@kiraSally
2018-03-12T10:43:28.000000Z
字数 19254
阅读 4519
集合番@TreeMap一文通(1.7版)
JAVA COLLECTIONS 源码 1.7版本
- 笔者个人博客 kiraSally的掘金个人博客 感谢支持
1.什么是TreeMap
TreeMap是一个有序、非同步的key-value集合,基于红黑树(Red-Black tree)实现有序性- 该映射根据其键的自然顺序进行排序,或根据创建映射时提供的
Comparator进行排序,具体取决于使用的构造方法 - 基本操作
containsKey()、get()、put()和remove()的时间复杂度是 log(n) - 本篇需要读者具备一定的红黑树基础,有机会再详述,读者可先参看(红黑树的复杂性主要体现在插入和删除的情况的多样性) 浅谈算法和数据结构: 九 平衡查找树之红黑树
2.TreeMap的数据结构
2.1 类定义
public class TreeMap<K,V>extends AbstractMap<K,V>implements NavigableMap<K,V>, Cloneable, java.io.Serializable
- 继承
AbstractMap,本质是个Map,即一个key-value集合- 实现
NavigableMap接口,支持一系列的导航方法,如返回有序的key集合- 实现
Cloneable接口,重写clone(),能被克隆(浅拷贝)- 实现
java.io.Serializable接口,支持序列化
2.2 重要全局变量
/*** The comparator used to maintain order in this tree map, or* null if it uses the natural ordering of its keys.* 比较器 用于指定排序规则:若该排序对象为null,默认使用自然排序* @serial*/private final Comparator<? super K> comparator;/*** 根节点 -即红黑树的根节点*/private transient Entry<K,V> root = null;/*** The number of entries in the tree* 拥有元素数量*/private transient int size = 0;/*** The number of structural modifications to the tree.*/private transient int modCount = 0;// Red-black mechanics 由于非黑即红,所有选择Boolean类型来表示红黑(而不是字符串)private static final boolean RED = false;private static final boolean BLACK = true;
2.3 构造器
/*** Constructs a new, empty tree map, using the natural ordering of its keys.* All keys inserted into the map must implement the {@link Comparable} interface.* Furthermore, all such keys must be <em>mutually comparable</em>: {@code k1.compareTo(k2)}* must not throw a {@code ClassCastException} for any keys {@code k1} and {@code k2} in the map.* If the user attempts to put a key into the map that violates this constraint (for example, the* user attempts to put a string key into a map whose keys are integers) ,* the {@code put(Object key, Object value)} call will throw a {@code ClassCastException}.* 1.默认构造器,默认使用自然排序;* 2.需要插入的键对象必须实现Comparable接口;* 3.同时每个键必须可比较(必须同类型),否则抛`ClassCastException`异常(类型转换错误)* eg:当插入其他类型对象时(调用put方法),将会抛`ClassCastException`异常*/public TreeMap() {comparator = null;}/*** Constructs a new, empty tree map, ordered according to the given comparator.* All keys inserted into the map must be <em>mutually comparable</em> by the given comparator:* {@code comparator.compare(k1,k2)} must not throw a {@code ClassCastException} for any keys* {@code k1} and {@code k2} in the map.If the user attempts to put a key into the map that* violates this constraint, the {@code put(Object key, Object value)} call will throw a* {@code ClassCastException}.* 自定义排序规则:不负责规则将抛出`ClassCastException`异常* @param comparator the comparator that will be used to order this map.