@nextleaf
2018-08-23T12:15:37.000000Z
字数 19207
阅读 1481
2018-08-22 工作日志
Java 序列化 多线程
1. 序列化
一个对象可以被表示为一个字节序列,该字节序列包括该对象的数据、有关对象的类型的信息和存储在对象中数据的类型。
两种用途:
- 1) 把对象的字节序列永久地保存到硬盘上,通常存放在一个文件中;
- 2) 在网络上传送对象的字节序列。
1.1 serialVersionUID的作用
serialVersionUID适用于Java的序列化机制。
简单来说,Java的序列化机制是通过判断类的serialVersionUID来验证版本一致性的。
序列化操作的时候系统会把当前类的serialVersionUID写入到序列化文件中,在进行反序列化时,JVM会把传来的字节流中的serialVersionUID与本地相应实体类的serialVersionUID进行比较,如果相同就认为是一致的,可以进行反序列化,否则会出InvalidCastException异常。
1.2 序列化示例:
package com.nl.sx820.io.stream.serializable;import com.alibaba.fastjson.JSON;import com.nl.statictest.UserTest;import java.io.*;import java.util.Date;/*** Created with IntelliJ IDEA 2018.* Description:Serializable序列化* 使用ObjectInputStream和阿里巴巴fastjson序列化以及反序列化** @author: 黄昭鸿* @date: 2018-08-21* Time: 16:00** 使用阿里 fastjson 作为JSON MessageConverter* https://github.com/alibaba/fastjson/wiki/JSONField** @JSONField(serialize=false)指定字段不序列化(java默认的不序列化方法是在属性上加关键字“transient”,反序列化时该属性为默认值)* @JSONField(ordinal = 1)使用ordinal指定字段的顺序,default 0,从一开始* @JSONField(format="yyyy-MM-dd",ordinal = 4)*/public class SerializableDemo {public static void main(String[] args) {UserTest userTest = new UserTest("黄", "123456", 12, 16.6, new Date());//新建两个文件File file = new File("E:" + File.separator + "Downloads" + File.separator + userTest.getClass().getName() + ".dat");File fastjsonfile = new File("E:" + File.separator + "Downloads" + File.separator + "fastjson.dat");//把对象序列化保存到文件中objToFileUseObjectOutputStream(file, userTest);//使用阿里巴巴fastjson序列化,String text = JSON.toJSONString( Object object);objToFileUseFastjson(fastjsonfile, userTest);//反序列化,使用ObjectInputStreamSystem.out.println("使用ObjectInputStream反序列化:");UserTest userTest1 = (UserTest) readFileUseObjectInputStream(file);System.out.println(userTest1);//反序列化,使用阿里巴巴fastjsonSystem.out.println("使用阿里巴巴fastjson反序列化:");UserTest userTest2 = JSON.parseObject(readFileUseFileReader(fastjsonfile), UserTest.class);System.out.println(userTest2);}//序列化对象到文件,使用ObjectOutputStreampublic static void objToFileUseObjectOutputStream(File targetfile, Object object) {try {//处理流套着节点流,节点流里套着文件ObjectOutputStream objectOutputStream = new ObjectOutputStream(new FileOutputStream(targetfile));objectOutputStream.writeObject(object);objectOutputStream.flush();objectOutputStream.close();} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {e.printStackTrace();} catch (IOException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}//序列化对象到文件,使用fastjsonpublic static void objToFileUseFastjson(File targetfile, Object object) {try {BufferedWriter bufferedWriter = new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter(targetfile));bufferedWriter.write(JSON.toJSONString(object));bufferedWriter.flush();bufferedWriter.close();} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {e.printStackTrace();} catch (IOException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}//反序列化,使用ObjectInputStreampublic static Object readFileUseObjectInputStream(File file) {try {//处理流套着节点流,节点流里套着文件ObjectInputStream