@nextleaf
2018-08-20T03:53:26.000000Z
字数 18686
阅读 942
2018-08-16 工作日志
Java 异常 工作日志 集合 List
手动抛出异常
throw new Exception("");//....getMessage;
自定义异常
TestMyException.java
package com.nl.sx816;import com.nl.sx807.HeapStackPractice.Student;/*** Created with IntelliJ IDEA 2018.* Description: 使用自定义异常类MyException** @author: 黄昭鸿* @date: 2018-08-16* Time: 11:23*/public class TestMyException {public static void main(String[] args){Student student=new Student("小明","hx001",10);try {student.showInfo();student.regist(-12);} catch (MyException e) {System.out.println(e.getMessage());//e.printStackTrace();}}}
Java 集合框架
集合是一个对象,可容纳其他对象的引用。集合接口声明对每一种类型的集合可以执行的操作。
集合框架的类和接口均在java.util包中。
任何对象加入集合类后,自动转变为Object类型,所以在取出的时候,需要进行强制类型转换。
主要包括两种类型的容器,一种是集合(Collection),存储一个元素集合,另一种是图(Map),存储键/值对映射。Collection 接口又有 3 种子类型,List、Set 和 Queue,再下面是一些抽象类,最后是具体实现类,常用的有 ArrayList、LinkedList、HashSet、LinkedHashSet、HashMap、LinkedHashMap 等等
所有集合里只能存放引用类型(对象、包装类)
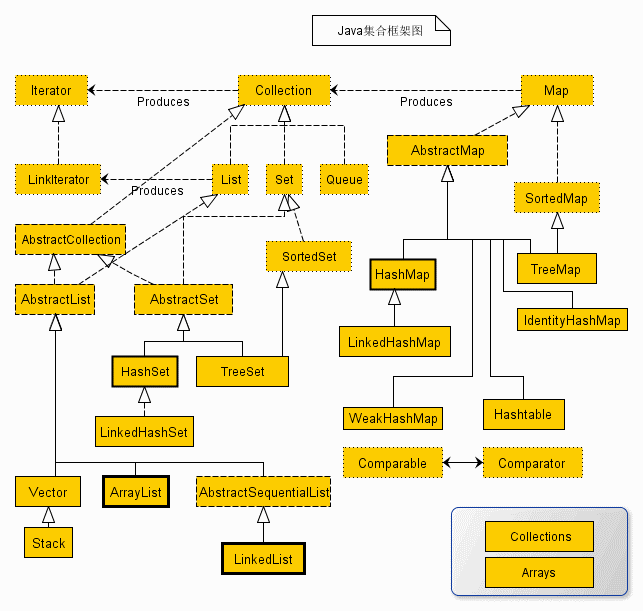
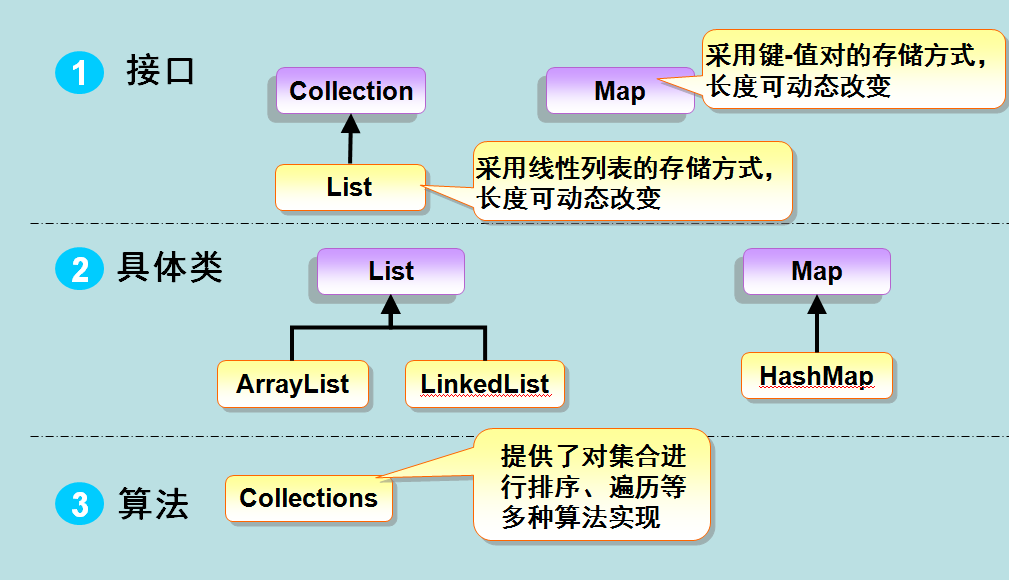
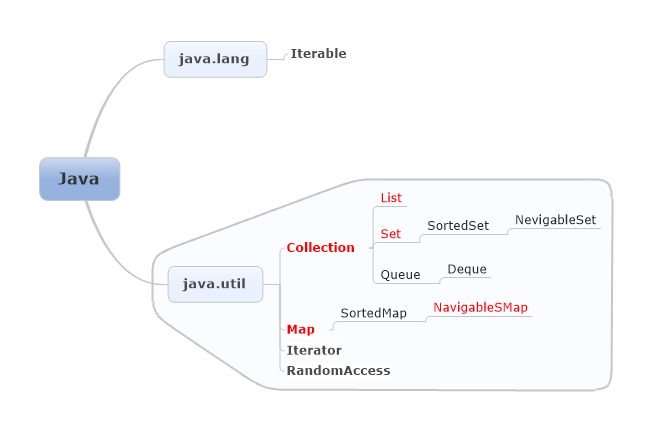
1. 接口:
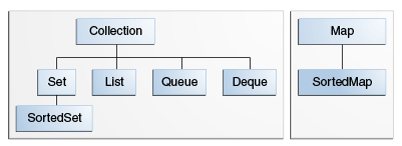
2. 实现:
| 接口 | 哈希表实现 | 可调整大小的数组实现 | 树实现 | 链接列表实现 | 哈希表+链表实现 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Set |
HashSet |
TreeSet |
LinkedHashSet |
||
List |
ArrayList |
LinkedList |
|||
Queue |
|||||
Deque |
ArrayDeque |
LinkedList |
|||
Map |
HashMap |
TreeMap |
LinkedHashMap |
3. 算法:
- Sorting归并排序
- Shuffling随机打乱
- Routine Data Manipulation
- Searching
- Composition
- Finding Extreme Values
集合接口
官方文档、相关博文: Java 集合深入理解

1. Collection 接口
Collection 是最基本的集合接口,继承于Iterable接口,一个 Collection 代表一组 Object,即 Collection 的元素, Java不提供直接继承自Collection的类,只提供继承于的子接口(如List和set)。Collection 接口存储一组不唯一,无序的对象。
List 接口
List接口是一个有序的 Collection,使用此接口能够精确的控制每个元素插入的位置,能够通过索引(元素在List中位置,类似于数组的下标)来访问List中的元素,第一个元素的索引为 0,而且允许有相同的元素。
List 接口存储一组不唯一,有序(插入顺序)的对象。
Set 接口
Set 具有与 Collection 完全一样的接口,只是行为上不同,Set 不保存重复的元素。
Set 接口存储一组唯一,无序的对象。
SortedSet接口,继承于Set保存有序的集合。
Queue接口
呃
Set和List的区别
- Set 接口实例存储的是无序的,不重复的数据。List 接口实例存储的是有序的,可以重复的元素。
- Set检索效率低下,删除和插入效率高,插入和删除不会引起元素位置改变 <实现类有HashSet,TreeSet>。
- List和数组类似,可以动态增长,根据实际存储的数据的长度自动增长List的长度。查找元素效率高,插入删除效率低,因为会引起其他元素位置改变 <实现类有ArrayList,LinkedList,Vector> 。
2. Map接口
Map 接口存储一组键值对象,提供key(键)到value(值)的映射。
主要子接口有SortedMap接口。
Map.Entry接口
描述在一个Map中的一个元素(键/值对)。是一个Map的内部接口。
SortedMap接口
继承于 Map,使 Key 保持在升序排列。
3. Enumeration接口
这是一个传统的接口和定义的方法,通过它可以枚举(一次获得一个)对象集合中的元素。这个传统接口已被迭代器取代
工具类
Collections类
对于List 的相关算法
- sort ,归并排序
- shuffle ,随机打乱
- reverse ,反转元素顺序
- swap ,交换
- binarySearch ,二分查找
- 。。。。。。