* If {@code null}, the {@linkplain Comparable natural ordering} of the keys will be used.*/public TreeMap(Comparator<? super K> comparator) {this.comparator = comparator;}/*** Constructs a new tree map containing the same mappings as the given map,* ordered according to the <em>natural ordering</em> of its keys.* All keys inserted into the new map must implement the {@link Comparable} interface.* Furthermore, all such keys must be <em>mutually comparable</em>:* {@code k1.compareTo(k2)} must not throw a {@code ClassCastException} for any keys* {@code k1} and {@code k2} in the map. This method runs in n*log(n) time.* 1.批量插入Map,默认自然排序(注意此构造器不支持自定义排序规则)* 2.不负责规则将抛出`ClassCastException`异常* 3.该方法时间复杂度为O(n*log(n))* @param m the map whose mappings are to be placed in this map* @throws ClassCastException if the keys in m are not {@link Comparable},* or are not mutually comparable* @throws NullPointerException if the specified map is null*/public TreeMap(Map<? extends K, ? extends V> m) {comparator = null;putAll(m);}/*** Constructs a new tree map containing the same mappings and using the same ordering* as the specified sorted map. This method runs in linear time.* 1.批量插入有序Map,排序规则与原有序Map的排序规则保持一致* 2.该方法时间复杂度呈线性增长,即O(n)* @param m the sorted map whose mappings are to be placed in this map,* and whose comparator is to be used to sort this map* @throws NullPointerException if the specified map is null*/public TreeMap(SortedMap<K, ? extends V> m) {comparator = m.comparator();//使用原排序Map的排序规则try {buildFromSorted(m.size(), m.entrySet().iterator(), null, null);} catch (java.io.IOException cannotHappen) {} catch (ClassNotFoundException cannotHappen) {}}
2.4 Entry
static final class Entry<K,V> implements Map.Entry<K,V> {K key;V value;Entry<K,V> left = null; //指向左孩子(左子节点)Entry<K,V> right = null; //指向右孩子(右子节点)Entry<K,V> parent; //指向父节点boolean color = BLACK; //默认为黑色属性/*** Make a new cell with given key, value, and parent, and with* {@code null} child links, and BLACK color.* 注意:左右子节点以及红黑属性的设置不在构造器阶段完成,而是在旋转和着色阶段完成*/Entry(K key, V value, Entry<K,V> parent) {this.key = key;this.value = value;this.parent = parent;}......}
2.5 SortedMap接口实现(红框重点)
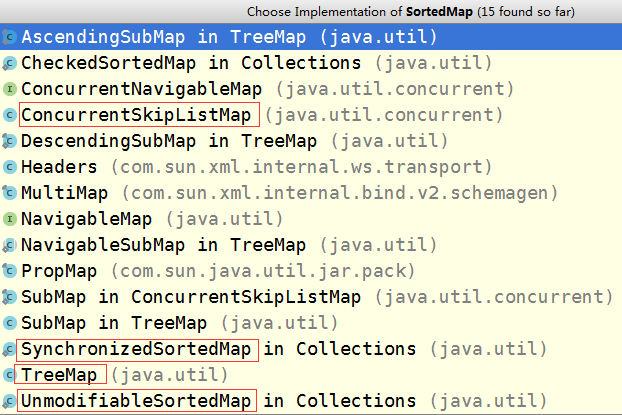
3.红黑树简述
3.1 二叉查找树
3.1.2 二叉查找树的性质定义
- (1)若任意节点的左子树不空,则左子树上所有节点的值均小于它的根节点的值;
- (2)若任意节点的右子树不空,则右子树上所有节点的值均大于它的根节点的值;
- (3)任意节点的左、右子树也分别为二叉查找树;
- (4)没有键值相等的节点,充分借用二分算法。
3.1.2 二叉查找树的结论
- 好处:一棵由n个节点,随机构造的二叉查找树的高度为lgn,一般操作的执行时间为
O(lgn)- 隐患:二叉树若退化成了一棵具有n个节点的线性链后,则此些操作最坏情况运行时间为
O(n)
3.2 红黑树
3.2.1 红黑树的性质定义
- (1)每个节点非黑即红;
- (2)根节点是黑的;
- (3)每个叶子节点(叶子节点即指树尾端NIL指针或NULL节点)是黑的;
- (4)如果一个节点是红色的,则它的子节点必须是黑色的;
- (5)从一个节点到该节点的子孙节点的所有路径上包含相同数目的黑节点(重点)。
3.2.2 红黑树的补充描述
- 定理:一棵含有n个节点的红黑树的高度至多为2log(n+1)