objectInputStream = new ObjectInputStream(new FileInputStream(file));//读取文件并反序列化UserTest temp = (UserTest) objectInputStream.readObject();//System.out.println(temp);objectInputStream.close();return temp;} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {e.printStackTrace();} catch (IOException e) {e.printStackTrace();} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {e.printStackTrace();}return null;}//读取文件内容到Stringpublic static String readFileUseFileReader(File file) {FileReader fileReader = null;String string = "";try {fileReader = new FileReader(file);char[] chars = new char[(int) file.length()];/* for (int i = 0; i <fileReader.read(chars); i++) {string.concat(String.valueOf(chars[i]));}*/fileReader.read(chars);string=new String(chars);} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {e.printStackTrace();} catch (IOException e) {e.printStackTrace();} finally {if (fileReader != null) {try {fileReader.close();} catch (IOException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}}System.out.println("读取:"+string);return string;}}
1.3 序列化机制
使用Java默认序列化机制时,实体类必须实现Serializable接口,实现后如果该类没有显式地定义一个serialVersionUID变量时候,Java序列化机制会根据编译的Class自动生成一个serialVersionUID作序列化版本比较用,这种情况下,如果Class文件(类名,方法明等)没有发生变化(增加空格,换行,增加注释等等),就算再编译多次,serialVersionUID也不会变化的,完全相同的一个类,在不同的编译器上编译,自动生成的serialVersionUID有可能会不一致,导致无法完成反序列化,所以通常会显式地定义serialVersionUID。
如上图,假设和是两台计算机上(相同)的实体类,显示地定义了相同的serialVersionUID;
序列化得到;
当删除某字段(属性,假设为),再通过反序列化时,得到的对象将没有字段(属性);
当transient某字段(属性,假设为),再通过反序列化时,得到的对象里字段(属性)的值为初始化值(引用类型为null,基本类型为相应的初始默认值);
当添加新字段(属性,假设为),再通过反序列化时,得到的对象会有字段(属性),其值为初始化值。
实例见附录
另外,序列化保存的是对象的状态,类的状态(比如静态变量)不会保存。
父类的序列化参见父类的序列化
总结:反序列化时,总是以的"结构"为准。
实体类UserTest.java
/*** 使用阿里 fastjson 作为JSON MessageConverter*https://github.com/alibaba/fastjson/wiki/JSONField** @JSONField(serialize=false)指定字段不序列化(java默认的不序列化方法是在属性上加关键字“transient”,反序列化时该属性为默认值)* @JSONField(ordinal = 1)使用ordinal指定字段的顺序,default 0,从一开始* @JSONField(format="yyyy-MM-dd",ordinal = 4)** String text = JSON.toJSONString(obj); //序列化* VO vo = JSON.parseObject("{...}", VO.class); //反序列化* 泛型反序列化:* import com.alibaba.fastjson.TypeReference;* List<VO> list = JSON.parseObject("...", new TypeReference<List<VO>>() {});** 如果需要输出对象属性中的null为空值,怎么做* JSON.toJSONString(obj, SerializerFeature.WriteMapNullValue);** String text = JSON.toJSONString(obj, SerializerFeature.WriteMapNullValue, SerializerFeature.WriteNullListAsEmpty);* */public class UserTest implements Serializable {private static final long serialVersionUID = 9166711291168034786L;//static final long serialVersionUID=1L;@JSONField(ordinal = 1)private String username;@JSONField(ordinal = 2)private String password;@JSONField(ordinal = 3)private int experience;@JSONField(ordinal = 4)private double money;@JSONField(ordinal = 5,format="yyyy年MM月dd日")private Date regtime;public UserTest() {}public UserTest(String username, String password, int experience, double money, Date regtime) {this.username = username;this.password = password;this.experience = experience;this.money = money;this.regtime = regtime;}@Overridepublic String toString() {return this.username+","+this.password+"(密码),经验:"+this.experience+",钱:"+this.money+",注册时间:"+this.regtime;}//省略setter和getter方法,项目中记得要补上}
