@nalan90
2017-09-08T01:18:35.000000Z
字数 5165
阅读 912
多线程开发
Java
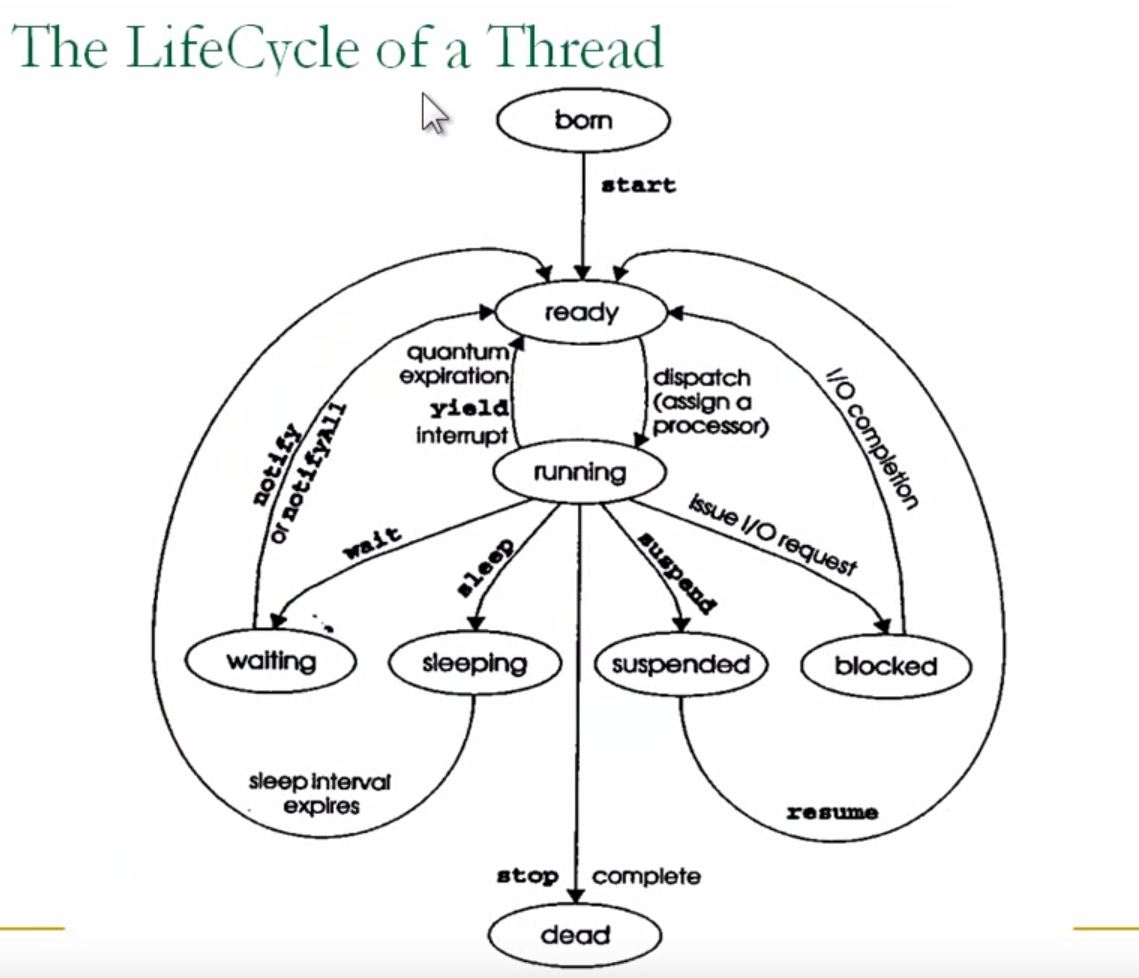
线程的生存周期
- 创建(new)状态: 准备好了一个多线程的对象
- 就绪(runnable)状态: 调用了start()方法, 等待CPU进行调度
- 运行(running)状态: 执行run()方法
- 阻塞(blocked)状态: 暂时停止执行, 可能将资源交给其它线程使用
- 终止(dead)状态: 线程销毁
线程的实现
- extends Thread class
- implements Runnable interface
线程相关类常用方法
- Runnable(interface)
- run() 【When an object implementing interface Runnable is used to create a thread, starting the thread causes the object's run method to be called in that separately executing thread.】
- Thread(class)
- 构造方法
- Thread() 【Allocates a new Thread object.】
- Thread(Runnable target) 【Allocates a new Thread object.】
- Thread(Runnable target, String name) 【Allocates a new Thread object.】
- Thread(String name) 【Allocates a new Thread object.】
- 常用普通函数
- currentThread() 【Returns a reference to the currently executing thread object.】
- getId() 【Returns the identifier of this Thread.】
- getName() 【Returns this thread's name.】
- getPriority() 【Returns this thread's priority.】
- interrupt() 【Interrupts this thread.】
- join() 【Waits for this thread to die.】
- setName(String name) 【Changes the name of this thread to be equal to the argument name.】
- sleep(long millis) 【Causes the currently executing thread to sleep (temporarily cease execution) for the specified number of milliseconds, subject to the precision and accuracy of system timers and schedulers.】
- start() 【Causes this thread to begin execution; the Java Virtual Machine calls the run method of this thread.】
- yield() 【A hint to the scheduler that the current thread is willing to yield its current use of a processor.】
- 构造方法
- Object(class)
- notify() 【Wakes up a single thread that is waiting on this object's monitor.】
- notifyAll() 【Wakes up all threads that are waiting on this object's monitor.】
- wait() 【Causes the current thread to wait until another thread invokes the notify() method or the notifyAll() method for this object.】
- wait(long timeout) 【Causes the current thread to wait until either another thread invokes the notify() method or the notifyAll() method for this object, or a specified amount of time has elapsed.】
- wait(long timeout, int nanos) 【Causes the current thread to wait until another thread invokes the notify() method or the notifyAll() method for this object, or some other thread interrupts the current thread, or a certain amount of real time has elapsed.】
示例代码
## extends Thread classclass MyThread extends Thread {private String name;public MyThread(String name) {this.name = name;}public void run() {System.out.println("Thread name:" + this.name + " Thread ID:" + Thread.currentThread().getId());}}public class Demo02 {public static void main(String args[]) {System.out.println("Main thread ID:" + Thread.currentThread().getId());MyThread t1 = new MyThread("thread1");t1.start();MyThread t2 = new MyThread("thread2");t2.start();}}## 运行结果Main thread ID:1Thread name:thread1 Thread ID:10Thread name:thread2 Thread ID:11----------## implements Runnable interfaceclass MyRunnable implements Runnable {public void run() {System.out.println("Thread ID:" + Thread.currentThread().getId());}}public class Demo03 {public static void main(String args[]) {System.out.println("Main thread ID:" + Thread.currentThread().getId());MyRunnable run = new MyRunnable();Thread t = new Thread(run);t.start();}}## 运行结果Main thread ID:1Thread ID:10
使用ExecutorService、Callable、Future实现有返回结果的多线程
