@EdwinTang
2019-01-10T02:16:17.000000Z
字数 17902
阅读 7531
Cucumber自动化测试指南
安装
ubuntu下安装
- 安装ruby
sudo apt-get install ruby
- 安装cucumber
sudo apt-get install cucumber
练习加法
- 创建用于练习的空间
sudo mkdir cucumber
sudo mkdir -p features/step_definitions
- 创建特性
cd cucumber/features/
sublime adding.feature
Feature:Adding
Scenario:Add two numbers
Given the input "2+2"
When the calculator is run
Then the output should be "4"
测试特性建立是否成功:
cucumber
输出结果为:
Feature: Adding
Scenario: Add two numbers # features/adding.feature:2
Given the input "2+2" # features/adding.feature:3
When the calculator is run # features/step_definitions/calculator_steps.rb:5
Then the output should be "4" # features/adding.feature:5
1 scenario (1 undefined)
3 steps (3 undefined)
0m0.024s
You can implement step definitions for undefined steps with these snippets:
Given(/^the input "(.*?)"$/) do |arg1|
pending # express the regexp above with the code you wish you had
end
Then(/^the output should be "(.*?)"$/) do |arg1|
pending # express the regexp above with the code you wish you had
end
- 创建步骤1
cd step_definitions
sublime calculator_steps.rb
Give /^the input "([^"]*)"$/ do |arg1|
pending # express the regexp above with the code you wish you had
end
when /^the calculator is run$/ do
pending # express the regexp above with the code you with you had
end
then /^the output should be "([^"]*)"$/ do |arg1|
pending # express the regexp above with the code you with you had
end
创建测试步骤时,让步骤进入等待状态,测试是否pending和skip
测试步骤,测试结果如下:
cucumber
Feature: Adding
Scenario: Add two numbers # features/adding.feature:2
Given the input "2+2" # features/step_definitions/calculator_steps.rb:1
TODO (Cucumber::Pending)
./features/step_definitions/calculator_steps.rb:2:in `/^the input "([^"]*)"$/'
features/adding.feature:3:in `Given the input "2+2"'
When the calculator is run # features/step_definitions/calculator_steps.rb:5
Then the output should be "4" # features/step_definitions/calculator_steps.rb:9
1 scenario (1 pending)
3 steps (2 skipped, 1 pending)
0m0.023s
- 创建步骤2
步骤2,主要实现参数传入和程序调用,代码如下:
Given /^the input "([^"]*)"$/ do |input|
@input=input
end
When /^the calculator is run$/ do
@output=`ruby calc.rb #{@input}`
raise('Command failed!') unless $?.success?
end
Then /^the output should be "([^"]*)"$/ do |arg1|
pending # express the regexp above with the code you with you had
end
这里需要需要传入参数input,并记着变量,试着调用calc.rb程序,传入参数,并把结果写入output变量,特别需要说明$?用来合适程序是否执行成功,如果失败就抛出错误。
另外执行抛出内容过多,我们通过添加cucumber参数进行限制如cucumber --format progress来获取重点突出的内容
cucumber有多种格式输出器,比如html和xml,那么只需执行cucumber --format xml或cucumber --format hmtl即可。执行cucumber --help可以查看更多格式输出器。
- 创建步骤3(添加执行程序)
步骤3,创建一个假程序让脚本调试通过touch calc.rb
- 创建步骤4(添加断言)
步骤4,修改最后步程序通过
Given /^the input "([^"]*)"$/ do |input|
@input=input
end
When /^the calculator is run$/ do
@output=`ruby calc.rb #{@input}`
raise('Command failed!') unless $?.success?