2. 多线程
一条线程指的是进程中一个单一顺序的控制流,一个进程中可以并发多个线程,每条线程并行执行不同的任务。
隐含的主线程:main()
2.1 一个线程的生命周期
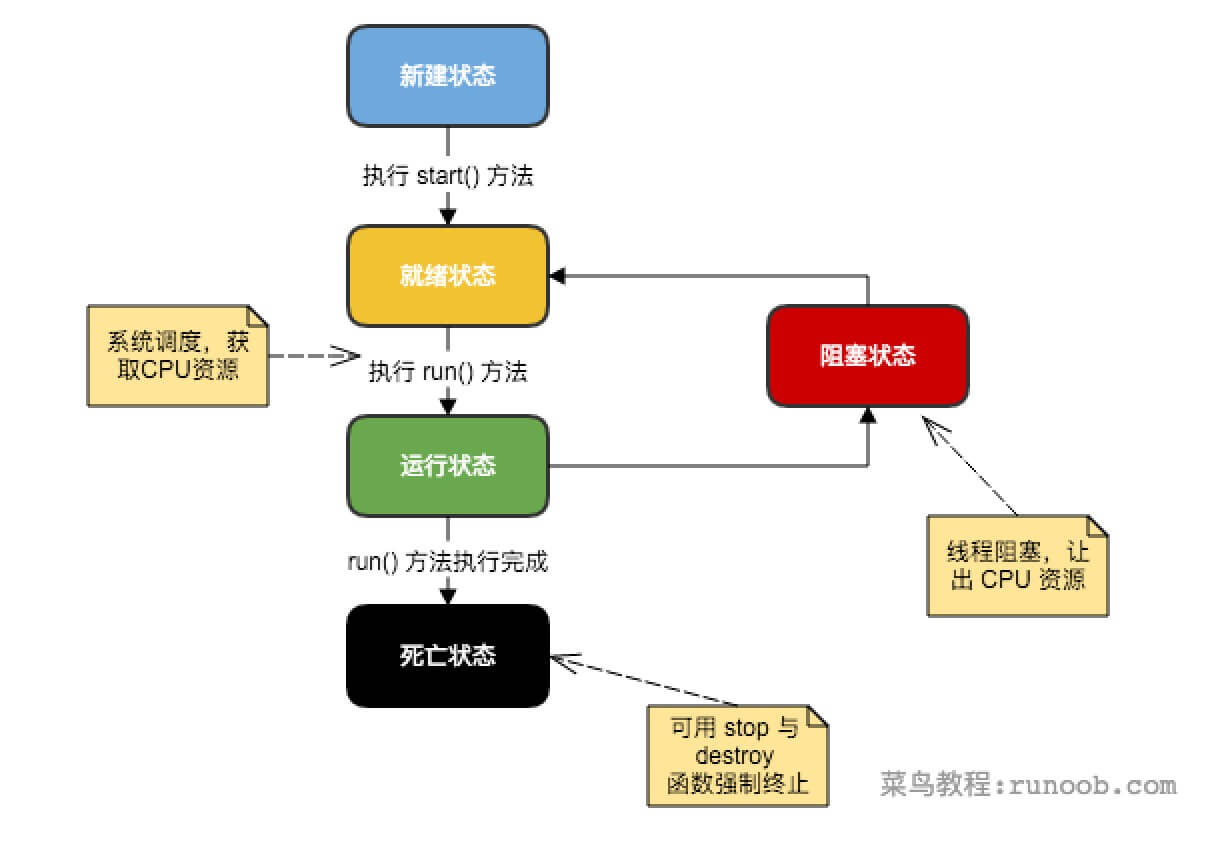
- 新建状态:
使用 new 关键字和 Thread 类或其子类建立一个线程对象后,该线程对象就处于新建状态。它保持这个状态直到程序 start() 这个线程。 - 就绪状态:
当线程对象调用了start()方法之后,该线程就进入就绪状态。就绪状态的线程处于就绪队列中,要等待JVM里线程调度器的调度。 - 运行状态:
如果就绪状态的线程获取 CPU 资源,就可以执行 run(),此时线程便处于运行状态。处于运行状态的线程最为复杂,它可以变为阻塞状态、就绪状态和死亡状态。 - 阻塞状态:
如果一个线程执行了sleep(睡眠)、suspend(挂起)等方法,失去所占用资源之后,该线程就从运行状态进入阻塞状态。在睡眠时间已到或获得设备资源后可以重新进入就绪状态。可以分为三种:
- 等待阻塞:运行状态中的线程执行 wait() 方法,使线程进入到等待阻塞状态。
- 同步阻塞:线程在获取 synchronized 同步锁失败(因为同步锁被其他线程占用)。
- 其他阻塞:通过调用线程的 sleep() 或 join() 发出了 I/O 请求时,线程就会进入到阻塞状态。当sleep() 状态超时,join() 等待线程终止或超时,或者 I/O 处理完毕,线程重新转入就绪状态。
- 死亡状态:一个运行状态的线程完成任务或者其他终止条件发生时,该线程就切换到终止状态。
2.2 单线程
package com.nl.sx822.multithread;public class SingleThread {public static void aVoid(String str) {System.out.println("a:" + str);}public static void bVoid(String str) {System.out.println("b:");aVoid(str);}public static void main(String[] args) {System.out.println("main:");System.out.println("单线程:b-->a");bVoid("黄");}}
2.3 多线程
- .yield()调用此方法的线程释放当前CPU执行权,但有可能被再次选中执行
- .join()在A线程(此例中为main)中调用B线程的join()方法,表示:当执行到此方法时,A线程等待B执行完毕,A线程再接着执行join()后的代码。
- .isAlive() 线程是否活着,通常用来判断线程是否已完成
- .sleep()
- .getPriority()获取线程优先级
- .setPriority()设置优先级,MAX_PRIORITY(10),NORM_PRIORITY(5),MIN_PRIORITY(1)
2.3.1 方式一,继承Thread类,子线程和主线程并发:
package com.nl.sx822.multithread;/*** Created with IntelliJ IDEA 2018.* Description:多线程——继承Thread方式* 主线程:输出1-20* 子线程:输出1-20* 实现步骤:【1】-【5】* .yield()调用此方法的线程释放当前CPU执行权,但有可能被再次选中执行* .join()在A线程(此例中为main)中调用B线程的join()方法,表示:当执行到此方法时,A线程等待B执行完毕,A线程再接着执行join()后的代码。* .isAlive() 线程是否活着,通常用来判断线程是否已完成* .sleep()* .getPriority()获取线程优先级* .setPriority()设置优先级,MAX_PRIORITY(10),NORM_PRIORITY(5),MIN_PRIORITY(1)** @author: 黄昭鸿* @date: 2018-08-22* Time: 10:40*//*** 类说明:【1】继承于Thread的子类* 【2】重写run()方法,作为子线程*/class Sub extends Thread {@Overridepublic void run() {//Thread.currentThread(),当前线程引用try {for (int i = 1; i < 21; i++) {String s = Thread.currentThread().getName() + ":" + i;System.out.println(s);sleep(300);}} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}}public class Multithread {public static void main(String[] args) {System.out.println("出现交替打印是明显的多线程体现");//【3】创建子线程类的对象Sub s = new Sub();Sub s2 = new Sub();//【4】调用start方法来启动线程s.setName("1号子线程");s.start();s2.setName("2号子线程");s2.start();//s.run()//直接调用run()方法会变成单线程//【5】主线程for (int j = 1; j < 21; j++) {String s1 = Thread.currentThread().getName() + ":" + j;if (j == 15) {try {s2.join();} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}//线程是否活着,用来判断线程是否已完成System.out.println(s2.isAlive());System.out.println(s1);}}}
2.3.2 方式二,实现Runnable类,(只有子线程并发?):
