@a5635268
2015-09-12T12:23:17.000000Z
字数 7449
阅读 2537
【mongoDB高级篇①】聚集运算之group,aggregate
mongoDB
group
语法
db.collection.group({key:{field:1},//按什么字段进行分组initial:{count:0},//进行分组前变量初始化,该处声明的变量可以在以下回调函数中作为result的属性使用cond:{},//类似mysql中的having,分组后的查询返回reduce: function ( curr, result ) { }, //The function takes two arguments: the current document and an aggregation result document for that group.先迭代出分组,然后再迭代分组中的文档,即curr变量就代表当前分组中此刻迭代到的文档,result变量就代表当前分组。keyf:function(doc){},//keyf和key二选一,传入的参数doc代表当前文档,如果分组的字段是经过运算后的字段用到,作用类似mysql中的group by left('2015-09-12 14:05:22',10);finalize:function(result) {}//该result也就是reduce的result,都是代表当前分组,这个函数是在走完当前分组结束后回调;})
除了分组的key字段外,就只返回有result参数的回调函数中的操作的属性字段;
实例
# 表结构如下{_id: ObjectId("5085a95c8fada716c89d0021"),ord_dt: ISODate("2012-07-01T04:00:00Z"),ship_dt: ISODate("2012-07-02T04:00:00Z"),item: { sku: "abc123",price: 1.99,uom: "pcs",qty: 25 }}
#Example1SELECT ord_dt, item_skuFROM ordersWHERE ord_dt > '01/01/2012'GROUP BY ord_dt, item_sku↓↓↓↓db.orders.group({key: { ord_dt: 1, 'item.sku': 1 },cond: { ord_dt: { $gt: new Date( '01/01/2012' ) } },reduce: function ( curr, result ) { },initial: { }})#Example2SELECT ord_dt, item_sku, SUM(item_qty) as totalFROM ordersWHERE ord_dt > '01/01/2012'GROUP BY ord_dt, item_sku↓↓↓↓db.orders.group({key: { ord_dt: 1, 'item.sku': 1 },cond: { ord_dt: { $gt: new Date( '01/01/2012' ) } },reduce: function( curr, result ) {result.total += curr.item.qty;},initial: { total : 0 }})#Example3db.orders.group({keyf: function(doc) {return { day_of_week: doc.ord_dt.getDay() };},cond: { ord_dt: { $gt: new Date( '01/01/2012' ) } },reduce: function( curr, result ) {result.total += curr.item.qty;result.count++;},initial: { total : 0, count: 0 },finalize: function(result) {var weekdays = ["Sunday", "Monday", "Tuesday","Wednesday", "Thursday","Friday", "Saturday"];result.day_of_week = weekdays[result.day_of_week];result.avg = Math.round(result.total / result.count);}})[{ "day_of_week" : "Sunday", "total" : 70, "count" : 4, "avg" : 18 },{ "day_of_week" : "Friday", "total" : 110, "count" : 6, "avg" : 18 },{ "day_of_week" : "Tuesday", "total" : 70, "count" : 3, "avg" : 23 }]
工作中用到的实例
#查询每个栏目最贵的商品价格, max()操作{key:{cat_id:1},cond:{},reduce:function(curr , result) {if(curr.shop_price > result.max) {result.max = curr.shop_price;}},initial:{max:0}}#查询每个栏目下商品的平均价格{key:{cat_id:1},cond:{},reduce:function(curr , result) {result.cnt += 1;result.sum += curr.shop_price;},initial:{sum:0,cnt:0},finalize:function(result) {result.avg = result.sum/result.cnt; //在每次分组完毕后进行运算}}
group其实略微有点鸡肋,因为既然用到了mongodb,那复制集和分片是避无可免的,而group是不支持分片的运算
Aggregation
聚合管道是一个基于数据处理管道概念的框架。通过使用一个多阶段的管道,将一组文档转换为最终的聚合结果。
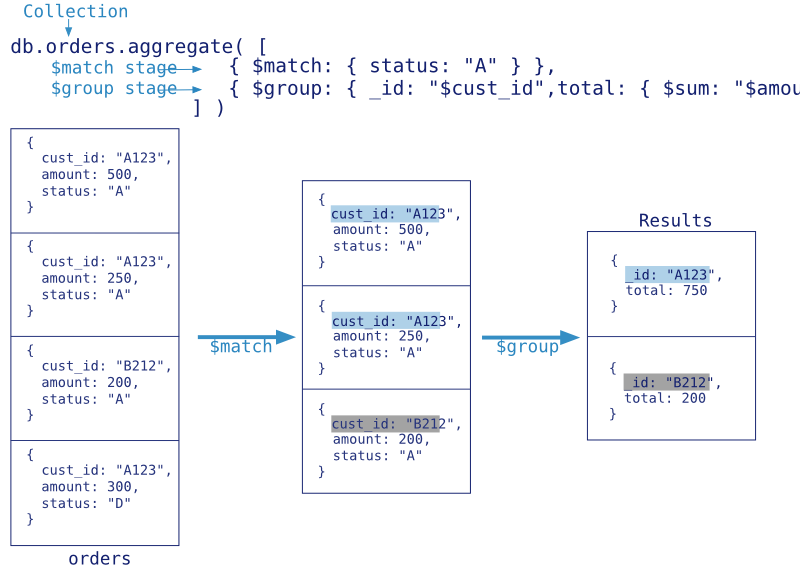
语法
参考手册: http://docs.mongoing.com/manual-zh/core/aggregation-pipeline.html