end
Then /^the output should be "([^"]*)"$/ do |expected_output|
@output==expected_output
end
提倡在项目中尽早构建一个可行走的骨架,以便发现技术选型的任何潜在问题。
- 步骤5(添加场景轮廓)
步骤4的问题
场景用例硬编码
程序硬编码
个人理解场景轮廓即场景实例,解决没有参数化场景和硬编码程序的问题。
Feature: Adding.feature
Scenario Outline: Add two numbers
Given the input "<input>"
When the calculator is run
Then the output should be "<output>"
Examples:
|input |output |
|2+2 |4 |
|98+1 |99 |
同时需要修改程序代码calc.rb
print(eval(ARGV[0]))
首先我们读取命令行参数argv[0],然后把它传给ruby的eval方法
- 总结
被测程序与cucumber之间是通过测试步骤进行毡合的如图【1】
1.表示被测程序
2.表示cucumber特性
3.表示测试步骤,用于连接被测程序与cucumber
二、理解活文档规则
活文档语言
活文档语言产生原因
用户能提出有价值,但模糊的需求。
验收标准与验收测试
系统应该防止客户输入非法的信用卡信息(验收标准)。
如果一名客户输入的信用卡号不是16位,当他提交表单时,系统应该显示错误信息,提示用户正确的位数。(验收测试)
使用一定的规则可以让计算机帮忙进行验收测试,称为自动化验收测试,能让计算机可读才能解决这个问题,因此产生了Gherkin语言。
活文档格式和语法
.feature作为扩展名
关键字
Feature
Background
Scenario
Given
When
Then
And
But
*
Scenario Outline
Examples
验证活文档是否有效
cucumber test.feature --dry-run
--dry-run告诉cucumber只验证语法是否有效不跑代码
Feature关键字
提供地方写测试相关参考文档
紧跟Feature关键字的是他的标题,其他行是他的描述信息。
特性文件命名使用小写,名字使用下划线分割如:user_login_in.feature
描述一般模板为:
为了<达到某些目标>
作为<某类利益相关人>
我想要<某个特性>
场景
一个特性文件包含5-20个场景,每个场景描述不同的具体实例。
(1)将系统置于某种特定状态;
(2)戳一下系统;
(3)检测系统新状态。
即,建立系统上下文,描述动作,检查状态。
场景同特性关键字一样,有标题和描述,场景命名注意避免带来歧义,避免老旧场景歧义,在实际使用中测试人员和研发人员不会去读具体测试步骤,而是关注场景标题。
场景应该关注于场景上下文和事件而非结果
Given/When/Then
Given建立上下文,When描述动作,Then检查状态
And/But
为建立上下文和描述动作、检查状态加入更多步骤。
Scenario:Attempt withdrawwal using stonlen card
Given I have $100 in my account
But my card is invalid
When I request $50
Then MyCard should not be returned
And I should be told to contact the bank
使用*代替Given/When/Then/And/But
Scenario:Attempt withdrawwal using stonlen card
* I have $100 in my account
* my card is invalid
* I request $50
* MyCard should not be returned
* I should be told to contact the bank
一样的效果
无状态
每个场景独立存在,不依赖任何场景
不推荐场景依赖
练习
做意大利面
Feature:做意大利面早餐
为了让全家三个人吃到早餐
作为全家的厨师
我想要为家人做一份意大利面
Scenario:取面时意大利面不够
Given 全家人需要吃2斤面
And 家里剩余1斤面
When 取面
Then 提示还差1斤面
And 提出送2斤面的需求单
Scenario:取面时意大利面够了
Given 全家人需要吃2斤面
And 家里剩余3斤面
When 取面
Then 提示可以取面
And 还剩余1斤面
注释
可以在特性前一行使用#号添加注释
可以注释掉一个步骤
注释用于放测试和研发的便利贴,而描述主要给利益干系人
语言
#language
cucumber --il8n help
总结
- 每个场景都是:上下文、动作描述、结果描述
- 可以使用同一种语言来描述场景
- 可以为feature添加描述和注释,描述给干系人,注释给研发和测试。
- 每个场景独立运行,时无状态的,减少场景之间依赖。