package com.nl.sx822.multithread;/*** Created with IntelliJ IDEA 2018.* Description:多线程——实现Runnable类的方式* 步骤:【1】-【5】** @author: 黄昭鸿* @date: 2018-08-22* Time: 15:50*//*** 类说明:【1】实现Runnable类,实现类记为A* 【2】重写run()方法*/class SubThread implements Runnable {/*** When an object implementing interface <code>Runnable</code> is used* to create a thread, starting the thread causes the object's* <code>run</code> method to be called in that separately executing* thread.* <p>* The general contract of the method <code>run</code> is that it may* take any action whatsoever.** @see Thread#run()*/@Overridepublic void run() {for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) {//if (i%2==0){System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + i);//}}}}public class Multithread2 {public static void main(String[] args) {//【3】创建A类的对象该对象记为aSubThread subThread = new SubThread();System.out.println("创建子线程类的对象");//【4】利用对象a创建子线程类的对象Thread thread1 = new Thread(subThread);Thread thread2 = new Thread(subThread);Thread thread3 = new Thread(subThread);thread1.setName("1号子线程");thread2.setName("2号子线程");thread3.setName("3号子线程");//【5】调用start方法来启动线程thread1.start();thread2.start();thread3.start();//main线程先执行,只有子线程并发?for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) {System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName());}}}
2.3.3 多线程应用例子——模拟多窗口卖票:
其一
package com.nl.sx822.multithread.demo;/*** Created with IntelliJ IDEA 2018.* Description:多线程(继承Thread类方式)——模拟多窗口卖票** @author: 黄昭鸿* @date: 2018-08-22* Time: 15:37*/class Window extends Thread {//总票数,staticstatic int ticket = 100;@Overridepublic void run() {while (true) {if (ticket > 0) {System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + ":" + ticket--);} else {break;}}}}public class StationTicketWindow {public static void main(String[] args) {System.out.println();Window window1 = new Window();Window window2 = new Window();Window window3 = new Window();window1.setName("1号窗口");window2.setName("2号窗口");window3.setName("3号窗口");window1.start();window2.start();window3.start();}}
其二
package com.nl.sx822.multithread.demo;/*** Created with IntelliJ IDEA 2018.* Description:多线程(实现Runnable类方式)——模拟多窗口卖票** @author: 黄昭鸿* @date: 2018-08-22* Time: 16:24*/class Window2 implements Runnable {int ticket = 100;@Overridepublic void run() {while (true) {if (ticket > 0) {/* try 处代码将引发线程同步问题try {Thread.sleep(10);} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}*/System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+":"+ticket--);} else {break;}}}}public class StationTicketWindow2 {public static void main(String[] args) {Window2 subThread = new Window2();System.out.println("创建子线程对象");Thread thread1 = new Thread(subThread);Thread thread2 = new Thread(subThread);Thread thread3 = new Thread(subThread);thread1.setName("1号窗口");thread2.setName("2号窗口");thread3.setName("3号窗口");thread1.start();thread2.start();thread3.start();//main线程不参与子线程的并发??????for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) {System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName());}}}
2.4 线程同步
针对上述“多线程(实现Runnable类方式)——模拟多窗口卖票”程序中try代码块可能引发的多线程并发时的安全问题,可使用Java线程同步机制来解决此线程安全问题。
