@flyouting
2014-07-12T06:48:51.000000Z
字数 7679
阅读 4991
Volley源码学习笔记二
Android volley
Request
这里看下网络请求类 Request。
先看下类图:
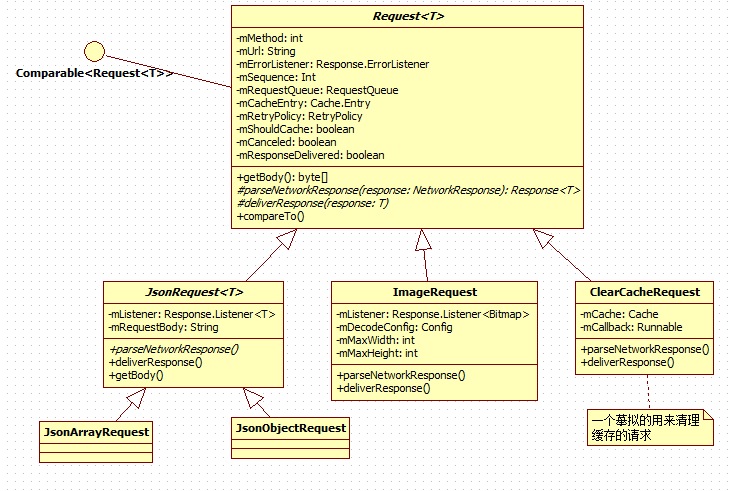
来看下Request类的重要属性:
public abstract class Request<T> implements Comparable<Request<T>> {/** 请求方法 目前支持 GET, POST, PUT, and DELETE. */private final int mMethod;/** 请求的api地址 */private final String mUrl;/** 发生错误的回调接口 */private final Response.ErrorListener mErrorListener;/** 请求的序号,相同优先级的请求在请求队列中根据序号来进行排序,序号低的排在队列前面。*/private Integer mSequence;/** 该请求所在的请求队列 */private RequestQueue mRequestQueue;/** 此请求的网络返回是否需要保存在缓存 */private boolean mShouldCache = true;/** 是否能被取消 */private boolean mCanceled = false;}
然后是主要方法:
/*** 返回请求体的字节数组表示。默认实现为返回null,所以如果是POST或PUT请求,子类需要重写这个方法。** @throws AuthFailureError in the event of auth failure*/public byte[] getBody() throws AuthFailureError {Map<String, String> params = getParams();if (params != null && params.size() > 0) {return encodeParameters(params, getParamsEncoding());}return null;}
/*** 抽象方法,需要子类实现,用以解析网路返回的原始数据* 并返回一个特定的响应类型即Response<T>中的T类* 传回null将会再deliverResponse时不进行分发处理*/abstract protected Response<T> parseNetworkResponse(NetworkResponse response);
/*** 用来将解析好的响应结果交付给监听器进行处理* 传入的参数response需要保证为非空* 解析失败的response将不会被分发处理*/abstract protected void deliverResponse(T response);
Request实现Comparable接口来对Request的优先级进行比较,从而决定Request在队列中的顺序。优先级越高,在请求队列中排得越前,相同优先级的序号越低,排得越前。
@Overridepublic int compareTo(Request<T> other) {Priority left = this.getPriority();Priority right = other.getPriority();// High-priority requests are "lesser" so they are sorted to the front.// Equal priorities are sorted by sequence number to provide FIFO ordering.return left == right ?this.mSequence - other.mSequence :right.ordinal() - left.ordinal();}
Requestv派生出三个子类JsonRequest、ImageRequest、ClearCacheRequest`。
JsonRequest
JsonRequest<T>也是一个抽象类,可以发送一个Json表示的请求体,并返回一个T类型的响应。
public JsonRequest(String url, String requestBody, Listener<T> listener,ErrorListener errorListener) {this(Method.DEPRECATED_GET_OR_POST, url, requestBody, listener, errorListener);}
默认的方法是GET,除非getPostBody()和getPostParams()方法被重写,会默认POST方法。构造方法需要传入的参数API地址,请求体的JSON字符串requestbody,数据成功返回后的回调方法,网络错误的回调方法。
JsonArrayRequest、JsonObjectRequest继承自JsonRequest,分别表示返回一个JsonArray响应的请求与返回一个JsonObject响应的请求。
ImageRequest
根据一个URL来请求一个位图Bitmap,看构造函数
public ImageRequest(String url, Response.Listener<Bitmap> listener, int maxWidth, int maxHeight,Config decodeConfig, Response.ErrorListener errorListener) {super(Method.GET, url, errorListener);setRetryPolicy(new DefaultRetryPolicy(IMAGE_TIMEOUT_MS, IMAGE_MAX_RETRIES, IMAGE_BACKOFF_MULT));mListener = listener;mDecodeConfig = decodeConfig;mMaxWidth = maxWidth;mMaxHeight = maxHeight;}
mMaxWidth: 解码位图的最大宽度,mMaxHeight:解码位图的最大高度,如果mMaxWidth,mMaxHeight都为0,则保持位图的原始尺寸,如果其中一个不为0,则按照原始位图的宽高比进行解码,如果都不为0,则将解码成最适合width * height区域并且保持原始位图宽高比的位图。另外还有个处理解码后的位图的监听器。