三、面向业务的步骤定义
步骤与步骤定义
步骤是文档,是面向业务的有一定规则的文档。
步骤定义是代码,是把步骤转换成代码能识别的代码。
步骤与步骤定义使用cucumber来桥接。
匹配步骤
第一步、cucumber扫描每一步骤,找到能识别的模式(正则表达式)
第二步、cucumber会问有没有对应的步骤定义
第三步、cucumber找到对应的步骤定义
第四步、cucumber调用指定的步骤定义
创建步骤定义
保存位置:features/step_definitions目录的ruby文件
cucumber通过关键字,告诉自己要注册一个步骤定义,这样告诉cucumber我们用使用哪个方法,通过do和end间的
Given/When/Then关键字
Given/When/Then关键字实际上只对应Cucumber::RbDsl#regiser_rb_step_definition方法。
这样一个方法可以支持多个步骤
由于这种对应关系,要求团队更有效、更清晰描述步骤信息,比如就会出现干扰步骤
捕获参数
使用正则表达式的特性
关键词:捕获组和参数化
捕获组
使用()括号包含正则表达式
Given(/^I have deposited (1|2) in my Account$/) do |show|,参数show可以取得1或2
多选分支
步骤描述:
Feature: Printting
Scenario Outline: Show Message
Given I have deposited <show> in my Account
Examples:
| show |
| 1 |
| 2 |
步骤定义代码:
Given(/^I have deposited (1|2) in my Account$/) do |show|
@show=show
end
输出结果:
Feature: Printting
Scenario Outline: Show Message #features/show.feature:2
Given I have deposited <show> in my Account #features/show.feature:3
Examples:
| show |
| 1 |
| 2 |
4 scenarios (4 passed)
8 steps (8 passed)
0m0.083s
.号与*号修饰
.号表示单字符,*号表示重复修饰,表示任意多次。
字符组
([0123456789]*)或([0-9]*),一系列连续数字
字符组简记法
| 简记法 | 表述 | 事例 |
|---|---|---|
| \d | 所有数字 | [0-9] |
| \w | 单词字符 | [A-Za-z0-9] |
| \D | 非数字字符 | [A-Za-z] |
| \s | 空白字符 | \t\r\n |
| \b | 单词边界 | 同\w相反 |
加号修饰符
*表示0次和0次以上,二+号表示至少一次
练习
步骤描述
Feature: getFlyNumber
Scenario Outline: getEveryNumber for fly
Given the flight <flynumber> is leaving today
Examples:
| flynumber |
| EZY4567 |
| C038 |
| ba01618 |
步骤定义代码
Given(/^the flight (\w*\d*) is leaving today$/) do |flynumber|
@flynumber=flynumber
end
多重捕获
可以把**步骤**中多个变量,使用多个**捕获组**,取得数据,转换成参数传给**步骤定义**
步骤定义描述:
Feature:muil get group
Scenario Outline: two param muil get group
Given the is a <property> <sexpro>, and <sex> is <age> old
Examples:
|property |sexpro |sex |age |
|bad |boy |he |20 |
|good |boy |he |50 |
|bad |girl |she |40 |
|bad |girl |she |10 |
步骤定义代码:
Feature: muil get group
Scenario Outline: two param muil get group
Given the is a <property> <sexpro>, and <sex> is <age> old
Examples:
| property | sexpro | sex | age |
| bad | boy | he | 20 |
| good | boy | he | 50 |
| bad | girl | she | 40 |
| bad | girl | she | 10 |
问号修饰符
问号表示0次或1次,对于复数特别有用,如cucumber和cucumbers表示为cucumber?