package com.nl.sx816.CollectionFramework.ArraysUtil;import java.util.Arrays;import java.util.List;/*** Created with IntelliJ IDEA 2018.* Description: Arrays类和Collections类* Arrays类包含用于操作数组的各种方法还包含一个静态工厂,允许将数组视为列表。** Collections类是操作集合的工具类,包含对集合进行操作或返回集合的静态方法。** 算法:* Collections对于List 的相关算法* sort ,归并排序(小-->大)* shuffle ,随机打乱* reverse ,反转元素顺序* swap ,交换* binarySearch ,二分查找** static <E> Collection<E> checkedCollection(Collection<E> c, Class<E> type) 返回指定集合的动态类型安全视图。* static <E> List<E> checkedList(List<E> list, Class<E> type) 返回指定列表的动态类型安全视图。* static <K,V> Map<K,V> checkedMap(Map<K,V> m, Class<K> keyType, Class<V> valueType) 返回指定映射的动态类型安全视图。** boolean addAll(Collection<? super T> c, T... elements) 将所有指定的元素添加到指定的集合中。* static <E> Set<E> checkedSet(Set<E> s, Class<E> type)返回指定集的动态类型安全视图。* static <K,V> SortedMap<K,V> checkedSortedMap(SortedMap<K,V> m, Class<K> keyType, Class<V> valueType) 返回指定有序映射的动态类型安全视图。* static <E> SortedSet<E> checkedSortedSet(SortedSet<E> s, Class<E> type) 返回指定有序集的动态类型安全视图。*** @author: 黄昭鸿* @date: 2018-08-17* Time: 10:45*/public class TestCollections {public static void main(String[] args){}}
Arrays类
package com.nl.sx816.CollectionFramework.ArraysUtil;import com.nl.sx807.HeapStackPractice.Student;import java.util.Arrays;/*** Created with IntelliJ IDEA 2018.* Description: Arrays工具类** @author: 黄昭鸿* @date: 2018-08-20* Time: 9:43*/public class TestArrays {public static void main(String[] args) {//sort 将指定的数组按升序排序,可指定范围。//asList,返回由指定数组支持的固定大小的列表//List<String> stooges = Arrays.asList("Larry","Moe","Curly");// binarySearch使用二进制搜索算法搜索指定值的数组的范围//copyOfRange将指定数组的指定范围复制到新数组中//fill 将值分配给数组的指定范围的每个元素。//parallelSort(int[] a, int fromIndex, int toIndex) 将指定的数组范围按数字升序排序。//parallelSort(T[] a, Comparator<? super T> cmp) //根据指定比较器引发的顺序对指定的对象数组进行排序。//parallelSort(T[] a, int fromIndex, int toIndex) //根据元素的自然顺序(compareTo(T o)),将指定对象数组的指定范围按升序 排序。//spliterator(T[] array, int startInclusive, int endExclusive) 返回Spliterator覆盖指定数组的指定范围。int[] arrs = {12, 23, 45, 56, 78, 89, 34, 45, 56, 67, 89, 98};print(arrs);//对数组排序Arrays.sort(arrs);print(arrs);Student[] students = {new Student("张三丰", "1", 105),new Student("里斯", "2", 46),new Student("王武", "3", 99),new Student("赵莉丰", "4", 13)};for (Student s : students) {System.out.println(s);}//当需要对某个类的对象进行排序时,该类需要实现Comparable<T>接口 必须重写compareTo方法Arrays.sort(students);System.out.println();for (Student s : students) {System.out.println(s);}}public static void print(int[] ints) {for (int i : ints) {System.out.print(i + " ");}System.out.println();}}
数组转成 List 的方法 asList :
@SafeVarargspublic static <T> List<T> asList(T... array) {return new ArrayList<T>(array);}
集合实现类(标准集合类)
| 序号 | 类描述 |
|---|---|