class A {}class Window2 implements Runnable {int ticket = 100;//同步监视器(共用的一把锁a)A obj = new A();@Overridepublic void run() {while (true) {//使用Java线程同步机制实现线程安全// 同步锁,括号里不能new新对象,否则不同步,此处用this也可以,this代表Window2的对象,在main方法中只被new了1次synchronized (obj) {if (ticket > 0) {/* try 处代码将引发多线程并发时的安全问题(线程同步问题),一个线程操作共享变量ticket且未完成时,另一个线程也对ticket进行操作。* 解决:必须让一个线程操作共享数据完毕后,其他线程才有机会参与共享数据的操作* */try {Thread.sleep(100);} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + ":" + ticket--);} else {break;}}}}}
synchronized置于方法声明中
class Window3 implements Runnable {int ticket = 100;//synchronized修饰方法时,其同步监视器(锁)为this。@Overridepublic void run() {while (true) {if (show()){break;}}}public synchronized boolean show(){if (ticket > 0) {try {Thread.sleep(10);} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + ":" + ticket--);return false;}else {return true;}}}
2.5 线程间通信
java.lang.Object的三个方法:
只在synchronized代码块或方法中使用。
wait();令当前线程挂起并放弃CPU、同步资源,使别的线程可访问并修改共享资源,二当前线程排队等候在此对资源的访问。
notify();唤醒正在排队等待同步资源的线程中优先级最高者结束等待。
notifyAll();唤醒正在排队等待资源的所有线程结束等待。
package com.nl.sx822.multithread.demo;/*** Created with IntelliJ IDEA 2018.* Description:俩线程交替打印1-100** @author: 黄昭鸿* @date: 2018-08-23* Time: 11:36*/class SubThread1 implements Runnable {private int anInt = 1;@Overridepublic void run() {while (true) {synchronized (this) {notify();if (anInt <= 100) {try {Thread.sleep(100);} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + ":" + anInt++);} else {break;}try {wait();} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}}}}public class Multithread4 {public static void main(String[] args) {SubThread1 subThread1 = new SubThread1();Thread thread1 = new Thread(subThread1);thread1.setName("甲");Thread thread2 = new Thread(subThread1);thread2.setName("乙");//Thread thread3 = new Thread(subThread1);//thread3.setName("3号");//thread3.start();thread1.start();thread2.start();}}
2.6 线程死锁
2.7 线程控制:挂起、停止和恢复
2.8 守护线程和用户线程
守护线程是用来服务用户线程的,通过在start方法前调用thread.setDaemon(true)可以把一个用户线程变成一个守护线程。
Java垃圾回收就是一个典型的守护线程。
若JVM中都是守护线程,当前JVM将推出。
疑问:
public class Multithread2 {public static void main(String[] args) {SubThread subThread = new SubThread();System.out.println("创建子线程对象");Thread thread1 = new Thread(subThread);Thread thread2 = new Thread(subThread);Thread thread3 = new Thread(subThread);thread1.setName("1号子线程");thread2.setName("2号子线程");thread3.setName("3号子线程");thread1.start();thread2.start();thread3.start();//main线程不参与子线程的并发??????for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) {System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName());}}}
附录:
transient字段、增加字段、减少字段对序列化的影响
其一