非捕获组
不会将值作为参数传递给代码(使用?:表示)
如:
When (/^I (?:visit |go to) the homepage/$) do
end
锚点
^开始,$结束
返回状态
undefined,未定义
pending,待定
failed,失败
passed,通过
未定义
没有找到步骤定义时,步骤被标记为未定义,此场景剩余步骤被跳过,使用黄色表示。
待定步骤
找到步骤定义,但是步骤定义只实现了部分内容,次场景剩余步骤被跳过或标识为未定义,使用黄色表示。
如何知道步骤待定义呢,需要使用pending关键词,cucumber会抛出pending异常。
待定场景成为我们的代办事项,驱动测试开发。
失败的步骤
执行的代码抛出异常,cucumber就会标识为失败的步骤,此次场景停止,使用红色表示。
通常失败有两个原因。
1.系统抛出异常,出现Bug
2.使用断言判断,出现失败
常用断言库:
MiniTest/Rspec/Wrong
ruby默认集成了MiniTest
断言通常都在Then步骤定义进行定义。
例子如下:
1步骤:
Feature: Cash Withdrawal
Scenario: Successful withdrawal from an account in credit
Given I have deposited $100 in my account
2步骤定义:
Given /^I have deposited \$(\d+) in my account$/ do |amount|
Account.new(amount.to_i)
end
总结
1.步骤定义提供一种映射,提供语言到代码映射
2.通过Given/When/Then注册到cucumber
3.使用正则表达式,所有一个步骤定义可能出来多个步骤
4.步骤定义通过抛出异常或不抛出异常把结果传给cucumber
富有表现力的场景
之前的Gherkin关键字不够,
那么加入Gherkin语法(场景轮廓和时间表)
那么加入便签和文件夹管理
背景
Background关键词,是将重复的Given(有时是When)移动到一个单独地方。
指定一组文件中所有场景的公共步骤
好处:
一处修改,全体使用
关注其他场景独特之处
Background出现在所有Scenario或Scenraio Outline之前
Background在一个特性文件中只能出现一次
Background有标题和描述
技巧:
不要使用Background设置复杂的状态
使Background短小简洁,建议不要超过四行
生动名称,设法讲故事
保持场景短小,不合适不合符背景的拆分成多个特性文件
避免讲技术细节放入背景
数据表
扩展Gherkin步骤
紧跟步骤后的第一行,如
步骤:
Given there Users:
|name |date of birth |
|Michael Jackson |August 29,1958 |
|Elvis |January 8, 1935 |
|John Lennon |October 9, 1940 |
步骤定义:
Given(/^there Users:$/) do |table|
end
每一列使用列标题,列标题可以放到最下方,或者省略列标题
数据表管道符后空格可以任意多个。
步骤定义中处理数据表
传输对象为Cucumber::Ast::Table
将数据表转成数组
使用变量的raw方法,把表数据转换到实例变量中,供后面使用
Given(/^there Users:$/) do |table|
@board=table.raw
end
使用diff!比较数据表
使用方法,board是一个已经事例化的变量
Then(/^the result like this:$/) do |expected_table|
expected_table.diff!(@board)
end
比较不一样的行为黄色,实际值为灰色
场景轮廓
在步骤中使用<...>表示场景轮廓的占位符,运行时被Examples表数据
一个特性中可以有多个场景轮廓。每个场景轮廓下可以有任意个实例表
场景轮廓的实例表与步骤中的数据表是不一样的:
事例表:每一行会被Cucumber执行一个完整的场景
数据表:单一场景的单一步骤的个块数据
更大占位符
使用表述更宽的展位符替代,表述更小的占位符。如使用outcome替换receved,这样可以返回实际值或报错信息,使列标题符合占位符表述的文本
多个实例表
Cucumber乐意处理Scenario Outline下任意数量的Examples元素,你可以把不同种类的实例归结到一起,如正向场景和异常场景
产生组合爆炸,解决方法为“核心实例”
可读性最重要
解释自己
分更多的Examples元素,为每个Examples元素添加标题进行说明。
嵌套步骤
避免命令式和过于细节化场景风险
嵌套重构
%{...}结果告诉ruby有一个跨行的字符串
步骤,可以吧常用的辅助的步骤抽象出来如:
And I have pushed my card into the slot
And I enter my PIN
And I press "OK"
可以使用一个步骤代替
Given I have authenticated with the correct PIN
步骤定义
Given(/^I have authenticatyed with the correnct PIN$/) do
steps %{
And I have pushed my card into the slot
And I enter my PIN
And I press "OK"
}
end
steps步骤调用以前的步骤。
嵌套和嵌套步骤
被调用的底层步骤带有参数,通过高层捕获传给低层步骤。steps方法只接受一个字符串
传入的参数为数据表时,steps参数失效。此时要使用step参数
最好的策略,一个高层步骤将任务代理给一些低层抽象步骤,例如:
Given(/^a (\w+) widget with the following details:$/) do |color, details_table|
step "I create a #{color} widget with the following details:", details_table
steps %{
And I register the #{color} widget
And I register the #{color} widget
}
文档字符串
没有看懂希望看懂了在回来?