- 根据性质(5)可知,确保没有一条路径会比其他路径长出两倍 --> 红黑树是相对是接近平衡的二叉树
3.2.3 红黑树的结论
- 红黑树,本质上来说就是一棵二叉查找树,但它在二叉查找树的基础上增加了着色和相关的性质使得红黑树相对平衡,从而保证了红黑树的查找、插入、删除的时间复杂度最坏为
O(lgn)
3.2.4 红黑树的实例
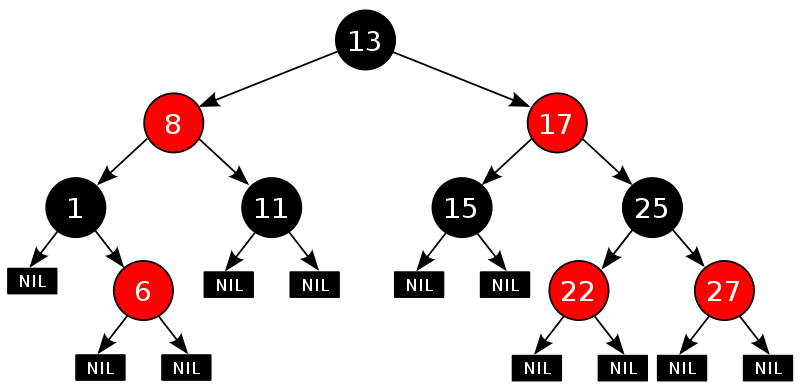
3.2.5 红黑树的左旋与外旋
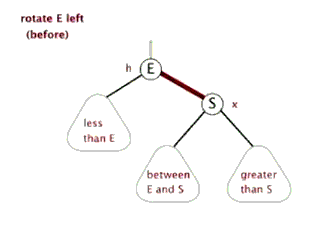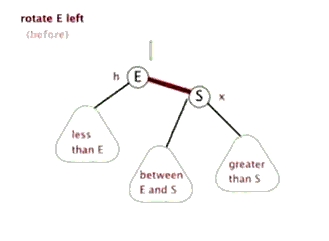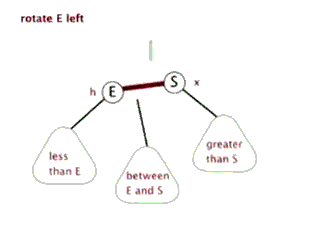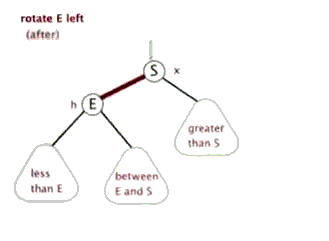
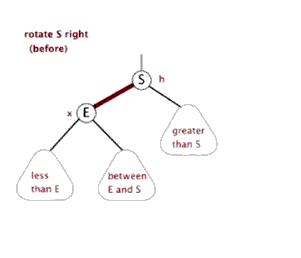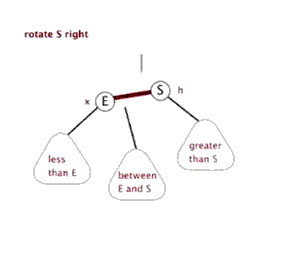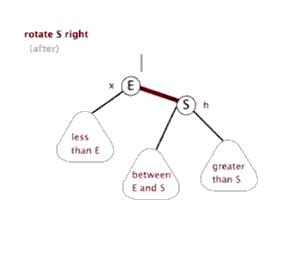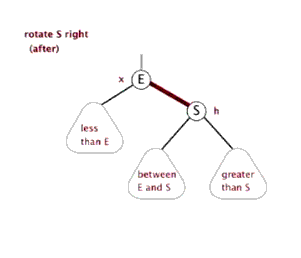
读者注意 between E and S 位置的变动即可
图片来源于http://www.cnblogs.com/yangecnu/p/Introduce-Red-Black-Tree.html
3.2.6 红黑树 VS B树
由于这两种树经常用来对比和提问,这里简单介绍一下两者的区别
B 树是为了磁盘或其它存储设备而设计的一种多叉查找树
- 场景:大规模数据存储,实现索引查询
- 问题:在上述场景下,由于树节点存储的元素数量是有限的(最多2个),导致二叉查找树结构由于树的深度过大而造成磁盘I/O读写过于频繁,进而导致查询效率低下(建议读者先理解一下磁盘运行原理)
- 原因:当元素数量过多,查找就退化成节点内部的线性查找了(最坏情况运行时间为
O(n)) - 解决方案:通过降低树的深度,从而减少磁盘查找存取的次数
- 解决思路:采用多叉树结构(由于树节点元素数量是有限的,自然该节点的子树数量也就是有限的)平衡多路查找树,即
B-tree(建议读者先研究2-3树) - 目的:通过各种操作令B树保持较低高度,从而有效避免磁盘过于频繁的查找存取操作,有效提高查找效率
B树 VS 红黑树
- B树与红黑树最大的不同在于,B树的节点可以有许多子女,从几个到几千个(红黑树最多2个)
- 不过B树与红黑树一样,一棵含n个节点的B树的高度也为
O(lgn),但可能比一棵红黑树的高度小许多,因为它的分支因子比较大。所以,B树可以在O(lgn)时间内,实现各种如插入,删除等动态集合操作(有兴趣的读者可以进一步研究B+和B*)
- B树实例
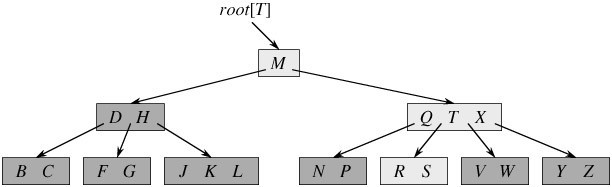
4.TreeMap的存储
4.1 put方法
/*** Associates the specified value with the specified key in this map.* If the map previously contained a mapping for the key, the old value is replaced.* 存储key-value键值对,主要有5个步骤:* 1.若Map为空,第一次需要设置根节点* 2.选择排序比较规则,若没有自定义排序比较器,默认使用自然排序* 3.对key进行二分比较,从根节点开始,遍历左(右)子树(根据非空左子节点<父节点<非空右子节点的规律)* 4.若之前的key已经存在,当找到位置时,value值就被替换,并返回原值* 5.若是新增key,需要通过旋转(左旋或右旋)以及着色 重新维护红黑树* @param key key with which the specified value is to be associated* @param value value to be associated with the specified key* @return the previous value associated with {@code key}, or {@code null} if there was no* mapping for {@code key}. (A {@code null} return can also indicate that the map* previously associated {@code null} with {@code key}.)* value允许为null* @throws ClassCastException if the specified key cannot be compared with the keys currently in* the map 同一个Map只允许存储相同类型的键值对,否则抛`ClassCastException`类型转换错误异常* @throws NullPointerException if the specified key is null and this map uses natural ordering,* or its comparator does not permit null keys* 不满足以下两种情况将抛`NullPointerException` 空指针异常* 1.使用自然排序时,key不为null* 2.