| 1 | AbstractCollection 实现了大部分的集合接口。 |
| 2 | AbstractList 继承于AbstractCollection 并且实现了大部分List接口。 |
| 3 | AbstractSequentialList 继承于 AbstractList ,提供了对数据元素的链式访问而不是随机访问。 |
| 4 | LinkedList 该类实现了List接口,允许有null(空)元素。主要用于创建链表数据结构,该类没有同步方法,如果多个线程同时访问一个List,则必须自己实现访问同步,解决方法就是在创建List时候构造一个同步的List。例如: Listlist=Collections.synchronizedList(newLinkedList(...)); LinkedList 查找效率低。 |
| 5 | ArrayList 该类也是实现了List的接口,实现了可变大小的数组,随机访问和遍历元素时,提供更好的性能。该类也是非同步的,在多线程的情况下不要使用。ArrayList 增长当前长度的50%,插入删除效率低。 线程不同步 |
| 6 | AbstractSet 继承于AbstractCollection 并且实现了大部分Set接口。 |
| 7 | HashSet 该类实现了Set接口,不允许出现重复元素,不保证集合中元素的顺序,允许包含值为null的元素,但最多只能一个。 |
| 8 | LinkedHashSet 具有可预知迭代顺序的 Set 接口的哈希表和链接列表实现。 |
| 9 | TreeSet 该类实现了Set接口,可以实现排序等功能。 |
| 10 | AbstractMap 实现了大部分的Map接口。 |
| 11 | HashMap
HashMap 是一个散列表,它存储的内容是键值对(key-value)映射。 该类实现了Map接口,根据键的HashCode值存储数据,具有很快的访问速度,最多允许一条记录的键为null,不支持线程同步。 |
| 12 | TreeMap
继承了AbstractMap,并且使用一颗树。 |
| 13 | WeakHashMap
继承AbstractMap类,使用弱密钥的哈希表。 |
| 14 | LinkedHashMap
继承于HashMap,使用元素的自然顺序对元素进行排序. |
| 15 | IdentityHashMap
继承AbstractMap类,比较文档时使用引用相等。 |
上午讲自定义异常类
下午讲了List
ArrayList VS LinkedList
ArrayList
- 基于数组,在数组中搜索和读取数据是很快的。因此 ArrayList 获取数据的时间复杂度是O(1);
- 但是添加、删除时该元素后面的所有元素都要移动,所以添加/删除数据效率不高;
- 另外其实还是有容量的,每次达到阈值需要扩容,这个操作比较影响效率。
LinkedList
- 基于双端链表,添加/删除元素只会影响周围的两个节点,开销很低;
- 只能顺序遍历,无法按照索引获得元素,因此查询效率不高;
- 没有固定容量,不需要扩容;
- 需要更多的内存,LinkedList每个节点中需要多存储前后节点的信息,占用空间更多些。
ArrayList与 Linkedlist的区别
Array List釆用的是数组形式来保存对象的,这种方式将对象放在连续的位置中,所以最大的缺点就是插入删除时非常麻烦
Linkedlist采用的将对象存放在独立的空间中而且在每个空间中还保存下一个链接的索引但是缺点就是查找非常麻烦要丛第一个索引开始,优点是插入和删除非常方便
ArrayListDemo.java
package com.nl.sx816.CollectionFramework.ListDemo;/*包名统一使用小写,点分隔符之间有且仅有一个自然语义的英语单词。包名统一使用单数形式*/import cn.hutool.core.lang.Console;import java.util.ArrayList;/*** Created with IntelliJ IDEA 2018.* Description: List——有序可重复、元素可以为 null* LinkedList,有List共有特点* 不同步(线程不安全)* 容量不固定,想放多少放多少(当然有最大阈值,但一般达不到)* 效率高:* size(), isEmpty(), get(), set() iterator(), ListIterator() 方法的时间复杂度都是 O(1)* add() 添加操作的时间复杂度平均为 O(n)* 其他所有操作的时间复杂度几乎都是 O(n)* 占用空间更小* 对比 LinkedList,不用占用额外空间维护链表结构** List——有序可重复、元素可以为 null** @author: 黄昭鸿* @date: 2018-08-16* Time: 16:21*//*** 类说明:* boolean add(E e) 将指定的元素添加到此列表的尾部。* void add(int index, E element) 将指定的元素插入此列表中的指定位置。* void clear() 移除此列表中的所有元素。* Object clone() 返回此 ArrayList 实例的浅表副本。* boolean contains(Object o) 如果此列表中包含指定的元素,则返回 true。* E get(int index) 返回此列表中指定位置上的元素。* int indexOf(Object o) 返回此列表中首次出现的指定元素的索引,或如果此列表不包含元素,则返回 -1。* boolean isEmpty() 如果此列表中没有元素,则返回 true* int lastIndexOf(Object o) 返回此列表中最后一次出现的指定元素的索引,或如果此列表不包含索引,则返回 -1。* E remove(int index) 移除此列表中指定位置上的元素。* boolean remove(Object o) 移除此列表中首次出现的指定元素(如果存在)。