可以用于API文档,用户可以传递参数输出文档
步骤:
Feature:Adding
Scenario Outline:Add two numbers
Given the input <input>
When the calculator is run
"""
运行程序
"""
Then the output should be <output>
Examples:
|input |output |
| 2+2 | 4 |
| 56+2 | 58 |
步骤定义:
When /^the calculator is run$/ do |arg1|
@output=`ruby calc.rb #{@input}`
raise('Command failed!') unless $?.success?
end
使用标签和文件夹保持条理性
用户组织、领域实体组织
子文件夹
不断尝试调整子文件夹结构
可以把子文件夹当成书的目录
运行子文件夹中的特性
直接在feature级直接运行,可以覆盖子文件夹
指定子文件夹运行
cucumber feature/reading_reports/widgets_report.feature -r features 需要使用-r来指定步骤定义所在目录
标签
可以把标签当成书的书签
在Scenario前加一个@带一个单词
可以在一个Scenario带上多个标签如:
@slow @widgets @nightly
Scenario: Generate overnight report
Given I am logged in
And there is a report "Total widget sales history"
如果你要给一个特性的所有场景打标签,只要在Feature上打标签即可,其他场景会继承此标签。
@nightly @slow
Feature: Nightly report
@widgets
Scenario:Widgets Nightly slow report
Given I am logged in
And there is report ....
给场景打标签的原因
文档:项目管理文档的ID作为标签,集合后成文档
过滤:运用筛选要执行或报告的特定场景
钩子:当带有提示标签的场景运行后,执行特定代码
执行特定标签的场景:
cucumber --tags @javascript
执行带有@javascript标签的场景
edwin@Edwin-Salve:/exec/cucumber$ cucumber --tags @adding
@adding
Feature: Adding
Scenario Outline: Add two numbers
Given the input <input>
When the calculator is run
"""
运行程序
"""
Then the output should be <output>
Examples:
| input | output |
| 2+2 | 4 |
| 56+2 | 58 |
2 scenarios (2 passed)
6 steps (6 passed)
0m0.143s
常见问题解决之道
感受痛苦
闪烁的场景
定义:偶尔失败,随机失败
原因:
- 共享的环境
- 渗露的场景
- 竞争条件和打瞌睡的步骤
脆弱的特性
定义:特性易被破坏,测试套件或主代码的某个部分做必要修改会破坏明显不相干场景
原因:
- 固件数据
- 重复
- 渗露的场景
- 被隔离的测试人员
缓慢的特性
原因:
- 竞争条件和打瞌睡的步骤
- 大量场景
- 大泥球
厌倦的利益相关人
原因:
- 偶然细节
- 命令式步骤
- 重复
- 语言不通
- 闭门造车式的特性
同心协力
特点:
- 活动
- 文档
运行慢的解决方法:
使用标签或文件夹来提高速度
使用Jenkins等slave machine来执行
偶然细节
在场景中提及但实际上与场景的目标毫无关系的细节
只管用直白的英语表述,而不要太注重细节。
业务人员场景:
Scenario:Check inbox
Given I have received an email from "sue"
When I sign in
Then I should see 1 email from "sue" in my inbox
部分测试人员应该会这样:
Scenario:Check inbox
Give a User "Dave"
And a User "Sue"
And an email to "Dave" from "Sue"
When I sign in as "Dave"
Then I should see 1 email from "use" in my inbox
部分测试人员应该会这样:
Scenario:Check inbox
Give a User "Dave" with password "password"
And a User "Sue" with password "password"
And an email to "Dave" from "Sue"
When I sign in as "Dave" with password "password"
Then I should see 1 email from "use" in my inbox
命令式步骤
命令式编程和声明式编程
命令式编程:ruby、Cherkin
声明式编程:css
命令式步骤(泛化步骤定义)定义出来的场景无法创建出领域语言。
Scenario: Redirect user to originally requested page after loggin in
Given a User "dave" exists with password "secret"
And I am not logged in
When Iavigate to the home page
Then I am redirected to the login form
When I fill in "username" with "dave"
And I fill in "password" with "secret"