ExecutorService、Callable、Future这个对象实际上都是属于Executor框架中的功能类。可返回值的任务必须实现Callable接口,类似的,无返回值的任务必须Runnable接口。执行Callable任务后,可以获取一个Future的对象,在该对象上调用get就可以获取到Callable任务返回的Object了,再结合线程池接口ExecutorService就可以实现传说中有返回结果的多线程了。
常用方法如下:
- ExecutorService(interface)
- shutdown() 【Initiates an orderly shutdown in which previously submitted tasks are executed, but no new tasks will be accepted.】
- submit(Callable task) 【Submits a value-returning task for execution and returns a Future representing the pending results of the task.】
- submit(Runnable task) 【Submits a Runnable task for execution and returns a Future representing that task.】
- submit(Runnable task, T result) 【Submits a Runnable task for execution and returns a Future representing that task.】
- Callable(interface)
- call() 【Computes a result, or throws an exception if unable to do so.】
- Future(interface)
- get() 【Waits if necessary for the computation to complete, and then retrieves its result.】
- Executors(class)
- static ExecutorService newFixedThreadPool(int nThreads)
示例代码
package com.jiudouyu.thread;import java.util.concurrent.*;import java.util.*;class MyCallable implements Callable<Object> {private String taskNum;MyCallable(String taskNum) {this.taskNum = taskNum;}public Object call() throws Exception {System.out.println(">>>" + taskNum + "任务启动");Date dateTmp1 = new Date();Thread.sleep(1000);Date dateTmp2 = new Date();long time = dateTmp2.getTime() - dateTmp1.getTime();System.out.println(">>>" + taskNum + "任务终止");return taskNum + "任务返回运行结果,当前任务时间【" + time + "毫秒】";}}public class Demo04 {public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {System.out.println("----程序开始运行----");Date date1 = new Date();int taskSize = 5;// 创建一个线程池ExecutorService pool = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(taskSize);// 创建多个有返回值的任务List<Future> list = new ArrayList<Future>();for (int i = 0; i < taskSize; i++) {Callable c = new MyCallable(i + " ");// 执行任务并获取Future对象Future f = pool.submit(c);// System.out.println(">>>" + f.get().toString());list.add(f);}// 关闭线程池pool.shutdown();// 获取所有并发任务的运行结果for (Future f : list) {// 从Future对象上获取任务的返回值,并输出到控制台System.out.println(">>>" + f.get().toString());}Date date2 = new Date();System.out.println("----程序结束运行----,程序运行时间【"+ (date2.getTime() - date1.getTime()) + "毫秒】");}}## 运行结果----程序开始运行---->>>0 任务启动>>>1 任务启动>>>2 任务启动>>>3 任务启动>>>4 任务启动>>>0 任务终止>>>0 任务返回运行结果,当前任务时间【1000毫秒】>>>2 任务终止>>>3 任务终止>>>1 任务终止>>>1 任务返回运行结果,当前任务时间【1001毫秒】>>>2 任务返回运行结果,当前任务时间【1001毫秒】>>>3 任务返回运行结果,当前任务时间【1000毫秒】>>>4 任务终止>>>4 任务返回运行结果,当前任务时间【1002毫秒】----程序结束运行----,程序运行时间【1010毫秒】