* protected void removeRange(int fromIndex, int toIndex) 移除列表中索引在 fromIndex(包括)和 toIndex(不包括)之间的所有元素,向左移动所有后续元素。* E set(int index, E element) 用指定的元素替代此列表中指定位置上的元素。* int size() 返回此列表中的元素数。* Object[] toArray() 按适当顺序(从第一个到最后一个元素)返回包含此列表中所有元素的数组。* <T> T[] toArray(T[] a) 按适当顺序(从第一个到最后一个元素)返回包含此列表中所有元素的数组;返回数组的运行时类型是指定数组的运行时类型。*/public class ArrayListDemo {public static void main(String[] args){//数组初始容量为10(private static final int DEFAULT_CAPACITY = 10;),size <= 容量//空数组ArrayList arrayList=new ArrayList();arrayList.add(1);arrayList.add(2);arrayList.add(3);//指定容量ArrayList arrayList2=new ArrayList(5);arrayList2.add("a");arrayList2.add("b");arrayList2.add("c");//直接创建和指定集合一样内容的 ArrayListArrayList arrayList3=new ArrayList(arrayList2);Console.log(arrayList.hashCode());Console.log(arrayList2.hashCode());Console.log(arrayList3.hashCode());arrayList.addAll(arrayList3);Console.log(arrayList);Console.log(arrayList2);Console.log(arrayList.hashCode());Console.log(arrayList2.hashCode());Console.log(arrayList3.hashCode());}}
运行输出:
30817126145126145[1, 2, 3, a, b, c][a, b, c]918165601126145126145Process finished with exit code 0
LinkedListDemo.java
package com.nl.sx816.CollectionFramework.ListDemo;import cn.hutool.core.lang.Console;import java.util.Iterator;import java.util.LinkedList;import java.util.ListIterator;/*** Created with IntelliJ IDEA 2018.* Description: List——有序可重复、元素可以为 null* LinkedList,有List共有特点* 双向链表实现* 所有指定位置的操作都是从头开始遍历进行的* 和 ArrayList 一样,不是同步容器(线程不安全)** @author: 黄昭鸿* @date: 2018-08-16* Time: 16:17*/public class LinkedListDemo {/*** 默认值长度为0*/private LinkedList<String> linkedList = new LinkedList<>();public static void main(String[] args) {//单个方法的总行数不要超过80行。LinkedListDemo linkedListDemo = new LinkedListDemo();//添加到此列表的结尾System.out.print(linkedListDemo.linkedList.add("天津"));System.out.print(linkedListDemo.linkedList.add("上海"));System.out.print(linkedListDemo.linkedList.add("北京"));System.out.print(linkedListDemo.linkedList.add("贵州"));System.out.print(linkedListDemo.linkedList.add("广州"));System.out.print(linkedListDemo.linkedList.add("杭州"));System.out.print(linkedListDemo.linkedList.add("苏州"));System.out.print(linkedListDemo.linkedList.add("荆州"));System.out.print(linkedListDemo.linkedList.add("郑州"));System.out.print(linkedListDemo.linkedList.add("兰州"));System.out.print(linkedListDemo.linkedList.add("福州"));System.out.print(linkedListDemo.linkedList.add("柳州"));System.out.print(linkedListDemo.linkedList.add(null));System.out.print(linkedListDemo.linkedList.add("钦州"));System.out.println(linkedListDemo.linkedList.add("北京"));System.out.print("add(E e) 方法:");Console.log(linkedListDemo.linkedList);//交换俩元素位置System.out.println("交换俩元素位置:");swap(linkedListDemo.linkedList, 0, 5);Console.log(linkedListDemo.linkedList);//插入此列表的开头addFirst(E e)System.out.print("addFirst(E e)方法:");linkedListDemo.linkedList.addFirst("开头");Console.log(linkedListDemo.linkedList);//addLast(E e)将指定元素添加到此列表的结尾。