@nextleaf
2018-08-20T13:52:14.000000Z
字数 15541
阅读 802
2018-08-20 工作日志
Java 工作日志 泛型 反射
上午
泛型
泛型与Map、ArrayList
Map中的键值对的类型是Entry
package com.nl.sx817.generics.map;import java.util.HashMap;import java.util.Map;import java.util.Set;public class MapGenerics {public static void main(String[] args){Map<String,Integer> map=new HashMap<String,Integer>();map.put("A",1);map.put("B",2);map.put("C",3);map.put("D",4);//map中的键值对的类型是EntrySet<Map.Entry<String,Integer>> set=map.entrySet();for (Map.Entry<String,Integer> o:set){System.out.println(o.getKey()+"-----------"+o.getValue());}}}
Arrays工具类
compareTo()
自然顺序
package com.nl.sx816.CollectionFramework.ArraysUtil;import com.nl.sx807.HeapStackPractice.Student;import java.util.Arrays;/*** Created with IntelliJ IDEA 2018.* Description: Arrays工具类** @author: 黄昭鸿* @date: 2018-08-20* Time: 9:43*/public class TestArrays {public static void main(String[] args) {//sort 将指定的数组按升序排序,可指定范围。//asList,返回由指定数组支持的固定大小的列表//List<String> stooges = Arrays.asList("Larry","Moe","Curly");// binarySearch使用二进制搜索算法搜索指定值的数组的范围//copyOfRange将指定数组的指定范围复制到新数组中//fill 将值分配给数组的指定范围的每个元素。//parallelSort(int[] a, int fromIndex, int toIndex) 将指定的数组范围按数字升序排序。//parallelSort(T[] a, Comparator<? super T> cmp) //根据指定比较器引发的顺序对指定的对象数组进行排序。//parallelSort(T[] a, int fromIndex, int toIndex) //根据元素的自然顺序(compareTo(T o)),将指定对象数组的指定范围按升序 排序。//spliterator(T[] array, int startInclusive, int endExclusive) 返回Spliterator覆盖指定数组的指定范围。int[] arrs = {12, 23, 45, 56, 78, 89, 34, 45, 56, 67, 89, 98};print(arrs);//对数组排序Arrays.sort(arrs);print(arrs);Student[] students = {new Student("张三丰", "1", 105),new Student("里斯", "2", 46),new Student("王武", "3", 99),new Student("赵莉丰", "4", 13)};for (Student s : students) {System.out.println(s);}//当需要对某个类的对象进行排序时,该类需要实现Comparable<T>接口 必须重写compareTo方法Arrays.sort(students);System.out.println();for (Student s : students) {System.out.println(s);}}public static void print(int[] ints) {for (int i : ints) {System.out.print(i + " ");}System.out.println();}}
反射
取得Class对象的方式
类对象的使用
通过 Class对象获取成员变量、成员方法、接口、超类、构造方法等:
getName():获得类的完整名字。
getFields():获得类的public类型的属性。
getDeclaredFields():获得类的所有属性。包括private 声明的和继承类
getMethods():获得类的public类型的方法。
getDeclaredMethods():获得类的所有方法。包括private 声明的和继承类
getMethod(String name, Class[] parameterTypes):获得类的特定方法,name参数指定方法的名字,parameterTypes参数指定方法的参数类型。
getConstructors():获得类的public类型的构造方法。
getConstructor(Class[] parameterTypes):获得类的特定构造方法,parameterTypes参数指定构造方法的参数类型。
newInstance():通过类的不带参数的构造方法创建这个类的一个对象。
。
package com.nl.sx820.reflection;import cn.hutool.core.lang.Console;import com.nl.sx813.abstractclass.Person;import java.lang.reflect.Constructor;import java.lang.reflect.Method;import java.lang.reflect.TypeVariable;/*** Created with IntelliJ IDEA 2018.* Description: 反射* Java反射就是在运行状态中,对于任意一个类,都能够知道这个类的所有属性和方法;对于任意一个对象,都能够调用它的任意方法和属性;并且能改变它的属性。* 而这也是Java被视为动态(或准动态,一般而言的动态语言定义是程序运行时,允许改变程序结构或变量类型)语言的一个关键性质** 取得Class对象的方式** @author: 黄昭鸿* @date: 2018-08-20* Time: 10:53*/public class ReflexDemo {public static void main(String[] args) {Class<?> c1 = null;Class<?> c2 = null;Class<?> c3 = null;Class<?> c4 = null;//取得Class对象的方式//方式一 getClass 获得Person的类对象Person person1 = new Person("孙兰芳", 16, '女');c1 = person1.getClass();//方式二,static method Class.forName()获得Person的类对象try {c2 = Class.forName("com.nl.sx813.abstractclass.Person");} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {e.printStackTrace();}//方式三.class 获得Person的类对象c3 = Person.class;//方式四 获得类对象,如果时Java封装对象,使用TYPE语法c4 = Integer.TYPE;System.out.println(c1.getName() + "---" + c2.getName() + "---" + c3.getName() + "---" + c4.getName());//获得所有公有构造方法System.out.println("所有公有构造方法");for (Constructor<?> constructor : c1.getConstructors()) {System.out.println(constructor.toGenericString());}//获得所有公有方法System.out.println("所有公有方法");for (Method method : c3.getMethods()) {System.out.println(method.toGenericString());}}}