And I press "login"
Then I should be on the home page
改用声明式风格:
Scenario: Redirect user to originally requested page after loggin in
Given I am an unauthenticated user
When I attempt to view som restricted content
Then I am shown a login form
When I authenticate with valid credentials
Then I should be shown the restricted content
声明式风格漂亮之处在于不与用户界面的任何特点实现相耦合
重复
避免重复的方法:Background和Scenario Outline和数据表
如果不断重复说明代码抽象的不够。
DAMP(Descriptive and Meaningfull Phrases)高于DRY(Don't Repeat Yourself)有意义的描述性的叙述高于不能重复原则。---故事感
语言不通
使用的语言将有领域来驱动,比如音乐爱好者,音乐会、演出、表演者和场地之类的词语。
讨论出大家要使用的语言比动手重要。
测试人员:破坏东西(找出没有覆盖的边界)
研发人员:做出东西(澄清问题,场景添加步骤)
产品负责人:功能范围()
闭门造车式的特性
业务利益相关人参加
照管好你的测试
特性可以充当反馈机制。
渗露的场景
cucumber测试本质是状态转换测试,将系统置于一个状态(Given),执行动作(When),然后(Then)带出其他状态。
渗露:两个测试件没有重置状态,我们就说状态在测试之间发生了渗露
相反的就是独立的场景
测试数据构造器:FactoryGirl
竞争条件和打瞌睡的步骤
并发执行,执行是否成功依赖某一部分执行是否结束。如果竞争势均力敌就会出现闪烁的场景,场景间歇成功间歇失败。
引入睡眠时间,可以减缓闪烁场景,但会延长执行时间。所以不是很好的方法。好方法是不免竞争条件产生。
共享的环境
执行自动化测试,执行功能测试,回归验证bug
数据资源造成沉重和不稳定负荷。
这样也会导致闪烁场景出现
解决方法,一键式搭建环境
使用ruby的activerecord gem 来管理数据库模式和迁移脚本
被隔离的测试人员
步骤定义和支持代码组织良好需要测试人员掌握
开发人员向测试人员展示如何组织代码
固件数据
不建议使用固件数据
固件数据体积会变大
复杂度变大,不同场景依都依赖于固件数据,为了保证执行成功会创造更多数据,这样就越来越复杂
容易发生渗露的场景
固件数据是一种反模式
测试数据构造器??需要研究
大量场景
使用文件夹和标签
场景中描述的行为是否可以下移一层,即使用单元测试来增加覆盖率。
大泥球
做好架构
http://alistair.cockburn.us/Hexagonal+architecture
端口和适配器的方法
停掉生产线和缺陷预防
维护的优先级在很多团队中都不会排再前面。这回再问题严重时不好补救。
方法:
1.检测异常情况
2.停下手边工作
3.修复或纠正眼下问题
4.调查根源并实施对策
步骤定义:内在篇
步骤定义如何与构建的应用程序解耦。
变形器来减少步骤定义中的重复并提高正则表达式的可读性。
world编写辅助方法
勾勒出领域模型
面向对象的核心都是领域模型,我们不用关注用户界面的各种花样。
我们通过步骤定义去勾勒领域模型
第一步:
步骤:
Feature: Cash Withdrawal
Scenario: Successful withdrawal from an account in credit
Given I have deposited $100 in my account
When I request $20
Then $20 should be dispensed
步骤定义:
Given(/^I have deposited \$(\d+) in my account$/) do |arg1|
Account.new(amount.to_i)
end
When(/^I request \$(\d+)$/) do |arg1|
pending # express the regexp above with the code you wish you had
end
Then(/^\$(\d+) should be dispensed$/) do |arg1|
pending # express the regexp above with the code you wish you had
end
第二步:优化
步骤定义中增加
class Account
def initialize(amount)
end
end
1.代码中混入了一些不一致的语言"depositing"
2.我们的账户中没有存款
3.把数据转换成整数不优雅amount.to_i
准确用词
先有账户,向账号中存钱
Given(/^I have deposited \$(\d+) in my account$/) do |arg1|
my_account=Account.new
my_account.deposit(amount.to_i)
end
修改步骤定义中的词语
class Account
def deposit(amount)
end
end
实话实说
资金存入,断言资金真实存入
做最简单的事情
步骤用来做最简单的事情,不要一步做多个事情
使用变形器消除重复
使用变形器Transform去重,Transform需要放在代码前面。
CAPTURE_A_NUMBER = Transform(/^(\d+)$/) do |number|
number.to_i
end
Given(/^I have deposited \$(#{CAPTURE_A_NUMBER}) in my account$/) do |amount|
my_account=Account.new
my_account.deposit(amount)
my_account.balance == amount