System.out.print("addLast(E e)方法:");linkedListDemo.linkedList.addLast("结尾");Console.log(linkedListDemo.linkedList);//contains(Object o) 如果此列表包含指定元素,则返回 true。System.out.println("是否包含“天津”:" + linkedListDemo.linkedList.contains("天津"));//element()获取但不移除此列表的头(第一个元素)。System.out.println("头:" + linkedListDemo.linkedList.element());//E get(int index)返回此列表中指定位置处的元素。System.out.println("指定位置的元素:" + linkedListDemo.linkedList.get(5));//getFirst()返回此列表的第一个元素。System.out.println("第一个元素:" + linkedListDemo.linkedList.getFirst());// E getLast()返回此列表的最后一个元素。System.out.println("最后一个元素:" + linkedListDemo.linkedList.getLast());// int indexOf(Object o) 返回此列表中首次出现的指定元素的索引,如果此列表中不包含该元素,则返回 -1。System.out.println("索引:" + linkedListDemo.indexOf("北京"));System.out.println("索引:" + linkedListDemo.indexOf("九州"));// int lastIndexOf(Object o) 返回此列表中最后出现的指定元素的索引,如果此列表中不包含该元素,则返回 -1。System.out.println("索引:" + linkedListDemo.lastIndexOf("北京"));//boolean offer(E e)将指定元素添加到此列表的末尾。System.out.println("元素添加到此列表的末尾(offer)" + linkedListDemo.linkedList.offer("A"));// boolean offerFirst(E e)在此列表的开头插入指定的元素。System.out.println("在列表的开头插入元素(offerFirst):" + linkedListDemo.linkedList.offerFirst("B"));// boolean offerLast(E e)在此列表末尾插入指定的元素System.out.println("元素添加到此列表的末尾(offerLast):" + linkedListDemo.linkedList.offerLast("C"));Console.log(linkedListDemo.linkedList);// E peek() 获取但不移除此列表的头(第一个元素)。// E peekFirst() 获取但不移除此列表的第一个元素;如果此列表为空,则返回 null。// E peekLast() 获取但不移除此列表的最后一个元素;如果此列表为空,则返回 null。// E poll() 获取并移除此列表的头(第一个元素)// E pollFirst() 获取并移除此列表的第一个元素;如果此列表为空,则返回 null。// E pollLast() 获取并移除此列表的最后一个元素;如果此列表为空,则返回 null。// E pop() 从此列表所表示的堆栈处弹出一个元素。System.out.println("弹出的是“" + linkedListDemo.linkedList.pop() + "”,结果:");Console.log(linkedListDemo.linkedList);// void push(E e) 将元素推入此列表所表示的堆栈。System.out.println("将元素推入此列表所表示的堆栈:");linkedListDemo.linkedList.push("push");Console.log(linkedListDemo.linkedList);// E remove() 获取并移除此列表的头(第一个元素)。// E remove(int index) 移除此列表中指定位置处的元素。System.out.println("移除指定位置(6)处的元素“" + linkedListDemo.linkedList.remove(6) + "”后:");Console.log(linkedListDemo.linkedList);// boolean remove(Object o) 从此列表中移除首次出现的指定元素(如果存在)。// E removeFirst() 移除并返回此列表的第一个元素。// E removeLast() 移除并返回此列表的最后一个元素。// E set(int index, E element) 将此列表中指定位置的元素替换为指定的元素。