package com.nl.sx822.serializable;/*** Created with IntelliJ IDEA 2018.* Description:使用Java默认序列化机制进行序列化* transient字段(属性)、增加字段(属性)、减少字段(属性)对默认机制序列化的影响** 另见package com.nl.sx820.io.stream.serializable;** @author: 黄昭鸿* @date: 2018-08-22* Time: 23:00*/import cn.hutool.core.lang.Console;import java.io.*;import java.util.Date;public class SerializableDemo2 {public static void main(String[] args) {//UserA userA=new UserA("A", "123456", 10, 166, new Date());//UserB userB=new UserB("B", "654123", 20, 199, new Date());UserA userA=new UserA();UserB userB=new UserB();File fileA = new File("E:" + File.separator + "Downloads" + File.separator + userA.getClass().getName() + ".data");File fileB = new File("E:" + File.separator + "Downloads" + File.separator + userB.getClass().getName() + ".data");//序列化//objToFileUseObjectOutputStream(fileA,userA);//objToFileUseObjectOutputStream(fileB,userB);System.out.println("反序列化");//如果类比序列化文件多了一个sex新字段,反序列化后对象的对应字段值为初始化值//如果类比序列化文件少了一个password字段,反序列化后对象将没有password字段UserA a= (UserA) readFileUseObjectInputStream(fileA);//UserA cannot be cast to UserB//即使UID一致也报错//UserB b= (UserB) readFileUseObjectInputStream(fileA);//如果类transient某个字段,反序列化后对象的对应字段值为初始化值UserB b= (UserB) readFileUseObjectInputStream(fileB);System.out.println(a);System.out.println(b);}//序列化对象到文件,使用对象字节流ObjectOutputStreampublic static void objToFileUseObjectOutputStream(File targetfile, Object object) {try {//处理流套着节点流,节点流里套着文件ObjectOutputStream objectOutputStream = new ObjectOutputStream(new FileOutputStream(targetfile));objectOutputStream.writeObject(object);objectOutputStream.flush();objectOutputStream.close();} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {e.printStackTrace();} catch (IOException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}//反序列化,使用ObjectInputStreampublic static Object readFileUseObjectInputStream(File file) {try {//处理流套着节点流,节点流里套着文件ObjectInputStream objectInputStream = new ObjectInputStream(new FileInputStream(file));//读取文件并反序列化Object temp = objectInputStream.readObject();//System.out.println(temp);objectInputStream.close();return temp;} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {e.printStackTrace();} catch (IOException e) {e.printStackTrace();} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {e.printStackTrace();}return null;}}class UserA implements Serializable {private static final long serialVersionUID = 3187377513146605030L;private String username;private String password;private String sex;private int experience;private double money;private Date regtime;public UserA() {}@Overridepublic String toString() {return this.username+","+this.password+",性别:"+this.sex+",经验:"+this.experience+",钱:"+this.money+",注册时间:"+this.regtime;}//省略setter和getter方法,项目中记得要补上}class UserB implements Serializable{private static final long serialVersionUID = 9166711291168034788L;private String username;private transient String password;private int experience;private double money;private Date regtime;public UserB() {}@Overridepublic String toString() {return this.username+","+this.password+",经验:"+this.experience+",钱:"+this.money+",注册时间:"+this.regtime;}//省略setter和getter方法,项目中记得要补上}
其二