附:
package com.nl.sx820.reflection;import cn.hutool.core.lang.Console;import com.nl.sx813.abstractclass.Person;import java.lang.reflect.Constructor;import java.lang.reflect.Method;import java.lang.reflect.TypeVariable;/*** Created with IntelliJ IDEA 2018.* Description: 反射* Java反射就是在运行状态中,对于任意一个类,都能够知道这个类的所有属性和方法;对于任意一个对象,都能够调用它的任意方法和属性;并且能改变它的属性。* 而这也是Java被视为动态(或准动态,一般而言的动态语言定义是程序运行时,允许改变程序结构或变量类型)语言的一个关键性质* 每个类都会产生一个对应的Class对象,Class对象仅在需要的时候才会加载** 通过Class对象访问这个类的所有属性和方法* 取得Class对象的方式** @author: 黄昭鸿* @date: 2018-08-20* Time: 10:53*/public class ReflexDemo {public static void main(String[] args) {Class<?> c1 = null;Class<?> c2 = null;Class<?> c3 = null;Class<?> c4 = null;//取得Class对象的方式//方式一 getClass 获得Person的类对象Person person1 = new Person("孙兰芳", 16, '女');c1 = person1.getClass();//方式二,static method Class.forName()获得Person的类对象try {c2 = Class.forName("com.nl.sx813.abstractclass.Person");} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {e.printStackTrace();}//方式三.class 获得Person的类对象//使用”.class”来创建Class对象的引用时,不会自动初始化该Class对象(例如不会初始化静态块),使用forName()会自动初始化该Class对象c3 = Person.class;//方式四 获得类对象,如果时Java封装对象,使用TYPE语法c4 = Integer.TYPE;System.out.println(c1.getName() + "---" + c2.getName() + "---" + c3.getName() + "---" + c4.getName());//获得所有公有构造方法System.out.println("所有公有构造方法");for (Constructor<?> constructor : c1.getConstructors()) {System.out.println(constructor.toGenericString());}//获得所有公有方法System.out.println("所有公有方法");for (Method method : c3.getMethods()) {System.out.println(method.toGenericString());}/** getName():获得类的完整名字。* getFields():获得类的public类型的属性。* getDeclaredFields():获得类的所有属性。包括private 声明的和继承类* getMethods():获得类的public类型的方法。* getDeclaredMethods():获得类的所有方法。包括private 声明的和继承类* getMethod(String name, Class[] parameterTypes):获得类的特定方法,name参数指定方法的名字,parameterTypes参数指定方法的参数类型。* getConstructors():获得类的public类型的构造方法。* getConstructor(Class[] parameterTypes):获得类的特定构造方法,parameterTypes参数指定构造方法的参数类型。* newInstance():通过类的不带参数的构造方法创建这个类的一个对象。*/}}
下午
Java 流(Stream)、文件(File)和IO
按流的角色不同,分为 节点流(对应文件),处理流。
按操作数据单位不同,分为 字节流(8bit),字符流。
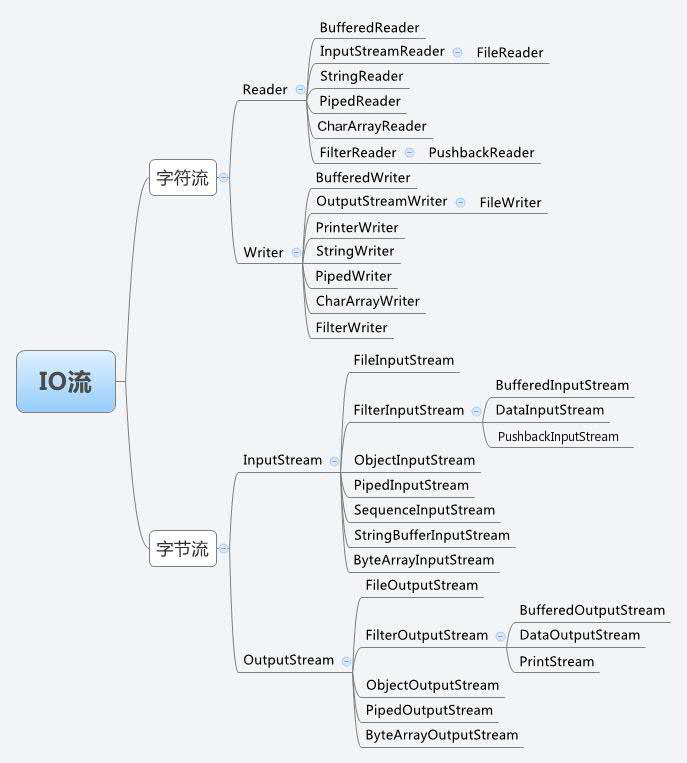
File
创建文件夹以及文件
package com.nl.sx820.io;import cn.hutool.core.lang.Console;import java.io.File;import java.io.IOException;/*** Created with IntelliJ IDEA 2018.* Description:文件* 创建目录* 创建文件** @author: 黄昭鸿* @date: 2018-08-20* Time: 14:53*/public class FileDemo {public static void main(String[] args) {//创建目录File parent = new File("E:" + File.separator + "Downloads" + File.separator + "java创建的文件夹");parent.mkdir();//创建文件try {new File(parent + File.separator + "通用分隔符(File.separator).txt").createNewFile();} catch (IOException e) {e.printStackTrace();}createNewFileTest();}public static void createNewFileTest() {//在工作中用到通用分隔符File.separatorFile parent2 = new File("E:" + File.separator + "Downloads" + File.separator + "java创建的文件夹2Test" + File.separator + "子文件夹");File child = new File(parent2, "子File.txt");try {if (!parent2.exists()) {//parent.mkdir()只创建一个文件夹,parent.mkdirs()可创建多个文件夹parent2.mkdirs();child.createNewFile();System.out.println("文件目录及文件创建成功");} else {child.createNewFile();System.out.println("文件创建成功");}} catch (IOException e) {e.printStackTrace();}showInfo(parent2);showListFiles(parent2);showInfo(child);showListFiles(child);//1秒后删除//timing(child);//重命名reName(child, "E:\\Downloads\\java创建的文件夹2Test\\子文件夹\\新的名字.txt");}public static void timing(File child) {for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {try {//线程休眠Thread.sleep(1600);} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}child.delete();}public static void showInfo(File f) {System.out.println("\n属性:");System.out.println("文件绝对路径:" + f.getAbsolutePath());System.out.println("文件名:" + f.getName());System.out.println("父目录的路径:" + f.getParent());System.out.println("是否时文件夹:" + f.isDirectory());System.out.println("是否时文件:" + f.isFile());System.out.println("文件长度(字节):" + f.length());System.out.println("是否隐藏:" + f.isHidden());System.out.println();}public static void showListFiles(File f) {if (f.exists()) {if (f.isDirectory()) {//System.out.println("包含的文件名列表:");//Console.log(f.list());System.out.println("[" + f.getAbsolutePath() + "]文件列表:");char str = ' ';System.out.println("文件名\t\t\t大小\t\t\t隐藏");for (File file : f.listFiles()) {if (file.isHidden()) {str = '✔';} else {str = ' ';}System.out.println(file.getName() + "\t\t" + file.length() + "字节\t\t" + str);}} else {System.out.println("不是一个目录...");}} else {System.out.println("路径不存在");}}/*** Description:* 重命名* @date 2018/8/20 18:30*/public static boolean reName(File file, String name) {if (file.exists()) {if (file.isFile()) {System.out.println("新名:" + name);return file.renameTo(new File(name));} else {System.out.println("不是一个文件");}} else {System.out.println("路径不存在");return false;}return false;}}
FileInputStream流和 FileOutputStream流
FileInputStream
FileInputStream流用于从文件读取数据
FileOutputStream
该类用来创建一个文件并向文件中写数据。
如果在打开文件进行输出前,目标文件不存在,那么该流会创建该文件。
问题
//如果文件不存在会自动新建OutputStream fileOutputStream = new FileOutputStream("E:" + File.separator + "Downloads" + File.separator + "nextleafwin.hello");//默认为操作系统默认编码,windows上是gbkOutputStreamWriter writer = new OutputStreamWriter(fileOutputStream, "UTF-8");//使用line.separator系统变量来换行,如下String lineSeparator = System.getProperty("line.separator");fileOutputStream.write(lineSeparator.getBytes());// 写入到缓冲区writer.append("中文输入");writer.append(stringBuffer);
同一个方法内(如果不在同一个方法内,未知),代码1会影响代码2,原因未知:
代码1:
//从文件输入流一次读取一个字节System.out.println("从文件输入流一次读取一个字节");byte byteData;while ((byteData = (byte) fileInputStream.read()) != -1) {//System.out.print((char) byteData);}System.out.println();
代码2:
//读取到StringBuffer中InputStreamReader reader = new InputStreamReader(fileInputStream, "UTF-8");//StringBuffer stringBuffer = new StringBuffer();while (reader.ready()) {// 转成char加到StringBuffer对象中stringBuffer.append((char) reader.read());}System.out.println(stringBuffer.toString());//关闭读取流reader.close();
要么