System.out.println("替换“" + linkedListDemo.linkedList.set(0, "呃") + "”后:");Console.log(linkedListDemo.linkedList);// Object[] toArray() 返回以适当顺序(从第一个元素到最后一个元素)包含此列表中所有元素的数组。//<T> T[] toArray(T[] a) 返回以适当顺序(从第一个元素到最后一个元素)包含此列表中所有元素的数组;返回数组的运行时类型为指定数组的类型。//如果指定数组能容纳列表,则在其中返回该列表。否则,分配具有指定数组的运行时类型和此列表大小的新数组。//如果指定数组能容纳列表,并有剩余空间(即数组比列表元素多),则紧跟在列表末尾的数组元素会被设置为 null(只有在调用者知道列表不包含任何 null 元素时,才可使用此方法来确定列表的长度。)//String[] strings=new String[linkedListDemo.linkedList.size()];//linkedListDemo.linkedList.toArray(strings);//Console.log(strings);Console.log((linkedListDemo.linkedList.toArray(new String[0])));//listIterator迭代器ListIterator lit = linkedListDemo.linkedList.listIterator();while (lit.hasNext()) {System.out.print(lit.next());}System.out.println();//倒序迭代器Iterator x =linkedListDemo.linkedList.descendingIterator();while (x.hasNext()) {System.out.print(x.next());}}public String indexOf(String o) {int t = linkedList.indexOf(o);if (t == (-1)) {return "此列表中不包含“" + o + "”元素";} else {return String.valueOf(t);}}public String lastIndexOf(String o) {int t = linkedList.lastIndexOf(o);if (t == (-1)) {return "此列表中不包含“" + o + "”元素";} else {return String.valueOf(t);}}//元素交换(工具类Collections中的方法)public static <E> void swap(LinkedList<E> a, int i, int j) {E tmp = a.get(i);a.set(i, a.get(j));a.set(j, tmp);}}
运行输出:
truetruetruetruetruetruetruetruetruetruetruetruetruetruetrueadd(E e) 方法:[天津, 上海, 北京, 贵州, 广州, 杭州, 苏州, 荆州, 郑州, 兰州, 福州, 柳州, null, 钦州, 北京]交换俩元素位置:[杭州, 上海, 北京, 贵州, 广州, 天津, 苏州, 荆州, 郑州, 兰州, 福州, 柳州, null, 钦州, 北京]addFirst(E e)方法:[开头, 杭州, 上海, 北京, 贵州, 广州, 天津, 苏州, 荆州, 郑州, 兰州, 福州, 柳州, null, 钦州, 北京]addLast(E e)方法:[开头, 杭州, 上海, 北京, 贵州, 广州, 天津, 苏州, 荆州, 郑州, 兰州, 福州, 柳州, null, 钦州, 北京, 结尾]是否包含“天津”:true头:开头指定位置的元素:广州第一个元素:开头最后一个元素:结尾索引:3索引:此列表中不包含“九州”元素索引:15元素添加到此列表的末尾(offer)true在列表的开头插入元素(offerFirst):true元素添加到此列表的末尾(offerLast):true[B, 开头, 杭州, 上海, 北京, 贵州, 广州, 天津, 苏州, 荆州, 郑州, 兰州, 福州, 柳州, null, 钦州, 北京, 结尾, A, C]弹出的是“B”,结果:[开头, 杭州, 上海, 北京, 贵州, 广州, 天津, 苏州, 荆州, 郑州, 兰州, 福州, 柳州, null, 钦州, 北京, 结尾, A, C]将元素推入此列表所表示的堆栈:[push, 开头, 杭州, 上海, 北京, 贵州, 广州, 天津, 苏州, 荆州, 郑州, 兰州, 福州, 柳州, null, 钦州, 北京, 结尾, A, C]移除指定位置(6)处的元素“广州”后:[push, 开头, 杭州, 上海, 北京, 贵州, 天津, 苏州, 荆州, 郑州, 兰州, 福州, 柳州, null, 钦州, 北京, 结尾, A, C]替换“push”后:[呃, 开头, 杭州, 上海, 北京, 贵州, 天津, 苏州, 荆州, 郑州, 兰州, 福州, 柳州, null, 钦州, 北京, 结尾, A, C][呃, 开头, 杭州, 上海, 北京, 贵州, 天津, 苏州, 荆州, 郑州, 兰州, 福州, 柳州, null, 钦州, 北京, 结尾, A, C]呃开头杭州上海北京贵州天津苏州荆州郑州兰州福州柳州null钦州北京结尾ACCA结尾北京钦州null柳州福州兰州郑州荆州苏州天津贵州北京上海杭州开头呃Process finished with exit code 0
附:
自定义异常类(检查性)
MyExceptionChecked.java