end
引入新角色,取款机
teller=Teller.new
teller.withdraw_from(my_account,amount)
步骤定义完整代码:
CAPTURE_A_NUMBER = Transform(/^(\d+)$/) do |number|
number.to_i
end
Given(/^I have deposited \$(#{CAPTURE_A_NUMBER}) in my account$/) do |amount|
my_account=Account.new
my_account.deposit(amount)
my_account.balance == amount
end
When(/^I request \$(#{CAPTURE_A_NUMBER})$/) do |amount|
teller=Teller.new
teller.withdraw_from(my_account,amount)
end
Then(/^\$(\d+) should be dispensed$/) do |arg1|
pending # express the regexp above with the code you wish you had
end
class Account
def deposit(amount)
@balance=amount
end
def balance
@balance
end
end
class Teller
def withdraw_from(account,amount)
end
end
问题:my_account不能共享
使用@my_account共享
步骤定义优化:
Given(/^I have deposited \$(#{CAPTURE_A_NUMBER}) in my account$/) do |amount|
@my_account=Account.new
@my_account.deposit(amount)
@my_account.balance == amount
end
When(/^I request \$(#{CAPTURE_A_NUMBER})$/) do |amount|
teller=Teller.new
teller.withdraw_from(@my_account,amount)
end
修改文字:把请求(request)修改为取款(withdraw)
When(/^I withdraw \$(#{CAPTURE_A_NUMBER})$/) do |amount|
teller=Teller.new
teller.withdraw_from(@my_account,amount)
end
使用其他方法优化:
为world添加自定义辅助方法
在world中存储状态
使用实例变量在步骤定义间传递状态,即@符号后跟随变量。实例变量如果不人为设置,它会返回nil,而nil回引发bug
创建自定义辅助方法
步骤定义中添加world模块:
module KnowsMyAccount
def my_account
@my_account ||= Account.new
end
end
World(KnowsMyAccount)
步骤中去掉实例变量为my_account方法。
自定义World
第二步通过,学习一些World知识
编写一些系统执行公共动作,编写自定义模块扩展World,用World的主要方式
默认格式:
module MyBusinessModuld
def my_helper_method
......
end
end
World(MyBusinessModuld)
比如pending方法就是World扩展出来的模块,可以使用puts self输出调用的World模块。
每个场景都有一个新的World创建,场景结束时自动销毁
设计抵达终点的方法
World模块:
def cash_slot
@cash_slot ||= CashSlot.new
end
步骤定义:
class CashSlot
def contents
raise("I'm empty!")
end
end
Then(/^\$(\d+) should be dispensed$/) do |amount|
cash_slot.contents == amount
end
可以使用ask来进行步骤定义中的交互。
把细节推入World,意味着步骤定义的代码处于更高的抽象层次
需要使用CashSlot来吐钞,负责交易的是Teller,它对CashSlot一无所知,需要依赖注入,把CashSlot传给Teller的构造函数。
优化后步骤定义代码:
Given(/^I have deposited \$(#{CAPTURE_A_NUMBER}) in my account$/) do |amount|
my_account.deposit(amount)
my_account.balance == amount
end
When(/^I withdraw \$(#{CAPTURE_A_NUMBER})$/) do |amount|
teller.withdraw_from(my_account,amount)
end
Then(/^\$(\d+) should be dispensed$/) do |amount|
cash_slot.contents == amount
end
class Account
def deposit(amount)
@balance=amount
end
def balance
@balance
end
end
class Teller
def initialize(cash_slot)
@cash_slot = cash_slot
end
def withdraw_from(account,amount)
@cash_slot.dispense(amount)
end
end
class CashSlot
def dispense(amount)
@contents = amount
end
def contents
@contents or raise("I'm empty!")