db.collection.aggregate(pipeline, options);pipeline Array# 与mysql中的字段对比说明$project # 返回哪些字段,select,说它像select其实是不太准确的,因为aggregate是一个阶段性管道操作符,$project是取出哪些数据进入下一个阶段管道操作,真正的最终数据返回还是在group等操作中;$match # 放在group前相当于where使用,放在group后面相当于having使用$sort # 排序1升-1降 sort一般放在group后,也就是说得到结果后再排序,如果先排序再分组没什么意义;$limit # 相当于limit m,不能设置偏移量$skip # 跳过第几个文档$unwind # 把文档中的数组元素打开,并形成多个文档,参考Example1$group: { _id: <expression>, <field1>: { <accumulator1> : <expression1> }, ... # 按什么字段分组,注意所有字段名前面都要加$,否则mongodb就为以为不加$的是普通常量,其中accumulator又包括以下几个操作符# $sum,$avg,$first,$last,$max,$min,$push,$addToSet#如果group by null就是 count(*)的效果$geoNear # 取某一点的最近或最远,在LBS地理位置中有用$out # 把结果写进新的集合中。注意1,不能写进一个分片集合中。注意2,不能写进
实例
Example1: unwind
> db.test.insert({ "_id" : 1, "item" : "ABC1", sizes: [ "S", "M", "L"] });WriteResult({ "nInserted" : 1 })> db.test.aggregate( [ { $unwind : "$sizes" } ] ){ "_id" : 1, "item" : "ABC1", "sizes" : "S" }{ "_id" : 1, "item" : "ABC1", "sizes" : "M" }{ "_id" : 1, "item" : "ABC1", "sizes" : "L" }db.test.insert({ "_id" : 2, "item" : "ABC1", sizes: [ "S", "M", "L",["XXL",'XL']] });WriteResult({ "nInserted" : 1 })> db.test.aggregate( [ { $unwind : "$sizes" } ] ){ "_id" : 1, "item" : "ABC1", "sizes" : "S" }{ "_id" : 1, "item" : "ABC1", "sizes" : "M" }{ "_id" : 1, "item" : "ABC1", "sizes" : "L" }{ "_id" : 2, "item" : "ABC1", "sizes" : "S" }{ "_id" : 2, "item" : "ABC1", "sizes" : "M" }{ "_id" : 2, "item" : "ABC1", "sizes" : "L" }{ "_id" : 2, "item" : "ABC1", "sizes" : [ "XXL", "XL" ] } # 只能打散一维数组
Example2
#数据源{ "_id" : 1, "item" : "abc", "price" : 10, "quantity" : 2, "date" : ISODate("2014-03-01T08:00:00Z") }{ "_id" : 2, "item" : "jkl", "price" : 20, "quantity" : 1, "date" : ISODate("2014-03-01T09:00:00Z") }{ "_id" : 3, "item" : "xyz", "price" : 5, "quantity" : 10, "date" : ISODate("2014-03-15T09:00:00Z") }{ "_id" : 4, "item" : "xyz", "price" : 5, "quantity" : 20, "date" : ISODate("2014-04-04T11:21:39.736Z") }{ "_id" : 5, "item" : "abc", "price" : 10, "quantity" : 10, "date" : ISODate("2014-04-04T21:23:13.331Z") }# 综合示例db.sales.aggregate([# 由上到下,分阶段的进行,注意该数组中的顺序是有意义的{$project:{item:1,price:1,quantity:1} # 1.取出什么元素待操作;},{$group:{ # 2. 对已取出的元素进行聚合运算;_id:"$item", # 根据什么来分组quantityCount:{$sum:'$quantity'},priceTotal:{$sum:'$price'}}},{$sort:{quantityCount:1 #3.升序}},# 4.基于上面的结果,取倒数第二名{$skip: 2},{$limit:1},# 5.然后把结果写到result集合中{$out:'result'}])#表达式$month,$dayOfMonth,$year,$sum,$avgdb.sales.aggregate([{$group : {_id : { month: { $month: "$date" }, day: { $dayOfMonth: "$date" }, year: { $year: "$date" } }, #按月日年分组totalPrice: { $sum: { $multiply: [ "$price", "$quantity" ] } },averageQuantity: { $avg: "$quantity" },count: { $sum: 1 }}}])#结果{ "_id" : { "month" : 3, "day" : 15, "year" : 2014 }, "totalPrice" : 50, "averageQuantity" : 10, "count" : 1 }{ "_id" : { "month" : 4, "day" : 4, "year" : 2014 }, "totalPrice" : 200, "averageQuantity" : 15, "count" : 2 }{ "_id" : { "month" : 3, "day" : 1, "year" : 2014 }, "totalPrice" : 40, "averageQuantity" : 