package com.nl.sx816;import java.security.PrivilegedActionException;/*** Created with IntelliJ IDEA 2018.* Description: Java异常——自定义异常类——checked exception** 如果要自定义异常类,则扩展Exception类即可,因此这样的自定义异常都属于检查异常(checked exception)。* 如果要自定义非检查异常,则扩展自RuntimeException。** 按照国际惯例,自定义的异常应该总是包含如下的构造函数:** 一个无参构造函数* 一个带有String参数的构造函数,并传递给父类的构造函数。* 一个带有String参数和Throwable参数,并都传递给父类构造函数* 一个带有Throwable 参数的构造函数,并传递给父类的构造函数。** 通常还会给出serialVersionUID* @author: 黄昭鸿* @date: 2018-08-16* Time: 11:25*/public class MyExceptionChecked extends Exception {private static final long serialVersionUID = -4407200639975626465L;/*** Constructs a new exception with {@code null} as its detail message.* The cause is not initialized, and may subsequently be initialized by a* call to {@link #initCause}.*/public MyExceptionChecked() { }/*** Constructs a new exception with the specified detail message. The* cause is not initialized, and may subsequently be initialized by* a call to {@link #initCause}.** @param message the detail message. The detail message is saved for* later retrieval by the {@link #getMessage()} method.*/public MyExceptionChecked(String message) {super(message);}/*** Constructs a new exception with the specified detail message and* cause. <p>Note that the detail message associated with* {@code cause} is <i>not</i> automatically incorporated in* this exception's detail message.** @param message the detail message (which is saved for later retrieval* by the {@link #getMessage()} method).* @param cause the cause (which is saved for later retrieval by the* {@link #getCause()} method). (A {@code null} value is* permitted, and indicates that the cause is nonexistent or* unknown.)* @since 1.4*/public MyExceptionChecked(String message, Throwable cause) {super(message, cause);}/*** Constructs a new exception with the specified cause and a detail* message of {@code (cause==null ? null : cause.toString())} (which* typically contains the class and detail message of {@code cause}).* This constructor is useful for exceptions that are little more than* wrappers for other throwables (for example, {@link* PrivilegedActionException}).** @param cause the cause (which is saved for later retrieval by the* {@link #getCause()} method). (A {@code null} value is* permitted, and indicates that the cause is nonexistent or* unknown.)* @since 1.4*/public MyExceptionChecked(Throwable cause) {super(cause);}/*** Constructs a new exception with the specified detail message,* cause, suppression enabled or disabled, and writable stack* trace enabled or disabled.** @param message the detail message.* @param cause the cause. (A {@code null} value is permitted,* and indicates that the cause is nonexistent or unknown.)* @param enableSuppression whether or not suppression is enabled* or disabled* @param writableStackTrace whether or not the stack trace should* be writable* @since 1.7*/public MyExceptionChecked(String message, Throwable cause, boolean enableSuppression, boolean writableStackTrace) {super(message, cause, enableSuppression, writableStackTrace);}}