package com.nl.sx822.serializable;import com.alibaba.fastjson.JSON;import com.alibaba.fastjson.annotation.JSONField;import java.io.*;import java.time.LocalDate;/*** Created with IntelliJ IDEA 2018.* Description:使用阿里巴巴fastjson序列化和反序列化* 增加字段、减少字段(属性)对阿里序列化的影响* JSONField(serialize=false)指定字段不序列化* @author: 黄昭鸿* @date: 2018-08-23* Time: 19:21*/public class SerializableAliDemo {public static void main(String[] args) {UserC userC = new UserC("张铁牛","甲","男",LocalDate.now());//D比C少一个字段UserD userD = new UserD("张铁男","乙","女");File fileC = new File("E:" + File.separator + "Downloads" + File.separator + userC.getClass().getName() + ".data");File fileD = new File("E:" + File.separator + "Downloads" + File.separator + userD.getClass().getName() + ".data");//使用阿里巴巴fastjson序列化,String text = JSON.toJSONString( Object object);objToFileUseFastjson(fileC, userC);objToFileUseFastjson(fileD, userD);//反序列化,不要求两个类必须一致UserC c = JSON.parseObject(readFileUseFileReader(fileC),UserC.class);//UserD转UserCUserC c2 = JSON.parseObject(readFileUseFileReader(fileD),UserC.class);//UserC转UserDUserD d = JSON.parseObject(readFileUseFileReader(fileC),UserD.class);System.out.println();//正常反序列化System.out.println(c);//类字段增加,反序列化后对象“新”字段的值为初始化值。System.out.println(c2);//类字段减少,反序列化时将忽略序列化文件中多出的字段。System.out.println(d);}//序列化对象到文件,使用fastjsonpublic static void objToFileUseFastjson(File targetfile, Object object) {try {BufferedWriter bufferedWriter = new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter(targetfile));bufferedWriter.write(JSON.toJSONString(object));bufferedWriter.flush();bufferedWriter.close();} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {e.printStackTrace();} catch (IOException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}//读取文件内容到Stringpublic static String readFileUseFileReader(File file) {FileReader fileReader = null;String string = "";try {fileReader = new FileReader(file);char[] chars = new char[(int) file.length()];/* for (int i = 0; i <fileReader.read(chars); i++) {string.concat(String.valueOf(chars[i]));}*/fileReader.read(chars);string = new String(chars);} catch (IOException e) {e.printStackTrace();} finally {if (fileReader != null) {try {fileReader.close();} catch (IOException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}}System.out.println("读取:" + string);return string;}}class UserC {/*** 可指定字段序列化顺序,否则按字母顺序(而不是声明顺序)*/@JSONField(ordinal = 2)private String username;@JSONField(ordinal = 1)private String id;@JSONField(ordinal = 3)private String sex;/*** 日期类可指定字段序列化格式*/@JSONField(ordinal = 4,format="yyyy年MM月dd日")private LocalDate birthday;public UserC() {}public UserC(String username, String id, String sex, LocalDate birthday) {this.username = username;this.id = id;this.sex = sex;this.birthday = birthday;}@Overridepublic String toString() {return "姓名:"+username+",ID:"+id+",性别:"+sex+",生日:"+birthday;}//省略setter和getter方法,项目中记得要补上}class UserD {@JSONField(ordinal = 1)private String username;@JSONField(ordinal = 2)private String id;@JSONField(ordinal = 3)private String sex;public UserD() {}public UserD(String username, String id, String sex) {this.username = username;this.id = id;this.sex = sex;}@Overridepublic String toString() {return "姓名:"+username+",ID:"+id+",性别:"+sex;}//省略setter和getter方法,项目中记得要补上}