ImageRequest的优先级是最低的。
@Overridepublic Priority getPriority() {return Priority.LOW;}
这里需要注意的是,回调是返回的一个bitmap对象。网络数据返回时是byte数组,然后编码成bitmap,并有对宽高进行处理的逻辑,最后将符合要求的bitmap返回。对于普通的图片可以这样做,但是对于特别的格式,比如gif文件,不能返回bitmap,否则就会只返回第一帧,对于有这样需求的地方,需要自己定义一个新的图片获取request类,可以讲byte数组封装成自己需要的类型返回。
private Response<Bitmap> doParse(NetworkResponse response) {byte[] data = response.data;BitmapFactory.Options decodeOptions = new BitmapFactory.Options();Bitmap bitmap = null;if (mMaxWidth == 0 && mMaxHeight == 0) {decodeOptions.inPreferredConfig = mDecodeConfig;bitmap = BitmapFactory.decodeByteArray(data, 0, data.length, decodeOptions);} else {// If we have to resize this image, first get the natural bounds.decodeOptions.inJustDecodeBounds = true;BitmapFactory.decodeByteArray(data, 0, data.length, decodeOptions);int actualWidth = decodeOptions.outWidth;int actualHeight = decodeOptions.outHeight;// Then compute the dimensions we would ideally like to decode to.int desiredWidth = getResizedDimension(mMaxWidth, mMaxHeight,actualWidth, actualHeight);int desiredHeight = getResizedDimension(mMaxHeight, mMaxWidth,actualHeight, actualWidth);// Decode to the nearest power of two scaling factor.decodeOptions.inJustDecodeBounds = false;// TODO(ficus): Do we need this or is it okay since API 8 doesn't support it?// decodeOptions.inPreferQualityOverSpeed = PREFER_QUALITY_OVER_SPEED;decodeOptions.inSampleSize =findBestSampleSize(actualWidth, actualHeight, desiredWidth, desiredHeight);Bitmap tempBitmap =BitmapFactory.decodeByteArray(data, 0, data.length, decodeOptions);// If necessary, scale down to the maximal acceptable size.if (tempBitmap != null && (tempBitmap.getWidth() > desiredWidth ||tempBitmap.getHeight() > desiredHeight)) {bitmap = Bitmap.createScaledBitmap(tempBitmap,desiredWidth, desiredHeight, true);tempBitmap.recycle();} else {bitmap = tempBitmap;}}if (bitmap == null) {return Response.error(new ParseError(response));} else {return Response.success(bitmap, HttpHeaderParser.parseCacheHeaders(response));}}}
ClearCacheRequest
一个模拟的用来清理缓存的请求
public ClearCacheRequest(Cache cache, Runnable callback) {super(Method.GET, null, null);mCache = cache;mCallback = callback;}
mCache:需要清理的缓存,mCallback:缓存清理完后在主线程中被调用的回调接口。parseNetworkResponse与deliverResponse都是空实现,因为这是一个模拟的Request,没有实际的网络请求。
ClearCacheRequest的优先级是最高的
@Overridepublic Priority getPriority() {return Priority.IMMEDIATE;}
在平时用的时候,我们可以写一些request的使用基类,因为有时候我们需要在每个请求里添加固定的几项参数,或者header。在基类里复写getHeaders(),getParams()方法。
cache
这里看看request的访问缓存机制。
request里用到的缓存对象是在RequestQueue的构造方法里传入的一个新创建的DiskBasedCache。
在volley中定义了一个Cache接口,并在此接口中定义了再cache中包存对象的数据结构Entry。