自定义异常类(非检查性异常)
MyException.java(RuntimeException)
package com.nl.sx816;/*** Created with IntelliJ IDEA 2018.* Description: Java异常——自定义异常类——RuntimeException** 如果要自定义异常类,则扩展Exception类即可,因此这样的自定义异常都属于检查异常(checked exception)。* 如果要自定义非检查异常,则扩展自RuntimeException。** 按照国际惯例,自定义的异常应该总是包含如下的构造函数:** 一个无参构造函数* 一个带有String参数的构造函数,并传递给父类的构造函数。* 一个带有String参数和Throwable参数,并都传递给父类构造函数* 一个带有Throwable 参数的构造函数,并传递给父类的构造函数。** 通常还会给出serialVersionUID** Author: 黄昭鸿* Date: 2018-08-16* Time: 10:56*/public class MyException extends RuntimeException{private static final long serialVersionUID = 2032238587799006983L;/*** Constructs a new runtime exception with {@code null} as its* detail message. The cause is not initialized, and may subsequently be* initialized by a call to {@link #initCause}.*/public MyException() {super();}/*** Constructs a new runtime exception with the specified detail message.* The cause is not initialized, and may subsequently be initialized by a* call to {@link #initCause}.** @param message the detail message. The detail message is saved for* later retrieval by the {@link #getMessage()} method.*/public MyException(String message) {super(message);}/*** Constructs a new runtime exception with the specified detail message and* cause. <p>Note that the detail message associated with* {@code cause} is <i>not</i> automatically incorporated in* this runtime exception's detail message.** @param message the detail message (which is saved for later retrieval* by the {@link #getMessage()} method).* @param cause the cause (which is saved for later retrieval by the* {@link #getCause()} method). (A {@code null} value is* permitted, and indicates that the cause is nonexistent or* unknown.)* @since 1.4*/public MyException(String message, Throwable cause) {super(message, cause);}/*** Constructs a new runtime exception with the specified cause and a* detail message of {@code (cause==null ? null : cause.toString())}* (which typically contains the class and detail message of* {@code cause}). This constructor is useful for runtime exceptions* that are little more than wrappers for other throwables.** @param cause the cause (which is saved for later retrieval by the* {@link #getCause()} method). (A {@code null} value is* permitted, and indicates that the cause is nonexistent or* unknown.)* @since 1.4*/public MyException(Throwable cause) {super(cause);}}