自定义排序规则时,该比较器不允许key为null*/public V put(K key, V value) {Entry<K,V> t = root; //根节点if (t == null) {//若根节点不存在(即Map为空时),设置为根节点compare(key, key); // type (and possibly null) check key的类型校验//这里隐藏了一点:根节点是黑色属性(性质2)是由构造器默认实现的root = new Entry<>(key, value, null);//设置为根节点,注意parent=nullsize = 1;modCount++;//新增属于结构性变动,modCount计数+1return null;//默认返回null}int cmp;Entry<K,V> parent;// split comparator and comparable pathsComparator<? super K> cpr = comparator;//获取比较器if (cpr != null) {//当拥有自定义比较器时,使用自定义比较器//根据二分法遍历树do {parent = t;//获取父节点(从根节点开始)cmp = cpr.compare(key, t.key);//使用自定义比较规则获取比较结果//二分法查找到当前key所在位置if (cmp < 0) //当前父节点的key小于当前key,往左子树方向继续向下找t = t.left;else if (cmp > 0) //当前父节点的key小于当前key,往右子树方向继续向下找t = t.right;elsereturn t.setValue(value); //当前父节点的key==当前key,说明就是当前位置,值覆盖} while (t != null);}else {//当没有自定义比较器时,默认使用自然排序,此时key不允许为nullif (key == null)throw new NullPointerException();//当key为null时,抛空指针异常Comparable<? super K> k = (Comparable<? super K>) key;//查找规则与 自定义比较器基本一致do {parent = t;cmp = k.compareTo(t.key);//唯一区别是使用了自定义的比较规则,而不是自然排序if (cmp < 0)t = t.left;else if (cmp > 0)t = t.right;elsereturn t.setValue(value);//若key已存在,返回原值} while (t != null);}//若是新增元素,需要先查找到指定位置,并通过旋转和重新着色维护红黑树性质Entry<K,V> e = new Entry<>(key, value, parent);//将新增节点当做parent的子节点if (cmp < 0)parent.left = e;//当前父节点的key小于当前key,当前key设置为左子节点elseparent.right = e;//当前父节点的key大于等于当前key,当前key设置为右子节点(注意:包含等于)fixAfterInsertion(e);//通过旋转和重新着色维护红黑树性质size++;modCount++;return null;//新增元素默认返回null}
4.2 compare方法
/*** Compares two keys using the correct comparison method for this TreeMap.* 比较两个key的类型是否一致:TreeMap只允许相同类型的key存在*/final int compare(Object k1, Object k2) {//当比较器为null时,key必须实现Comparable接口,且两者自然排序必须可比较//当有自定义比较器时,key必须通过comparator可比较return comparator==null ? ((Comparable<? super K>)k1).compareTo((K)k2): comparator.compare((K)k1, (K)k2);}
4.3 插入情况
- 情况1:插入的是根节点,由于原树是空树
- 策略:直接把此节点涂为黑色
- 情况2:如果插入的节点的父节点是黑色
- 策略:由于此不会违反性质2和性质4,红黑树没有被破坏,所以此时什么也不做
- 情况3:有两个子节点
- 情况3.1:当前节点的父节点是红色且祖父节点的另一个子节点(叔叔节点)是红色
- 策略:将父节点和叔叔节点涂黑,祖父节点涂红同时指向当前节点
- 情况3.2:当前节点的父节点是红色,叔叔节点是黑色,当前节点是其父节点的右子
- 策略:当前节点的父节点做为新的当前节点,以新当前节点为支点重新旋转
- 情况3.3:当前节点的父节点是红色,叔叔节点是黑色,当前节点是其父节点的左孩子
- 策略:父节点变为黑色,祖父节点变为红色,以祖父节点为支点重新旋转
4.4 fixAfterInsertion方法
/*** 对于新节点的插入有如下三个关键地方:* 1、插入新节点总是红色节点;* 2、如果插入节点的父节点是黑色, 能保持性质(性质4);* 3、如果插入节点的父节点是红色, 性质被破坏,通过旋转和重新着色维护红黑树性质。* 4、换言之,性质1-3都好实现,复杂的是要实现性质4-5(删除操作一样)*/private void fixAfterInsertion(Entry<K,V> x) {x.color = RED;//新增元素默认红色,后面根据所在位置重新着色(比较有趣的是Entry构造器默认是BLACK)//循环 直到 x不是根节点,且x的父节点不为红色while (x != null && x != root && x.parent.color == RED) {if (parentOf(x) == leftOf(parentOf(parentOf(x)))) {//父节点为祖父节点左子Entry<K,V> y = rightOf(parentOf(parentOf(x)));//叔叔节点(右节点)/** 情况3.1:父节点是红色且祖父节点的另一个子节点(叔叔节点)是红色* 策略:将父节点和叔叔节点涂黑,祖父节点涂红同时指向当前节点*/if (colorOf(y) == RED) {setColor(parentOf(x), BLACK);setColor(y, BLACK);setColor(parentOf(parentOf(x)), RED);x = parentOf(parentOf(x));} else {/** 情况3.2:父节点是红色,叔叔节点是黑色,当前节点是其父节点的右子* 策略:当前节点的父节点做为新的当前节点,以新当前节点为支点左旋* 这时情况会转变为3.2(当前节点是其父节点的左子)*/if (x == rightOf(parentOf(x))) {x = parentOf(x);rotateLeft(x);}/** 情况3.3:父节点是红色,叔叔节点是黑色,当前节点是其父节点的左子* 策略:将父节点和叔叔节点涂黑,祖父节点涂红,以祖父节点右旋*/setColor(parentOf(x), BLACK);setColor(parentOf(parentOf(x)), RED);rotateRight(parentOf(parentOf(x)));}} else {//父节点为祖父节点右子 操作从左换成右Entry<K,V> y = leftOf(parentOf(parentOf(x)));if (colorOf(y) == RED) {setColor(parentOf(x), BLACK);setColor(y, BLACK);setColor(parentOf(parentOf(x)), RED);x = parentOf(parentOf(x));} else {if (x == leftOf(parentOf(x))) {x = parentOf(x);rotateRight(x);}setColor(parentOf(x), BLACK);setColor(parentOf(parentOf(x)), RED);rotateLeft(parentOf(parentOf(x)));}}}root.color = BLACK;//红黑树性质(2):根节点是黑色}
5.TreeMap的移除
5.1 remove方法
/*** Removes the mapping for this key from this TreeMap if present.* 移除key-value键值对,主要有3个步骤:* 1.选择排序比较器,若没有自定义排序比较器,默认使用自然排序(此时key不能为null)* 2.根据比较器对key进行二分比较,从根节点开始,遍历左(右)子树,直到找到该key所在节点* 3.移除成功,返回原值,并通过旋转(左旋或右旋)以及着色 重新维护红黑树* @param key key for which mapping should be removed* @return the previous value associated with {@code key}, or {@code null} if there was no* mapping for {@code key}. (A {@code null} return can also indicate that the map* previously associated {@code null} with {@code key}.)* 若key存在,返回原值;若key不存在,返回null* @throws ClassCastException if the specified key cannot be compared with the keys currently in* the map 同一个Map只允许存储相同类型的键值对,否则抛`ClassCastException`类型转换错误异常* @throws NullPointerException if the specified key is null and this map uses natural ordering* , or its comparator does not permit null keys* 不满足以下两种情况将抛`NullPointerException` 空指针异常* 1.使用自然排序时,key不为null* 2.自定义排序规则时,该比较器不允许key为null*/public V remove(Object key) {Entry<K,V> p = getEntry(key);//查找节点元素if (p == null)return null;V oldValue = p.value;deleteEntry(p);//删除节点元素return oldValue;//返回原值}
5.2 getEntry方法
/*** Returns this map's entry for the given key, or {@code null} if the map* does not contain an entry for the key.* 该值存在,返回原值;否则返回null* @return this map's entry for the given key, or {@code null} if the map* does not contain an entry for the key* @throws ClassCastException if the specified key cannot be compared* with the keys currently in the map* @throws NullPointerException if the specified key is null and this map uses natural ordering,* or its comparator does not permit null keys*/final Entry<K,V> getEntry(Object key) {// Offload comparator-based version for sake of performanceif (comparator != null)//若有自定义选择器,使用自定义选择器查找;否则按照自然排序查找return getEntryUsingComparator(key);if (key == null) //自然排序情况下,不允许key为nullthrow new NullPointerException();Comparable<? super K> k = (Comparable<? super K>) key;Entry<K,V> p = root;//从根节点开始遍历左右子树,直到找到该元素while (p != null) {int cmp = k.compareTo(p.key);if (cmp < 0)p = p.left;else if (cmp > 0)p = p.right;elsereturn p;}return null;}