public interface Cache {public Entry get(String key);public void put(String key, Entry entry);public void initialize();public void invalidate(String key, boolean fullExpire);public void remove(String key);public void clear();public static class Entry {/** The data returned from cache. */public byte[] data;/** Date of this response as reported by the server. */public long serverDate;/** TTL for this record. */public long ttl;/** Soft TTL for this record. */public long softTtl;/** Immutable response headers as received from server; must be non-null. */public Map<String, String> responseHeaders = Collections.emptyMap();/** True if the entry is expired. */public boolean isExpired() {return this.ttl < System.currentTimeMillis();}/** True if a refresh is needed from the original data source. */public boolean refreshNeeded() {return this.softTtl < System.currentTimeMillis();}}}
由代码可以看到接口中定义了常用的获取,添加,删除,清空方法。Entry的数据结构包含了字节数组对象,服务器时间,数据在本地生成的时间,软生成时间,这两个时间用于判断是否过期以及是否需要刷新数据。
DiskBasedCache实现了Cache接口,重写了接口中的几个方法。先看一下添加进缓冲区对象:
@Overridepublic synchronized void put(String key, Entry entry) {pruneIfNeeded(entry.data.length);File file = getFileForKey(key);try {FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream(file);CacheHeader e = new CacheHeader(key, entry);boolean success = e.writeHeader(fos);if (!success) {fos.close();VolleyLog.d("Failed to write header for %s", file.getAbsolutePath());throw new IOException();}fos.write(entry.data);fos.close();putEntry(key, e);return;} catch (IOException e) {}boolean deleted = file.delete();if (!deleted) {VolleyLog.d("Could not clean up file %s", file.getAbsolutePath());}}
首先是检查对象的大小,当缓冲区空间足够新对象的加入时就直接添加进来,否则会删除部分对象,一直到新对象添加进来后还会有10%的空间剩余时为止。文件引用以LinkHashMap保存,默认的LRU策略。添加时,首先以URL为key,经过个文本转换后,以转换后的文本为名称,获取一个file对象。首先向这个对象写入缓存的头文件,然后是真正有用的网络返回数据。最后是当前内存占有量数值的更新,这里需要注意的是真实数据被写入磁盘文件后,在内存中维护的应用,存的只是数据的相关属性。
再看怎么从缓冲区获取数据:
@Overridepublic synchronized Entry get(String key) {CacheHeader entry = mEntries.get(key);// if the entry does not exist, return.if (entry == null) {return null;}File file = getFileForKey(key);CountingInputStream cis = null;try {cis = new CountingInputStream(new FileInputStream(file));CacheHeader.readHeader(cis); // eat headerbyte[] data = streamToBytes(cis, (int) (file.length() - cis.bytesRead));return entry.toCacheEntry(data);} catch (IOException e) {VolleyLog.d("%s: %s", file.getAbsolutePath(), e.toString());remove(key);return null;} finally {if (cis != null) {try {cis.close();} catch (IOException ioe) {return null;}}}}
首先根据key从缓存中获取CacheHeader,这里包含了真实数据的各种属性,然后再拿到存有数据的磁盘文件,先从文件中把头文件过滤,然后读取剩下的真正的数据部分到CacheHeader对象中,这样,一个完整的CacheHeader对象得到了,可以返回了。
由此可见,Volley中的第二层缓冲区即文件缓冲区对外不可见,是因为RequestQueue的构造方法直接生成了一个新的DiskBasedCache,如果开放出这个接口,可以传入自定义的DiskCache,只要实现cache接口,重写必要的方法就行,至于存储对象的数据结构,就看具体需求了。那些头文件中的数据属性信息其实也可以不存,直接把数据存成文件。比如在gif文件的支持中,我们需要在文件缓冲区中直接拿到gif的文件对象。这就需要在这一层次中添加接口了。
参考资料:
http://www.cnblogs.com/spec-dog/p/3821417.html
作者:flyouting