1.5, "count" : 2 }### 表达式$pushdb.sales.aggregate([{$group:{_id: { day: { $dayOfYear: "$date"}, year: { $year: "$date" } },itemsSold: { $push: { item: "$item", quantity: "$quantity" } }}}])# result{"_id" : { "day" : 46, "year" : 2014 },"itemsSold" : [{ "item" : "abc", "quantity" : 10 },{ "item" : "xyz", "quantity" : 10 },{ "item" : "xyz", "quantity" : 5 },{ "item" : "xyz", "quantity" : 10 }]}{"_id" : { "day" : 34, "year" : 2014 },"itemsSold" : [{ "item" : "jkl", "quantity" : 1 },{ "item" : "xyz", "quantity" : 5 }]}{"_id" : { "day" : 1, "year" : 2014 },"itemsSold" : [ { "item" : "abc", "quantity" : 2 } ]}### 表达式$addToSetdb.sales.aggregate([{$group:{_id: { day: { $dayOfYear: "$date"}, year: { $year: "$date" } },itemsSold: { $addToSet: "$item" }}}])#result{ "_id" : { "day" : 46, "year" : 2014 }, "itemsSold" : [ "xyz", "abc" ] }{ "_id" : { "day" : 34, "year" : 2014 }, "itemsSold" : [ "xyz", "jkl" ] }{ "_id" : { "day" : 1, "year" : 2014 }, "itemsSold" : [ "abc" ] }### 表达式 $firstdb.sales.aggregate([{ $sort: { item: 1, date: 1 } },{$group:{_id: "$item",firstSalesDate: { $first: "$date" }}}])# result{ "_id" : "xyz", "firstSalesDate" : ISODate("2014-02-03T09:05:00Z") }{ "_id" : "jkl", "firstSalesDate" : ISODate("2014-02-03T09:00:00Z") }{ "_id" : "abc", "firstSalesDate" : ISODate("2014-01-01T08:00:00Z") }
Example3
db.sales.aggregate([{$group : {_id : null, # 如果为null,就统计出全部totalPrice: { $sum: { $multiply: [ "$price", "$quantity" ] } },averageQuantity: { $avg: "$quantity" },count: { $sum: 1 }}}])
Example4
# 数据源{ "_id" : 8751, "title" : "The Banquet", "author" : "Dante", "copies" : 2 }{ "_id" : 8752, "title" : "Divine Comedy", "author" : "Dante", "copies" : 1 }{ "_id" : 8645, "title" : "Eclogues", "author" : "Dante", "copies" : 2 }{ "_id" : 7000, "title" : "The Odyssey", "author" : "Homer", "copies" : 10 }{ "_id" : 7020, "title" : "Iliad", "author" : "Homer", "copies" : 10 }# 根据作者分组,获得其著多少书籍db.books.aggregate([{ $group : { _id : "$author", books: { $push: "$title" } } }])# result{ "_id" : "Homer", "books" : [ "The Odyssey", "Iliad" ] }{ "_id" : "Dante", "books" : [ "The Banquet", "Divine Comedy", "Eclogues" ] }# 通过系统变量$$ROOT(当前的根文档)来分组db.books.aggregate([{ $group : { _id : "$author", books: { $push: "$$ROOT" } } }])# result{"_id" : "Homer","books" :[{ "_id" : 7000, "title" : "The Odyssey", "author" : "Homer", "copies" : 10 },{ "_id" : 7020, "title" : "Iliad", "author" : "Homer", "copies" : 10 }]}{"_id" : "Dante","books" :[{ "_id" : 8751, "title" : "The Banquet", "author" : "Dante", "copies" : 2 },{ "_id" : 8752, "title" : "Divine Comedy", "author" : "Dante", "copies" : 1 },{ "_id" : 8645, "title" : "Eclogues", "author" : "Dante", "copies" : 2 }]}
邮政编码数据集的聚合实例: http://docs.mongoing.com/manual-zh/tutorial/aggregation-zip-code-data-set.html
对用户爱好数据做聚合实例:
http://docs.mongoing.com/manual-zh/tutorial/aggregation-with-user-preference-data.html