5.3 getEntryUsingComparator方法
/*** Version of getEntry using comparator. Split off from getEntry for performance.* (This is not worth doing for most methods,that are less dependent on comparator performance,* but is worthwhile here.)* 使用自定义排序比较规则进行比较:对于大多数方法而言,这并不适用,因为其性能会受到比较器效率的影响* 当然,如果自定义比较器能够高效的比较的话,是非常有价值的*/final Entry<K,V> getEntryUsingComparator(Object key) {K k = (K) key;Comparator<? super K> cpr = comparator;if (cpr != null) {Entry<K,V> p = root;//从根节点开始遍历左右子树,直到找到该元素while (p != null) {int cmp = cpr.compare(k, p.key);//自定义比较if (cmp < 0)p = p.left;else if (cmp > 0)p = p.right;elsereturn p;}}return null;}
5.4 deleteEntry方法
/*** Delete node p, and then rebalance the tree.* 删除节点,并再平衡红黑树*/private void deleteEntry(Entry<K,V> p) {modCount++;//删除操作属于结构性变动,modCount计数+1size--;// If strictly internal, copy successor's element to p and then make p point to successor.//当左节点和右节点都非空时,可以通过子树找到该节点的替换中继节点if (p.left != null && p.right != null) {//找到中继节点,用于替换当前待删除节点的位置;规则是右分支最左边,或者左分支最右边的节点Entry<K,V> s = successor(p);p.key = s.key;p.value = s.value;p = s;} // p has 2 children// Start fixup at replacement node, if it exists.//replacement为替代节点,如果p的左子树存在那么就用左子树替代,否则用右子树替代Entry<K,V> replacement = (p.left != null ? p.left : p.right);if (replacement != null) {// Link replacement to parentreplacement.parent = p.parent;if (p.parent == null)//当前节点的parent为空,说明此时只剩下replacement一个节点root = replacement;//设置根节点else if (p == p.parent.left)//如果p为左节点,则用replacement来替代为左节点p.parent.left = replacement;else //如果p为右节点,则用replacement来替代为右节点p.parent.right = replacement;// Null out links so they are OK to use by fixAfterDeletion.// 将p节点从这棵树中剔除掉,help gcp.left = p.right = p.parent = null;// Fix replacement/** 重点:* 1.若p为红色直接删除,红黑树保持平衡* 2.若p为黑色,则需要调整红黑树使其保持平衡*/if (p.color == BLACK)fixAfterDeletion(replacement);} else if (p.parent == null) { // return if we are the only node. 清空最后一个元素root = null;//若p没有父节点,表示为p根节点,直接删除} else { // No children. Use self as phantom replacement and unlink.//当自身没有子节点(即自身就是叶子节点)/** 重点:* 1.若p为红色直接删除,红黑树保持平衡* 2.若p为黑色,则需要调整红黑树使其保持平衡*/if (p.color == BLACK)fixAfterDeletion(p);//删除p节点if (p.parent != null) {if (p == p.parent.left)p.parent.left = null;else if (p == p.parent.right)p.parent.right = null;p.parent = null;}}}
5.5 successor方法