package com.nl.sx820.io.stream;import java.io.*;public class stream {public static void main(String[] args) {StringBuffer stringBuffer = new StringBuffer();try {//创建一个输入流对象来读取文件:(还可以使用一个文件对象来创建一个输入流对象来读取文件)InputStream fileInputStream = new FileInputStream("E:" + File.separator + "Downloads" + File.separator + "nextleafwin.txt");//从文件输入流一次读取一个字节System.out.println("从文件输入流一次读取一个字节");byte byteData;while ((byteData = (byte) fileInputStream.read()) != -1) {System.out.print((char) byteData);stringBuffer.append((char)byteData);}System.out.println();} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {e.printStackTrace();} catch (IOException e) {e.printStackTrace();}//使用字符串类型的文件名来创建一个输出流对象(也可以使用一个文件对象来创建一个输出流来写文件)try {//BufferedOutputStream bos = new BufferedOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("your output file path"));//如果文件不存在会自动新建OutputStream fileOutputStream = new FileOutputStream("E:" + File.separator + "Downloads" + File.separator + "nextleafwin.hello");//默认为操作系统默认编码,windows上是gbkOutputStreamWriter writer = new OutputStreamWriter(fileOutputStream, "UTF-8");//使用line.separator系统变量来换行,如下String lineSeparator = System.getProperty("line.separator");fileOutputStream.write(lineSeparator.getBytes());// 写入到缓冲区writer.append("中文输入");writer.append(stringBuffer);//System.out.println(stringBuffer);//换行writer.append("\r\n");// 刷新缓存冲,写入到文件,直接close也会写入writer.flush();// 关闭写入流,同时会把缓冲区内容写入文件writer.close();// 关闭输出流,释放系统资源fileOutputStream.close();} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {e.printStackTrace();} catch (UnsupportedEncodingException e) {e.printStackTrace();} catch (IOException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}}
要么
package com.nl.sx820.io.stream;import java.io.*;public class stream {public static void main(String[] args) {StringBuffer stringBuffer = new StringBuffer();try {//创建一个输入流对象来读取文件:(还可以使用一个文件对象来创建一个输入流对象来读取文件)InputStream fileInputStream = new FileInputStream("E:" + File.separator + "Downloads" + File.separator + "nextleafwin.txt");//读取到StringBuffer中InputStreamReader reader = new InputStreamReader(fileInputStream, "UTF-8");//StringBuffer stringBuffer = new StringBuffer();while (reader.ready()) {// 转成char加到StringBuffer对象中stringBuffer.append((char) reader.read());}System.out.println("啦啦啦"+stringBuffer.toString());//关闭读取流reader.close();} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {e.printStackTrace();} catch (IOException e) {e.printStackTrace();}//使用字符串类型的文件名来创建一个输出流对象(也可以使用一个文件对象来创建一个输出流来写文件)try {//BufferedOutputStream bos = new BufferedOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("your output file path"));//如果文件不存在会自动新建OutputStream fileOutputStream = new FileOutputStream("E:" + File.separator + "Downloads" + File.separator + "nextleafwin.hello");//默认为操作系统默认编码,windows上是gbkOutputStreamWriter writer = new OutputStreamWriter(fileOutputStream, "UTF-8");//使用line.separator系统变量来换行,如下String lineSeparator = System.getProperty("line.separator");fileOutputStream.write(lineSeparator.getBytes());// 写入到缓冲区writer.append("中文输入");writer.append(stringBuffer);//System.out.println(stringBuffer);//换行writer.append("\r\n");// 刷新缓存冲,写入到文件,直接close也会写入writer.flush();// 关闭写入流,同时会把缓冲区内容写入文件writer.close();// 关闭输出流,释放系统资源fileOutputStream.close();} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {e.printStackTrace();} catch (UnsupportedEncodingException e) {e.printStackTrace();} catch (IOException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}}
附:
package com.nl.sx820.io.stream;import java.io.*;import java.nio.charset.StandardCharsets;/*** Created with IntelliJ IDEA 2018.* Description: 文件内容读取和写入** @author: 黄昭鸿* @date: 2018-08-20* Time: 17:52*/public class stream {public static void main(String[] args) {StringBuffer stringBuffer = new StringBuffer();try {//创建一个输入流对象来读取文件:(还可以使用一个文件对象来创建一个输入流对象来读取文件)InputStream fileInputStream = new FileInputStream("E:" + File.separator + "Downloads" + File.separator + "nextleafwin.txt");//读取到StringBuffer中InputStreamReader reader = new InputStreamReader(fileInputStream, StandardCharsets.UTF_8);//StringBuffer stringBuffer = new StringBuffer();while (reader.ready()) {// 转成char加到StringBuffer对象中stringBuffer.append((char) reader.read());}System.out.println("啦啦啦" + stringBuffer.toString());//关闭读取流reader.close();/*这里的代码也可以实现文件读取,但会影响上面的读取流代码,只能选其一使用//从文件输入流一次读取一个字节System.out.println("从文件输入流一次读取一个字节");byte byteData;while ((byteData = (byte) fileInputStream.read()) != -1) {System.out.print((char) byteData);}System.out.println();*/} catch (IOException e) {e.printStackTrace();}//使用字符串类型的文件名来创建一个输出流对象(也可以使用一个文件对象来创建一个输出流来写文件)try {//BufferedOutputStream bos = new BufferedOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("your output file path"));//如果文件不存在会自动新建OutputStream fileOutputStream = new FileOutputStream("E:" + File.separator + "Downloads" + File.separator + "新nextleafwin.txt");//默认为操作系统默认编码,windows上是gbkOutputStreamWriter writer = new OutputStreamWriter(fileOutputStream, StandardCharsets.UTF_8);//使用line.separator系统变量来换行,如下String lineSeparator = System.getProperty("line.separator");fileOutputStream.write(lineSeparator.getBytes());// 写入到缓冲区writer.append("中文输入");writer.append(stringBuffer);//System.out.println(stringBuffer);//换行writer.append("\r\n");// 刷新缓存冲,写入到文件,直接close也会写入writer.flush();// 关闭写入流,同时会把缓冲区内容写入文件writer.close();// 关闭输出流,释放系统资源fileOutputStream.close();} catch (IOException e) {e.printStackTrace();}System.out.println("-------------------------------------");File file = new File("E:" + File.separator + "Downloads" + File.separator + "nextleafwin.txt");File newFile = new File("E:" + File.separator + "Downloads" + File.separator + "NewNextleafwin.txt");rf(file);//如果文件不存在,FileWriter的write()方法会自动新建文件wf(newFile, "Java.io 包几乎包含了所有操作输入、输出需要的类。所有这些流类代表了输入源和输出目标。" +"Java.io 包中的流支持很多种格式,比如:基本类型、对象、本地化字符集等等。\n" + "一个流可以理解为一个数据的序列。输入流表示从一个源读取数据,输出流表示向一个目标写数据。");}//文件内容读取public static void rf(File file) {if (file.isFile()) {try {// 创建 FileReader 对象FileReader fileReader = new FileReader(file);System.out.println("读取的内容为:");/* byte byteData;while ((byteData = (byte) fileReader.read()) != -1) {System.out.print((char) byteData);}System.out.println();*/char[] a = new char[(int) file.length()];// 读取数组中的内容fileReader.read(a);for (char c : a) {System.out.print(c);}fileReader.close();} catch (IOException e) {e.printStackTrace();}} else {System.out.println("不是一个文件,读取??");}}//文件内容写入//如果文件不存在,FileWriter的write()方法会自动新建public static void wf(File file, String writeString) {try {if (file.exists()) {if (file.isDirectory()) {file = new File(file, File.separator + "aNewFile.txt");file.createNewFile();// creates a FileWriter ObjectFileWriter writer = new FileWriter(file);// 向文件写入内容System.out.println("开始写入到" + file.getAbsolutePath());writer.write(writeString);writer.flush();writer.close();} else if (file.isFile()) {//覆写System.out.println("覆写!");file.createNewFile();FileWriter writer = new FileWriter(file);System.out.println("开始写入到" + file.getAbsolutePath());writer.write(writeString);writer.flush();writer.close();}} else {//新建System.out.println("新建"+file.getAbsolutePath());file.createNewFile();FileWriter writer = new FileWriter(file);writer.write(writeString);writer.flush();writer.close();}} catch (IOException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}}
