,然后将程序运行到执行完<string_length>,发现%eax中的值为6,正好为asdqwe的长度,所以这个函数应该就是计算字符串长度,那么我们继续往下分析
接下来的
mov 0xc(%ebp),%eaxmov %eax,(%esp)call 80490a9 <string_length>
即把%ebp+0xc指向的值赋给%eax,然后计算一个字符串长度,根据栈帧的知识,%ebp+0xc指向的是函数的第二个参数,那么这个参数是什么呢,既然调用了<string_length>,那么猜测他是一个string,可以用gdb验证一下

果然,是一个字符串,并且值为"I turned the moon into something I like to call a Death Star."
再联想到我们的函数名<strings_not_equal>,答案简直呼之欲出,就是输入一个字符串,和上面这个字符串进行比较,如果相等就通过!
运行一下程序验证猜想(红框内为输入的字符串)
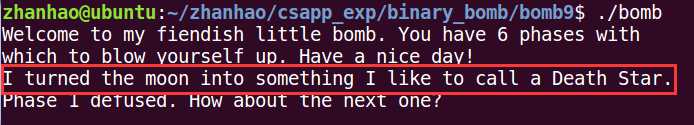
果然,phase1通过了,知道这点后,阅读后面的汇编代码我们就可以发现这是一个简单的字符串比较函数,获取两个字符串长度,如果不一样则返回1,如果一样则依次比较,遇到不一样的就返回1,直到比较完毕,返回0。