/*** Returns the successor of the specified Entry, or null if no such.* 返回节点t的后继节点,没有就是null* 类似的predecessor()返回前继节点,没有就是null* 此操作相当于树的中序遍历(LDR - 左根右),主要用于保证其迭代输出是有序* (在it.next()的调用中会使用nextEntry调用successor)* 判断步骤:* 1.空节点,中继为null* 2.若右子树非空,找寻找右子树的最左子树* 3.若右子树为空,找左子树第一个向右走的祖先*/static <K,V> TreeMap.Entry<K,V> successor(Entry<K,V> t) {if (t == null) //1.空节点,没有后继return null;//2.有右子树的节点,后继节点就是右子树的“最左节点”,因为“最左子树”是右子树的最小节点else if (t.right != null) {//若右孩子非空,获取右子树最小的一个值(即比t大的最小值)Entry<K,V> p = t.right;while (p.left != null)//遍历右孩子的左子树,直到找到最后一个非空的值(最靠近t的比t大的最小值)p = p.left;return p;} else {//3.如果右子树为空,则寻找当前节点所在左子树的第一个祖先节点Entry<K,V> p = t.parent;Entry<K,V> ch = t;while (p != null && ch == p.right) {ch = p;p = p.parent;}return p;}}
5.6 二叉树排序补充(题外话)
- 前序遍历:根节点->左子树->右子树 (子树内部查找规则是从左往右)
- 中序遍历:左子树->根节点->右子树 (子树内部查找规则是先左后右)
- 后序遍历:左子树->右子树->根节点 (子树内部查找规则是从右往左)
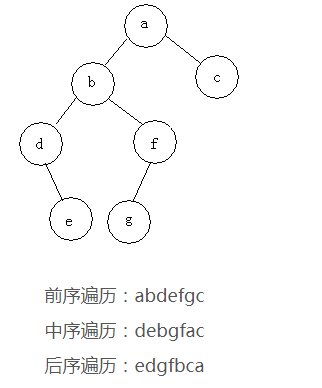
5.7 删除情况
- 难点:最大的麻烦是要保持 各分支黑色节点数目相等
- 情况1:无子节点(红色节点)
- 策略:直接把父节点的对应儿子指针设为NULL,删除子节点
- 情况2:有一个子节点
- 策略把父节点的相应儿子指针指向儿子的独生子,删除子节点
- 情况3:有两个子节点
- 情况3.1:当前节点是黑色且兄弟节点为红色(此时父节点和兄弟节点的子节点分为黑色)
- 策略:把父节点染成红色,把兄弟节点染成黑色,然后以父节点为支点重新旋转
- 此变换后原红黑树性质5不变,而把问题转化为兄弟节点为黑色的情况
- 情况3.2:当前节点是黑色且兄弟是黑色且兄弟节点的两个子节点全为黑色
- 策略:将兄弟节点变成红色,把父节点当成新的当前节点
- 情况3.3:当前节点是黑色,兄弟节点是黑色,兄弟的左子是红色,右子是黑色
- 策略:将兄弟节点与其左子树进行颜色互换然后进行重新旋转
- 情况3.4:当前节点是黑色,兄弟节点是黑色,但是兄弟节点的右子是红色,兄弟节点左子的颜色任意
- 策略:兄弟节点染成当前节点父节点的颜色,把当前节点父节点染成黑色,兄弟节点右子染成黑色,之后以当前节点的父节点为支点重新旋转
5.7 fixAfterDeletion方法
private void fixAfterDeletion(Entry<K,V> x) {// 循环,直到 x 不是根节点,且 x 的颜色是黑色while (x != root && colorOf(x) == BLACK) {if (x == leftOf(parentOf(x))) { //当前节点为父节点的左子节点Entry<K,V> sib = rightOf(parentOf(x));//兄弟节点为父节点的右子节点/** 情况3.1:当前节点是黑色且兄弟节点为红色(此时父节点和兄弟节点的子节点分为黑)* 策略:把父节点染成红色,把兄弟节点染成黑色,然后以父节点为支点左旋* 这时情况会转变为3.2(兄弟节点是黑色且兄弟节点的两个子节点全为黑)*/if (colorOf(sib) == RED) {setColor(sib, BLACK);setColor(parentOf(x), RED);rotateLeft(parentOf(x));sib = rightOf(parentOf(x));}/** 情况3.2:当前节点是黑色且兄弟节点是黑色且兄弟节点的两个子节点全为黑色* 策略:将兄弟节点变成红色,把父节点当成新的当前节点*/if (colorOf(leftOf(sib)) == BLACK &&colorOf(rightOf(sib)) == BLACK) {setColor(sib, RED);x = parentOf(x);} else {/** 情况3.3:当前节点颜色是黑色,兄弟节点是黑色,兄弟的左子是红色,右子是黑色* 策略:将兄弟节点与其左子树进行颜色互换然后以兄弟节点为支点右转* 这时情况会转变为3.4 (兄弟节点的右子是红色)*/if (colorOf(rightOf(sib)) == BLACK) {setColor(leftOf(sib), BLACK);setColor(sib, RED);rotateRight(sib);sib = rightOf(parentOf(x));}/** 情况3.4 :当前节点颜色是黑色,兄弟节点是黑色,但是兄弟节点的右子是红色,* 兄弟节点左子的颜色任意* 策略:交换兄弟节点和父节点的颜色,同时将兄弟节点右子树设置为黑色,最后以父节点为支点左旋*/setColor(sib, colorOf(parentOf(x)));setColor(parentOf(x), BLACK);setColor(rightOf(sib), BLACK);rotateLeft(parentOf(x));x = root;}} else { // 当前节点为父节点的右子节点 ,然后左改成了右,左旋改成右旋Entry<K,V> sib = leftOf(parentOf(x));//兄弟节点为父节点的左子节点if (colorOf(sib) == RED) {setColor(sib, BLACK);setColor(parentOf(x), RED);rotateRight(parentOf(x));sib = leftOf(parentOf(x));}if (colorOf(rightOf(sib)) == BLACK &&colorOf(leftOf(sib)) == BLACK) {setColor(sib, RED);x = parentOf(x);} else {if (colorOf(leftOf(sib)) == BLACK) {setColor(rightOf(sib), BLACK);setColor(sib, RED);rotateLeft(sib);sib = leftOf(parentOf(x));}setColor(sib, colorOf(parentOf(x)));setColor(parentOf(x), BLACK);setColor(leftOf(sib), BLACK);rotateRight(parentOf(x));x = root;}}}setColor(x, BLACK);}