end
end
module KnowsMyAccount
def my_account
@my_account ||= Account.new
end
def cash_slot
@cash_slot ||= CashSlot.new
end
def teller
@teller ||= Teller.new(cash_slot)
end
end
World(KnowsMyAccount)
组织代码
- 应用程序的领域模型类,放在项目根目录下的lib子目录
- World扩展模块应该移到自己的目录中
- 变形器也移动到自己的目录中
- 步骤文件可以切分
隔离应用程序代码
移走领域模型类,使用代码引入移走的领域模型类
require File.join(File.dirname(__FILE__),'..','..','lib','nice_bank')
lib是cucumber命令执行的子目录,nice_bank是领域模型类所在的ruby文件nice_bank.rb,可是每次都要加载时我们不希望的。
启动Cucumber环境
cucumber运行时会加载一个特殊目录,这个目录叫features/support,cucumber运行时会加载这个目录下的ruby文件,但载入文件顺序没有控制,在表明文件间不能依赖。
但也有例外的features/support/env.rb就是一个会被首先加载的文件。因此我们可以把请求转移到env.rb下。
require File.join(File.dirname(__FILE__),'..','..','lib','nice_bank')
变形器和world模块
把world模块放入features/support/world_extensions.rb下
module KnowsMyAccount
def my_account
@my_account ||= Account.new
end
def cash_slot
@cash_slot ||= CashSlot.new
end
def teller
@teller ||= Teller.new(cash_slot)
end
end
把变形器代码放入features/support/transfrom.rb下
CAPTURE_A_NUMBER = Transform(/^(\d+)$/) do |number|
number.to_i
end
组织步骤定义
比较好的这种方法为:领域实体对应一个文件
模拟运行和env.rb
cucumber --dry-run
模拟运行不会启动cucumber环境,因此不会加载env.rb.
因此未来env.rb是否加载,support目录下的其他文件都能成功加载。
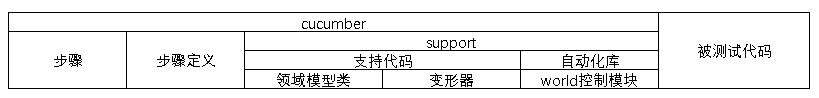
支持代码
features/support目录下的代码,连接和耦合真正的应用程序
修复bug
没有判断余额是否$80,需要在步骤中增加。在一定程度上说,没有bug,只是没有预料到的边界。
优化账号代码和ATM机代码
class Account
def deposit(amount)
@balance=amount
end
def balance
@balance
end
def debit(amount)
@balance -= amount
end
end
class Teller
def initialize(cash_slot)
@cash_slot = cash_slot
end
def withdraw_from(account,amount)
account.debit(amount)
@cash_slot.dispense(amount)
end
end
检查与重构
原则:
1.通过所有测试
2.展示所有意图
3.不包含如何重复
4.所有尽可能少的类和方法
展示意图时,看看是否使用通用语言,
依赖编译器,《重构-改善既有代码的设计》
依赖测试
比如把:领域模型类、步骤定义、步骤中的deposit改为credit;
开启用户界面
安装gem
第一步:ubuntu下安装apt-get install bundler
这样可能会出问题,怎么解决呢?可以会用一下方法:gem install bundle=3.27进行安装
第二步:生成Gemfile
做出转换
使用钩子
构建用户界面
处理消息队列和异步组件
我们全新的异步架构
如何同步
实现新架构
修复闪烁的场景
数据库
ActiveRecord介绍
重构至使用数据库
读取及写入数据库
用事物清理数据库
cucumber命令行界面
cucumber命令行选项
运行一个场景子集
改变cucumber输出
指定步骤定义的位置
管理进行中的工作
使用profile
从Rake运行cucumber
持续集成中运行cucumber
测试rest web服务
进程内测试基于rack的RestAPI
进程外测试任意rest api
为遗留应用添加测试
特性描述测试
消灭bug
添加新的行为
代码覆盖率
引导Rails
运行生成器
创建用户
发布消息
关联消息与用户
手工创建控制器
实现视图
使用Capybara测试Ajax Web应用
实现不要Ajax的简单搜索
基于Ajax的搜索
Capybara Api
抓取屏幕截图
使用Aruba测试命令行应用
简单界面
我们的第一个Aruba特性
使用文件与可执行程序
与用户输入交互
使用Aruba的Ruby DSL
shu