6.TreeMap的旋转和着色
6.1 旋转和着色方法
/*** 返回父节点,有parent返回parent,否则返回null*/private static <K,V> Entry<K,V> parentOf(Entry<K,V> p) {return (p == null ? null: p.parent);}/*** 返回左子节点,有left返回left,否则返回null*/private static <K,V> Entry<K,V> leftOf(Entry<K,V> p) {return (p == null) ? null: p.left;}/*** 返回右子节点,有right返回right,否则返回null*/private static <K,V> Entry<K,V> rightOf(Entry<K,V> p) {return (p == null) ? null: p.right;}/*** 当前节点重新着色* @param c false:红色,true:黑色*/private static <K,V> void setColor(Entry<K,V> p, boolean c) {if (p != null) p.color = c;}
6.2 rotateLeft方法
/*** 左旋:以当前节点为支点,和其右子节点的连线为支轴左旋*/private void rotateLeft(Entry<K,V> p) {if (p != null) {Entry<K,V> r = p.right;//右子节点p.right = r.left;//右子节点的左节点作为当前节点的右子节点if (r.left != null)r.left.parent = p;//当前节点重新作为其右子节点的左节点的父节点r.parent = p.parent;//当前节点的父节点变更为其右子节点的父节点//支点无父节点,即右子上移做根节点if (p.parent == null)root = r;//若当前节点为其父节点的左子节点,需将其右子节点作为其父节点的左节点else if (p.parent.left == p)p.parent.left = r;//若当前节点为其父节点的右子节点,需将其右子节点作为其父节点的右节点elsep.parent.right = r;r.left = p;//当前节点重新作为其右子节点的左子节点p.parent = r;}}
 以
以E为支点,与其E的右子节点S的连线为支轴左旋
6.3 rotateRight方法
/*** 右旋:以当前节点为支点,和其左子节点的连线为支轴右旋(类似左旋,区别是左右互换)*/private void rotateRight(Entry<K,V> p) {if (p != null) {Entry<K,V> l = p.left;p.left = l.right;if (l.right != null) l.right.parent = p;l.parent = p.parent;if (p.parent == null)root = l;else if (p.parent.right == p)p.parent.right = l;else p.parent.left = l;l.right = p;p.parent = l;}}
 以
以S为支点,与其S的左子节点E的连线为支轴右旋
7.TreeMap的遍历方式
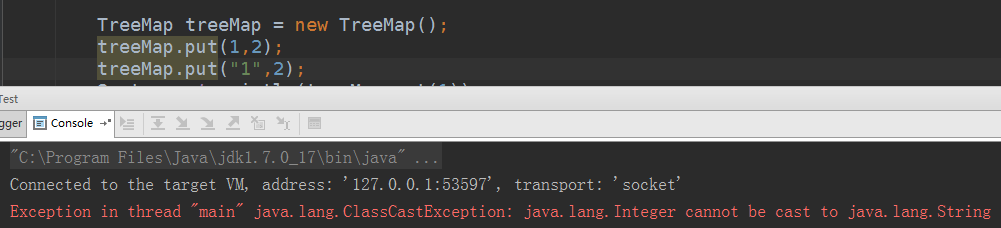
7.1 遍历TreeMap的键值对
TreeMap<Integer,Integer> treeMap = new TreeMap<Integer,Integer>();Iterator iterator = treeMap.entrySet().iterator();while(iterator.hasNext()) {Map.Entry entry = (Map.Entry)iterator.next();Integer key = (Integer)entry.getKey();// 获取keyInteger value = (Integer)entry.getValue();// 获取value}
7.2 遍历TreeMap的键
TreeMap<Integer,Integer> treeMap = new TreeMap<Integer,Integer>();Iterator iterator = treeMap.keySet().iterator();while (iterator.hasNext()) {Integer key = (Integer)iterator.next();// 获取keyInteger value = (Integer)map.get(key);// 根据key,获取value}
7.3 遍历TreeMap的值
TreeMap<Integer,Integer> treeMap = new TreeMap<Integer,Integer>();Collection c = map.values();Iterator iterator= c.iterator();while (iterator.hasNext()) {Integer value = (Integer)iterator.next();}
8.HashMap vs LinkedHashMap vs TreeMap
HashMap存储键值对,可以实现键值对的快速查询,适用于插入、删除和定位元素。TreeMap取出来的是排序后的键值对,适用于需要自然顺序或自定义顺序遍历键的情况。LinkedHashMap为有序的HashMap,适用于需要输出的顺序和输入的相同或按读取顺序来排列,如连接池。
集合番@TreeMap一文通(1.7版) 由 黄志鹏kira 创作,采用 知识共享 署名-非商业性使用 4.0 国际 许可协议 进行许可。
本站文章除注明转载/出处外,均为本站原创或翻译,转载前请务必署名。
